Abstract
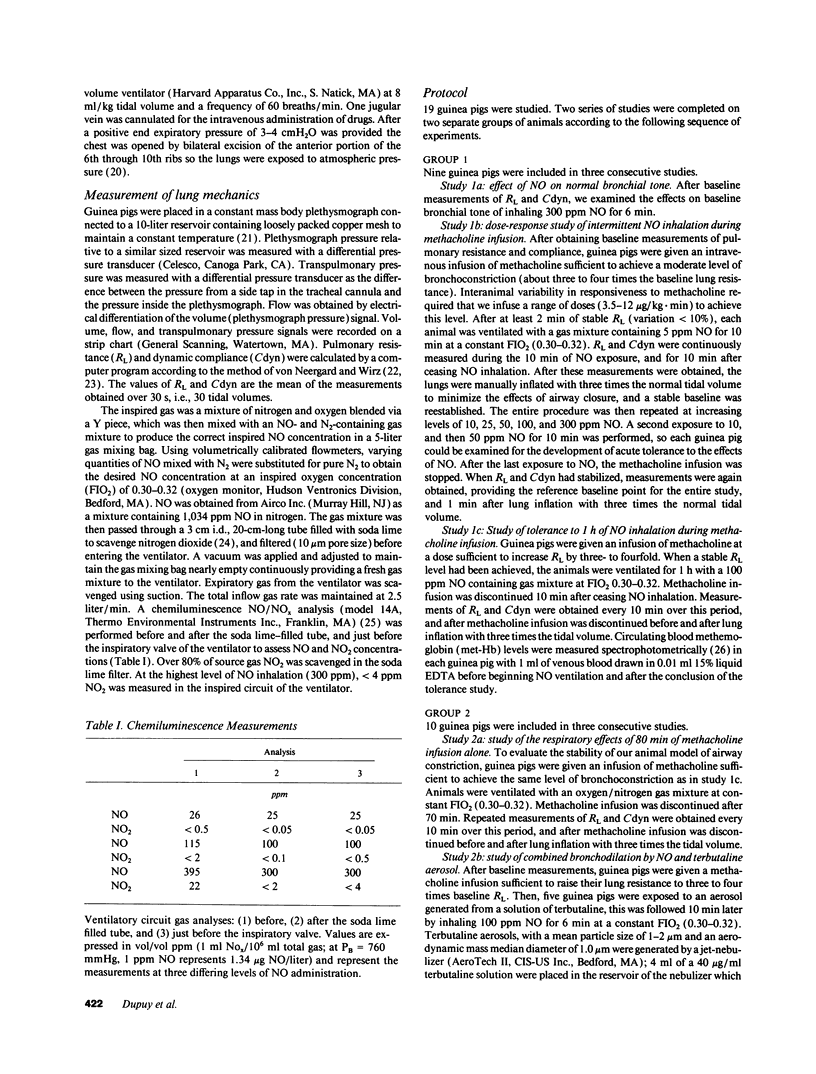
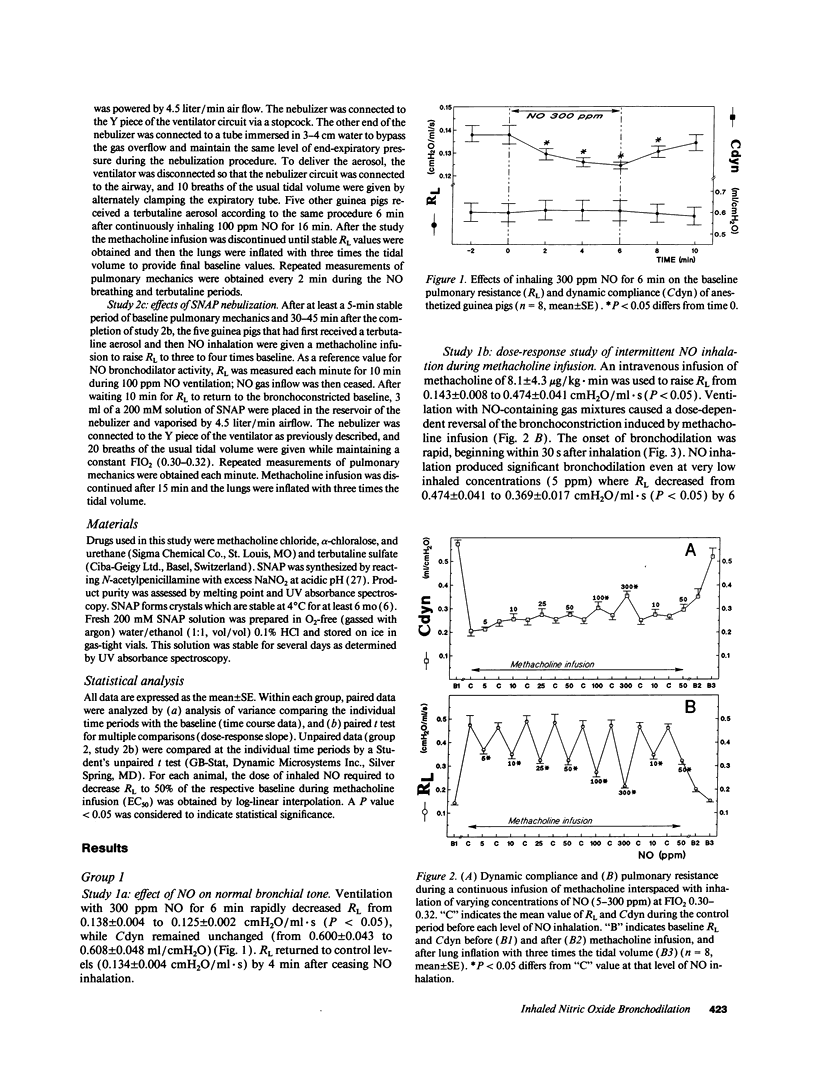
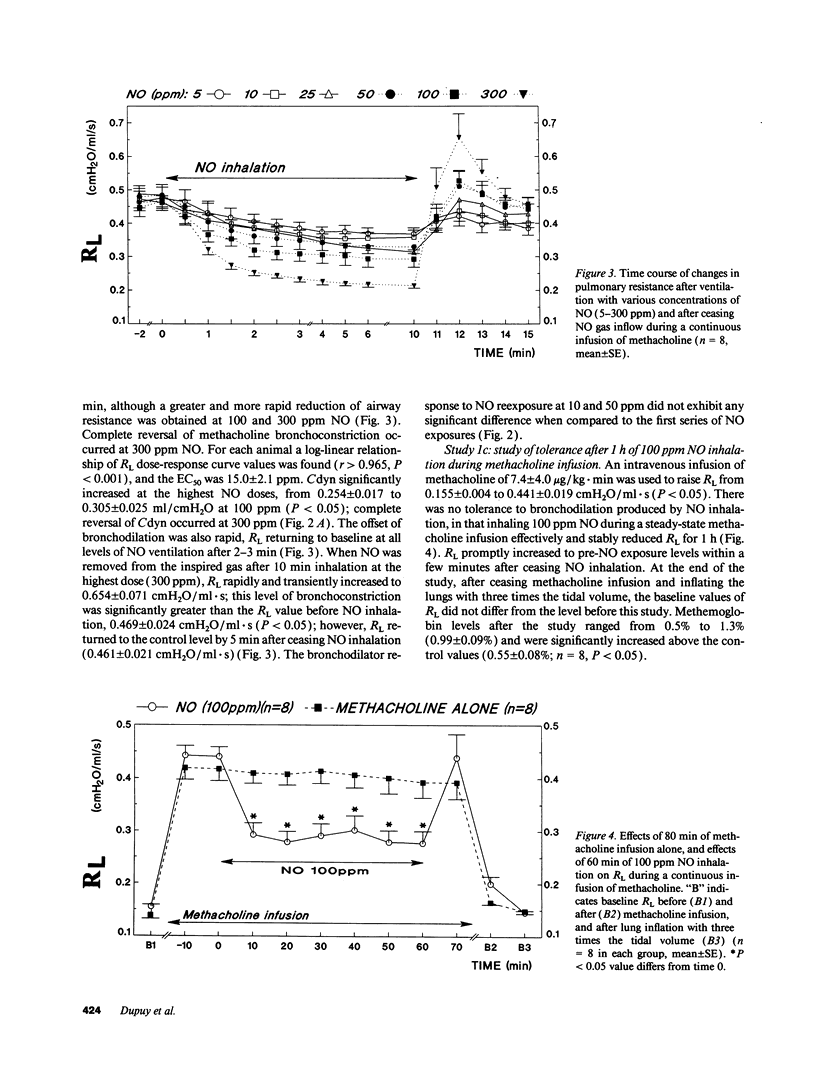
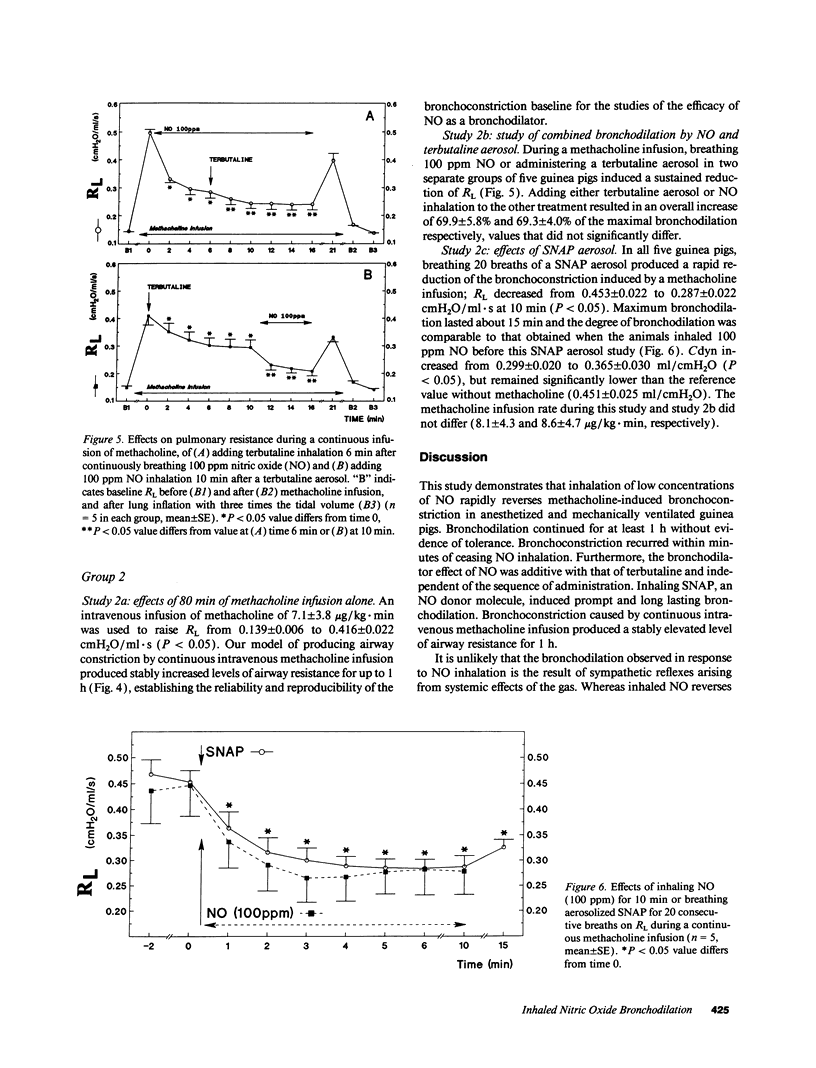
The effects of inhaling nitric oxide (NO) on airway mechanics were studied in anesthetized and mechanically ventilated guinea pigs. In animals without induced bronchoconstriction, breathing 300 ppm NO decreased baseline pulmonary resistance (RL) from 0.138 +/- 0.004 (mean +/- SE) to 0.125 +/- 0.002 cmH2O/ml.s (P less than 0.05). When an intravenous infusion of methacholine (3.5-12 micrograms/kg.min) was used to increase RL from 0.143 +/- 0.008 to 0.474 +/- 0.041 cmH2O/ml.s (P less than 0.05), inhalation of 5-300 ppm NO-containing gas mixtures produced a dose-related, rapid, consistent, and reversible reduction of RL and an increase of dynamic lung compliance. The onset of bronchodilation was rapid, beginning within 30 s after commencing inhalation. An inhaled NO concentration of 15.0 +/- 2.1 ppm was required to reduce RL by 50% of the induced bronchoconstriction. Inhalation of 100 ppm NO for 1 h did not produce tolerance to its bronchodilator effect nor did it induce substantial methemoglobinemia (less than 2%). The bronchodilating effects of NO were additive with the effects of inhaled terbutaline, irrespective of the sequence of NO and terbutaline administration. Inhaling aerosol generated from S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine also induced a rapid and profound decrease of RL from 0.453 +/- 0.022 to 0.287 +/- 0.022 cmH2O/ml.s, which lasted for over 15 min in guinea pigs broncho-constricted with methacholine. Our results indicate that low levels of inhaled gaseous NO, or an aerosolized NO-releasing compound are potent bronchodilators in guinea pigs.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMDUR M. O., MEAD J. Mechanics of respiration in unanesthetized guinea pigs. Am J Physiol. 1958 Feb;192(2):364–368. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.192.2.364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold W. P., Aldred R., Murad F. Cigarette smoke activates guanylate cyclase and increases guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate in tissues. Science. 1977 Dec 2;198(4320):934–936. doi: 10.1126/science.22126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold W. P., Mittal C. K., Katsuki S., Murad F. Nitric oxide activates guanylate cyclase and increases guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate levels in various tissue preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3203–3207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin A. T. The chemistry of the higher oxides of nitrogen as related to the manufacture, storage and administration of nitrous oxide. Br J Anaesth. 1967 May;39(5):345–350. doi: 10.1093/bja/39.5.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belvisi M. G., Stretton D., Barnes P. J. Nitric oxide as an endogenous modulator of cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea-pig airways. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 6;198(2-3):219–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90626-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buga G. M., Gold M. E., Wood K. S., Chaudhuri G., Ignarro L. J. Endothelium-derived nitric oxide relaxes nonvascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb 14;161(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrick R. J., Hobbs E. G., Martineau R., Noble W. H. Nitroglycerin relaxes large airways. Anesth Analg. 1983 Apr;62(4):421–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesrown S. E., Venugopalan C. S., Gold W. M., Drazen J. M. In vivo demonstration of nonadrenergic inhibitory innervation of the guinea pig trachea. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):314–320. doi: 10.1172/JCI109674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross C. E., Halliwell B., Allen A. Antioxidant protection: a function of tracheobronchial and gastrointestinal mucus. Lancet. 1984 Jun 16;1(8390):1328–1330. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91822-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazen J. M., Venugopalan C. S., Schneider M. W. Alteration of histamine response by H2-receptor antagonism in the guinea pig. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Apr;48(4):613–618. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.48.4.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feelisch M., Noack E. A. Correlation between nitric oxide formation during degradation of organic nitrates and activation of guanylate cyclase. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul 2;139(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90493-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratacci M. D., Frostell C. G., Chen T. Y., Wain J. C., Jr, Robinson D. R., Zapol W. M. Inhaled nitric oxide. A selective pulmonary vasodilator of heparin-protamine vasoconstriction in sheep. Anesthesiology. 1991 Dec;75(6):990–999. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199112000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frostell C., Fratacci M. D., Wain J. C., Jones R., Zapol W. M. Inhaled nitric oxide. A selective pulmonary vasodilator reversing hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Circulation. 1991 Jun;83(6):2038–2047. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.6.2038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON Q. H., ROUGHTON F. J. The kinetics and equilibria of the reactions of nitric oxide with sheep haemoglobin. J Physiol. 1957 May 23;136(3):507–524. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruetter C. A., Barry B. K., McNamara D. B., Gruetter D. Y., Kadowitz P. J., Ignarro L. Relaxation of bovine coronary artery and activation of coronary arterial guanylate cyclase by nitric oxide, nitroprusside and a carcinogenic nitrosoamine. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;5(3):211–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruetter C. A., Childers C. E., Bosserman M. K., Lemke S. M., Ball J. G., Valentovic M. A. Comparison of relaxation induced by glyceryl trinitrate, isosorbide dinitrate, and sodium nitroprusside in bovine airways. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 May;139(5):1192–1197. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.5.1192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruetter C. A., Gruetter D. Y., Lyon J. E., Kadowitz P. J., Ignarro L. J. Relationship between cyclic guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate formation and relaxation of coronary arterial smooth muscle by glyceryl trinitrate, nitroprusside, nitrite and nitric oxide: effects of methylene blue and methemoglobin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Oct;219(1):181–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaslip R. J., Giesa F. R., Rimele T. J., Grimes D. Co-regulation of tracheal tone by cyclic AMP- and cyclic GMP-dependent mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Dec;243(3):1018–1026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Gruetter C. A. Requirement of thiols for activation of coronary arterial guanylate cyclase by glyceryl trinitrate and sodium nitrite: possible involvement of S-nitrosothiols. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 13;631(2):221–231. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90297-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Lippton H., Edwards J. C., Baricos W. H., Hyman A. L., Kadowitz P. J., Gruetter C. A. Mechanism of vascular smooth muscle relaxation by organic nitrates, nitrites, nitroprusside and nitric oxide: evidence for the involvement of S-nitrosothiols as active intermediates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Sep;218(3):739–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson D. D., Taylor K. M. Comparison of the bronchodilator and vasodilator activity of sodium azide and sodium nitroprusside in the guinea-pig. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1979 Sep-Oct;6(5):515–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1979.tb00034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuki S., Arnold W., Mittal C., Murad F. Stimulation of guanylate cyclase by sodium nitroprusside, nitroglycerin and nitric oxide in various tissue preparations and comparison to the effects of sodium azide and hydroxylamine. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1977 Feb;3(1):23–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuki S., Murad F. Regulation of adenosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate and guanosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate levels and contractility in bovine tracheal smooth muscle. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;13(2):330–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. P., Morgan K. G. Alteration of cytoplasmic ionized calcium levels in smooth muscle by vasodilators in the ferret. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:539–551. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow P. E. Toxicological data on NOx: an overview. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1984;13(2-3):205–227. doi: 10.1080/15287398409530494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munakata M., Masaki Y., Sakuma I., Ukita H., Otsuka Y., Homma Y., Kawakami Y. Pharmacological differentiation of epithelium-derived relaxing factor from nitric oxide. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 Aug;69(2):665–670. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.69.2.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda H., Kusumoto S., Nakajima T. Nitrosyl-hemoglobin formation in the blood of animals exposed to nitric oxide. Arch Environ Health. 1975 Sep;30(9):453–456. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1975.10666749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. A., Drazen J. M. Degradative enzymes modulate airway responses to intravenous neurokinins A and B. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Dec;67(6):2504–2511. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.6.2504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torphy T. J., Zhou H. L., Burman M., Huang L. B. Role of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isozymes in intact canine trachealis. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;39(3):376–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner P. D., Dantzker D. R., Iacovoni V. E., Tomlin W. C., West J. B. Ventilation-perfusion inequality in asymptomatic asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Sep;118(3):511–524. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.3.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwart A., Buursma A., Oeseburg B., Zijlstra W. G. Determination of hemoglobin derivatives with IL 282 CO-oximeter as compared with a manual spectrophotometric five-wavelength method. Clin Chem. 1981 Nov;27(11):1903–1907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


