Abstract
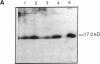
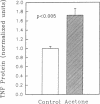
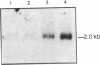
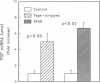
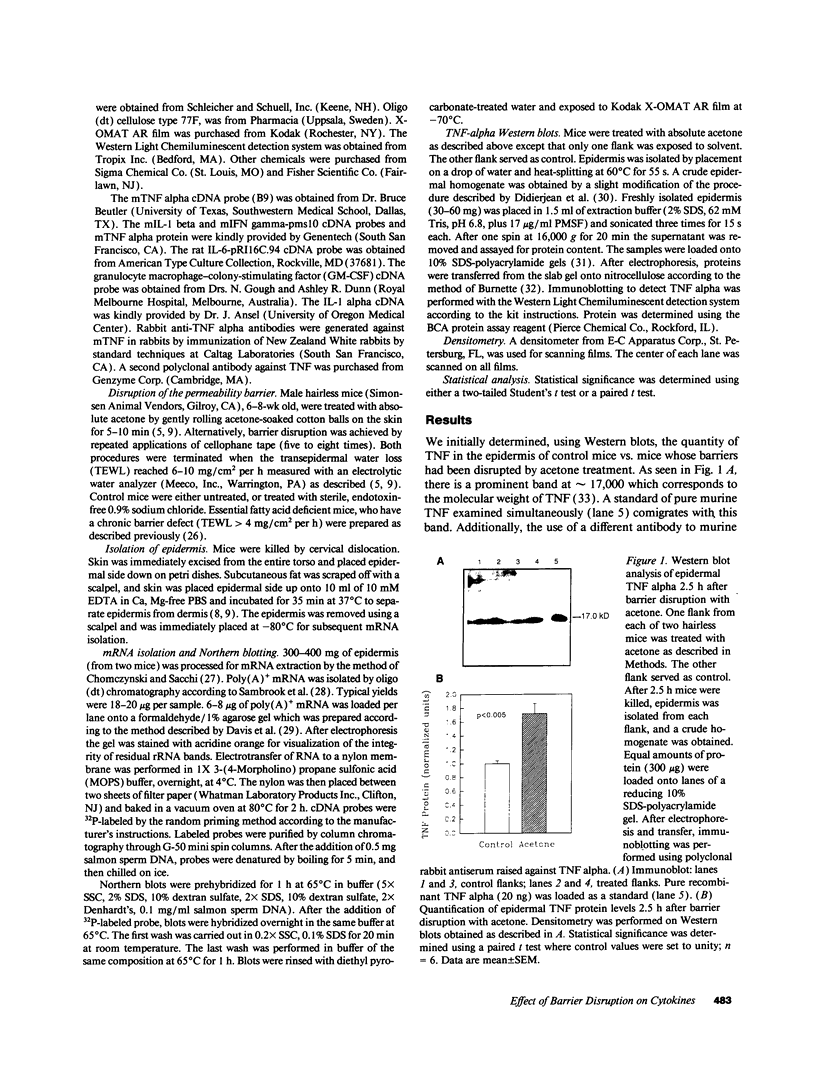
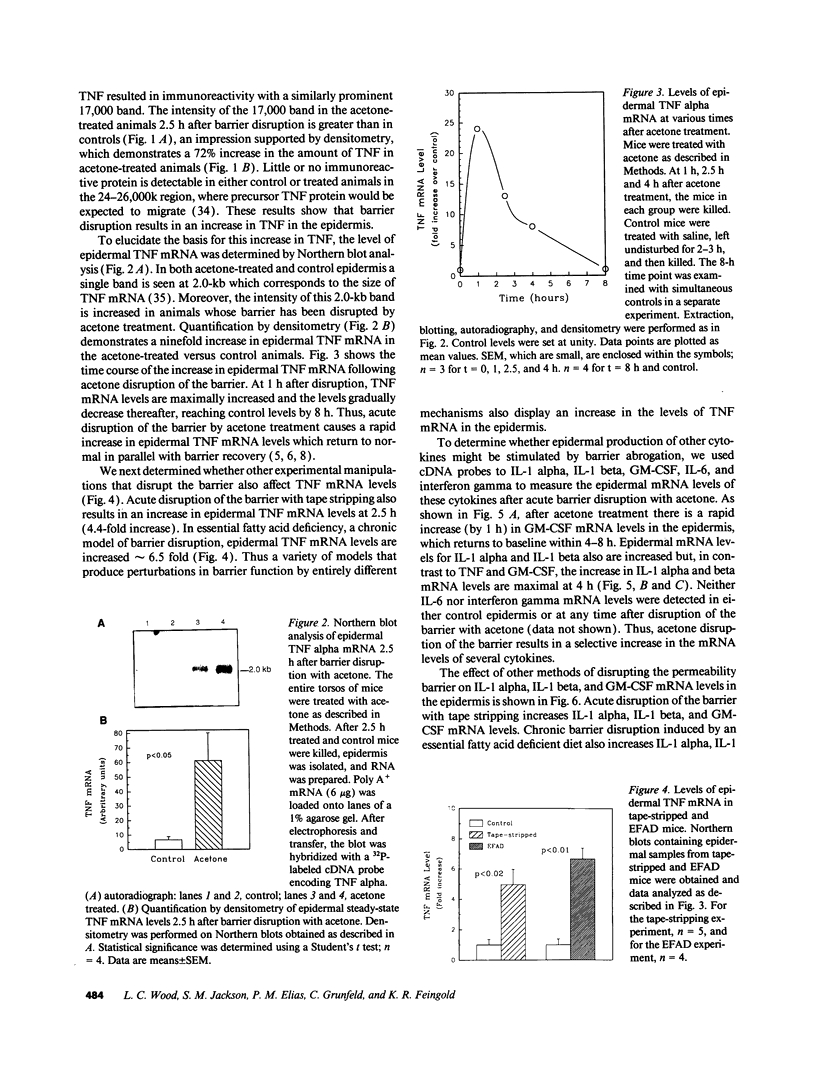
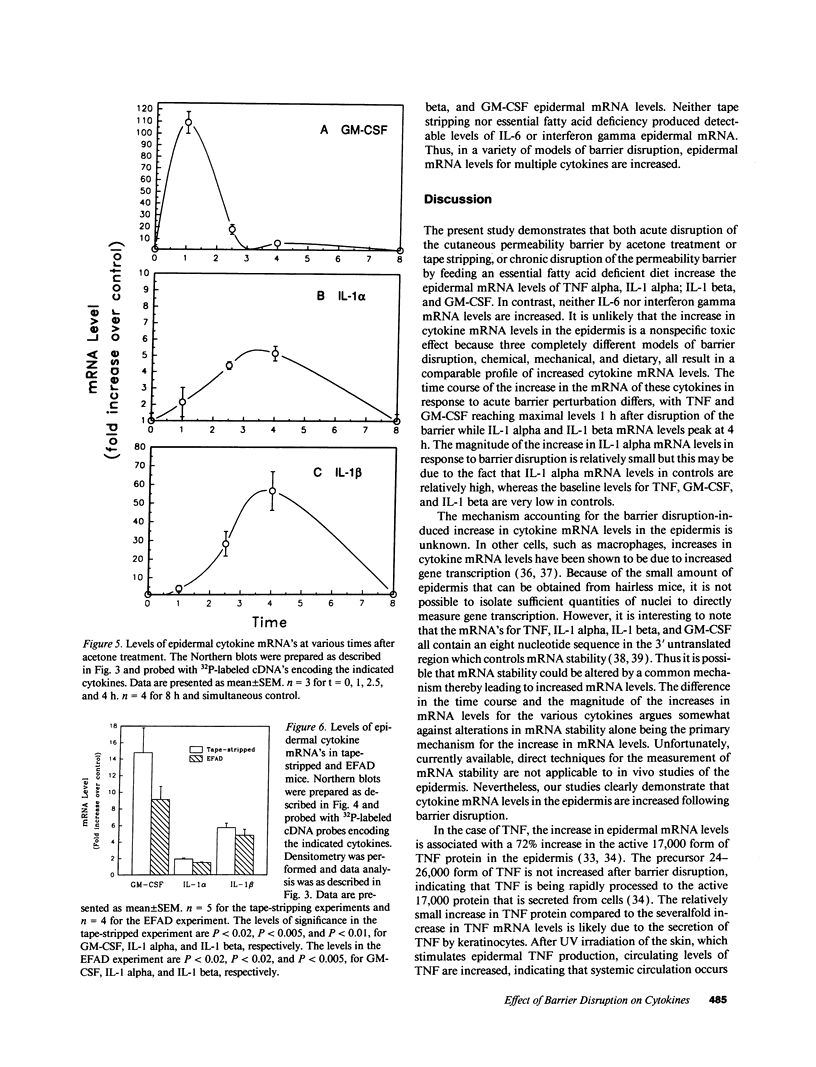
The disruption of the cutaneous permeability barrier results in metabolic events that ultimately restore barrier function. These include increased epidermal sterol, fatty acid, and sphingolipid synthesis, as well as increased epidermal DNA synthesis. Because tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and other cytokines are known products of keratinocytes and have been shown to modulate lipid and DNA synthesis in other systems, their levels were examined in two acute models and one chronic model of barrier perturbation in hairless mice. Acute barrier disruption with acetone results in a 72% increase in epidermal TNF 2.5 h after treatment, as determined by Western blotting. Furthermore, epidermal TNF mRNA was elevated ninefold over controls 2.5 h after acetone treatment. This elevation in TNF mRNA was maximal at 1 h after acetone, and decreased to control levels by 8 h. After tape stripping, a second acute model of barrier disruption that avoids application of potentially toxic chemicals, TNF mRNA was elevated fivefold over controls at 2.5 h. Moreover, the mRNA levels for epidermal IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, and granulocyte macrophage-colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) also were elevated several-fold over controls, after either acetone treatment or tape stripping, but their kinetics differed. GM-CSF mRNA reached a maximal level at 1 h after acetone, while IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta were maximal at 4 h after treatment. In contrast, mRNAs encoding IL-6 and IFN gamma were not detected either in control murine epidermis or in samples obtained at various times after tape stripping or acetone treatment. The relationship of the cytokine response to barrier function is further strengthened by results obtained in essential fatty acid deficient mice. In this chronic model of barrier perturbation mRNA levels for epidermal TNF, IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, and GM-CSF were each elevated several-fold over controls. These results suggest that epidermal cytokine production is increased after barrier disruption and may play a role in restoring the cutaneous permeability barrier.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal B. B., Kohr W. J., Hass P. E., Moffat B., Spencer S. A., Henzel W. J., Bringman T. S., Nedwin G. E., Goeddel D. V., Harkins R. N. Human tumor necrosis factor. Production, purification, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2345–2354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. D. The pathomechanisms of psoriasis; the skin immune system and cyclosporin. Br J Dermatol. 1988 Feb;118(2):141–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1988.tb01768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didierjean L., Salomon D., Mérot Y., Siegenthaler G., Shaw A., Dayer J. M., Saurat J. H. Localization and characterization of the interleukin 1 immunoreactive pool (IL-1 alpha and beta forms) in normal human epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Jun;92(6):809–816. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12696825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P. M., Brown B. E. The mammalian cutaneous permeability barrier: defective barrier function is essential fatty acid deficiency correlates with abnormal intercellular lipid deposition. Lab Invest. 1978 Dec;39(6):574–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P. M., Feingold K. R. Lipid-related barriers and gradients in the epidermis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;548:4–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb18788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P. M., Menon G. K. Structural and lipid biochemical correlates of the epidermal permeability barrier. Adv Lipid Res. 1991;24:1–26. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024924-4.50005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre R. W., Krueger G. G. Response to injury of skin involved and uninvolved with psoriasis, and its relation to disease activity: Koebner and 'reverse' Koebner reactions. Br J Dermatol. 1982 Feb;106(2):153–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1982.tb00924.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farb R. M., Dykes R., Lazarus G. S. Anti-epidermal-cell-surface pemphigus antibody detaches viable epidermal cells from culture plates by activation of proteinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):459–463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Brown B. E., Lear S. R., Moser A. H., Elias P. M. Effect of essential fatty acid deficiency on cutaneous sterol synthesis. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Nov;87(5):588–591. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12455835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Grunfeld C. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulates hepatic lipogenesis in the rat in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):184–190. doi: 10.1172/JCI113046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Man M. Q., Menon G. K., Cho S. S., Brown B. E., Elias P. M. Cholesterol synthesis is required for cutaneous barrier function in mice. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1738–1745. doi: 10.1172/JCI114899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Soued M., Serio M. K., Moser A. H., Dinarello C. A., Grunfeld C. Multiple cytokines stimulate hepatic lipid synthesis in vivo. Endocrinology. 1989 Jul;125(1):267–274. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-1-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geelen M. J., Harris R. A., Beynen A. C., McCune S. A. Short-term hormonal control of hepatic lipogenesis. Diabetes. 1980 Dec;29(12):1006–1022. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.12.1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths C. E., Barker J. N., Kunkel S., Nickoloff B. J. Modulation of leucocyte adhesion molecules, a T-cell chemotaxin (IL-8) and a regulatory cytokine (TNF-alpha) in allergic contact dermatitis (rhus dermatitis). Br J Dermatol. 1991 Jun;124(6):519–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1991.tb04943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman R. M., Krueger J., Yourish D., Granelli-Piperno A., Murphy D. P., May L. T., Kupper T. S., Sehgal P. B., Gottlieb A. B. Interleukin 6 is expressed in high levels in psoriatic skin and stimulates proliferation of cultured human keratinocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6367–6371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubauer G., Elias P. M., Feingold K. R. Transepidermal water loss: the signal for recovery of barrier structure and function. J Lipid Res. 1989 Mar;30(3):323–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubauer G., Feingold K. R., Elias P. M. Relationship of epidermal lipogenesis to cutaneous barrier function. J Lipid Res. 1987 Jun;28(6):746–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubauer G., Feingold K. R., Harris R. M., Elias P. M. Lipid content and lipid type as determinants of the epidermal permeability barrier. J Lipid Res. 1989 Jan;30(1):89–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunfeld C., Adi S., Soued M., Moser A., Fiers W., Feingold K. R. Search for mediators of the lipogenic effects of tumor necrosis factor: potential role for interleukin 6. Cancer Res. 1990 Jul 15;50(14):4233–4238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunfeld C., Verdier J. A., Neese R., Moser A. H., Feingold K. R. Mechanisms by which tumor necrosis factor stimulates hepatic fatty acid synthesis in vivo. J Lipid Res. 1988 Oct;29(10):1327–1335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock G. E., Kaplan G., Cohn Z. A. Keratinocyte growth regulation by the products of immune cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1395–1402. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holleran W. M., Feingold K. R., Man M. Q., Gao W. N., Lee J. M., Elias P. M. Regulation of epidermal sphingolipid synthesis by permeability barrier function. J Lipid Res. 1991 Jul;32(7):1151–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holleran W. M., Man M. Q., Gao W. N., Menon G. K., Elias P. M., Feingold K. R. Sphingolipids are required for mammalian epidermal barrier function. Inhibition of sphingolipid synthesis delays barrier recovery after acute perturbation. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1338–1345. doi: 10.1172/JCI115439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriegler M., Perez C., DeFay K., Albert I., Lu S. D. A novel form of TNF/cachectin is a cell surface cytotoxic transmembrane protein: ramifications for the complex physiology of TNF. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90486-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Krane J. F., Carter D. M., Gottlieb A. B. Role of growth factors, cytokines, and their receptors in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Jun;94(6 Suppl):135S–140S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12876121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupper T. S. Immune and inflammatory processes in cutaneous tissues. Mechanisms and speculations. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1783–1789. doi: 10.1172/JCI114907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köck A., Schwarz T., Kirnbauer R., Urbanski A., Perry P., Ansel J. C., Luger T. A. Human keratinocytes are a source for tumor necrosis factor alpha: evidence for synthesis and release upon stimulation with endotoxin or ultraviolet light. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks R., Hill S., Barton S. P. The effects of an abrasive agent on normal skin and on photoaged skin in comparison with topical tretinoin. Br J Dermatol. 1990 Oct;123(4):457–466. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1990.tb01450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon G. K., Feingold K. R., Elias P. M. Lamellar body secretory response to barrier disruption. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Mar;98(3):279–289. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12497866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon G. K., Feingold K. R., Moser A. H., Brown B. E., Elias P. M. De novo sterologenesis in the skin. II. Regulation by cutaneous barrier requirements. J Lipid Res. 1985 Apr;26(4):418–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani H., Black R., Kupper T. S. Human keratinocytes produce but do not process pro-interleukin-1 (IL-1) beta. Different strategies of IL-1 production and processing in monocytes and keratinocytes. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):1066–1071. doi: 10.1172/JCI115067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff B. J., Karabin G. D., Barker J. N., Griffiths C. E., Sarma V., Mitra R. S., Elder J. T., Kunkel S. L., Dixit V. M. Cellular localization of interleukin-8 and its inducer, tumor necrosis factor-alpha in psoriasis. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):129–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxholm A., Oxholm P., Staberg B., Bendtzen K. Immunohistological detection of interleukin I-like molecules and tumour necrosis factor in human epidermis before and after UVB-irradiation in vivo. Br J Dermatol. 1988 Mar;118(3):369–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1988.tb02430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Hayflick J. S., Bringman T. S., Palladino M. A., Goeddel D. V. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the cDNA for murine tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6060–6064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet P. F., Grau G. E., Hauser C., Vassalli P. Tumor necrosis factor is a critical mediator in hapten induced irritant and contact hypersensitivity reactions. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):673–679. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillai S., Bikle D. D., Eessalu T. E., Aggarwal B. B., Elias P. M. Binding and biological effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha on cultured human neonatal foreskin keratinocytes. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):816–821. doi: 10.1172/JCI113963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinnagoda J., Tupker R. A., Coenraads P. J., Nater J. P. Prediction of susceptibility to an irritant response by transepidermal water loss. Contact Dermatitis. 1989 May;20(5):341–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0536.1989.tb03170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powles A. V., Baker B. S., Rutman A. J., McFadden J. P., Valdimarsson H., Fry L. Epidermal rupture is the initiating factor for the Koebner response in psoriasis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1990;70(1):35–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proksch E., Elias P. M., Feingold K. R. Localization and regulation of epidermal 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase activity by barrier requirements. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 24;1083(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(91)90126-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proksch E., Elias P. M., Feingold K. R. Regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase activity in murine epidermis. Modulation of enzyme content and activation state by barrier requirements. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):874–882. doi: 10.1172/JCI114514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proksch E., Feingold K. R., Man M. Q., Elias P. M. Barrier function regulates epidermal DNA synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1991 May;87(5):1668–1673. doi: 10.1172/JCI115183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sariban E., Imamura K., Luebbers R., Kufe D. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of tumor necrosis factor gene expression in human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1506–1510. doi: 10.1172/JCI113482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz T., Luger T. A. Effect of UV irradiation on epidermal cell cytokine production. J Photochem Photobiol B. 1989 Oct;4(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/1011-1344(89)80097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucla C., Roux-Lombard P., Fey S., Dayer J. M., Mach B. Interferon gamma drastically modifies the regulation of interleukin 1 genes by endotoxin in U937 cells. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):185–191. doi: 10.1172/JCI114411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbanski A., Schwarz T., Neuner P., Krutmann J., Kirnbauer R., Köck A., Luger T. A. Ultraviolet light induces increased circulating interleukin-6 in humans. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Jun;94(6):808–811. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]