Abstract
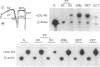
We have cloned two closely related putative Cl- channels from both rat kidney (designated rClC-K1 and rClC-K2) and human kidney (hClC-Ka and hClC-Kb) by sequence homology to the ClC family of voltage-gated Cl- channels. While rClC-K1 is nearly identical to ClC-K1, a channel recently isolated by a similar strategy, rClC-K2 is 80% identical to rClC-K1 and is encoded by a different gene. hClC-Ka and hClC-Kb show approximately 90% identity, while being approximately 80% identical to the rat proteins. All ClC-K gene products are expressed predominantly in the kidney. While rClC-K1 is expressed strongly in the cortical thick ascending limb and the distal convoluted tubule, with minor expression in the S3 segment of the proximal tubule and the cortical collecting tubule, rClC-K2 is expressed in all segments of the nephron examined, including the glomerulus. Since they are related more closely to each other than to the rat proteins, hClC-Ka and hClC-Kb cannot be regarded as strict homologs of rClC-K1 or rClC-K2. After injection of ClC-K cRNAs into oocytes, corresponding proteins were made and glycosylated, though no additional Cl- currents were detectable. Glycosylation occurs between domains D8 and D9, leading to a revision of the transmembrane topology model for ClC channels.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akli S., Chelly J., Lacorte J. M., Poenaru L., Kahn A. Seven novel Tay-Sachs mutations detected by chemical mismatch cleavage of PCR-amplified cDNA fragments. Genomics. 1991 Sep;11(1):124–134. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90109-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attali B., Guillemare E., Lesage F., Honoré E., Romey G., Lazdunski M., Barhanin J. The protein IsK is a dual activator of K+ and Cl- channels. Nature. 1993 Oct 28;365(6449):850–852. doi: 10.1038/365850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer C. K., Steinmeyer K., Schwarz J. R., Jentsch T. J. Completely functional double-barreled chloride channel expressed from a single Torpedo cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11052–11056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boton R., Singer D., Dascal N. Inactivation of calcium-activated chloride conductance in Xenopus oocytes: roles of calcium and protein kinase C. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Apr;416(1-2):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF00370214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartier N., Lacave R., Vallet V., Hagege J., Hellio R., Robine S., Pringault E., Cluzeaud F., Briand P., Kahn A. Establishment of renal proximal tubule cell lines by targeted oncogenesis in transgenic mice using the L-pyruvate kinase-SV40 (T) antigen hybrid gene. J Cell Sci. 1993 Mar;104(Pt 3):695–704. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.3.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford I., Maloney P. C., Zeitlin P. L., Guggino W. B., Hyde S. C., Turley H., Gatter K. C., Harris A., Higgins C. F. Immunocytochemical localization of the cystic fibrosis gene product CFTR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9262–9266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Rienitz A., Schmitt B., Methfessel C., Zensen M., Beyreuther K., Gundelfinger E. D., Betz H. The strychnine-binding subunit of the glycine receptor shows homology with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):215–220. doi: 10.1038/328215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gründer S., Thiemann A., Pusch M., Jentsch T. J. Regions involved in the opening of CIC-2 chloride channel by voltage and cell volume. Nature. 1992 Dec 24;360(6406):759–762. doi: 10.1038/360759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch T. J., Steinmeyer K., Schwarz G. Primary structure of Torpedo marmorata chloride channel isolated by expression cloning in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):510–514. doi: 10.1038/348510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montrose-Rafizadeh C., Guggino W. B. Cell volume regulation in the nephron. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:761–772. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peres A., Bernardini G. A hyperpolarization-activated chloride current in Xenopus laevis oocytes under voltage-clamp. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Oct;399(2):157–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00663914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M., Steinmeyer K., Jentsch T. J. Low single channel conductance of the major skeletal muscle chloride channel, ClC-1. Biophys J. 1994 Jan;66(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80753-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. B., Andreoli T. E. Renal epithelial chloride channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:29–50. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Darlison M. G., Fujita N., Burt D. R., Stephenson F. A., Rodriguez H., Rhee L. M., Ramachandran J., Reale V., Glencorse T. A. Sequence and functional expression of the GABA A receptor shows a ligand-gated receptor super-family. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):221–227. doi: 10.1038/328221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmeyer K., Lorenz C., Pusch M., Koch M. C., Jentsch T. J. Multimeric structure of ClC-1 chloride channel revealed by mutations in dominant myotonia congenita (Thomsen). EMBO J. 1994 Feb 15;13(4):737–743. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06315.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmeyer K., Ortland C., Jentsch T. J. Primary structure and functional expression of a developmentally regulated skeletal muscle chloride channel. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):301–304. doi: 10.1038/354301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemann A., Gründer S., Pusch M., Jentsch T. J. A chloride channel widely expressed in epithelial and non-epithelial cells. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):57–60. doi: 10.1038/356057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida S., Sasaki S., Furukawa T., Hiraoka M., Imai T., Hirata Y., Marumo F. Molecular cloning of a chloride channel that is regulated by dehydration and expressed predominantly in kidney medulla. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3821–3824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandewalle A., Wirthensohn G., Heidrich H. G., Guder W. G. Distribution of hexokinase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase along the rabbit nephron. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):F492–F500. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.6.F492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb D. J., Nuccitelli R. Fertilization potential and electrical properties of the Xenopus laevis egg. Dev Biol. 1985 Feb;107(2):395–406. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90321-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]