Abstract
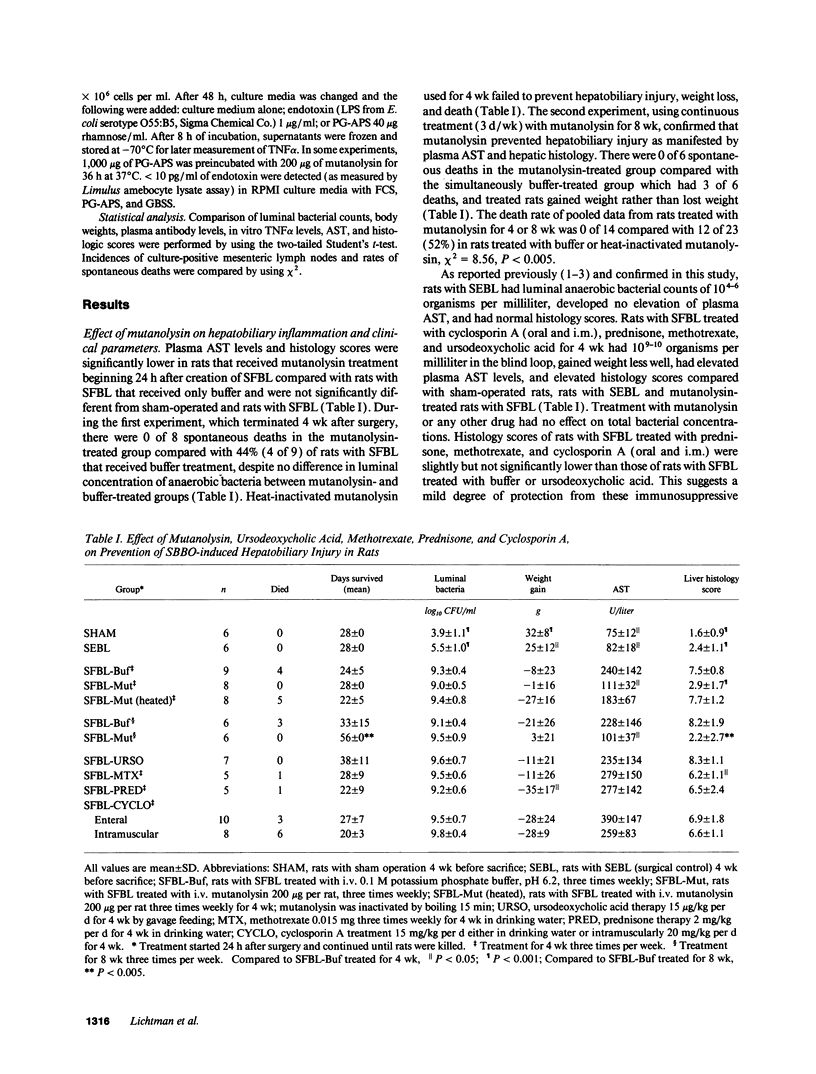
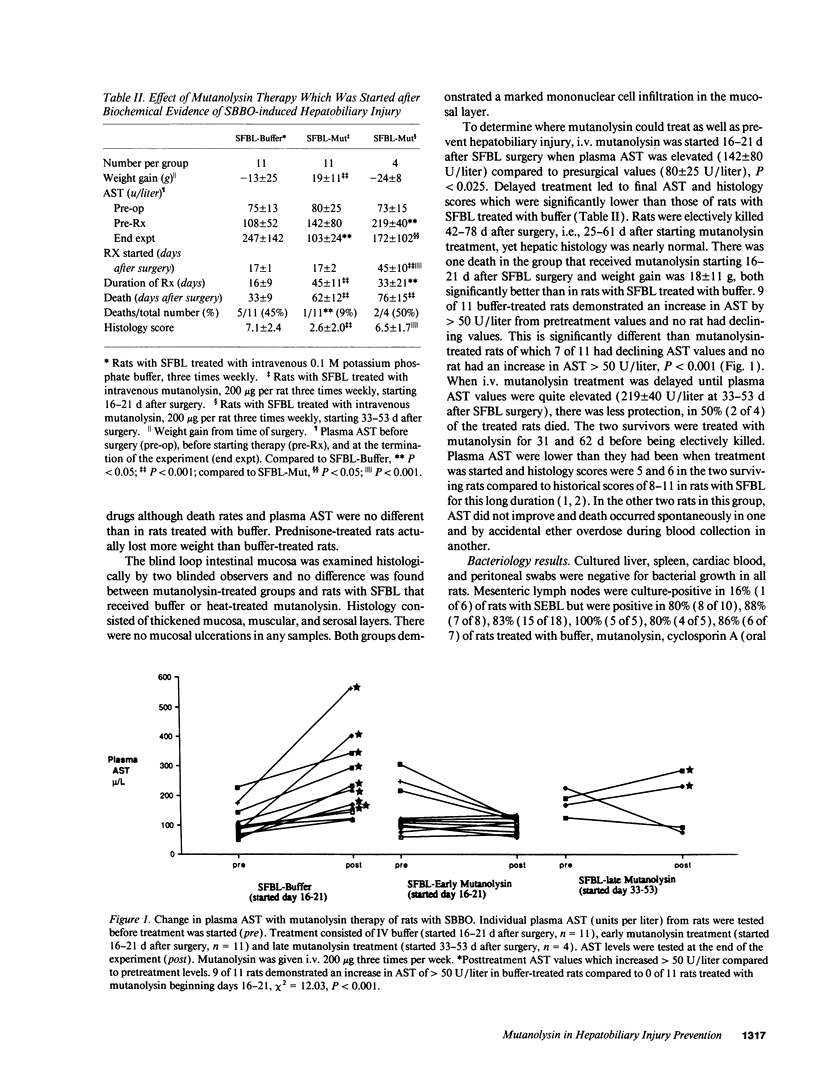
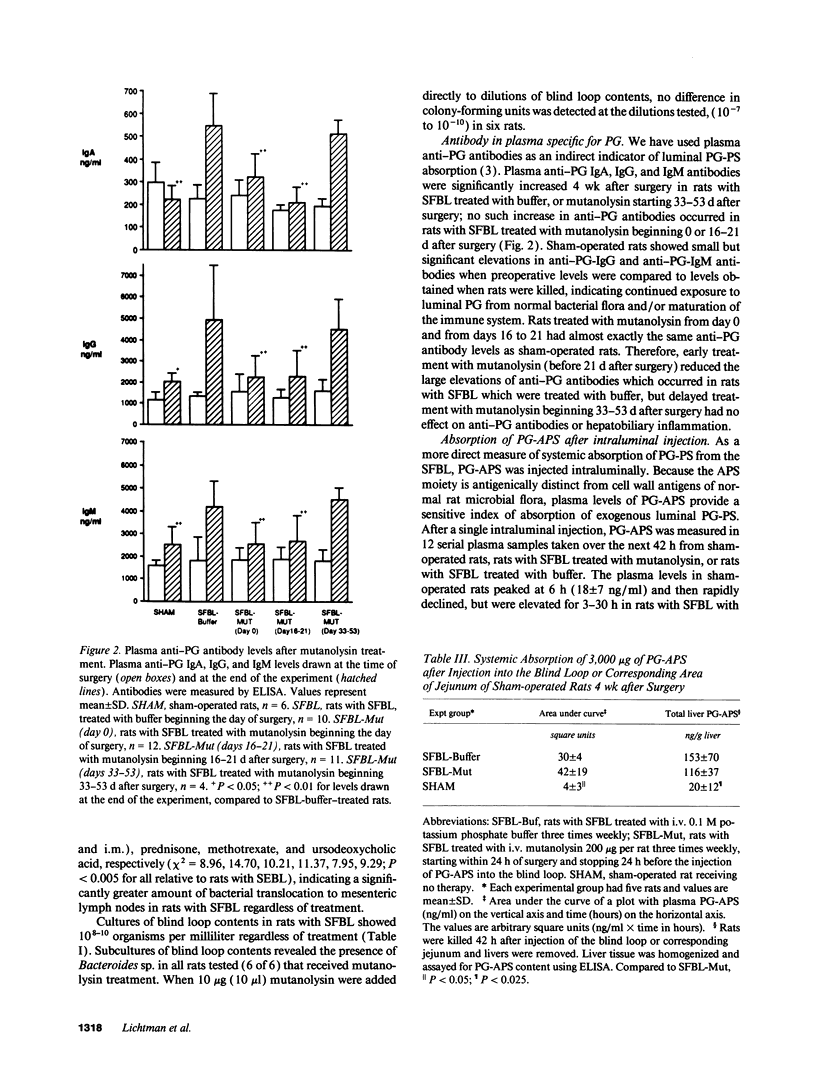
Jejunal self-filling blind loops with subsequent small bowel bacterial overgrowth (SBBO) induce hepatobiliary injury in genetically susceptible Lewis rats. Lesions consist of portal tract inflammation, bile duct proliferation, and destruction. To determine the pathogenesis of SBBO-induced hepatobiliary injury, we treated Lewis rats with SBBO by using several agents with different mechanisms of activity. Buffer treatment, ursodeoxycholic acid, prednisone, methotrexate, and cyclosporin A failed to prevent SBBO-induced injury as demonstrated by increased plasma aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and elevated histology scores. However, hepatic injury was prevented by mutanolysin, a muralytic enzyme whose only known activity is to split the beta 1-4 N-acetylmuramyl-N-acetylglucosamine linkage of peptidoglycan-polysaccharide (PG-PS), a bacterial cell wall polymer with potent inflammatory and immunoregulatory properties. Mutanolysin therapy started on the day blind loops were surgically created and continued for 8 wk significantly diminished AST (101 +/- 37 U/liter) and liver histology scores (2.2 +/- 2.7) compared to buffer-treated rats (228 +/- 146 U/liter, P < 0.05, 8.2 +/- 1.9, P < 0.001 respectively). Mutanolysin treatment started during the early phase of hepatic injury, 16-21 d after surgery, decreased AST in 7 of 11 rats from 142 +/- 80 to 103 +/- 24 U/liter contrasted to increased AST in 9 of 11 buffer-treated rats from 108 +/- 52 to 247 +/- 142 U/liter, P < 0.05. Mutanolysin did not change total bacterial numbers within the loop, eliminate Bacteroides sp., have in vitro antibiotic effects, or diminish mucosal PG-PS transport. However, mutanolysin treatment prevented elevation of plasma anti-PG antibodies and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF alpha) levels which occurred in buffer treated rats with SBBO and decreased TNF alpha production in isolated Kupffer cells stimulated in vitro with PG-PS. Based on the preventive and therapeutic activity of this highly specific muralytic enzyme, we conclude that systemic uptake of PG-PS derived from endogenous enteric bacteria contributes to hepatobiliary injury induced by SBBO in susceptible rat strains.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderle S. K., Allen J. B., Wilder R. L., Eisenberg R. A., Cromartie W. J., Schwab J. H. Measurement of streptococcal cell wall in tissues of rats resistant or susceptible to cell wall-induced chronic erosive arthritis. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):836–837. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.836-837.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. D. Promotion of the translocation of enteric bacteria from the gastrointestinal tracts of mice by oral treatment with penicillin, clindamycin, or metronidazole. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):854–861. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.854-861.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J., Aslam M., Pusey C. D., Ryan C. J. Protection from endotoxemia: a rat model of plasmapheresis and specific adsorption with polymyxin B. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):690–695. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromartie W. J., Craddock J. G., Schwab J. H., Anderle S. K., Yang C. H. Arthritis in rats after systemic injection of streptococcal cells or cell walls. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1585–1602. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalldorf F. G., Cromartie W. J., Anderle S. K., Clark R. L., Schwab J. H. The relation of experimental arthritis to the distribution of streptococcal cell wall fragments. Am J Pathol. 1980 Aug;100(2):383–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLa Cadena R. A., Laskin K. J., Pixley R. A., Sartor R. B., Schwab J. H., Back N., Bedi G. S., Fisher R. S., Colman R. W. Role of kallikrein-kinin system in pathogenesis of bacterial cell wall-induced inflammation. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 1):G213–G219. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.260.2.G213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R., Fox A., Greenblatt J. J., Anderle S. K., Cromartie W. J., Schwab J. H. Measurement of bacterial cell wall in tissues by solid-phase radioimmunoassay: correlation of distribution and persistence with experimental arthritis in rats. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):127–135. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.127-135.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A., Brown R. R., Anderle S. K., Chetty C., Cromartie W. J., Gooder H., Schwab J. H. Arthropathic properties related to the molecular weight of peptidoglycan-polysaccharide polymers of streptococcal cell walls. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1003–1010. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1003-1010.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J. J., Hunter N., Schwab J. H. Antibody response to streptococcal cell wall antigens associated with experimental arthritis in rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Dec;42(3):450–457. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janusz M. J., Chetty C., Eisenberg R. A., Cromartie W. J., Schwab J. H. Treatment of experimental erosive arthritis in rats by injection of the muralytic enzyme mutanolysin. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1360–1374. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janusz M. J., Esser R. E., Schwab J. H. In vivo degradation of bacterial cell wall by the muralytic enzyme mutanolysin. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):459–467. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.459-467.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. E., Toskes P. P. Small intestine bacterial overgrowth. Gastroenterology. 1979 May;76(5 Pt 1):1035–1055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knook D. L., Sleyster E. C. Separation of Kupffer and endothelial cells of the rat liver by centrifugal elutriation. Exp Cell Res. 1976 May;99(2):444–449. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90605-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman S. N., Keku J., Clark R. L., Schwab J. H., Sartor R. B. Biliary tract disease in rats with experimental small bowel bacterial overgrowth. Hepatology. 1991 Apr;13(4):766–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman S. N., Keku J., Schwab J. H., Sartor R. B. Evidence for peptidoglycan absorption in rats with experimental small bowel bacterial overgrowth. Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):555–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.555-562.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman S. N., Keku J., Schwab J. H., Sartor R. B. Hepatic injury associated with small bowel bacterial overgrowth in rats is prevented by metronidazole and tetracycline. Gastroenterology. 1991 Feb;100(2):513–519. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90224-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman S. N., Sartor R. B., Keku J., Schwab J. H. Hepatic inflammation in rats with experimental small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Gastroenterology. 1990 Feb;98(2):414–423. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90833-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podda M., Ghezzi C., Battezzati P. M., Crosignani A., Zuin M., Roda A. Effects of ursodeoxycholic acid and taurine on serum liver enzymes and bile acids in chronic hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1990 Apr;98(4):1044–1050. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90032-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poo J. L., Feldmann G., Erlinger S., Braillon A., Gaudin C., Dumont M., Lebrec D. Ursodeoxycholic acid limits liver histologic alterations and portal hypertension induced by bile duct ligation in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1992 May;102(5):1752–1759. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91739-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartor R. B., Bond T. M., Schwab J. H. Systemic uptake and intestinal inflammatory effects of luminal bacterial cell wall polymers in rats with acute colonic injury. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2101–2108. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2101-2108.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartor R. B., Cromartie W. J., Powell D. W., Schwab J. H. Granulomatous enterocolitis induced in rats by purified bacterial cell wall fragments. Gastroenterology. 1985 Sep;89(3):587–595. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90455-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. H., Anderle S. K., Brown R. R., Dalldorf F. G., Thompson R. C. Pro- and anti-inflammatory roles of interleukin-1 in recurrence of bacterial cell wall-induced arthritis in rats. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4436–4442. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4436-4442.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severijnen A. J., Hazenberg M. P., van de Merwe J. P. Induction of chronic arthritis in rats by cell wall fragments of anaerobic coccoid rods isolated from the faecal flora of patients with Crohn's disease. Digestion. 1988;39(2):118–125. doi: 10.1159/000199614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P., Wesley A., Forstner G. Sequential disaccharidase loss in rat intestinal blind loops: impact of malnutrition. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jun;248(6 Pt 1):G626–G632. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.248.6.G626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimpson S. A., Brown R. R., Anderle S. K., Klapper D. G., Clark R. L., Cromartie W. J., Schwab J. H. Arthropathic properties of cell wall polymers from normal flora bacteria. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):240–249. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.240-249.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimpson S. A., Esser R. E., Cromartie W. J., Schwab J. H. Comparison of in vivo degradation of 125I-labeled peptidoglycan-polysaccharide fragments from group A and group D streptococci. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):390–396. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.390-396.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimpson S. A., Lerch R. A., Cleland D. R., Yarnall D. P., Clark R. L., Cromartie W. J., Schwab J. H. Effect of acetylation on arthropathic activity of group A streptococcal peptidoglycan-polysaccharide fragments. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):16–23. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.16-23.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A. Enzyme immunoassays in diagnostic medicine. Theory and practice. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;53(1):55–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Allen J. B., Dougherty S., Evequoz V., Pluznik D. H., Wilder R. L., Hand A. R., Wahl L. M. T lymphocyte-dependent evolution of bacterial cell wall-induced hepatic granulomas. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2199–2209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Hunt D. A., Allen J. B., Wilder R. L., Paglia L., Hand A. R. Bacterial cell wall-induced hepatic granulomas. An in vivo model of T cell-dependent fibrosis. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):884–902. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells A., Pararajasegaram G., Baldwin M., Yang C. H., Hammer M., Fox A. Uveitis and arthritis induced by systemic injection of streptococcal cell walls. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1986 Jun;27(6):921–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


