Abstract
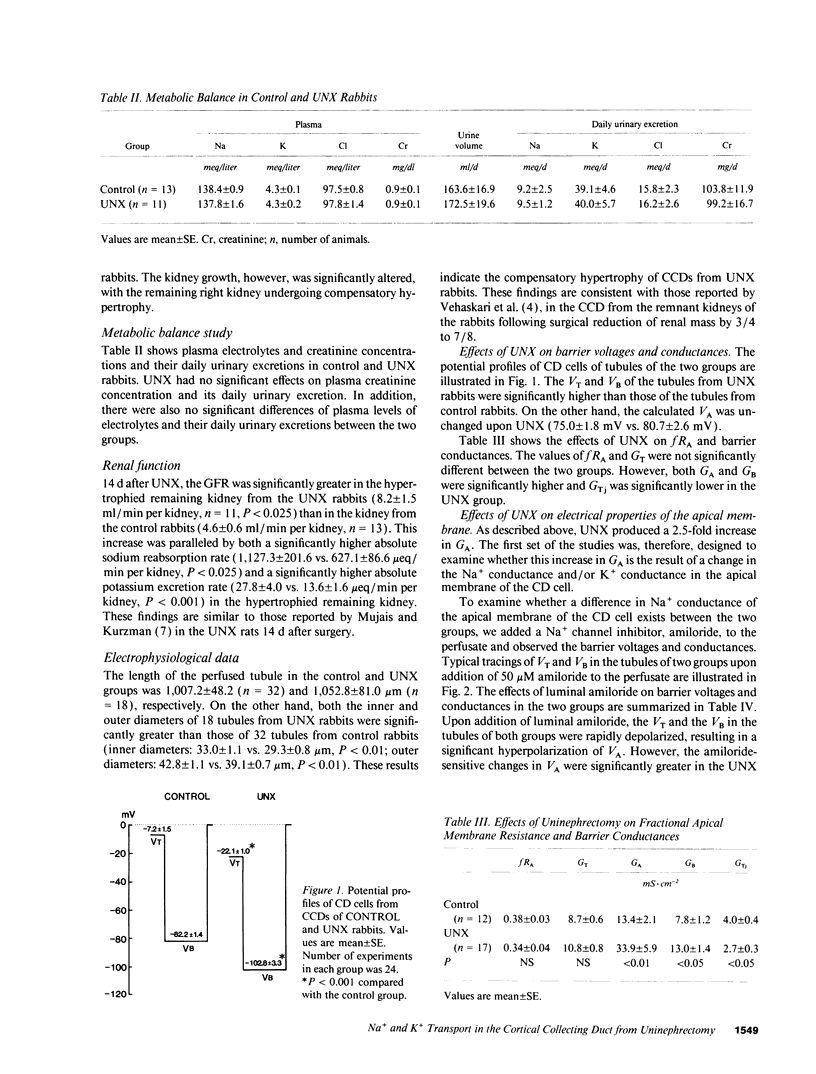
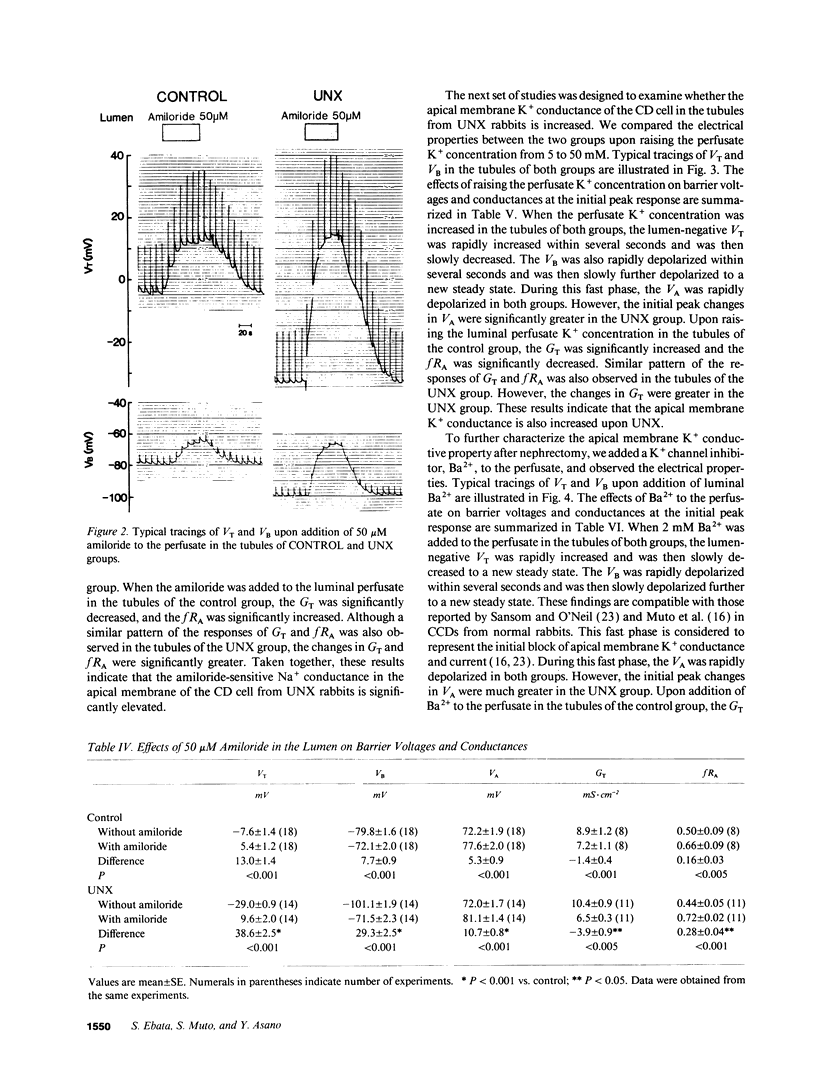
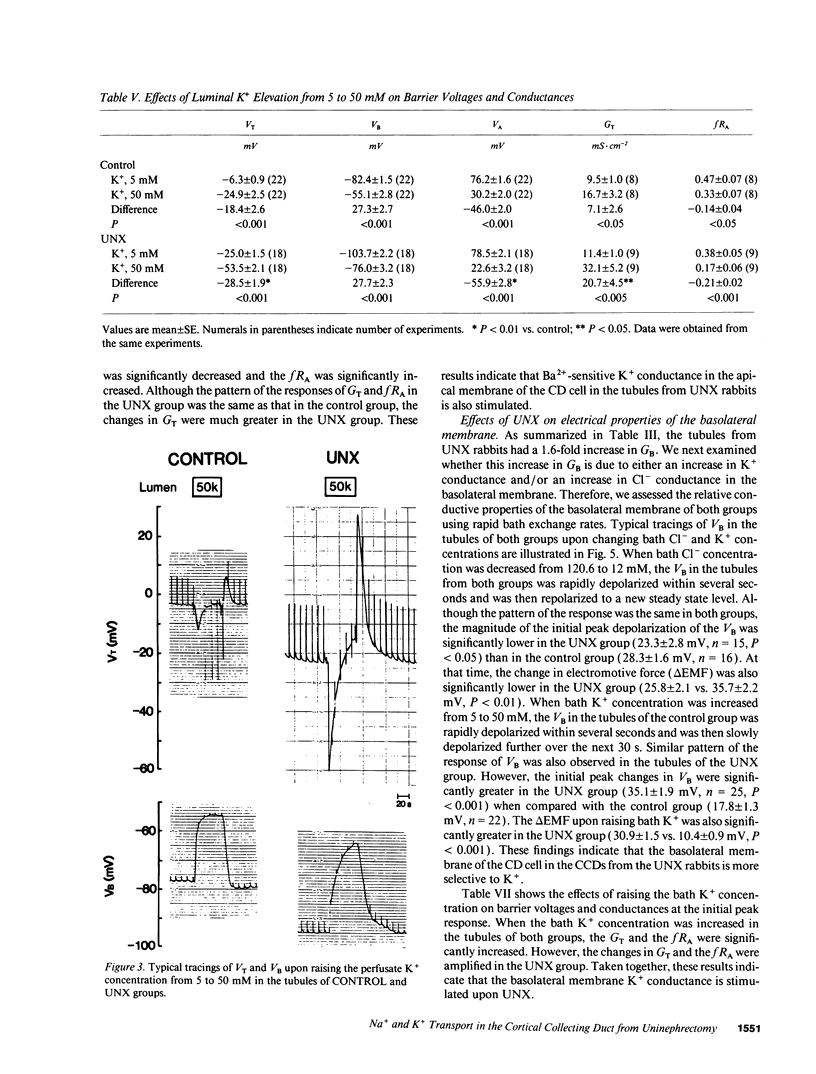
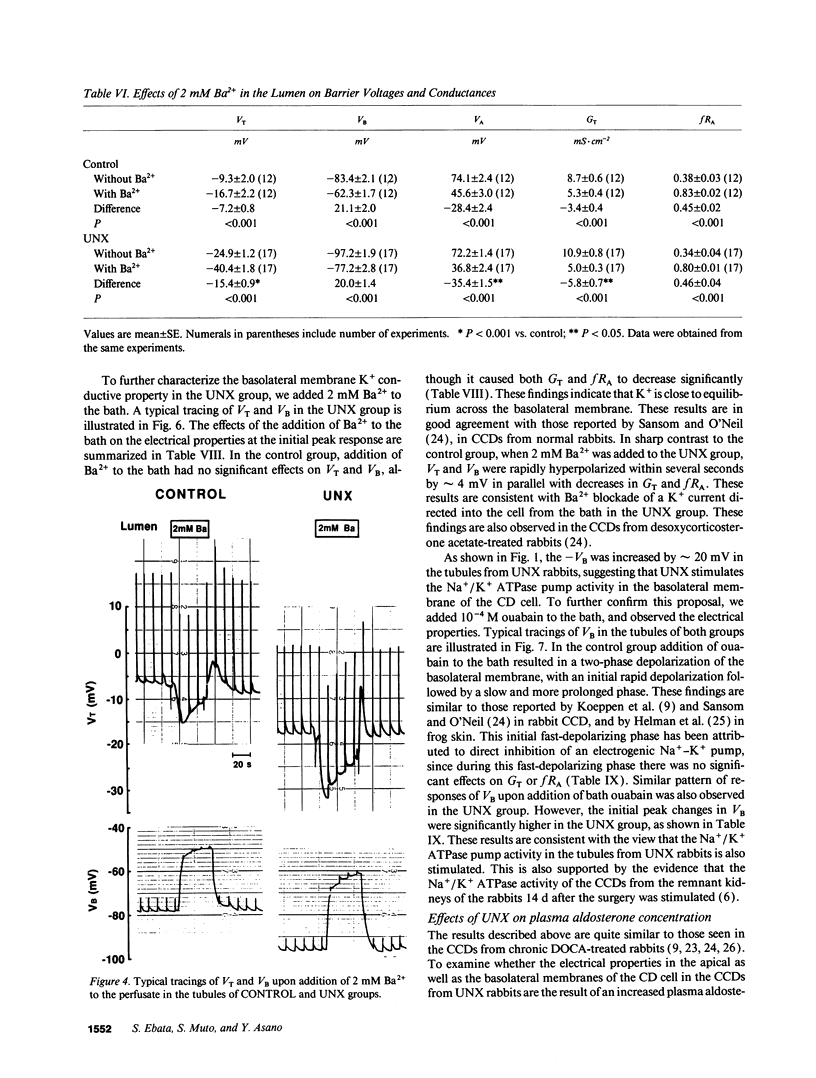
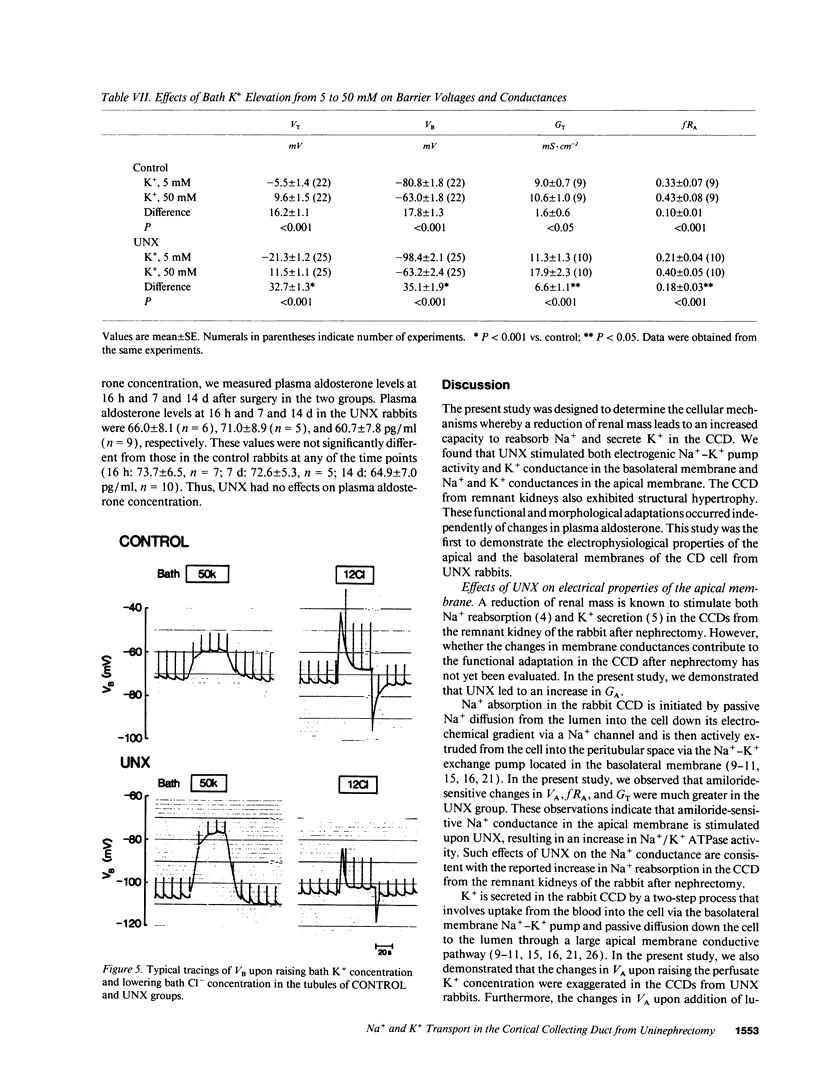
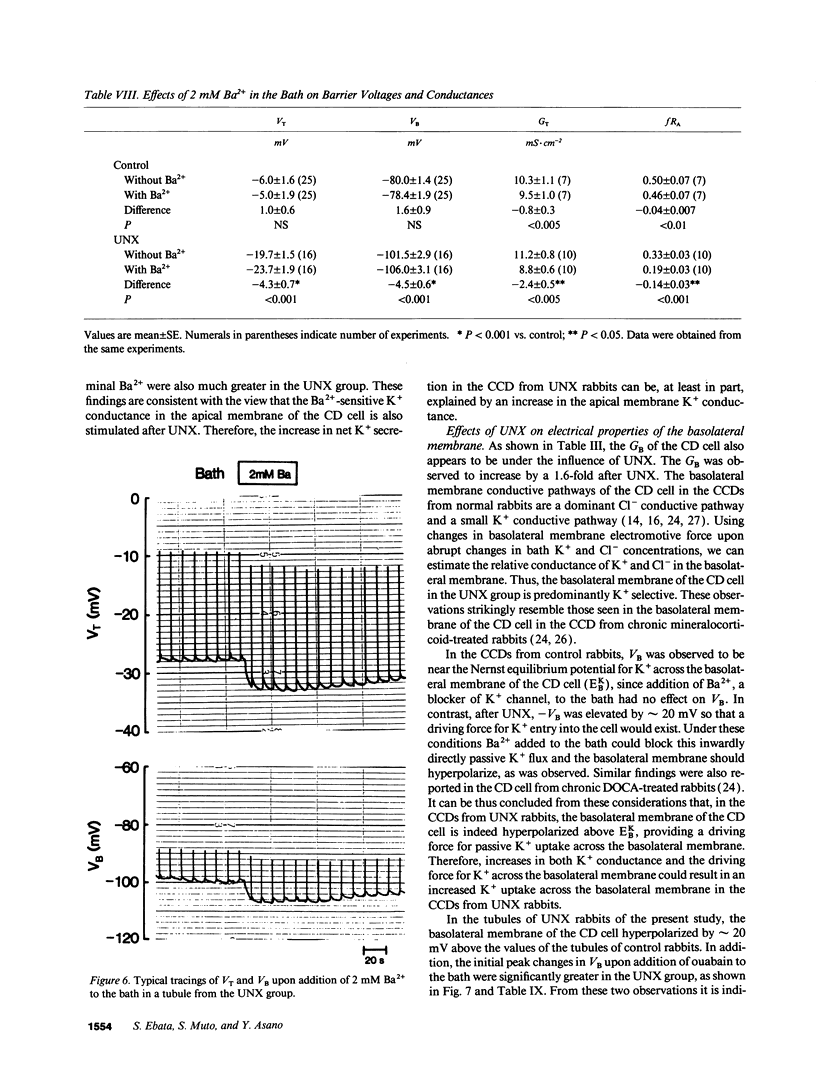
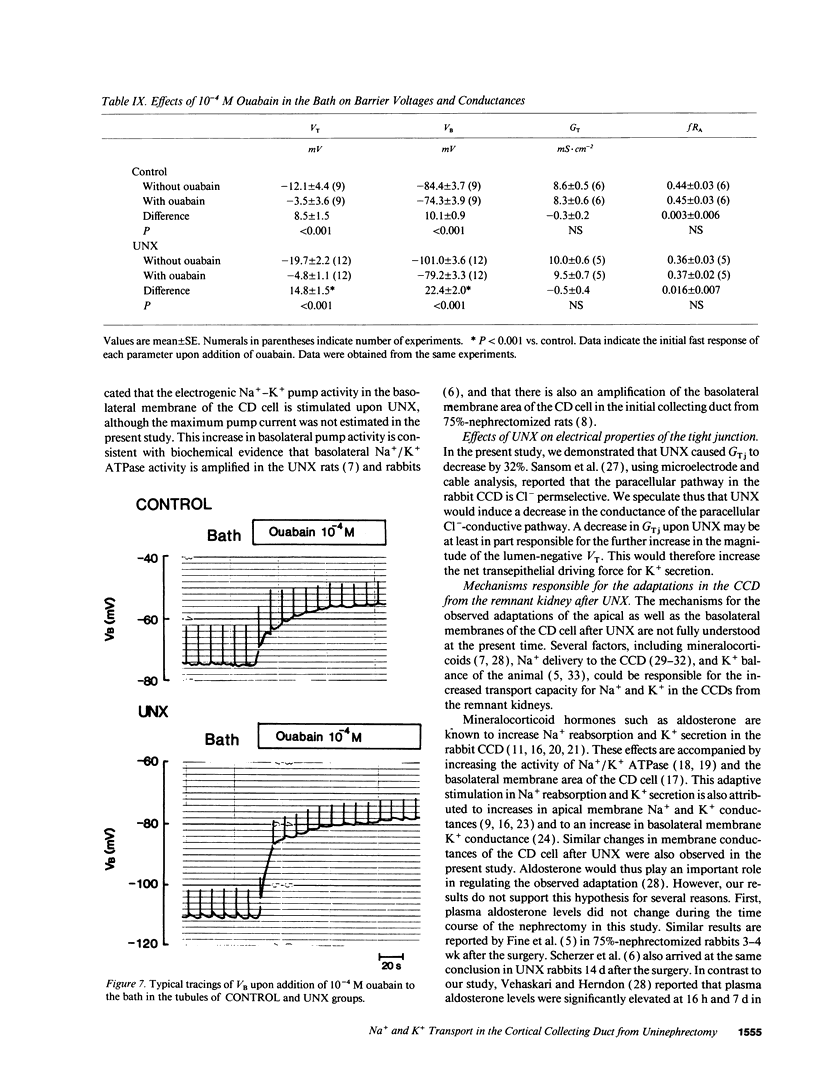
Microelectrode techniques were used to determine the Na+ and K+ transport properties of the collecting duct cell in the isolated cortical collecting duct (CCD) from rabbits 14 d after uninephrectomy (UNX); results were compared with those from sham-operated rabbits (control). UNX had no effects on plasma aldosterone levels. The CCDs from UNX rabbits exhibited structural hypertrophy. The lumen negative transepithelial voltage and the basolateral membrane voltage (VB) were elevated in the UNX group. Although the transepithelial conductance (GT) and the fractional apical membrane resistance (fRA) were not different between the two groups, the conductances of the apical and the basolateral membranes were increased, and the tight junction conductance was decreased in the UNX group. The amiloride-sensitive changes in apical membrane voltage (VA), fRA, and GT were greater in the UNX group. The changes in VA upon raising the perfusate K+ concentration and the changes in VA and GT upon addition of Ba2+ to the perfusate were elevated in the UNX group. Upon raising K+ in the bath, a large depolarization of VB was observed in the UNX group. Lowering the bath Cl- resulted in a small depolarization of VB in the UNX group. Addition of Ba2+ to the bath in the UNX group caused the VB to hyperpolarize in parallel with decreases in GT and fRA whereas in the control group it had no effect on VB. Addition of ouabain to the bath resulted in a large depolarization of VB in the UNX group. We conclude that (a) UNX stimulates conductances of Na+ and K+ in the apical membrane, active Na(+)-K+ pump activity, and K+ conductance in the basolateral membrane, independently of plasma aldosterone; (b) The basolateral membrane in the tubules of UNX rabbits is more selective to K+; and (c) the hyperpolarization of VB upon UNX may increase passive K+ entry into the cell across the basolateral membrane.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burg M., Grantham J., Abramow M., Orloff J. Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1293–1298. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diezi J., Michoud P., Grandchamp A., Giebisch G. Effects of nephrectomy on renal salt and water transport in the remaining kidney. Kidney Int. 1976 Dec;10(6):450–462. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine L. G., Yanagawa N., Schultze R. G., Tuck M., Trizna W. Functional profile of the isolated uremic nephron: potassium adaptation in the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;64(4):1033–1043. doi: 10.1172/JCI109540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg L. C., Knepper M. A., Burg M. B. Mineralocorticoid effects on Na-K-ATPase in individual nephron segments. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):F536–F544. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.6.F536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg L. C., Narang N. Renal adaptation to potassium in the adrenalectomized rabbit. Role of distal tubular sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):1065–1070. doi: 10.1172/JCI112059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayslett J. P. Functional adaptation to reduction in renal mass. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jan;59(1):137–164. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helman S. I., Nagel W., Fisher R. S. Ouabain on active transepithelial sodium transport in frog skin: studies with microelectrodes. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Jul;74(1):105–127. doi: 10.1085/jgp.74.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hené R. J., Boer P., Koomans H. A., Mees E. J. Plasma aldosterone concentrations in chronic renal disease. Kidney Int. 1982 Jan;21(1):98–101. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaissling B., Stanton B. A. Adaptation of distal tubule and collecting duct to increased sodium delivery. I. Ultrastructure. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 2):F1256–F1268. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.6.F1256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppen B. M., Biagi B. A., Giebisch G. H. Intracellular microelectrode characterization of the rabbit cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):F35–F47. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.1.F35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mernissi G. E., Doucet A. Stimulation of Na-K-ATPase in the rat collecting tubule by two diuretics: furosemide and amiloride. Am J Physiol. 1984 Sep;247(3 Pt 2):F485–F490. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.3.F485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mujais S. K., Chekal M. A., Jones W. J., Hayslett J. P., Katz A. I. Modulation of renal sodium-potassium-adenosine triphosphatase by aldosterone. Effect of high physiologic levels on enzyme activity in isolated rat and rabbit tubules. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):170–176. doi: 10.1172/JCI111942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mujais S. K., Kurtzman N. A. Regulation of renal Na-K-ATPase in the rat: effect of uninephrectomy. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 2):F506–F512. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.3.F506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto S., Giebisch G., Sansom S. An acute increase of peritubular K stimulates K transport through cell pathways of CCT. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jul;255(1 Pt 2):F108–F114. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.1.F108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto S., Giebisch G., Sansom S. Effects of adrenalectomy on CCD: evidence for differential response of two cell types. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 2):F742–F752. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.4.F742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto S., Sansom S., Giebisch G. Effects of a high potassium diet on electrical properties of cortical collecting ducts from adrenalectomized rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):376–380. doi: 10.1172/JCI113329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto S., Yasoshima K., Yoshitomi K., Imai M., Asano Y. Electrophysiological identification of alpha- and beta-intercalated cells and their distribution along the rabbit distal nephron segments. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1829–1839. doi: 10.1172/JCI114913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil R. G., Helman S. I. Transport characteristics of renal collecting tubules: influences of DOCA and diet. Am J Physiol. 1977 Dec;233(6):F544–F558. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.6.F544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil R. G., Sansom S. C. Electrophysiological properties of cellular and paracellular conductive pathways of the rabbit cortical collecting duct. J Membr Biol. 1984;82(3):281–295. doi: 10.1007/BF01871637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom S. C., Agulian S., Muto S., Illig V., Giebisch G. K activity of CCD principal cells from normal and DOCA-treated rabbits. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 2):F136–F142. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.1.F136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom S. C., O'Neil R. G. Effects of mineralocorticoids on transport properties of cortical collecting duct basolateral membrane. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 2):F743–F757. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.4.F743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom S. C., O'Neil R. G. Mineralocorticoid regulation of apical cell membrane Na+ and K+ transport of the cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jun;248(6 Pt 2):F858–F868. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.6.F858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom S. C., Weinman E. J., O'Neil R. G. Microelectrode assessment of chloride-conductive properties of cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1984 Aug;247(2 Pt 2):F291–F302. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.2.F291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherzer P., Wald H., Czaczkes J. W. Na-K-ATPase in isolated rabbit tubules after unilateral nephrectomy and Na+ loading. Am J Physiol. 1985 Apr;248(4 Pt 2):F565–F573. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.4.F565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherzer P., Wald H., Popovtzer M. M. Enhanced glomerular filtration and Na+-K+-ATPase with furosemide administration. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 2):F910–F915. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.5.F910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. J., Burg M. B. Mineralocorticoid effects on cation transport by cortical collecting tubules in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1978 Dec;235(6):F576–F585. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.235.6.F576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton B. A., Kaissling B. Adaptation of distal tubule and collecting duct to increased Na delivery. II. Na+ and K+ transport. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 2):F1269–F1275. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.6.F1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton B., Pan L., Deetjen H., Guckian V., Giebisch G. Independent effects of aldosterone and potassium on induction of potassium adaptation in rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):198–206. doi: 10.1172/JCI112783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B., Ingram M. J., Williams A. D., Ingram D. Heterogeneity of the rabbit collecting tubule: localization of mineralocorticoid hormone action to the cortical portion. Kidney Int. 1981 Sep;20(3):340–347. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehaskari V. M., Hering-Smith K. S., Klahr S., Hamm L. L. Increased sodium transport by cortical collecting tubules from remnant kidneys. Kidney Int. 1989 Jul;36(1):89–95. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehaskari V. M., Herndon J. Role of mineralocorticoids in adaptation of rabbit cortical collecting duct after loss of renal mass. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jun;260(6 Pt 2):F793–F799. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.6.F793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. B., O'Neil R. G., Pryor J. L., Boulpaep E. L. Modulation of cell membrane area in renal collecting tubules by corticosteroid hormones. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):439–445. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingo C. S., Seldin D. W., Kokko J. P., Jacobson H. R. Dietary modulation of active potassium secretion in the cortical collecting tubule of adrenalectomized rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):579–586. doi: 10.1172/JCI110650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalups R. K. Effect of dietary K+ and 75% nephrectomy on the morphology of principal cells in CCDs. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 2):F387–F396. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.3.F387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalups R. K., Stanton B. A., Wade J. B., Giebisch G. Structural adaptation in initial collecting tubule following reduction in renal mass. Kidney Int. 1985 Apr;27(4):636–642. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




