Abstract
The genetically obese Zucker rat (fa/fa) is characterized by a severe resistance to the action of insulin to stimulate skeletal muscle glucose transport. The goal of the present study was to identify whether the defect associated with this insulin resistance involves an alteration of transporter translocation and/or transporter activity. Various components of the muscle glucose transport system were investigated in plasma membranes isolated from basal or maximally insulin-treated skeletal muscle of lean and obese Zucker rats. Measurements of D- and L-glucose uptake by membrane vesicles under equilibrium exchange conditions indicated that insulin treatment resulted in a four-fold increase in the Vmax for carrier-mediated transport for lean animals [from 4.5 to 17.5 nmol/(mg.s)] but only a 2.5-fold increase for obese rats [from 3.6 to 9.1 nmol/(mg.s)]. In the lean animals, this increase in glucose transport function was associated with a 1.8-fold increase in the transporter number as indicated by cytochalasin B binding, a 1.4-fold increase in plasma membrane GLUT4 protein, and a doubling of the average carrier turnover number (intrinsic activity). In the obese animals, there was no change in plasma membrane transporter number measured by cytochalasin B binding, or in GLUT4 or GLUT1 protein. However, there was an increase in carrier turnover number similar to that seen in the lean litter mates. Measurements of GLUT4 mRNA in red gastrocnemius muscle showed no difference between lean and obese rats. We conclude that the insulin resistance of the obese rats involves the failure of translocation of transporters, while the action of insulin to increase the average carrier turnover number is normal.
Full text
PDF

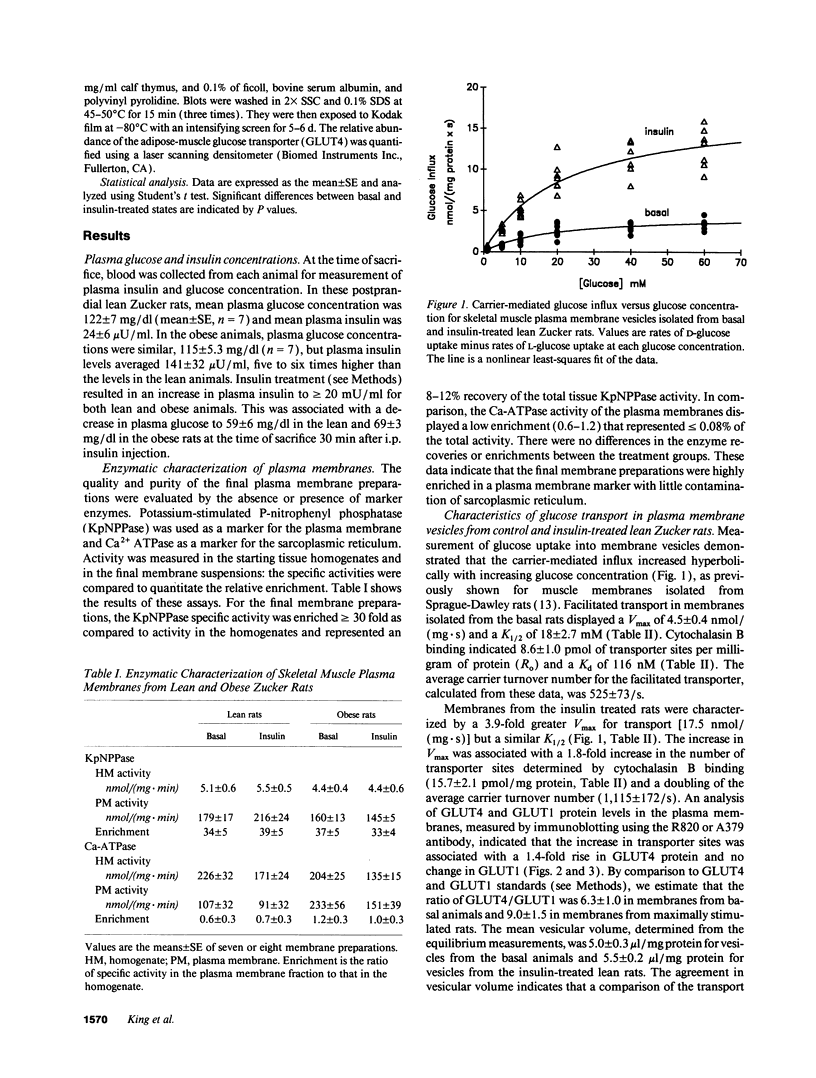
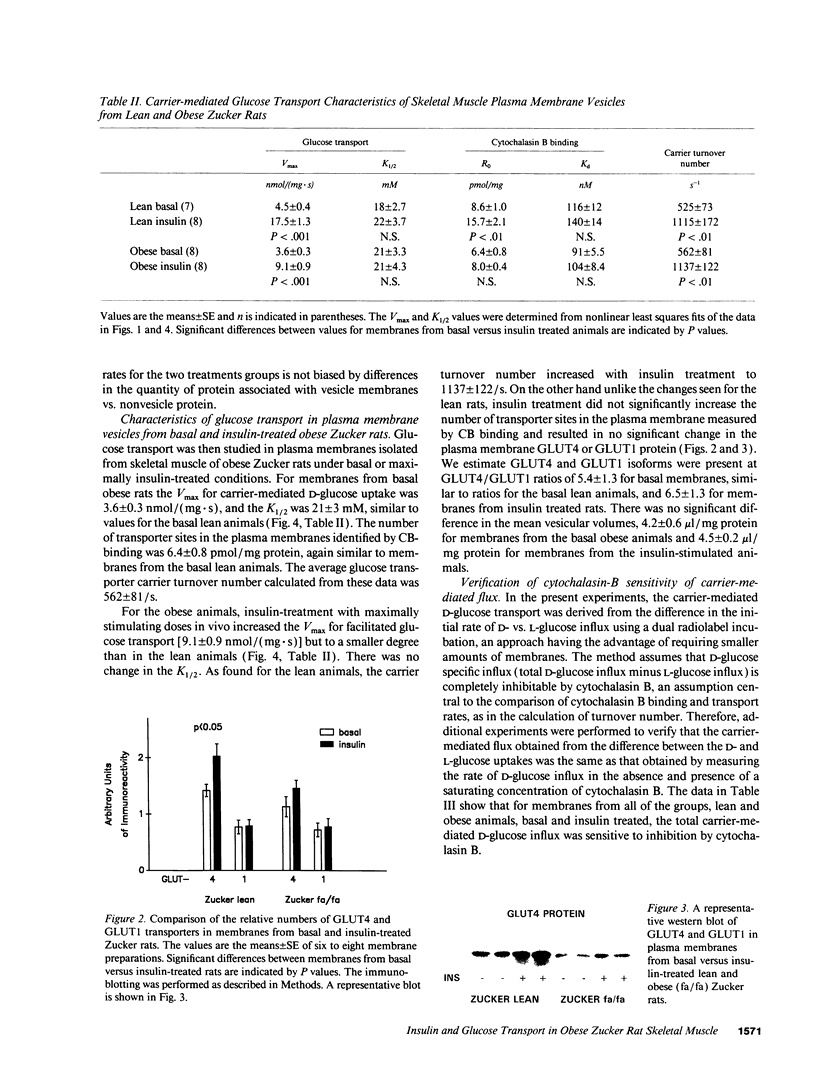
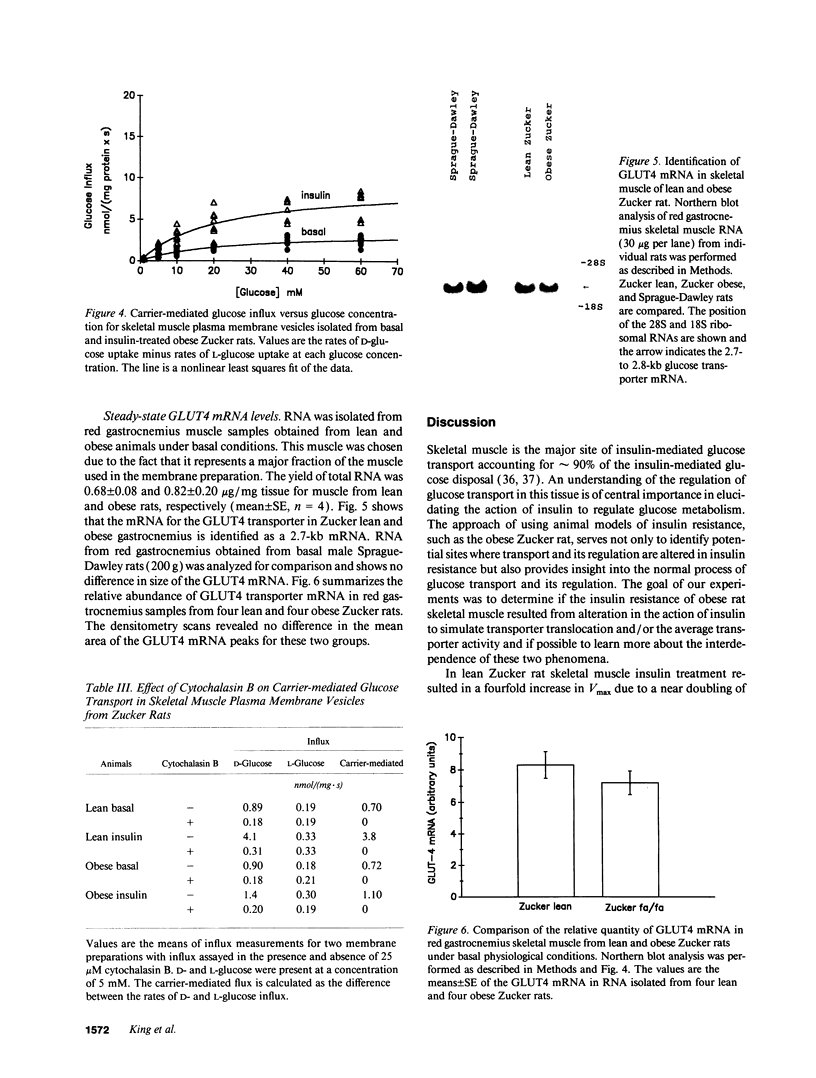



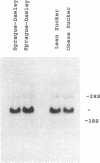
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E. Monoclonal antibodies to the glucose transporter from human erythrocytes. Identification of the transporter as a Mr = 55,000 protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8668–8675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arner P., Pollare T., Lithell H., Livingston J. N. Defective insulin receptor tyrosine kinase in human skeletal muscle in obesity and type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1987 Jun;30(6):437–440. doi: 10.1007/BF00292549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin S. A., Lienhard G. E. Purification and reconstitution of glucose transporter from human erythrocytes. Methods Enzymol. 1989;174:39–50. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)74008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard R. J., Youngren J. F., Kartel D. S., Martin D. A. Effects of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on glucose transport in skeletal muscle. Endocrinology. 1990 Apr;126(4):1921–1926. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-4-1921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M. Isolation and characterization of cardiac sarcolemma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 19;555(1):131–146. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourey R. E., Koranyi L., James D. E., Mueckler M., Permutt M. A. Effects of altered glucose homeostasis on glucose transporter expression in skeletal muscle of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):542–547. doi: 10.1172/JCI114742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G. A. The Zucker-fatty rat: a review. Fed Proc. 1977 Feb;36(2):148–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderhead D. M., Kitagawa K., Tanner L. I., Holman G. D., Lienhard G. E. Insulin regulation of the two glucose transporters in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13801–13808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter-Su C., Okamoto K. Effect of glucocorticoids on hexose transport in rat adipocytes. Evidence for decreased transporters in the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11091–11098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron M. J., Brosius F. C., 3rd, Alper S. L., Lodish H. F. A glucose transport protein expressed predominately in insulin-responsive tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2535–2539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron M. J., Kahn B. B. Divergent molecular mechanisms for insulin-resistant glucose transport in muscle and adipose cells in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7994–8000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy B. M., Czech M. P. Hexose transport stimulation and membrane redistribution of glucose transporter isoforms in response to cholera toxin, dibutyryl cyclic AMP, and insulin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12434–12443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy B. M., Harrison S. A., Buxton J. M., Czech M. P. Protein synthesis inhibitors activate glucose transport without increasing plasma membrane glucose transporters in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10122–10130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crettaz M., Prentki M., Zaninetti D., Jeanrenaud B. Insulin resistance in soleus muscle from obese Zucker rats. Involvement of several defective sites. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 15;186(2):525–534. doi: 10.1042/bj1860525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W. Structure-function relationships in the adipose cell. I. Ultrastructure of the isolated adipose cell. J Cell Biol. 1970 Aug;46(2):326–341. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.2.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Richardson D. K., Becker S. G., Walters C. G., Gitomer W., Heinrich J. Insulin response in skeletal muscle and fat cells of the genetically obese Zucker rat. Metabolism. 1978 Dec;27(12 Suppl 2):1967–1981. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(78)80013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A. Lilly lecture 1987. The triumvirate: beta-cell, muscle, liver. A collusion responsible for NIDDM. Diabetes. 1988 Jun;37(6):667–687. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.6.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douen A. G., Ramlal T., Rastogi S., Bilan P. J., Cartee G. D., Vranic M., Holloszy J. O., Klip A. Exercise induces recruitment of the "insulin-responsive glucose transporter". Evidence for distinct intracellular insulin- and exercise-recruitable transporter pools in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13427–13430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M. R., Horwitz B. A., Stern J. S. Effect of adrenalectomy and glucocorticoid replacement on development of obesity. Am J Physiol. 1986 Apr;250(4 Pt 2):R595–R607. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1986.250.4.R595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. E., Sherman W. M., Reed M. J., Elton C. W., Dohm G. L. Exercise training increases glucose transporter protein GLUT-4 in skeletal muscle of obese Zucker (fa/fa) rats. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jul 30;268(1):13–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80960-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey W. T., Kolterman O. G. Correlation of in vivo and in vitro actions of insulin in obesity and noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: role of the glucose transport system. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1988 Sep;4(6):543–569. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610040602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gougos A., Letarte M. Biochemical characterization of the 44G4 antigen from the HOON pre-B leukemic cell line. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):1934–1940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimditch G. K., Barnard R. J., Kaplan S. A., Sternlicht E. Insulin binding and glucose transport in rat skeletal muscle sarcolemmal vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1985 Oct;249(4 Pt 1):E398–E408. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.249.4.E398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerre-Millo M., Lavau M., Horne J. S., Wardzala L. J. Proposed mechanism for increased insulin-mediated glucose transport in adipose cells from young, obese Zucker rats. Large intracellular pool of glucose transporters. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2197–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. A., Buxton J. M., Clancy B. M., Czech M. P. Evidence that erythroid-type glucose transporter intrinsic activity is modulated by cadmium treatment of mouse 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19438–19449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. A., Buxton J. M., Czech M. P. Suppressed intrinsic catalytic activity of GLUT1 glucose transporters in insulin-sensitive 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7839–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspel H. C., Rosenfeld M. G., Rosen O. M. Characterization of antisera to a synthetic carboxyl-terminal peptide of the glucose transporter protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):398–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirshman M. F., Goodyear L. J., Wardzala L. J., Horton E. D., Horton E. S. Identification of an intracellular pool of glucose transporters from basal and insulin-stimulated rat skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):987–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hissin P. J., Foley J. E., Wardzala L. J., Karnieli E., Simpson I. A., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Mechanism of insulin-resistant glucose transport activity in the enlarged adipose cell of the aged, obese rat. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):780–790. doi: 10.1172/JCI110674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hissin P. J., Karnieli E., Simpson I. A., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. A possible mechanism of insulin resistance in the rat adipose cell with high-fat/low-carbohydrate feeding. Depletion of intracellular glucose transport systems. Diabetes. 1982 Jul;31(7):589–592. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.7.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horner H. C., Munck A., Lienhard G. E. Dexamethasone causes translocation of glucose transporters from the plasma membrane to an intracellular site in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17696–17702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horuk R., Matthaei S., Olefsky J. M., Baly D. L., Cushman S. W., Simpson I. A. Biochemical and functional heterogeneity of rat adipocyte glucose transporters. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1823–1828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu E., Sauter J. F., Jeanrenaud B. Abnormal oral glucose tolerance in genetically obese (fa/fa) rats. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):E500–E506. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.5.E500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivy J. L., Brozinick J. T., Jr, Torgan C. E., Kastello G. M. Skeletal muscle glucose transport in obese Zucker rats after exercise training. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Jun;66(6):2635–2641. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.6.2635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Strube M., Mueckler M. Molecular cloning and characterization of an insulin-regulatable glucose transporter. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):83–87. doi: 10.1038/338083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Cushman S. W. Mechanism for markedly hyperresponsive insulin-stimulated glucose transport activity in adipose cells from insulin-treated streptozotocin diabetic rats. Evidence for increased glucose transporter intrinsic activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5118–5124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Cushman S. W. Subcellular translocation of glucose transporters: role in insulin action and its perturbation in altered metabolic states. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1985;1(3):203–227. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610010301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Horton E. S., Cushman S. W. Mechanism for enhanced glucose transport response to insulin in adipose cells from chronically hyperinsulinemic rats. Increased translocation of glucose transporters from an enlarged intracellular pool. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):853–858. doi: 10.1172/JCI112894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Rossetti L., Lodish H. F., Charron M. J. Decreased in vivo glucose uptake but normal expression of GLUT1 and GLUT4 in skeletal muscle of diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):2197–2206. doi: 10.1172/JCI115254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Divergent mechanisms for the insulin resistant and hyperresponsive glucose transport in adipose cells from fasted and refed rats. Alterations in both glucose transporter number and intrinsic activity. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):691–699. doi: 10.1172/JCI113649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnieli E., Hissin P. J., Simpson I. A., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. A possible mechanism of insulin resistance in the rat adipose cell in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. Depletion of intracellular glucose transport systems. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):811–814. doi: 10.1172/JCI110318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemmer F. W., Berger M., Herberg L., Gries F. A., Wirdeier A., Becker K. Glucose metabolism in perfused skeletal muscle. Demonstration of insulin resistance in the obese Zucker rat. Biochem J. 1979 Mar 15;178(3):733–741. doi: 10.1042/bj1780733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Ramlal T., Young D. A., Holloszy J. O. Insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters in rat hindlimb muscles. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 16;224(1):224–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80452-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koranyi L., James D., Mueckler M., Permutt M. A. Glucose transporter levels in spontaneously obese (db/db) insulin-resistant mice. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):962–967. doi: 10.1172/JCI114526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Grémeaux T., Ballotti R., Van Obberghen E. Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase is defective in skeletal muscle of insulin-resistant obese mice. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):676–679. doi: 10.1038/315676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D. A., Maegawa H., Thies R. S., Olefsky J. M. Dissection of the growth versus metabolic effects of insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I in transfected cells expressing kinase-defective human insulin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1678–1682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Asano T., Shibasaki Y., Kasuga M., Kanazawa Y., Takaku F. Studies with antipeptide antibody suggest the presence of at least two types of glucose transporter in rat brain and adipocyte. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13432–13439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramlal T., Rastogi S., Vranic M., Klip A. Decrease in glucose transporter number in skeletal muscle of mildly diabetic (streptozotocin-treated) rats. Endocrinology. 1989 Aug;125(2):890–897. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-2-890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodnick K. J., Slot J. W., Studelska D. R., Hanpeter D. E., Robinson L. J., Geuze H. J., James D. E. Immunocytochemical and biochemical studies of GLUT4 in rat skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6278–6285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler S., Fleischer S. Isolation of plasma membrane vesicles from rabbit skeletal muscle and their use in ion transport studies. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13862–13871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman W. M., Katz A. L., Cutler C. L., Withers R. T., Ivy J. L. Glucose transport: locus of muscle insulin resistance in obese Zucker rats. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 1):E374–E382. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.255.3.E374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slieker L. J., Roberts E. F., Shaw W. N., Johnson W. T. Effect of streptozocin-induced diabetes on insulin-receptor tyrosine kinase activity in obese Zucker rats. Diabetes. 1990 May;39(5):619–625. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.5.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Gigengack S., James D. E., Lienhard G. E. Translocation of the glucose transporter GLUT4 in cardiac myocytes of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7815–7819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternlicht E., Barnard R. J., Grimditch G. K. Mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 1):E633–E638. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.5.E633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thies R. S., Ullrich A., McClain D. A. Augmented mitogenesis and impaired metabolic signaling mediated by a truncated insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12820–12825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardzala L. J., Cushman S. W., Salans L. B. Mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Enhancement of the number of functional transport systems. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8002–8005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardzala L. J., Jeanrenaud B. Identification of the D-glucose-inhibitable cytochalasin B binding site as the glucose transporter in rat diaphragm plasma and microsomal membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Apr 21;730(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90315-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Werve G., Zaninetti D., Lang U., Vallotton M. B., Jeanrenaud B. Identification of a major defect in insulin-resistant tissues of genetically obese (fa/fa) rats. Impaired protein kinase C. Diabetes. 1987 Mar;36(3):310–314. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.3.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]