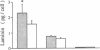Abstract
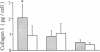
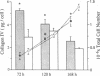
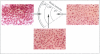
To define the interplay of glomerular hypertension and hypertrophy with mesangial extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition, we examined the effects of glomerular capillary distention and mesangial cell stretching on ECM synthesis. The volume of microdissected rat glomeruli (Vg), perfused ex vivo at increasing flows, was quantified and related to the proximal intraglomerular pressure (PIP). Glomerular compliance, expressed as the slope of the positive linear relationship between PIP and Vg was 7.68 x 10(3) microns 3/mmHg. Total Vg increment (PIP 0-150 mmHg) was 1.162 x 10(6) microns 3 or 61% (n = 13). A 16% increase in Vg was obtained over the PIP range equivalent to the pathophysiological limits of mean transcapillary pressure difference. A similar effect of renal perfusion on Vg was also noted histologically in tissue from kidneys perfused/fixed in vivo. Cultured mesangial cells undergoing cyclic stretching increased their synthesis of protein, total collagen, and key components of ECM (collagen IV, collagen I, laminin, fibronectin). Synthetic rates were stimulated by cell growth and the degree of stretching. These results suggest that capillary expansion and stretching of mesangial cells by glomerular hypertension provokes increased ECM production which is accentuated by cell growth and glomerular hypertrophy. Mesangial expansion and glomerulosclerosis might result from this interplay of mechanical and metabolic forces.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Meyer T. W., Rennke H. G., Brenner B. M. Control of glomerular hypertension limits glomerular injury in rats with reduced renal mass. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):612–619. doi: 10.1172/JCI112013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S., Meyer T. W., Rennke H. G., Brenner B. M. Control of glomerular hypertension limits glomerular injury in rats with reduced renal mass. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):612–619. doi: 10.1172/JCI112013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardaillou N., Bellon G., Nivez M. P., Rakotoarison S., Ardaillou R. Quantification of collagen synthesis by cultured human glomerular cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jun 27;991(3):445–452. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(89)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayo S. H., Radnik R. A., Glass W. F., 2nd, Garoni J. A., Rampt E. R., Appling D. R., Kreisberg J. I. Increased extracellular matrix synthesis and mRNA in mesangial cells grown in high-glucose medium. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 2):F185–F191. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.2.F185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidani A. K., Schwartz M. M., Lewis E. J. Renal autoregulation and vulnerability to hypertensive injury in remnant kidney. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jun;252(6 Pt 2):F1003–F1010. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.6.F1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border W. A., Okuda S., Languino L. R., Ruoslahti E. Transforming growth factor-beta regulates production of proteoglycans by mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1990 Feb;37(2):689–695. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland K. R., Yatscoff R. W., Thliveris J. A., Mehta A., Penner B. Non-enzymatic glycation and altered renal structure and function in the diabetic rat. Kidney Int. 1987 Nov;32(5):664–670. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes P., Dumler F., Paielli D. L., Levin N. W. Glomerular uracil nucleotide synthesis: effects of diabetes and protein intake. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):F647–F655. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.4.F647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes P., Dumler F., Sastry K. S., Verghese C. P., Levin N. W. Effects of early diabetes on uridine diphosphosugar synthesis in the rat renal cortex. Kidney Int. 1982 May;21(5):676–682. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes P., Dumler F., Venkatachalam K. K., Goldman J., Sastry K. S., Venkatachalam H., Bernstein J., Levin N. W. Alterations in glomerular RNA in diabetic rats: roles of glucagon and insulin. Kidney Int. 1981 Oct;20(4):491–499. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes P., Zhao X., Dumler F., Tilley B. C., Atherton J. Age-related changes in glomerular volume and hydroxyproline content in rat and human. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992 Jun;2(12):1716–1725. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V2121716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels B. S., Hostetter T. H. Adverse effects of growth in the glomerular microcirculation. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):F1409–F1416. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.5.F1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi E., Shibata D., Matoba T. Modified colorimetric ninhydrin methods for peptidase assay. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):173–184. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi T., Striker L. J., Quaife C., Conti F. G., Palmiter R., Behringer R., Brinster R., Striker G. E. Progressive glomerulosclerosis develops in transgenic mice chronically expressing growth hormone and growth hormone releasing factor but not in those expressing insulinlike growth factor-1. Am J Pathol. 1988 Jun;131(3):398–403. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drumond M. C., Deen W. M. Analysis of pulsatile pressures and flows in glomerular filtration. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 2):F409–F419. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.3.F409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumler F., Cortes P. Uracil ribonucleotide metabolism in rat and human glomerular epithelial and mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 1):C712–C718. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.6.C712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin L. D., Feiner H. D. Glomerular injury in uninephrectomized spontaneously hypertensive rats. A consequence of glomerular capillary hypertension. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):797–809. doi: 10.1172/JCI112377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk R. J., Scheinman J. I., Mauer S. M., Michael A. F. Polyantigenic expansion of basement membrane constituents in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 1983 May;32 (Suppl 2):34–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.2.s34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipovic D., Sackin H. A calcium-permeable stretch-activated cation channel in renal proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jan;260(1 Pt 2):F119–F129. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.1.F119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries J. W., Sandstrom D. J., Meyer T. W., Rennke H. G. Glomerular hypertrophy and epithelial cell injury modulate progressive glomerulosclerosis in the rat. Lab Invest. 1989 Feb;60(2):205–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grond J., Beukers J. Y., Schilthuis M. S., Weening J. J., Elema J. D. Analysis of renal structural and functional features in two rat strains with a different susceptibility to glomerular sclerosis. Lab Invest. 1986 Jan;54(1):77–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haneda M., Kikkawa R., Horide N., Togawa M., Koya D., Kajiwara N., Ooshima A., Shigeta Y. Glucose enhances type IV collagen production in cultured rat glomerular mesangial cells. Diabetologia. 1991 Mar;34(3):198–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00418276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto Y., Ideura T., Yoshimura A., Koshikawa S. Autoregulation of renal blood flow in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1989 Sep;38(9):1109–1113. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.9.1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holderbaum D., Ehrhart L. A. Modulation of types I and III procollagen synthesis at various stages of arterial smooth muscle cell growth in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Jul;153(1):16–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90443-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter T. H., Meyer T. W., Rennke H. G., Brenner B. M. Chronic effects of dietary protein in the rat with intact and reduced renal mass. Kidney Int. 1986 Oct;30(4):509–517. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter T. H., Olson J. L., Rennke H. G., Venkatachalam M. A., Brenner B. M. Hyperfiltration in remnant nephrons: a potentially adverse response to renal ablation. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jul;241(1):F85–F93. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.1.F85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter T. H., Troy J. L., Brenner B. M. Glomerular hemodynamics in experimental diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int. 1981 Mar;19(3):410–415. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikoma M., Kawamura T., Kakinuma Y., Fogo A., Ichikawa I. Cause of variable therapeutic efficiency of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor on glomerular lesions. Kidney Int. 1991 Aug;40(2):195–202. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen B. M., Ofstad J. Loss of renal blood flow autoregulation in chronic glomerulonephritic rats. Am J Physiol. 1988 Feb;254(2 Pt 2):F284–F290. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.2.F284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsson B., Bohman S. O., Sundelin B., Aperia A. Mitotic response to high protein intake in different renal cell types in weanling rats. Kidney Int. 1988 Mar;33(3):662–666. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. B., Gundersen H. J., Osterby R. Determination of membrane thickness distribution from orthogonal intercepts. J Microsc. 1979 Jan;115(1):19–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1979.tb00149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa R., Kitamura E., Fujiwara Y., Arimura T., Haneda M., Shigeta Y. Impaired contractile responsiveness of diabetic glomeruli to angiotensin II: a possible indication of mesangial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 14;136(3):1185–1190. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90459-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klahr S., Schreiner G., Ichikawa I. The progression of renal disease. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 23;318(25):1657–1666. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806233182505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollros P. R., Bates S. R., Mathews M. B., Horwitz A. L., Glagov S. Cyclic AMP inhibits increased collagen production by cyclically stretched smooth muscle cells. Lab Invest. 1987 Apr;56(4):410–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriz W., Elger M., Lemley K., Sakai T. Structure of the glomerular mesangium: a biomechanical interpretation. Kidney Int Suppl. 1990 Nov;30:S2–S9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeDoux J. E., Tucker L. W., Del Bo A., Harshfield G., Green L., Talman W. T., Reis D. J. A hierarchical organization of blood pressure during natural behaviour in rat and the effects of central catecholamine neurons thereon. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Dec;59 (Suppl 6):271s–273s. doi: 10.1042/cs059271s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay K., Striker L. J., Stauffer J. W., Agodoa L. Y., Striker G. E. Relationship of glomerular hypertrophy and sclerosis: studies in SV40 transgenic mice. Kidney Int. 1990 Feb;37(2):741–748. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Timpl R., Kühn K. Basement membrane proteins: molecular structure and function. Adv Protein Chem. 1988;39:1–50. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60374-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauer S. M., Steffes M. W., Azar S., Brown D. M. Effects of dietary protein content in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Kidney Int. 1989 Jan;35(1):48–59. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. L., Meyer T. W. Effects of tissue preparation on glomerular volume and capillary structure in the rat. Lab Invest. 1990 Dec;63(6):862–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. L., Rennke H. G., Meyer T. W. Glomerular hypertrophy accelerates hypertensive glomerular injury in rats. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 2):F459–F465. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.3.F459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. L., Scholey J. W., Rennke H. G., Meyer T. W. Glomerular hypertrophy aggravates epithelial cell injury in nephrotic rats. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1119–1126. doi: 10.1172/JCI114543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro H. N. The determination of nucleic acids. Methods Biochem Anal. 1966;14:113–176. doi: 10.1002/9780470110324.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negro A., Garbisa S., Gotte L., Spina M. The use of reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography and precolumn derivatization with dansyl chloride for quantitation of specific amino acids in collagen and elastin. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jan;160(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90611-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell M. P., Kasiske B. L., Schmitz P. G., Keane W. F. High protein intake accelerates glomerulosclerosis independent of effects on glomerular hemodynamics. Kidney Int. 1990 May;37(5):1263–1269. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohyama K., Seyer J. M., Raghow R., Kang A. H. Extracellular matrix phenotype of rat mesangial cells in culture. Biosynthesis of collagen types I, III, IV, and V and a low molecular weight collagenous component and their regulation by dexamethasone. J Lab Clin Med. 1990 Aug;116(2):219–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivetti G., Anversa P., Rigamonti W., Vitali-Mazza L., Loud A. V. Morphometry of the renal corpuscle during normal postnatal growth and compensatory hypertrophy. A light microscope study. J Cell Biol. 1977 Nov;75(2 Pt 1):573–585. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.2.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. L., Heptinstall R. H. Nonimmunologic mechanisms of glomerular injury. Lab Invest. 1988 Nov;59(5):564–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. L., Wilson S. K., Heptinstall R. H. Relation of glomerular injury to preglomerular resistance in experimental hypertension. Kidney Int. 1986 Apr;29(4):849–857. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osgood R. W., Patton M., Hanley M. J., Venkatachalam M., Reineck H. J., Stein J. H. In vitro perfusion of the isolated dog glomerulus. Am J Physiol. 1983 Mar;244(3):F349–F354. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.3.F349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterby R., Gundersen H. J. Fast accumulation of basement membrane material and the rate of morphological changes in acute experimental diabetic glomerular hypertrophy. Diabetologia. 1980 Jun;18(6):493–500. doi: 10.1007/BF00261706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelayo J. C., Westcott J. Y. Impaired autoregulation of glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure in the rat remnant nephron. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):101–105. doi: 10.1172/JCI115264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesce C. M., Striker L. J., Peten E., Elliot S. J., Striker G. E. Glomerulosclerosis at both early and late stages is associated with increased cell turnover in mice transgenic for growth hormone. Lab Invest. 1991 Nov;65(5):601–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raij L., Azar S., Keane W. Mesangial immune injury, hypertension, and progressive glomerular damage in Dahl rats. Kidney Int. 1984 Aug;26(2):137–143. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Integrins. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):1–5. doi: 10.1172/JCI114957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. O., Pusey C. D., Kershaw M. J., Cashman S. J., Harrison P., Hartley B., Turner D. R., Cameron J. S., Evans D. J., Lockwood C. M. The Goodpasture antigen in Alport's syndrome: studies with a monoclonal antibody. Kidney Int. 1986 Jul;30(1):107–112. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singhal P. C., DeCandido S., Satriano J. A., Schlondorff D., Hays R. M. Atrial natriuretic peptide and nitroprusside cause relaxation of cultured rat mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jul;257(1 Pt 1):C86–C93. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.1.C86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterzel R. B., Lovett D. H., Foellmer H. G., Perfetto M., Biemesderfer D., Kashgarian M. Mesangial cell hillocks. Nodular foci of exaggerated growth of cells and matrix in prolonged culture. Am J Pathol. 1986 Oct;125(1):130–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumpio B. E., Banes A. J., Link W. G., Johnson G., Jr Enhanced collagen production by smooth muscle cells during repetitive mechanical stretching. Arch Surg. 1988 Oct;123(10):1233–1236. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1988.01400340059010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSANEV R., MARKOV G. G. Substances interfering with spectrophotometric estimation of nucleic acids and their elimination by the two-wavelength method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Aug 26;42:442–452. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90822-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorner P., Jansen B., Baumal R., Valli V. E., Goldberger A. Samoyed hereditary glomerulopathy. Immunohistochemical staining of basement membranes of kidney for laminin, collagen type IV, fibronectin, and Goodpasture antigen, and correlation with electron microscopy of glomerular capillary basement membranes. Lab Invest. 1987 Apr;56(4):435–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varani J., Nickoloff B. J., Riser B. L., Mitra R. S., O'Rourke K., Dixit V. M. Thrombospondin-induced adhesion of human keratinocytes. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1537–1544. doi: 10.1172/JCI113486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolthuis A., Boes A., Rodemann H. P., Grond J. Vasoactive agents affect growth and protein synthesis of cultured rat mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1992 Jan;41(1):124–131. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida Y., Fogo A., Ichikawa I. Glomerular hemodynamic changes vs. hypertrophy in experimental glomerular sclerosis. Kidney Int. 1989 Feb;35(2):654–660. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz R., Dunn B. R., Meyer T. W., Anderson S., Rennke H. G., Brenner B. M. Prevention of diabetic glomerulopathy by pharmacological amelioration of glomerular capillary hypertension. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1925–1930. doi: 10.1172/JCI112521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz R., Meyer T. W., Rennke H. G., Brenner B. M. Predominance of hemodynamic rather than metabolic factors in the pathogenesis of diabetic glomerulopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5963–5967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Nahas A. M., Bassett A. H., Cope G. H., Le Carpentier J. E. Role of growth hormone in the development of experimental renal scarring. Kidney Int. 1991 Jul;40(1):29–34. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- le Pape A., Guitton J. D., Muh J. P. Modification of glomerular basement membrane cross-links in experimental diabetic rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jun 16;100(3):1214–1221. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91953-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]