Abstract
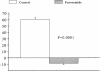
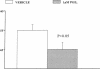
The hypothesis that endogenous PGE2 mediates defective thick ascending limb (TAL) Cl reabsorption (percent delivered load: FRCl%) in rats with vitamin D-induced chronic hypercalcemia (HC) was tested by measuring FRCl% in loop segments microperfused in vivo in HC and control rats treated acutely with indomethacin (Indo) or its vehicle, and obtaining the corresponding outer medullary [PGE2]. Microperfusion conditions were developed in which FRCl% was exclusively furosemide sensitive. To determine the cellular mechanism, tubules were perfused acutely with forskolin (FSK), cAMP, or the protein kinase C inhibitor staurosporine (SSP). Outer medullary [PGE2] in HC rats was 9 to 10 times greater than control and could be normalized by Indo. FRCl% was 20% lower in HC rats infused with vehicle, and Indo, FSK, and cAMP returned FRCl% to normal despite sustained HC. Indo or FSK had no effect on FRCl% in control rats and Indo did not prevent inhibition of FRCl% by luminal PGE2 (1 microM). Luminal SSP (10(-7), 10(-8) M) in HC did not return FRCl% to control values. We conclude that impaired TAL FRCl% in HC occurs at a pre-cAMP site and is due to endogenous PGE2 and not to HC.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berl T. The cAMP system in vasopressin-sensitive nephron segments of the vitamin D-treated rat. Kidney Int. 1987 May;31(5):1065–1071. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonvalet J. P., Pradelles P., Farman N. Segmental synthesis and actions of prostaglandins along the nephron. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 2):F377–F387. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.3.F377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. G., Fuhro R., Silva P. Isolated MTAL cells produce an inhibitor of ouabain-sensitive oxygen consumption. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 2):F210–F215. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.2.F210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capasso G., Unwin R., Agulian S., Giebisch G. Bicarbonate transport along the loop of Henle. I. Microperfusion studies of load and inhibitor sensitivity. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):430–437. doi: 10.1172/JCI115322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capdevila J., Gil L., Orellana M., Marnett L. J., Mason J. I., Yadagiri P., Falck J. R. Inhibitors of cytochrome P-450-dependent arachidonic acid metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Mar;261(2):257–263. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90340-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. A., Sala A., Dunn C. E., McGiff J. C., Murphy R. C. Structural identification of cytochrome P450-dependent arachidonate metabolites formed by rabbit medullary thick ascending limb cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12306–12312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culpepper R. M., Andreoli T. E. Interactions among prostaglandin E2, antidiuretic hormone, and cyclic adenosine monophosphate in modulating Cl- absorption in single mouse medullary thick ascending limbs of Henle. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1588–1601. doi: 10.1172/JCI110915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culpepper R. M., Andreoli T. E. PGE2, forskolin, and cholera toxin interactions in modulating NaCl transport in mouse mTALH. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 2):F784–F792. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.5.F784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escalante B., Erlij D., Falck J. R., McGiff J. C. Effect of cytochrome P450 arachidonate metabolites on ion transport in rabbit kidney loop of Henle. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):799–802. doi: 10.1126/science.1846705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIEBISCH G., KLOSE R. M., MALNIC G., SULLIVAN W. J., WINDHAGER E. E. SODIUM MOVEMENT ACROSS SINGLE PERFUSED PROXIMAL TUBULES OF RAT KIDNEYS. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Jul;47:1175–1194. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.6.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galla J. H., Booker B. B., Luke R. G. Role of the loop segment in the urinary concentrating defect of hypercalcemia. Kidney Int. 1986 May;29(5):977–982. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashihara E., Stokes J. B., Kokko J. P., Campbell W. B., DuBose T. D., Jr Cortical and papillary micropuncture examination of chloride transport in segments of the rat kidney during inhibition of prostaglandin production. Possible role for prostaglandins in the chloruresis of acute volume expansion. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1277–1287. doi: 10.1172/JCI109583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert R. L., Jacobson H. R., Breyer M. D. PGE2 inhibits AVP-induced water flow in cortical collecting ducts by protein kinase C activation. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 2):F318–F325. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.2.F318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert R. L., Jacobson H. R., Breyer M. D. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits sodium transport in rabbit cortical collecting duct by increasing intracellular calcium. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):1992–1998. doi: 10.1172/JCI115227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert R. L., Jacobson H. R., Breyer M. D. Triple signal transduction model for the mechanism of PGE2 actions in rabbit cortical collecting duct. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1991 Mar;42(3):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0952-3278(91)90148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung K. Y., Endou H. Furosemide acts on short loop of descending thin limb, but not on long loop. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Jun;253(3):1184–1188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lear S., Silva P., Kelley V. E., Epstein F. H. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits oxygen consumption in rabbit medullary thick ascending limb. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):F1372–F1378. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.5.F1372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi M., Peterson L., Berl T. Mechanism of concentrating defect in hypercalcemia. Role of polydipsia and prostaglandins. Kidney Int. 1983 Mar;23(3):489–497. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao A., Allen M. L., Sonnenburg W. K., Smith W. L. Regulation of cAMP metabolism by PGE2 in cortical and medullary thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 1):C652–C657. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.3.C652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. N., Carpenter B., Guttierrez G. A., Fajardo C., Levine D. Z. Potassium depletion enhances renal compensatory hypertrophy in the nephrectomized rat. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1987;13(1):57–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. N., De Rouffignac C., Sonnenberg H., Levine D. Z. Thick ascending limb response to dDAVP and atrial natriuretic factor in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 2):F374–F381. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.3.F374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. N. Time-dependent changes in inner medullary plasma flow rate during potassium-depletion. Kidney Int. 1984 Jun;25(6):899–905. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. N. Vitamin D-induced chronic hypercalcemia inhibits thick ascending limb NaCl reabsorption in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jul;259(1 Pt 2):F122–F129. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.1.F122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RADTKE H. W., Rumrich G., Kinne-saffran E., Ulrich K. J. Dual action of acetazolamide and furosemide on proximal volume absorption in the rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1972 Feb;1(2):100–105. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüegg U. T., Burgess G. M. Staurosporine, K-252 and UCN-01: potent but nonspecific inhibitors of protein kinases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Jun;10(6):218–220. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serros E. R., Kirschenbaum M. A. Prostaglandin-dependent polyuria in hypercalcemia. Am J Physiol. 1981 Sep;241(3):F224–F230. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.3.F224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. L. Prostanoid biosynthesis and mechanisms of action. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 2):F181–F191. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.2.F181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl R. A., Attallah A. A., Bloch D. L., Lee J. B. Stimulation of rabbit renal PGE2 biosynthesis by dietary sodium restriction. Am J Physiol. 1979 Nov;237(5):F344–F349. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.237.5.F344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun A., Grossman E. B., Lombardi M., Hebert S. C. Vasopressin alters the mechanism of apical Cl- entry from Na+:Cl- to Na+:K+:2Cl- cotransport in mouse medullary thick ascending limb. J Membr Biol. 1991 Feb;120(1):83–94. doi: 10.1007/BF01868594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaichi K., Uchida S., Kurokawa K. High Ca2+ inhibits AVP-dependent cAMP production in thick ascending limbs of Henle. Am J Physiol. 1986 May;250(5 Pt 2):F770–F776. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.5.F770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M., Schnermann J. Microdissection study of the length of different tubular segments of rat superficial nephrons. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1969;129(2):128–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00522242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald H., Scherzer P., Rubinger D., Popovtzer M. M. Effect of indomethacin in vivo and PGE2 in vitro on MTAL Na-K-ATPase of the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Feb;415(5):648–650. doi: 10.1007/BF02583521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins M. R., Needleman P. Effect of pharmacological manipulation of endogenous atriopeptin activity on renal function. Am J Physiol. 1992 Feb;262(2 Pt 2):F161–F167. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.2.F161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S. "Enzymatic" lipid peroxidation: reactions of mammalian lipoxygenases. Free Radic Biol Med. 1991;10(2):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(91)90008-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara N., Tachikawa E., Izumi F., Yasugawa S., Yamamoto H., Miyamoto E. Staurosporine: an effective inhibitor for Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J Neurochem. 1991 Jan;56(1):294–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02595.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]