Abstract
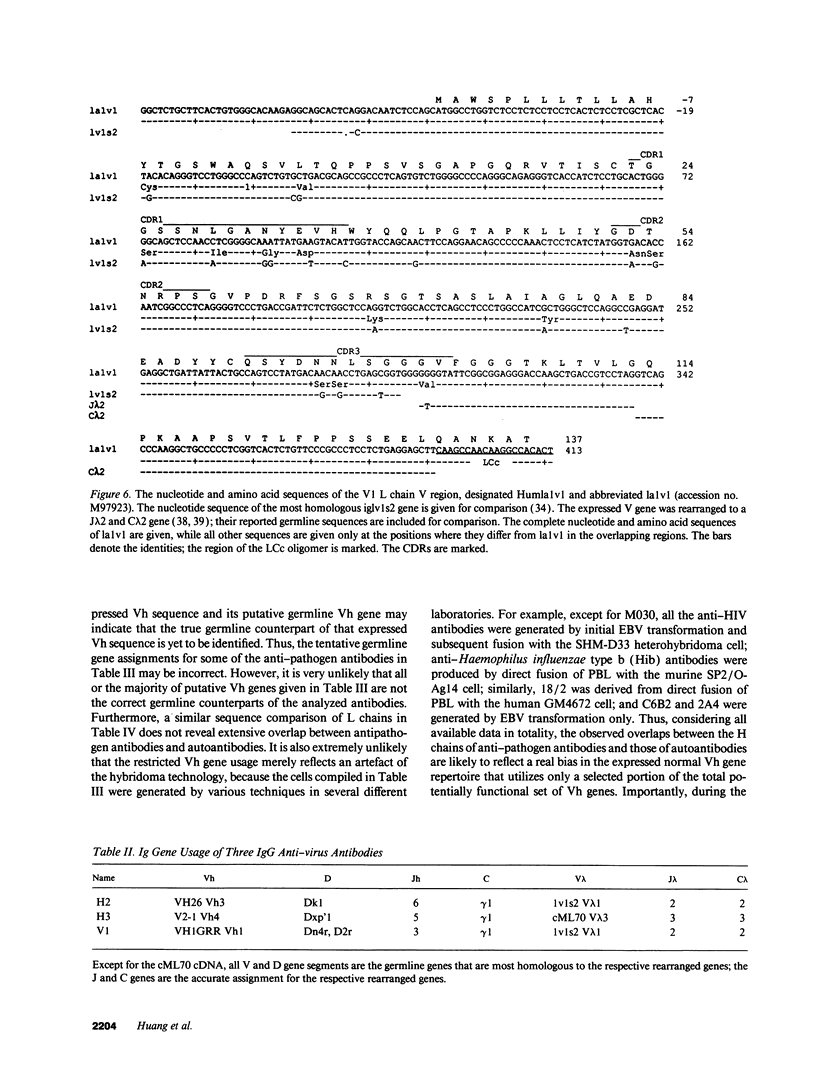
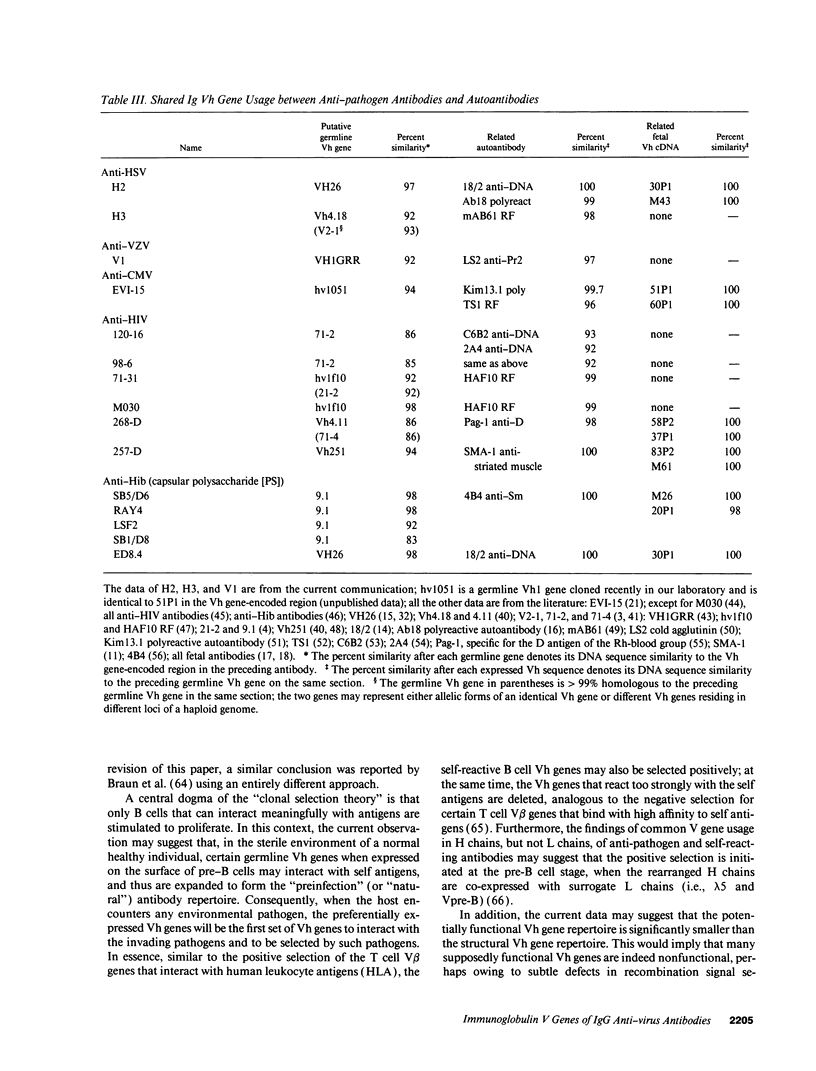
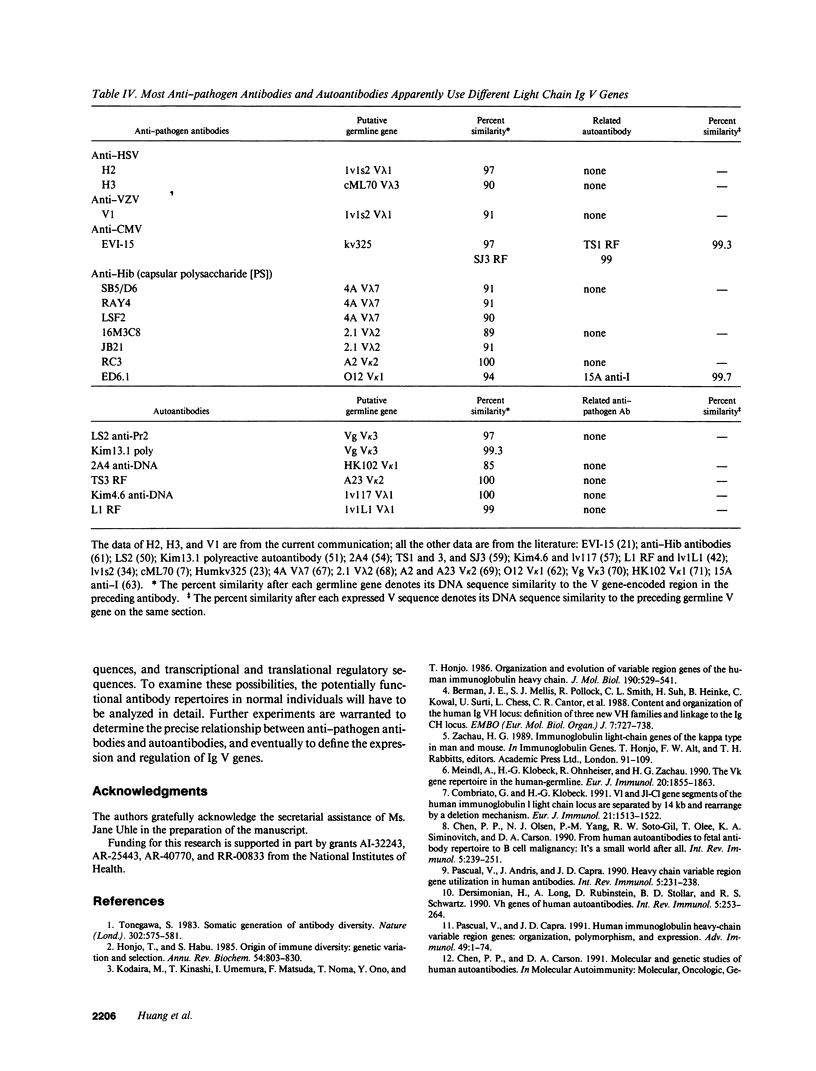
Accumulated sequence analyses of the antibody repertoire have revealed that most autoantibodies and developmentally regulated antibodies share a small set of germline Ig-variable region (V) genes. The findings have prompted speculation that certain autoantibodies are of developmental importance and may be instrumental in maintaining homeostasis of the adult antibody repertoire. In order to evaluate this hypothesis critically, it is first necessary to determine the V gene usage in human antibodies against foreign substances. Unfortunately, only a few such antibodies have had their heavy and light chains characterized. To rectify the situation, we adapted the anchored polymerase chain reaction to clone and analyze rapidly the expressed V genes for three anti-virus IgG antibodies. The results show that all three heavy chain V (Vh) genes are highly homologous to the known autoantibody-related Vh genes. In contrast, two light chain V (VL) genes of the V lambda 1 subgroup are similar to a non-autoantibody-related germline V lambda 1 gene. Taken together with the reported Vh and VL sequences of several antibodies against viruses and bacteria, the data show that many antipathogen antibodies may use the same small set of Vh genes that encode autoantibodies, but diverse VL genes that are distinct from autoantibody-related VL genes. Thus, only a small portion of the potentially functional germline Vh genes are used recurrently to generate most antibodies in a normal antibody repertoire, regardless of their reactivities with either self or non-self.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adderson E. E., Shackelford P. G., Insel R. A., Quinn A., Wilson P. M., Carroll W. L. Immunoglobulin light chain variable region gene sequences for human antibodies to Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide are dominated by a limited number of V kappa and V lambda segments and VJ combinations. J Clin Invest. 1992 Mar;89(3):729–738. doi: 10.1172/JCI115649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adderson E. E., Shackelford P. G., Quinn A., Carroll W. L. Restricted Ig H chain V gene usage in the human antibody response to Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1667–1674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandre D., Chuchana P., Brockly F., Blancher A., Lefranc G., Lefranc M. P. First genomic sequence of a human Ig variable lambda gene belonging to subgroup I. Functional genes, pseudogenes and vestigial sequences are interspersed in the IGLV locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3975–3975. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. L., Szajnert M. F., Kaplan J. C., McColl L., Young B. D. The isolation of a human Ig V lambda gene from a recombinant library of chromosome 22 and estimation of its copy number. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 11;12(17):6647–6661. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.17.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andris J. S., Johnson S., Zolla-Pazner S., Capra J. D. Molecular characterization of five human anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 antibody heavy chains reveals extensive somatic mutation typical of an antigen-driven immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7783–7787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Rabbitts T. H. Human immunoglobulin variable region genes--DNA sequences of two V kappa genes and a pseudogene. Nature. 1980 Dec 25;288(5792):730–733. doi: 10.1038/288730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman J. E., Mellis S. J., Pollock R., Smith C. L., Suh H., Heinke B., Kowal C., Surti U., Chess L., Cantor C. R. Content and organization of the human Ig VH locus: definition of three new VH families and linkage to the Ig CH locus. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):727–738. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02869.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackman M., Kappler J., Marrack P. The role of the T cell receptor in positive and negative selection of developing T cells. Science. 1990 Jun 15;248(4961):1335–1341. doi: 10.1126/science.1972592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Berberian L., King L., Sanz I., Govan H. L., 3rd Restricted use of fetal VH3 immunoglobulin genes by unselected B cells in the adult. Predominance of 56p1-like VH genes in common variable immunodeficiency. J Clin Invest. 1992 May;89(5):1395–1402. doi: 10.1172/JCI115728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockly F., Alexandre D., Chuchana P., Huck S., Lefranc G., Lefranc M. P. First nucleotide sequence of a human immunoglobulin variable lambda gene belonging to subgroup II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3976–3976. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Chen P. P., Kipps T. J. New roles for rheumatoid factor. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):379–383. doi: 10.1172/JCI115007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Albrandt K., Kipps T. J., Radoux V., Liu F. T., Carson D. A. Isolation and characterization of human VkIII germ-line genes. Implications for the molecular basis of human VkIII light chain diversity. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1727–1733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Fong S., Goni F., Silverman G. J., Fox R. I., Liu M. F., Frangione B., Carson D. A. Cross-reacting idiotypes on cryoprecipitating rheumatoid factor. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1988;10(1):35–55. doi: 10.1007/BF02054022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Liu M. F., Sinha S., Carson D. A. A 16/6 idiotype-positive anti-DNA antibody is encoded by a conserved VH gene with no somatic mutation. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Nov;31(11):1429–1431. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Olsen N. J., Yang P. M., Soto-Gil R. W., Olee T., Siminovitch K. A., Carson D. A. From human autoantibodies to the fetal antibody repertoire to B cell malignancy: it's a small world after all. Int Rev Immunol. 1990;5(3-4):239–251. doi: 10.3109/08830189009056732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P. Structural analyses of human developmentally regulated Vh3 genes. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Mar;31(3):257–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combriato G., Klobeck H. G. V lambda and J lambda-C lambda gene segments of the human immunoglobulin lambda light chain locus are separated by 14 kb and rearrange by a deletion mechanism. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jun;21(6):1513–1522. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho A. Beyond clonal selection and network. Immunol Rev. 1989 Aug;110:63–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dariavach P., Lefranc G., Lefranc M. P. Human immunoglobulin C lambda 6 gene encodes the Kern+Oz-lambda chain and C lambda 4 and C lambda 5 are pseudogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9074–9078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson A., Manheimer-Lory A., Aranow C., Peterson R., Hannigan N., Diamond B. Molecular characterization of a somatically mutated anti-DNA antibody bearing two systemic lupus erythematosus-related idiotypes. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1401–1409. doi: 10.1172/JCI114584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dersimonian H., Long A., Rubinstein D., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. VH genes of human autoantibodies. Int Rev Immunol. 1990;5(3-4):253–264. doi: 10.3109/08830189009056733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dersimonian H., Schwartz R. S., Barrett K. J., Stollar B. D. Relationship of human variable region heavy chain germ-line genes to genes encoding anti-DNA autoantibodies. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2496–2501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison J., Hood L. Linkage and sequence homology of two human immunoglobulin gamma heavy chain constant region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1984–1988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezaki I., Kanda H., Sakai K., Fukui N., Shingu M., Nobunaga M., Watanabe T. Restricted diversity of the variable region nucleotide sequences of the heavy and light chains of a human rheumatoid factor. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Mar;34(3):343–350. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. F., Cho E. A., Goldman J., Carmack C. E., Besa E. C., Hardy R. R., Silberstein L. E. The role of clonal selection in the pathogenesis of an autoreactive human B cell lymphoma. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):525–537. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinaga S., Sugano T., Matsumoto Y., Masuho Y., Mori R. Antiviral activities of human monoclonal antibodies to herpes simplex virus. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):45–53. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harindranath N., Goldfarb I. S., Ikematsu H., Burastero S. E., Wilder R. L., Notkins A. L., Casali P. Complete sequence of the genes encoding the VH and VL regions of low- and high-affinity monoclonal IgM and IgA1 rheumatoid factors produced by CD5+ B cells from a rheumatoid arthritis patient. Int Immunol. 1991 Sep;3(9):865–875. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.9.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillson J. L., Perlmutter R. M. Autoantibodies and the fetal antibody repertoire. Int Rev Immunol. 1990;5(3-4):215–229. doi: 10.3109/08830189009056730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch S., Schwaber J. Identification and sequence of the VH gene elements encoding a human anti-DNA antibody. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1689–1693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Habu S. Origin of immune diversity: genetic variation and selection. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:803–830. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes-Jones N. C., Bye J. M., Beale D., Coadwell J. Nucleotide sequences and three-dimensional modelling of the VH and VL domains of two human monoclonal antibodies specific for the D antigen of the human Rh-blood-group system. Biochem J. 1990 May 15;268(1):135–140. doi: 10.1042/bj2680135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries C. G., Shen A., Kuziel W. A., Capra J. D., Blattner F. R., Tucker P. W. A new human immunoglobulin VH family preferentially rearranged in immature B-cell tumours. Nature. 1988 Feb 4;331(6155):446–449. doi: 10.1038/331446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodaira M., Kinashi T., Umemura I., Matsuda F., Noma T., Ono Y., Honjo T. Organization and evolution of variable region genes of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 20;190(4):529–541. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90239-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W., Danielsson L., Brenner C. A., Abrahamson M., Fry K. E., Borrebaeck C. A. Rapid cloning of rearranged immunoglobulin genes from human hybridoma cells using mixed primers and the polymerase chain reaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 May 15;160(3):1250–1256. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80138-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Matsuda F., Kinashi T., Kodaira M., Honjo T. A novel family of variable region genes of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):761–768. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90482-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh E. Y., Elliott J. F., Cwirla S., Lanier L. L., Davis M. M. Polymerase chain reaction with single-sided specificity: analysis of T cell receptor delta chain. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):217–220. doi: 10.1126/science.2463672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuho Y., Sugano T., Matsumoto Y., Sawada S., Tomibe K. Generation of hybridomas producing human monoclonal antibodies against herpes simplex virus after in vitro stimulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):495–500. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthyssens G., Rabbitts T. H. Structure and multiplicity of genes for the human immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6561–6565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meindl A., Klobeck H. G., Ohnheiser R., Zachau H. G. The V kappa gene repertoire in the human germ line. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Aug;20(8):1855–1863. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newkirk M. M., Gram H., Heinrich G. F., Ostberg L., Capra J. D., Wasserman R. L. Complete protein sequences of the variable regions of the cloned heavy and light chains of a human anti-cytomegalovirus antibody reveal a striking similarity to human monoclonal rheumatoid factors of the Wa idiotypic family. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1511–1518. doi: 10.1172/JCI113483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olee T., Lu E. W., Huang D. F., Soto-Gil R. W., Deftos M., Kozin F., Carson D. A., Chen P. P. Genetic analysis of self-associating immunoglobulin G rheumatoid factors from two rheumatoid synovia implicates an antigen-driven response. J Exp Med. 1992 Mar 1;175(3):831–842. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.3.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pargent W., Meindl A., Thiebe R., Mitzel S., Zachau H. G. The human immunoglobulin kappa locus. Characterization of the duplicated O regions. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Aug;21(8):1821–1827. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascual V., Andris J., Capra J. D. Heavy chain variable region gene utilization in human antibodies. Int Rev Immunol. 1990;5(3-4):231–238. doi: 10.3109/08830189009056731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascual V., Capra J. D. Human immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable region genes: organization, polymorphism, and expression. Adv Immunol. 1991;49:1–74. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60774-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascual V., Randen I., Thompson K., Sioud M., Forre O., Natvig J., Capra J. D. The complete nucleotide sequences of the heavy chain variable regions of six monospecific rheumatoid factors derived from Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B cells isolated from the synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Further evidence that some autoantibodies are unmutated copies of germ line genes. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1320–1328. doi: 10.1172/JCI114841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pech M., Zachau H. G. Immunoglobulin genes of different subgroups are interdigitated within the VK locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9229–9236. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins D. L., Kenny T. P., Coloma M. J., Gavilondo-Cowley J. V., Soto-Gil R. W., Chen P. P., Larrick J. W. Serologic and molecular characterization of a human monoclonal rheumatoid factor derived from rheumatoid synovial cells. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Aug;33(8):1188–1195. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolink A., Melchers F. Molecular and cellular origins of B lymphocyte diversity. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1081–1094. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90032-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz I., Casali P., Thomas J. W., Notkins A. L., Capra J. D. Nucleotide sequences of eight human natural autoantibody VH regions reveals apparent restricted use of VH families. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):4054–4061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz I., Dang H., Takei M., Talal N., Capra J. D. VH sequence of a human anti-Sm autoantibody. Evidence that autoantibodies can be unmutated copies of germline genes. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):883–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz I., Kelly P., Williams C., Scholl S., Tucker P., Capra J. D. The smaller human VH gene families display remarkably little polymorphism. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3741–3748. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08550.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W., Jr, Hillson J. L., Perlmutter R. M. Early restriction of the human antibody repertoire. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):791–793. doi: 10.1126/science.3118465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W., Jr, Wang J. Y. Preferential utilization of conserved immunoglobulin heavy chain variable gene segments during human fetal life. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6146–6150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomchik M. J., Marshak-Rothstein A., Wolfowicz C. B., Rothstein T. L., Weigert M. G. The role of clonal selection and somatic mutation in autoimmunity. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):805–811. doi: 10.1038/328805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein L. E., Jefferies L. C., Goldman J., Friedman D., Moore J. S., Nowell P. C., Roelcke D., Pruzanski W., Roudier J., Silverman G. J. Variable region gene analysis of pathologic human autoantibodies to the related i and I red blood cell antigens. Blood. 1991 Nov 1;78(9):2372–2386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein L. E., Litwin S., Carmack C. E. Relationship of variable region genes expressed by a human B cell lymphoma secreting pathologic anti-Pr2 erythrocyte autoantibodies. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1631–1643. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siminovitch K. A., Misener V., Kwong P. C., Song Q. L., Chen P. P. A natural autoantibody is encoded by germline heavy and lambda light chain variable region genes without somatic mutation. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1675–1678. doi: 10.1172/JCI114347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siminovitch K. A., Misener V., Kwong P. C., Yang P. M., Laskin C. A., Cairns E., Bell D., Rubin L. A., Chen P. P. A human anti-cardiolipin autoantibody is encoded by developementally restricted heavy and light chain variable region genes. Autoimmunity. 1990;8(2):97–105. doi: 10.3109/08916939008995727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soto-Gil R. W., Olee T., Klink B. K., Kenny T. P., Robbins D. L., Carson D. A., Chen P. P. A systematic approach to defining the germline gene counterparts of a mutated autoantibody from a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Mar;35(3):356–363. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straubinger B., Huber E., Lorenz W., Osterholzer E., Pargent W., Pech M., Pohlenz H. D., Zimmer F. J., Zachau H. G. The human VK locus. Characterization of a duplicated region encoding 28 different immunoglobulin genes. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):23–34. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90376-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugano T., Matsumoto Y., Miyamoto C., Masuho Y. Hybridomas producing human monoclonal antibodies against varicella-zoster virus. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Mar;17(3):359–364. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udey J. A., Blomberg B. Human lambda light chain locus: organization and DNA sequences of three genomic J regions. Immunogenetics. 1987;25(1):63–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00768834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Victor K. D., Randen I., Thompson K., Forre O., Natvig J. B., Fu S. M., Capra J. D. Rheumatoid factors isolated from patients with autoimmune disorders are derived from germline genes distinct from those encoding the Wa, Po, and Bla cross-reactive idiotypes. J Clin Invest. 1991 May;87(5):1603–1613. doi: 10.1172/JCI115174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


