Abstract
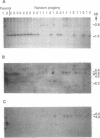
Sexual compatibility requires self vs. non-self recognition. Genetically, two compatibility or mating-type systems govern recognition in heterothallic basidiomycete fungi such as the edible and woodrotting mushrooms and the economically important rust and smut phytopathogens. A bipolar system is defined by a single genetic locus (MAT) that can have two or multiple alleles. A tetrapolar system has two loci, each with two or more specificities. We have employed two species from the genus Ustilago (smut fungi) to discover a molecular explanation for the genetic difference in mating systems. Ustilago maydis, a tetrapolar species, has two genetically unlinked loci that encode the distinct mating functions of cell fusion (a locus) and subsequent sexual development and pathogenicity (b locus). We have recently described a b locus in a bipolar species, Ustilago hordei, wherein the existence of an a locus has been suspected, but not demonstrated. We report here the cloning of an allele of the a locus (a1) from U. hordei and the discovery that physical linkage of the a and b loci in this bipolar fungus accounts for the distinct mating system. Linkage establishes a large complex MAT locus in U. hordei; this locus appears to be in a region suppressed for recombination.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakkeren G., Gibbard B., Yee A., Froeliger E., Leong S., Kronstad J. The a and b loci of Ustilago maydis hybridize with DNA sequences from other smut fungi. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1992 Jul-Aug;5(4):347–355. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-5-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakkeren G., Kronstad J. W. Conservation of the b mating-type gene complex among bipolar and tetrapolar smut fungi. Plant Cell. 1993 Jan;5(1):123–136. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banuett F. Ustilago maydis, the delightful blight. Trends Genet. 1992 May;8(5):174–180. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölker M., Urban M., Kahmann R. The a mating type locus of U. maydis specifies cell signaling components. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):441–450. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90182-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egel R. Microbial genetics. Sexual identity and smut. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):23–24. doi: 10.1038/357023a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris P. J., Goodenough U. W. The mating-type locus of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii contains highly rearranged DNA sequences. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1135–1145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90389-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froeliger E. H., Leong S. A. The a mating-type alleles of Ustilago maydis are idiomorphs. Gene. 1991 Apr;100:113–122. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90356-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillissen B., Bergemann J., Sandmann C., Schroeer B., Bölker M., Kahmann R. A two-component regulatory system for self/non-self recognition in Ustilago maydis. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):647–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinscherf T. G., Leong S. A. Molecular analysis of the karyotype of Ustilago maydis. Chromosoma. 1988;96(6):427–433. doi: 10.1007/BF00303036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koltin Y., Stamberg J., Lemke P. A. Genetic structure and evolution of the incompatibility factors in higher fungi. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Jun;36(2):156–171. doi: 10.1128/br.36.2.156-171.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronstad J. W., Leong S. A. Isolation of two alleles of the b locus of Ustilago maydis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):978–982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronstad J. W., Leong S. A. The b mating-type locus of Ustilago maydis contains variable and constant regions. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1384–1395. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzenberg R. L., Glass N. L. Mating type and mating strategies in Neurospora. Bioessays. 1990 Feb;12(2):53–59. doi: 10.1002/bies.950120202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz B., Banuett F., Dahl M., Schlesinger R., Schäfer W., Martin T., Herskowitz I., Kahmann R. The b alleles of U. maydis, whose combinations program pathogenic development, code for polypeptides containing a homeodomain-related motif. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):295–306. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90744-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trueheart J., Herskowitz I. The a locus governs cytoduction in Ustilago maydis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(23):7831–7833. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7831-7833.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee A. R., Kronstad J. W. Construction of chimeric alleles with altered specificity at the b incompatibility locus of Ustilago maydis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]