Abstract
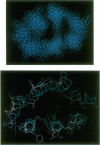
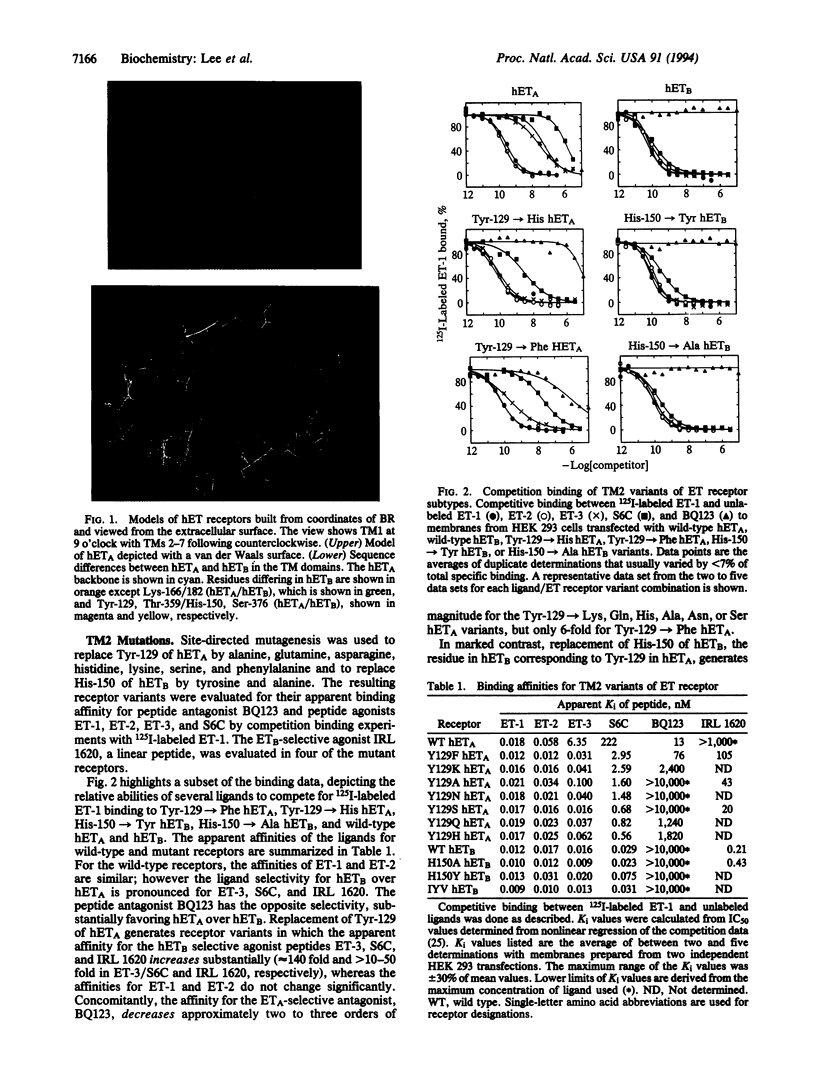
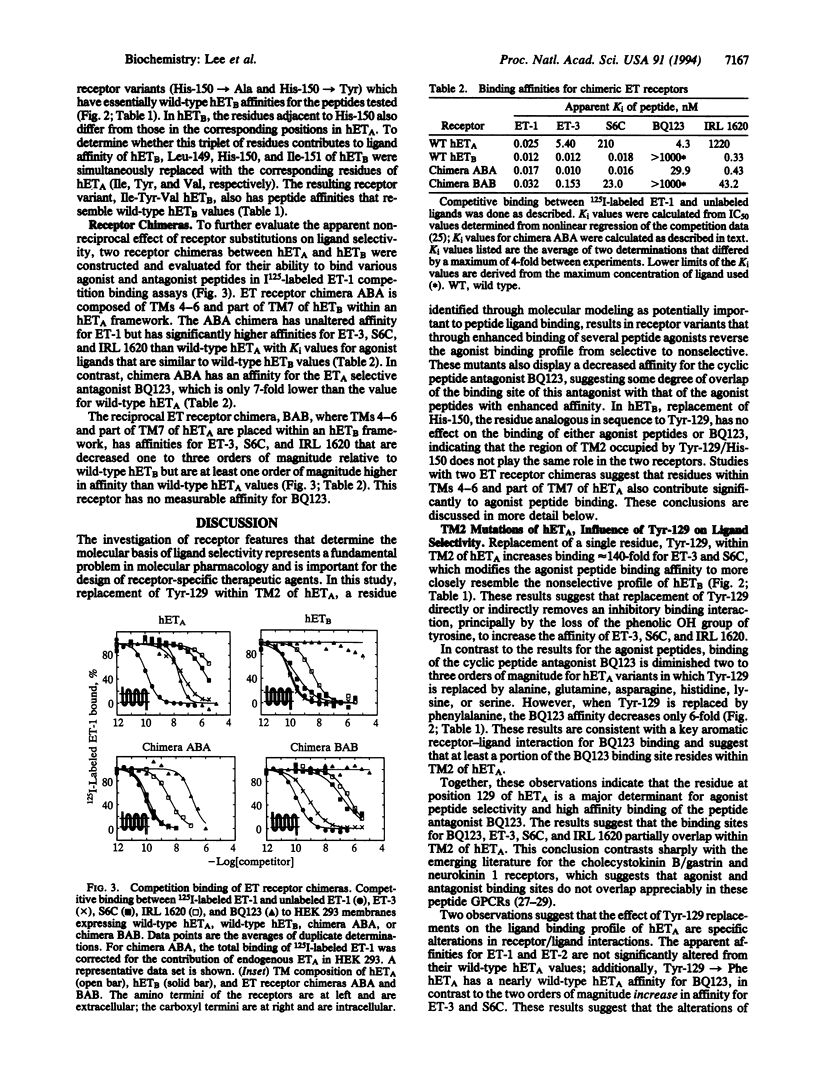
Molecular modeling and protein engineering techniques have been used to study residues within G-protein-coupled receptors that are potentially important to ligand binding and selectivity. In this study, Tyr-129 located in transmembrane domain 2 of the human endothelin (ET) type A receptor A (hETA) was targeted on the basis of differences between the hETA and type B receptor (hETB) sequences and the position of the residue on ET receptor models built using the coordinates of bacteriorhodopsin. Replacement of Tyr-129 of hETA by alanine, glutamine, asparagine, histidine, lysine, serine, or phenylalanine results in receptor variants with enhanced ET-3 and sarafotoxin 6C affinities but with unchanged ET-1 and ET-2 affinities. Except for Tyr-129-->Phe hETA, these hETA variants have two to three orders of magnitude lower binding affinity for the ETA-selective antagonist BQ123. Replacement of His-150, the residue in hETB that is analogous in sequence to Tyr-129 of hETA, by either tyrosine or alanine does not affect the affinity of peptide ligands. These results indicate that although transmembrane domain 2 is important in ligand selectivity for hETA, it does not play a significant role in the lack of ligand selectivity shown by hETB. Chimeric receptors have been constructed that further support these conclusions and indicate that at least two hETA regions contribute to ligand selectivity. Additionally, the data support an overlap in the binding site in hETA of agonists ET-3 and sarafotoxin 6C with that of the antagonist BQ123.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin J. M. The probable arrangement of the helices in G protein-coupled receptors. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1693–1703. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05814.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beinborn M., Lee Y. M., McBride E. W., Quinn S. M., Kopin A. S. A single amino acid of the cholecystokinin-B/gastrin receptor determines specificity for non-peptide antagonists. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):348–350. doi: 10.1038/362348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. A., Okayama H. Calcium phosphate-mediated gene transfer: a highly efficient transfection system for stably transforming cells with plasmid DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Jul-Aug;6(7):632–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronet P., Sander C., Vriend G. Modeling of transmembrane seven helix bundles. Protein Eng. 1993 Jan;6(1):59–64. doi: 10.1093/protein/6.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Korman D. R., Wu H. L., Sylvester D. R., Lee J. A., Nuthalaganti P., Bergsma D. J., Kumar C. S., Nambi P. Molecular characterization and regulation of the human endothelin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3873–3879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Lee J. A., Korman D. R., Nuthalaganti P., Sylvester D. R., Dilella A. G., Sutiphong J. A., Kumar C. S. Molecular cloning and characterization of the major endothelin receptor subtype in porcine cerebellum. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;41(3):465–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fathi Z., Benya R. V., Shapira H., Jensen R. T., Battey J. F. The fifth transmembrane segment of the neuromedin B receptor is critical for high affinity neuromedin B binding. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14622–14626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong T. M., Cascieri M. A., Yu H., Bansal A., Swain C., Strader C. D. Amino-aromatic interaction between histidine 197 of the neurokinin-1 receptor and CP 96345. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):350–353. doi: 10.1038/362350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gether U., Johansen T. E., Snider R. M., Lowe J. A., 3rd, Nakanishi S., Schwartz T. W. Different binding epitopes on the NK1 receptor for substance P and non-peptide antagonist. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):345–348. doi: 10.1038/362345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Baldwin J. M., Ceska T. A., Zemlin F., Beckmann E., Downing K. H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Schertler G. F. The structure of bacteriorhodopsin and its relevance to the visual opsins and other seven-helix G-protein coupled receptors. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 Jan 30;326(1236):379–389. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1990.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoflack J., Trumpp-Kallmeyer S., Hibert M. Re-evaluation of bacteriorhodopsin as a model for G protein-coupled receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Jan;15(1):7–9. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara M., Noguchi K., Saeki T., Fukuroda T., Tsuchida S., Kimura S., Fukami T., Ishikawa K., Nishikibe M., Yano M. Biological profiles of highly potent novel endothelin antagonists selective for the ETA receptor. Life Sci. 1992;50(4):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90331-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MaloneyHuss K., Lybrand T. P. Three-dimensional structure for the beta 2 adrenergic receptor protein based on computer modeling studies. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 5;225(3):859–871. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90406-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardo L., Ballesteros J. A., Osman R., Weinstein H. On the use of the transmembrane domain of bacteriorhodopsin as a template for modeling the three-dimensional structure of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein-coupled receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4009–4012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst W. C., Snyder L. A., Schuster D. I., Brosius J., Sealfon S. C. Sequence alignment of the G-protein coupled receptor superfamily. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Jan-Feb;11(1):1–20. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto A., Yanagisawa M., Sawamura T., Enoki T., Ohtani T., Sakurai T., Nakao K., Toyo-oka T., Masaki T. Distinct subdomains of human endothelin receptors determine their selectivity to endothelinA-selective antagonist and endothelinB-selective agonists. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8547–8553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savarese T. M., Fraser C. M. In vitro mutagenesis and the search for structure-function relationships among G protein-coupled receptors. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 1;283(Pt 1):1–19. doi: 10.1042/bj2830001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schertler G. F., Villa C., Henderson R. Projection structure of rhodopsin. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):770–772. doi: 10.1038/362770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolovsky M. Structure-function relationships of endothelins, sarafotoxins, and their receptor subtypes. J Neurochem. 1992 Sep;59(3):809–821. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb08318.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai M., Umemura I., Yamasaki K., Watakabe T., Fujitani Y., Oda K., Urade Y., Inui T., Yamamura T., Okada T. A potent and specific agonist, Suc-[Glu9,Ala11,15]-endothelin-1(8-21), IRL 1620, for the ETB receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Apr 30;184(2):953–959. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90683-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayanagi R., Ohnaka K., Takasaki C., Ohashi M., Nawata H. Multiple subtypes of endothelin receptors in porcine tissues: characterization by ligand binding, affinity labeling and regional distribution. Regul Pept. 1991 Jan 1;32(1):23–37. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(91)90004-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trumpp-Kallmeyer S., Hoflack J., Bruinvels A., Hibert M. Modeling of G-protein-coupled receptors: application to dopamine, adrenaline, serotonin, acetylcholine, and mammalian opsin receptors. J Med Chem. 1992 Sep 18;35(19):3448–3462. doi: 10.1021/jm00097a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu G., Wu L. H., Mauzy C., Egloff A. M., Mirzadegan T., Chung F. Z. Replacement of lysine-181 by aspartic acid in the third transmembrane region of endothelin type B receptor reduces its affinity to endothelin peptides and sarafotoxin 6c without affecting G protein coupling. J Cell Biochem. 1992 Oct;50(2):159–164. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240500206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]