Abstract
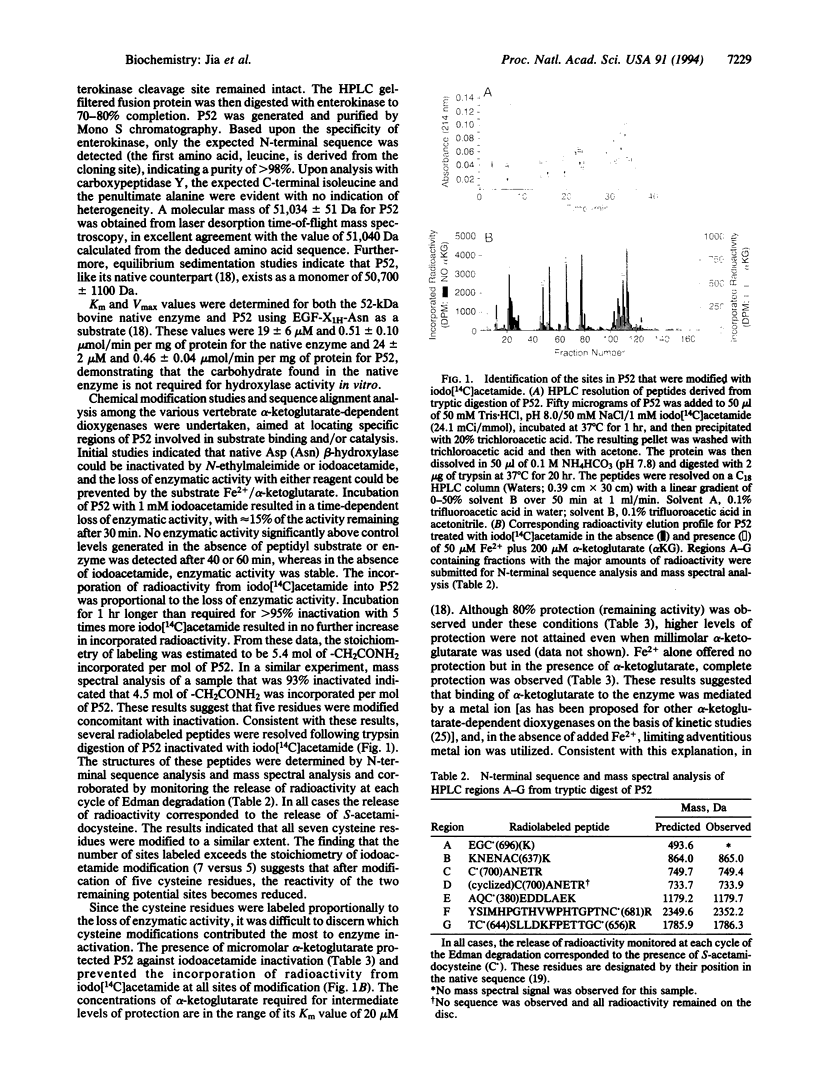
The alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase aspartyl (asparaginyl) beta-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.11.16) specifically hydroxylates one aspartic or asparagine residue in certain epidermal growth factor-like domains of a number of proteins. The expression in Escherichia coli, purification, characterization of a fully active catalytic domain, and evidence for the identification of an active-site region of this enzyme are described. Sequence alignment analyses among the vertebrate alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases and chemical modification studies were undertaken aimed at locating specific regions of 52-kDa recombinant aspartyl (asparaginyl) beta-hydroxylase involved in substrate binding and/or catalysis. Based upon these studies, an alignment of the C-terminal regions of prolyl and lysyl hydroxylase and of aspartyl (asparaginyl) beta-hydroxylase is proposed. When histidine-675, an invariant residue located in a region of homology within this alignment, was mutated to an alanine residue in aspartyl (asparaginyl) beta-hydroxylase (H675A), no enzymatic activity was detected. Chemical modification studies show that the wild-type protein is protected from iodo[14C]acetamide labeling by Fe2+/alpha-ketoglutarate whereas the H675A mutant protein is not, suggesting that this mutant does not bind Fe2+/alpha-ketoglutarate.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann E., Brosius J. "ATG vectors' for regulated high-level expression of cloned genes in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appella E., Robinson E. A., Ullrich S. J., Stoppelli M. P., Corti A., Cassani G., Blasi F. The receptor-binding sequence of urokinase. A biological function for the growth-factor module of proteases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4437–4440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appella E., Weber I. T., Blasi F. Structure and function of epidermal growth factor-like regions in proteins. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 11;231(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80690-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astermark J., Hogg P. J., Björk I., Stenflo J. Effects of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid and epidermal growth factor-like modules of factor IX on factor X activation. Studies using proteolytic fragments of bovine factor IX. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3249–3256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M., Norman D. G., Campbell I. D. Protein modules. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jan;16(1):13–17. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90009-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassuk J. A., Kao W. W., Herzer P., Kedersha N. L., Seyer J., DeMartino J. A., Daugherty B. L., Mark G. E., 3rd, Berg R. A. Prolyl 4-hydroxylase: molecular cloning and the primary structure of the alpha subunit from chicken embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7382–7386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Frohm B., Nelsestuen G. High affinity interaction between C4b-binding protein and vitamin K-dependent protein S in the presence of calcium. Suggestion of a third component in blood regulating the interaction. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16082–16087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derian C. K., VanDusen W., Przysiecki C. T., Walsh P. N., Berkner K. L., Kaufman R. J., Friedman P. A. Inhibitors of 2-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases block aspartyl beta-hydroxylation of recombinant human factor IX in several mammalian expression systems. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6615–6618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. EGF-like domains in extracellular matrix proteins: localized signals for growth and differentiation? FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81417-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehon R. G., Kooh P. J., Rebay I., Regan C. L., Xu T., Muskavitch M. A., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Molecular interactions between the protein products of the neurogenic loci Notch and Delta, two EGF-homologous genes in Drosophila. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):523–534. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90534-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronke R. S., VanDusen W. J., Garsky V. M., Jacobs J. W., Sardana M. K., Stern A. M., Friedman P. A. Aspartyl beta-hydroxylase: in vitro hydroxylation of a synthetic peptide based on the structure of the first growth factor-like domain of human factor IX. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3609–3613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronke R. S., Welsch D. J., VanDusen W. J., Garsky V. M., Sardana M. K., Stern A. M., Friedman P. A. Partial purification and characterization of bovine liver aspartyl beta-hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8558–8565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hautala T., Byers M. G., Eddy R. L., Shows T. B., Kivirikko K. I., Myllylä R. Cloning of human lysyl hydroxylase: complete cDNA-derived amino acid sequence and assignment of the gene (PLOD) to chromosome 1p36.3----p36.2. Genomics. 1992 May;13(1):62–69. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helaakoski T., Vuori K., Myllylä R., Kivirikko K. I., Pihlajaniemi T. Molecular cloning of the alpha-subunit of human prolyl 4-hydroxylase: the complete cDNA-derived amino acid sequence and evidence for alternative splicing of RNA transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4392–4396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg P. J., Ohlin A. K., Stenflo J. Identification of structural domains in protein C involved in its interaction with thrombin-thrombomodulin on the surface of endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):703–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jia S., VanDusen W. J., Diehl R. E., Kohl N. E., Dixon R. A., Elliston K. O., Stern A. M., Friedman P. A. cDNA cloning and expression of bovine aspartyl (asparaginyl) beta-hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14322–14327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa S., Stearns D. J., Jackson K. W., Esmon C. T. A 10-kDa cyanogen bromide fragment from the epidermal growth factor homology domain of rabbit thrombomodulin contains the primary thrombin binding site. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):5993–5996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monkovic D. D., VanDusen W. J., Petroski C. J., Garsky V. M., Sardana M. K., Zavodszky P., Stern A. M., Friedman P. A. Invertebrate aspartyl/asparaginyl beta-hydroxylase: potential modification of endogenous epidermal growth factor-like modules. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 30;189(1):233–241. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91549-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myllylä R., Günzler V., Kivirikko K. I., Kaska D. D. Modification of vertebrate and algal prolyl 4-hydroxylases and vertebrate lysyl hydroxylase by diethyl pyrocarbonate. Evidence for histidine residues in the catalytic site of 2-oxoglutarate-coupled dioxygenases. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 15;286(Pt 3):923–927. doi: 10.1042/bj2860923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myllylä R., Pihlajaniemi T., Pajunen L., Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T., Kivirikko K. I. Molecular cloning of chick lysyl hydroxylase. Little homology in primary structure to the two types of subunit of prolyl 4-hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2805–2810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlin A. K., Landes G., Bourdon P., Oppenheimer C., Wydro R., Stenflo J. Beta-hydroxyaspartic acid in the first epidermal growth factor-like domain of protein C. Its role in Ca2+ binding and biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19240–19248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebay I., Fleming R. J., Fehon R. G., Cherbas L., Cherbas P., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Specific EGF repeats of Notch mediate interactions with Delta and Serrate: implications for Notch as a multifunctional receptor. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):687–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander-Sunnerhagen M., Ullner M., Persson E., Teleman O., Stenflo J., Drakenberg T. How an epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domain binds calcium. High resolution NMR structure of the calcium form of the NH2-terminal EGF-like domain in coagulation factor X. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19642–19649. doi: 10.2210/pdb1ccf/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Holme E., Lindstedt S., Chandramouli N., Huang L. H., Tam J. P., Merrifield R. B. Hydroxylation of aspartic acid in domains homologous to the epidermal growth factor precursor is catalyzed by a 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):444–447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J. Structure-function relationships of epidermal growth factor modules in vitamin K-dependent clotting factors. Blood. 1991 Oct 1;78(7):1637–1651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Hayashi T., Nishioka J., Kosaka Y., Zushi M., Honda G., Yamamoto S. A domain composed of epidermal growth factor-like structures of human thrombomodulin is essential for thrombin binding and for protein C activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4872–4876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q. P., VanDusen W. J., Petroski C. J., Garsky V. M., Stern A. M., Friedman P. A. Bovine liver aspartyl beta-hydroxylase. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):14004–14010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]