Abstract
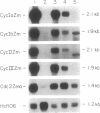
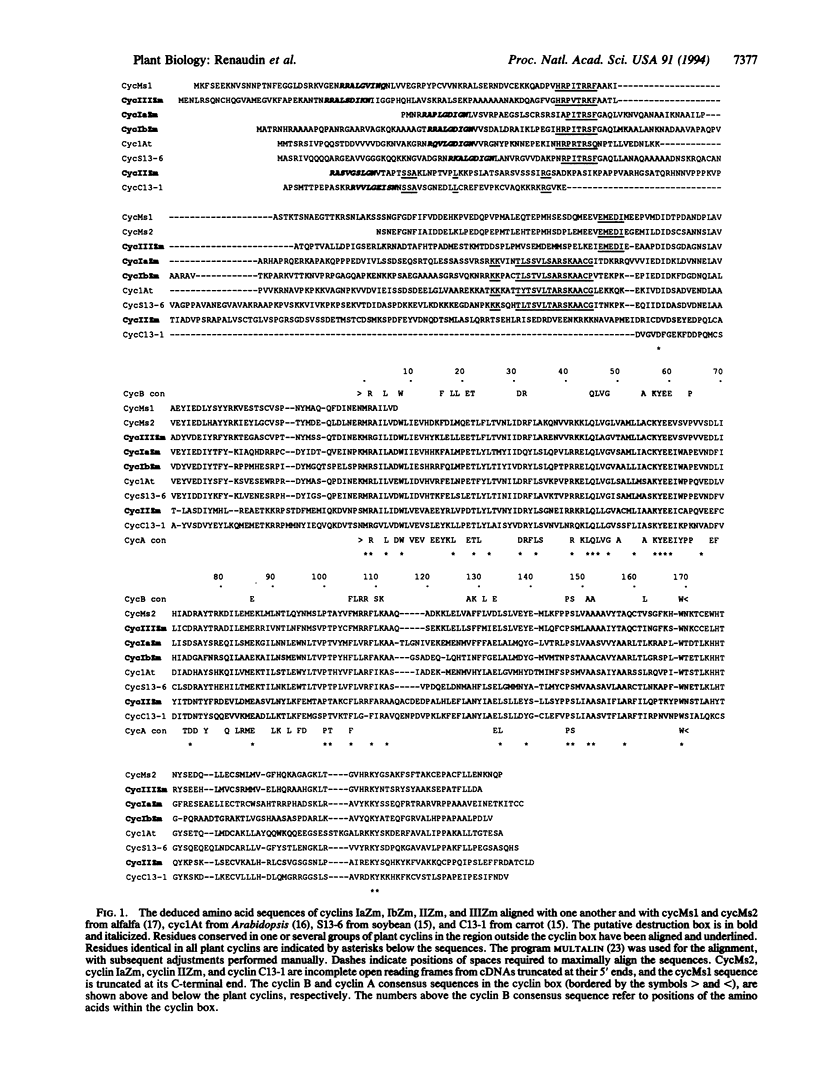
While a large number of cyclins have been described in animals and yeasts, very limited information is available regarding cyclins in plants. We describe here the isolation of cDNA clones encoding four putative mitotic cyclins from maize. All four cyclins were able to induce maturation of Xenopus oocytes, demonstrating that they can act as mitotic cyclins in this system. Northern analysis showed that all four cyclins were expressed only in actively dividing tissues and organs, with a stronger correlation between expression and mitotic activity than is observed with cdc2. The deduced protein sequences suggest that the four maize cyclins belong to the cyclin A and B families identified from animal and yeast studies but that they cannot be described easily as either A-type or B-type cyclins. However, comparison with previously cloned plant cyclins shows that cyclins in higher plants form three distinct structural groups that have been conserved in both monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous species and that cyclins from all three groups are present within a single plant species.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Colasanti J., Cho S. O., Wick S., Sundaresan V. Localization of the Functional p34cdc2 Homolog of Maize in Root Tip and Stomatal Complex Cells: Association with Predicted Division Sites. Plant Cell. 1993 Sep;5(9):1101–1111. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.9.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colasanti J., Tyers M., Sundaresan V. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones encoding a functional p34cdc2 homologue from Zea mays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3377–3381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corpet F. Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical clustering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10881–10890. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Rosenthal E. T., Youngblom J., Distel D., Hunt T. Cyclin: a protein specified by maternal mRNA in sea urchin eggs that is destroyed at each cleavage division. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):389–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiler H. S., Jacobs T. W. Cell division in higher plants: a cdc2 gene, its 34-kDa product, and histone H1 kinase activity in pea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5397–5401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira P. C., Hemerly A. S., Villarroel R., Van Montagu M., Inzé D. The Arabidopsis functional homolog of the p34cdc2 protein kinase. Plant Cell. 1991 May;3(5):531–540. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.5.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch I., Dahmann C., Surana U., Amon A., Nasmyth K., Goetsch L., Byers B., Futcher B. Characterization of four B-type cyclin genes of the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jul;3(7):805–818. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.7.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotzer M., Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):132–138. doi: 10.1038/349132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata S., Kouchi H., Suzuka I., Ishii T. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for plant cyclins. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2681–2688. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07811.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemerly A., Bergounioux C., Van Montagu M., Inzé D., Ferreira P. Genes regulating the plant cell cycle: isolation of a mitotic-like cyclin from Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3295–3299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama T., Imajuku Y., Anai T., Matsui M., Oka A. Identification of two cell-cycle-controlling cdc2 gene homologs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene. 1991 Sep 15;105(2):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90146-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt H., Mink M., Pfosser M., Bögre L., Györgyey J., Jonak C., Gartner A., Dudits D., Heberle-Bors E. Alfalfa cyclins: differential expression during the cell cycle and in plant organs. Plant Cell. 1992 Dec;4(12):1531–1538. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.12.1531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt H., Páy A., Györgyey J., Bakó L., Németh K., Bögre L., Schweyen R. J., Heberle-Bors E., Dudits D. Complementation of a yeast cell cycle mutant by an alfalfa cDNA encoding a protein kinase homologous to p34cdc2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1636–1640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs T. Control of the cell cycle. Dev Biol. 1992 Sep;153(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90087-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorca T., Devault A., Colas P., Van Loon A., Fesquet D., Lazaro J. B., Dorée M. Cyclin A-Cys41 does not undergo cell cycle-dependent degradation in Xenopus extracts. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 13;306(1):90–93. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80844-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luca F. C., Shibuya E. K., Dohrmann C. E., Ruderman J. V. Both cyclin A delta 60 and B delta 97 are stable and arrest cells in M-phase, but only cyclin B delta 97 turns on cyclin destruction. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4311–4320. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyndon R. F., Cunninghame M. E. Control of shoot apical development via cell division. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1986;40:233–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütcke H. A., Chow K. C., Mickel F. S., Moss K. A., Kern H. F., Scheele G. A. Selection of AUG initiation codons differs in plants and animals. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):43–48. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martienssen R. A., Barkan A., Freeling M., Taylor W. C. Molecular cloning of a maize gene involved in photosynthetic membrane organization that is regulated by Robertson's Mutator. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1633–1639. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03553.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez M. C., Jørgensen J. E., Lawton M. A., Lamb C. J., Doerner P. W. Spatial pattern of cdc2 expression in relation to meristem activity and cell proliferation during plant development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7360–7364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miao G. H., Hong Z., Verma D. P. Two functional soybean genes encoding p34cdc2 protein kinases are regulated by different plant developmental pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):943–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A. Cellular substrates of p34(cdc2) and its companion cyclin-dependent kinases. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;3(9):296–301. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90011-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Nurse P. Animal cell cycles and their control. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:441–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Cyclin-dependent kinases: a new cell cycle motif? Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;1(5):117–121. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90116-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cell division: the involvement of cyclins A and B1, and multiple cdc2s. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:449–463. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclins A and B1 are differentially located in the cell and undergo cell cycle-dependent nuclear transport. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):1–17. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rime H., Huchon D., Jessus C., Goris J., Merlevede W., Ozon R. Characterization of MPF activation by okadaic acid in Xenopus oocyte. Cell Differ Dev. 1990 Jan;29(1):47–58. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(90)90023-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rime H., Yang J., Jessus C., Ozon R. MPF is activated in growing immature Xenopus oocytes in the absence of detectable tyrosine dephosphorylation of P34cdc2. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Oct;196(2):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90257-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson K. I., Farrell K. M., Ruderman J. V. The clam embryo protein cyclin A induces entry into M phase and the resumption of meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):861–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90801-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick S. M. Spatial aspects of cytokinesis in plant cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;3(2):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90149-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Beach D. Population explosion in the cyclin family. Curr Biol. 1991 Dec;1(6):362–364. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(91)90193-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]