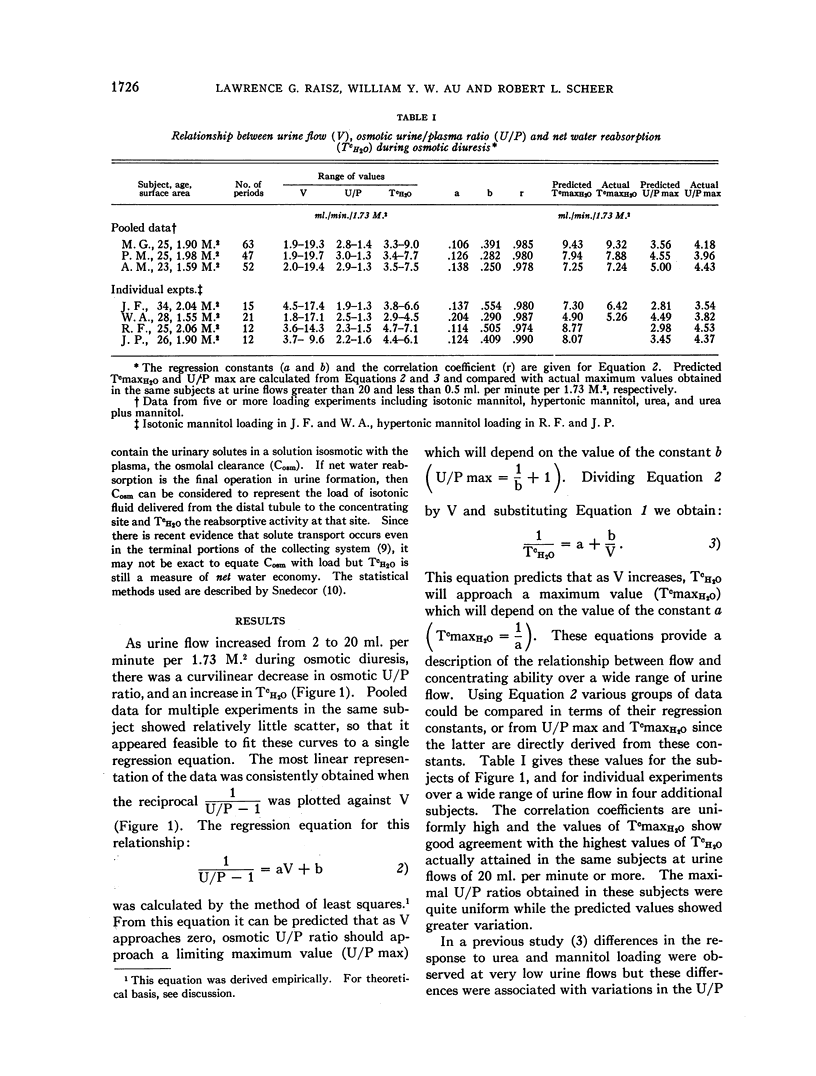
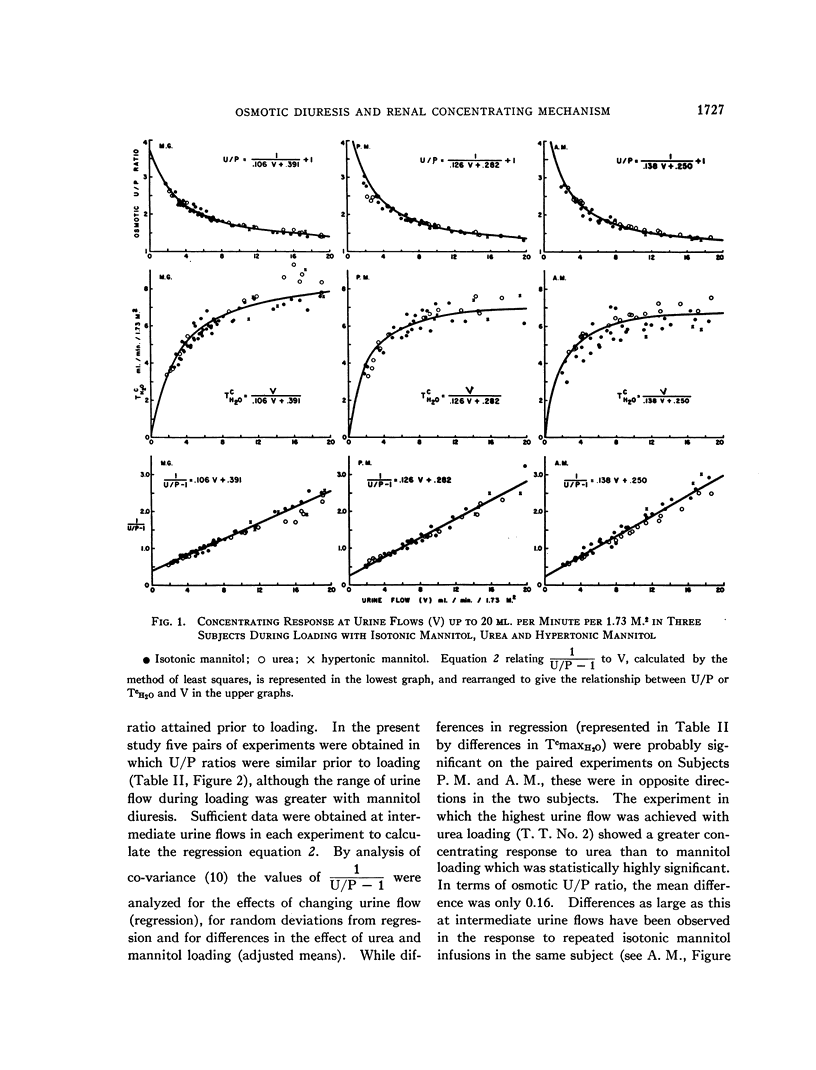
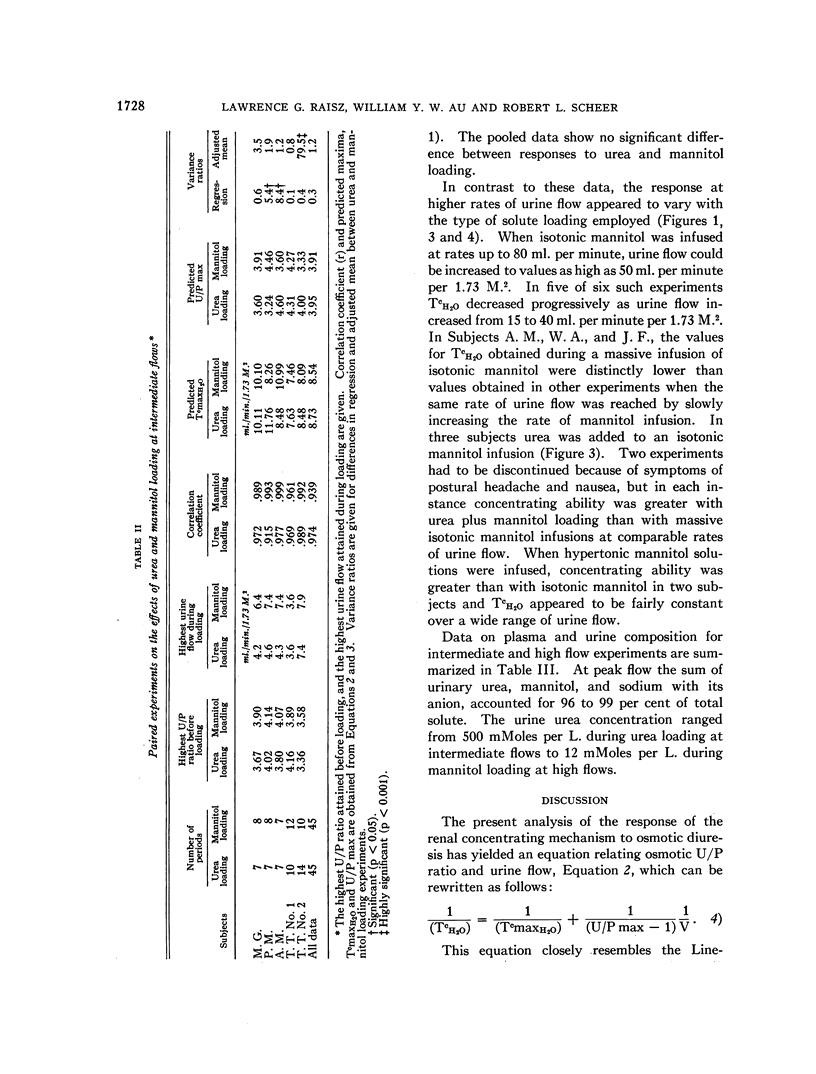
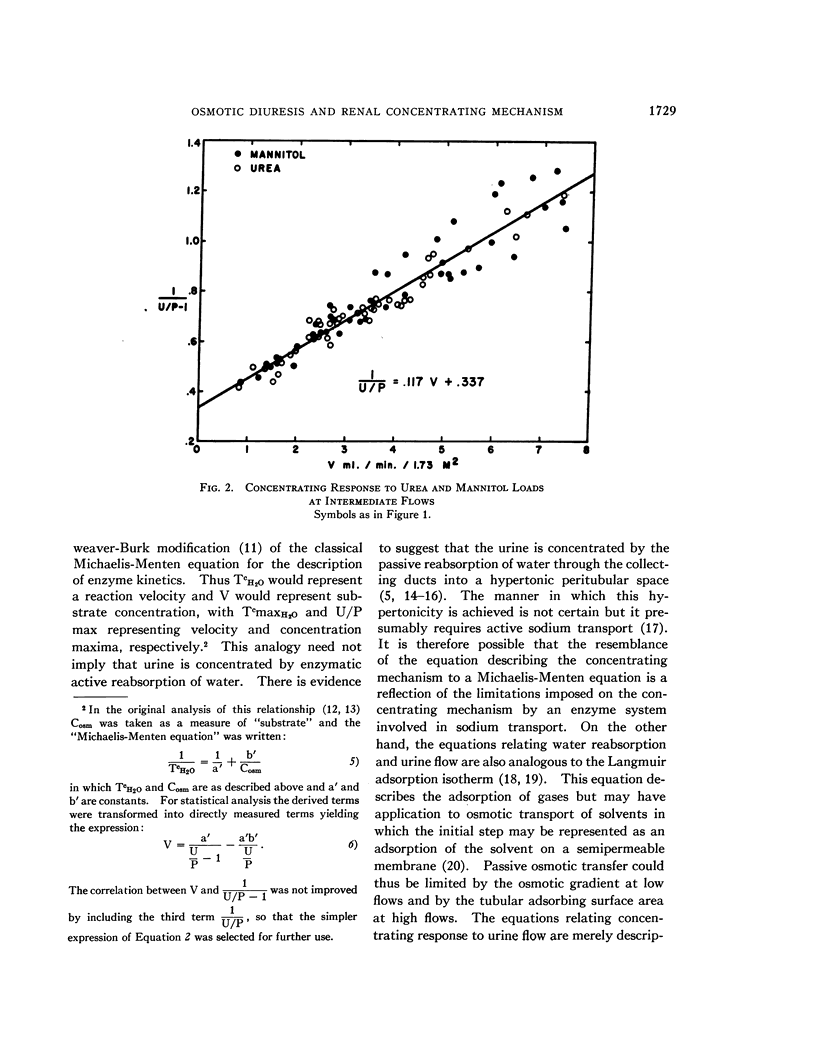
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERLINER R. W., LEVINSKY N. G., DAVIDSON D. G., EDEN M. Dilution and concentration of the urine and the action of antidiuretic hormone. Am J Med. 1958 May;24(5):730–744. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90377-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babbitt J. D. Osmotic Pressure. Science. 1955 Aug 12;122(3163):285–287. doi: 10.1126/science.122.3163.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPSTEIN F. H., KLEEMAN C. R., PURSEL S., HENDRIKX A. The effect of feeding protein and urea on the renal concentrating process. J Clin Invest. 1957 May;36(5):635–641. doi: 10.1172/JCI103463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILGER H. H., KLUMPER J. D., ULLRICH K. J. Wasserrückresorption und Ionentransport durch die Sammelrohrzellen der Säugetierniere; mikroanalytische Untersuchungen. Pflugers Arch. 1958;267(3):218–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00362426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JARAUSCH K. H., ULLRICH K. J. Untersuchungen zum Problem der Harnkonzentrierung und Harnverdünnung; Uber die Verteilung von Elektrolyten (Na, K, Ca, Mg, Cl, anorganischem Phosphat), Harnstoff, Aminosäuren und exogenem Kreatinin in Rinde und Mark der Hundeniere bei verschiedenen Diuresezuständen. Pflugers Arch. 1956;262(6):537–550. doi: 10.1007/BF00362116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINSKY N. G., BERLINER R. W. The role of urea in the urine concentrating mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1959 May;38(5):741–748. doi: 10.1172/JCI103854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance R. A. The excretion of urea, salts and water during periods of hydropaenia in man. J Physiol. 1945 Oct 15;104(2):196–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1945.sp004115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAISZ L. G., AU W. Y., SCHEER R. L. Studies on the renal concentrating mechanism. III. Effect of heavy exercise. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jan 1;38(1 Pt 1):8–13. doi: 10.1172/JCI103797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAISZ L. G., SCHEER R. L. Studies on the renal concentrating mechanism. II. Effect of small acute changes in solute excretion. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jan 1;38(1 Pt 1):1–7. doi: 10.1172/JCI103778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT-NIELSEN B. Urea excretion in mammals. Physiol Rev. 1958 Apr;38(2):139–168. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1958.38.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetten D., Jr Relationship of Hormone Dosage to Physiological Response. Science. 1956 Aug 24;124(3217):365–366. doi: 10.1126/science.124.3217.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ULLRICH K. J. Aktiver Natriumtransport und Sauerstoffverbrauch in der äusseren Markzone der Niere. Pflugers Arch. 1958;267(3):207–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00362425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIRZ H. Der osmotische Druck in den corticalen Tubuli der Rattenniere. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1956;14(3):353–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIRZ H., HARGITAY B., KUHN W. Lokalisation des Konzentrierungsprozesses in der Niere durch direkte Kryoskopie. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1951 Jun;9(2):196–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZAK G. A., BRUN C., SMITH H. W. The mechanism of formation of osmotically concentrated urine during the antidiuretic state. J Clin Invest. 1954 Jul;33(7):1064–1074. doi: 10.1172/JCI102974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


