Abstract
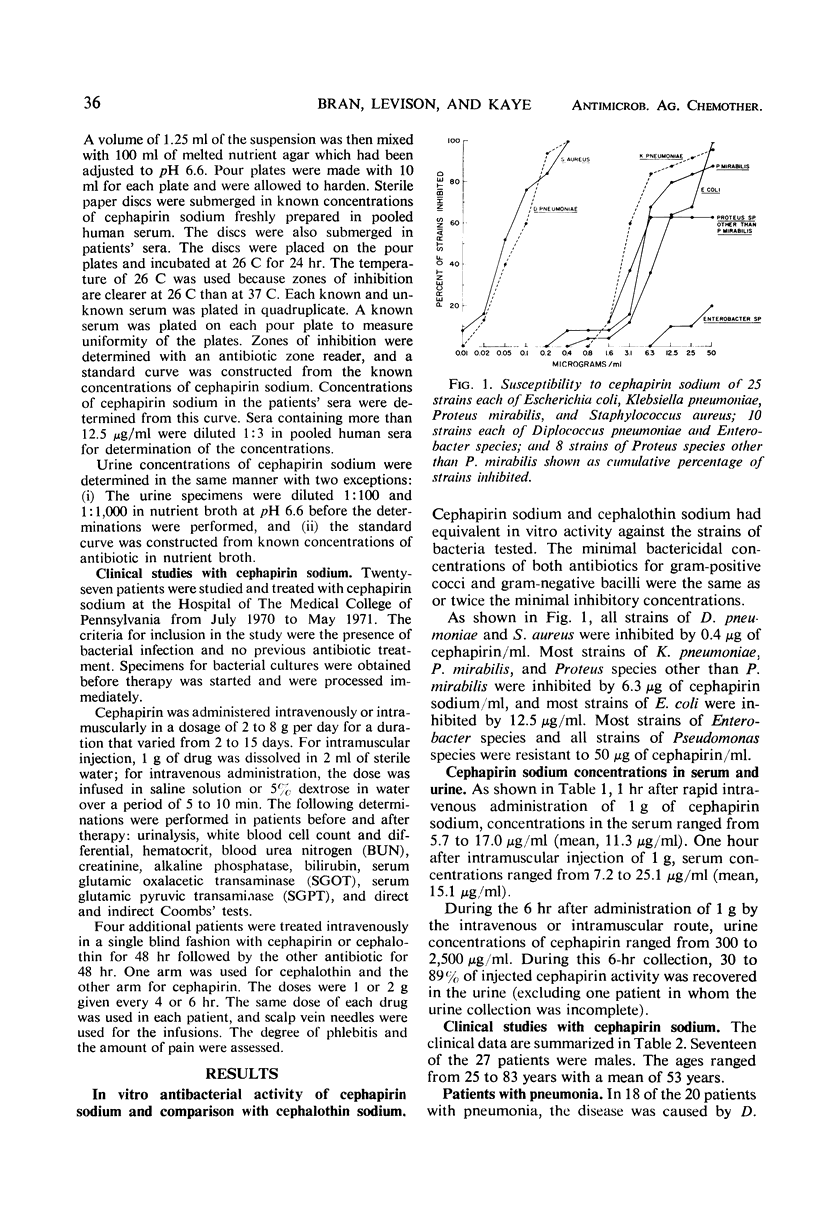
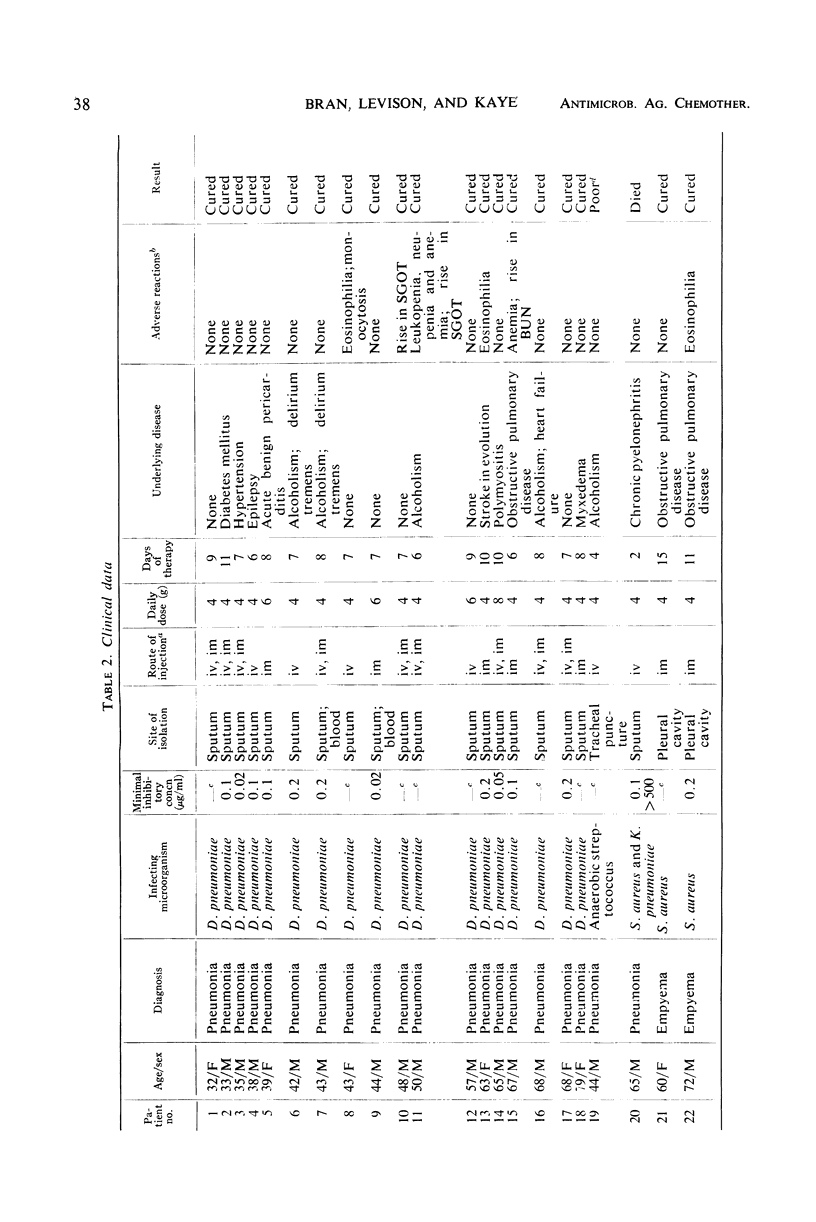
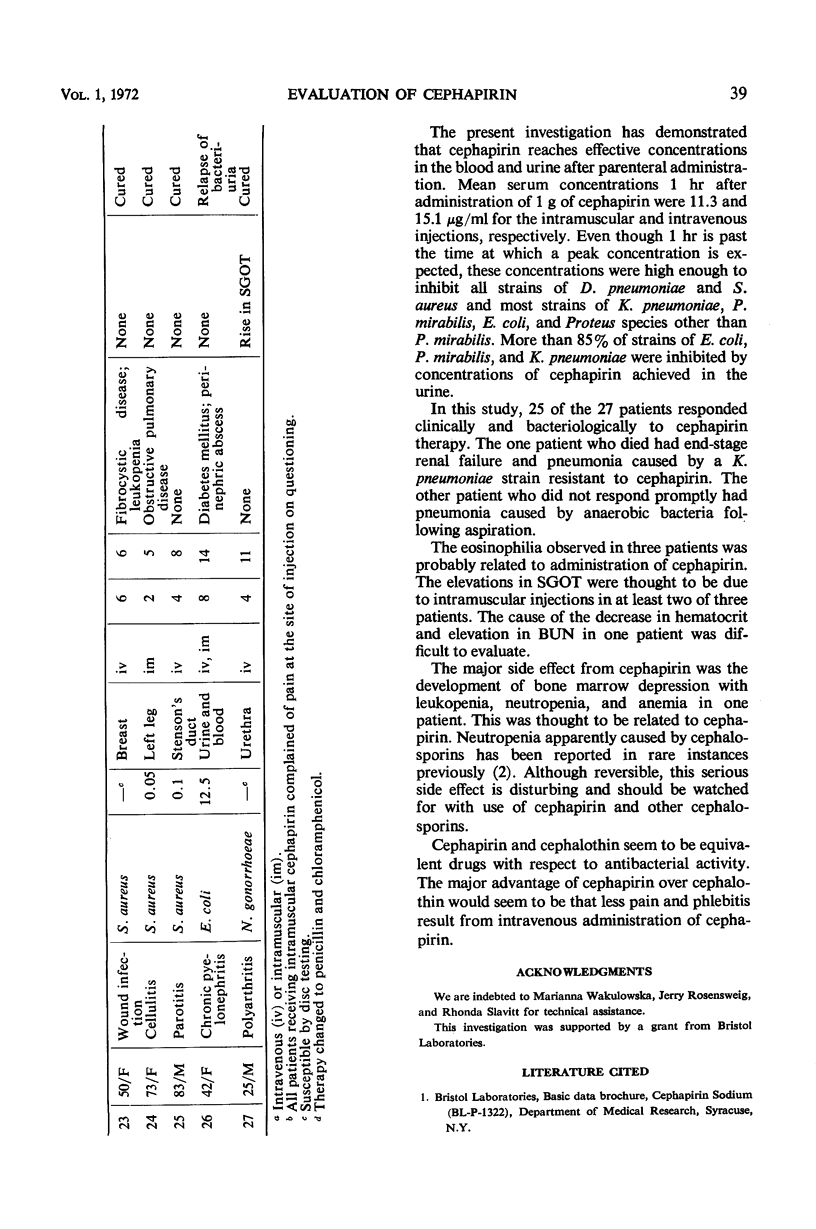
Cephapirin sodium, a cephalosporin for parenteral use, was evaluated in vitro and in 27 patients. Cephapirin had activity equivalent to cephalothin against 25 strains each of Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, and Staphylococcus aureus; 10 strains each of Diplococcus pneumoniae, Pseudomonas species, and Enterobacter species; and 8 strains of Proteus species other than P. mirabilis. All strains of S. aureus and D. pneumoniae and most strains of E. coli, K. pneumoniae, and Proteus species were inhibited by concentrations of cephapirin achieved in the serum. Of 27 patients (20 with pneumonia, 2 with S. aureus empyema, and 5 with miscellaneous infections), 25 responded to cephapirin therapy. The only major toxicity thought to be drug-related occurred in a patient who developed reversible bone marrow depression with leukopenia, neutropenia, and anemia. Although cephapirin was painful on intramuscular injection, phlebitis and pain were absent in patients treated intravenously. In a controlled comparison of intravenously administered cephalothin and cephapirin in four additional patients, the latter caused much less pain than the former and caused no phlebitis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAVIS A., SELIGMAN S. J., HEWITT W. L., FINEGOLD S. M. NEUTROPENIC REACTION TO CEPHALOTHIN THERAPY. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1963;161:272–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. C., Barrett F. F., Clark D. J., Yow M. D. Laboratory and pharmacologic studies of BL-P-1322 (cephapirin sodium) in children. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1971 Jun;13(6):398–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WICK W. E., BONIECE W. S. IN VITRO AND IN VIVO LABORATORY EVALUATION OF CEPHALOGLYCIN AND CEPHALORIDINE. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:248–253. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.248-253.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


