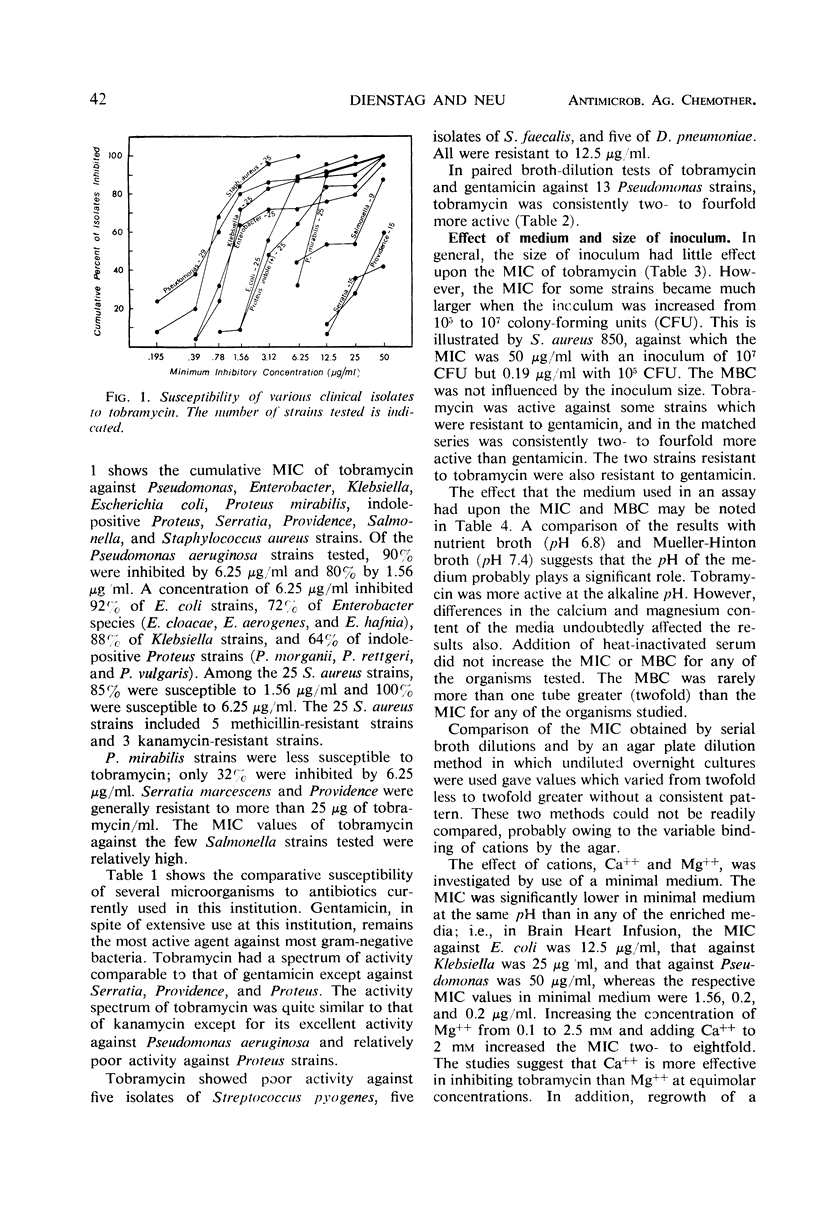
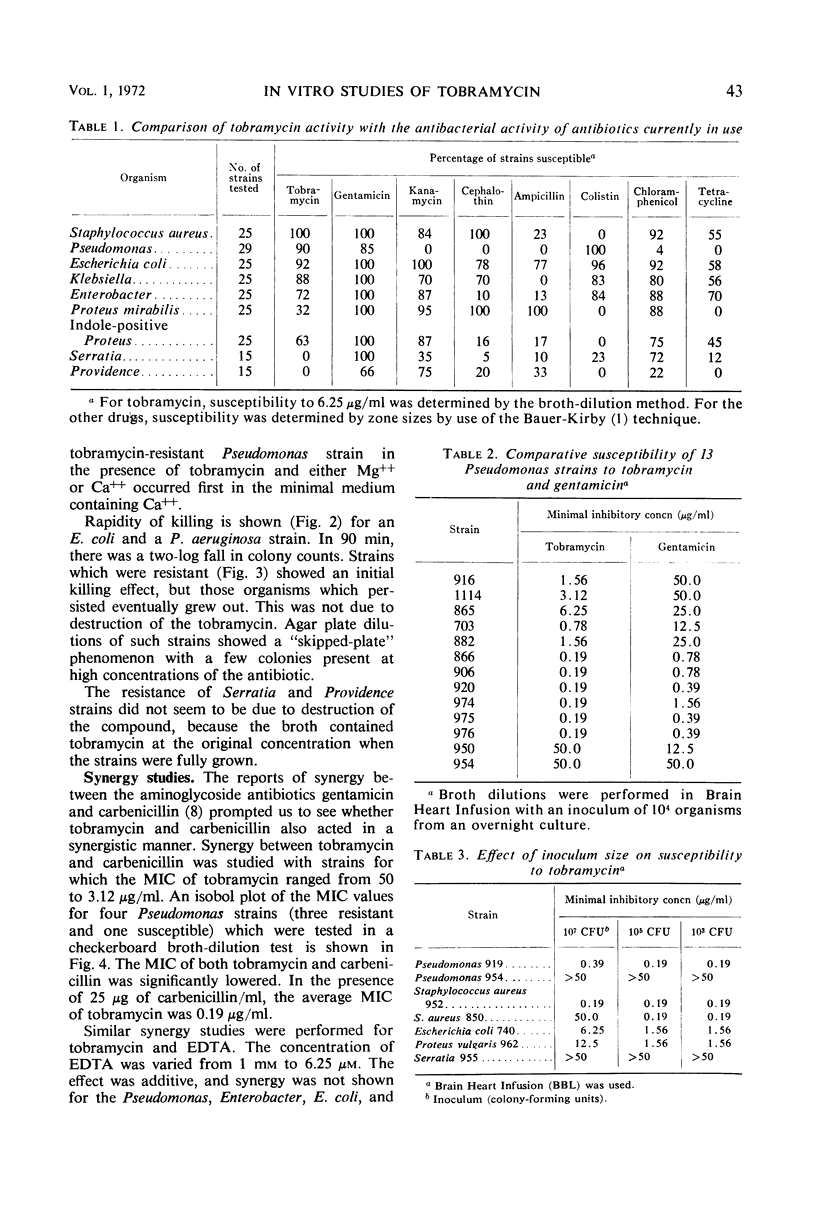
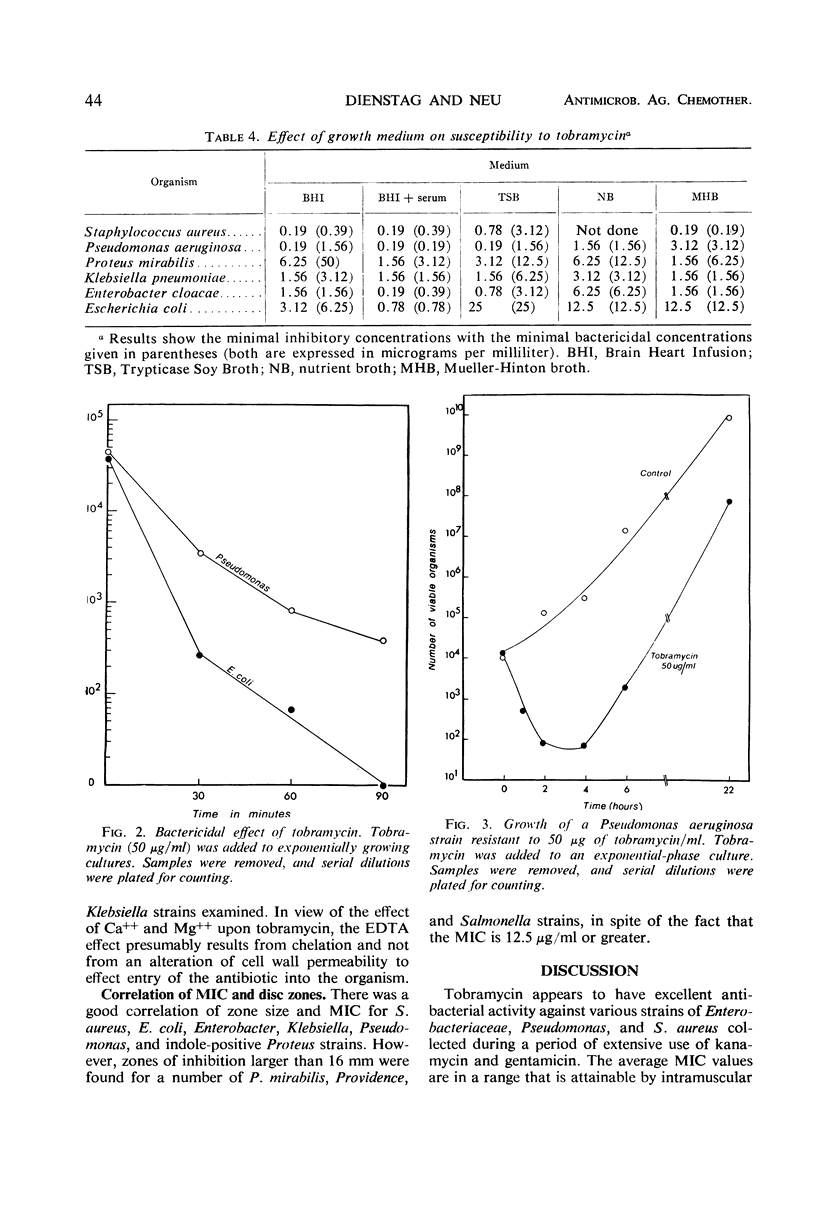
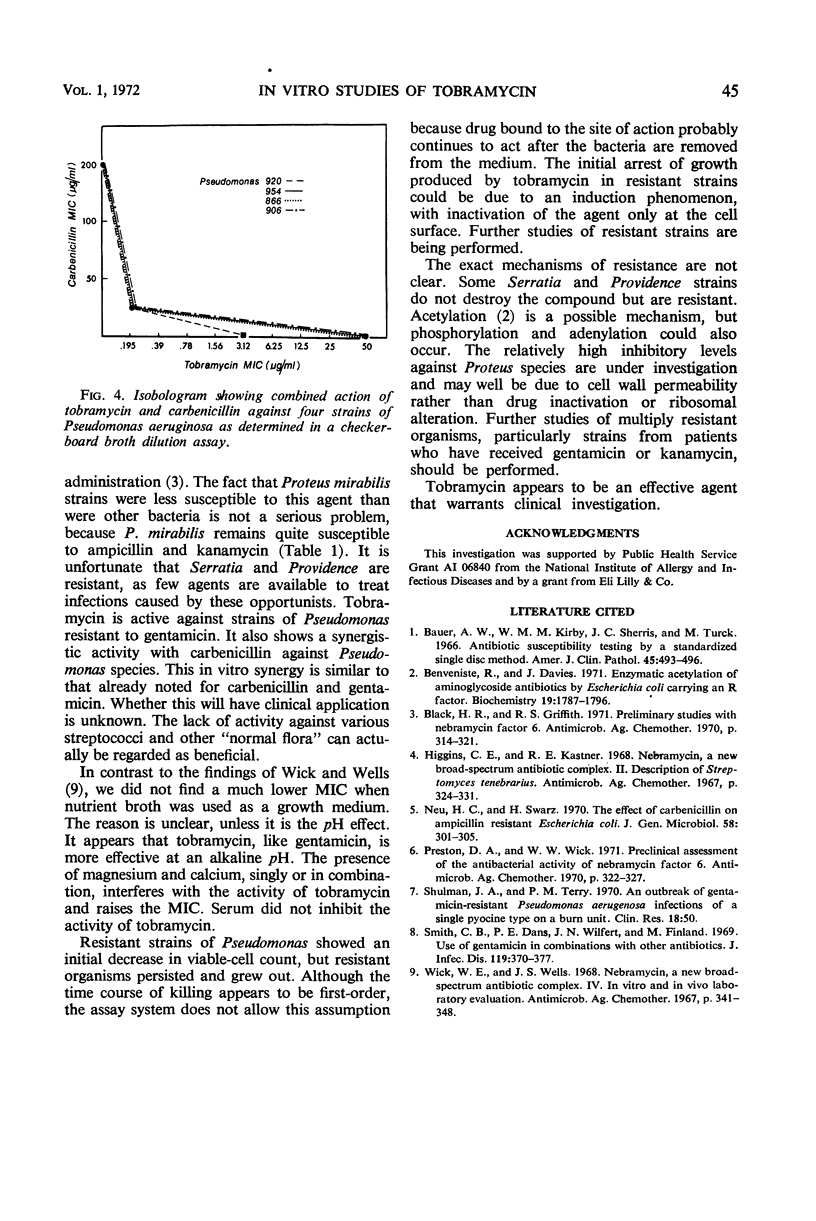
Abstract
Tobramycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic which has excellent antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas, Staphylococcus aureus, and many members of the Enterobacteriaceae. Most strains of Serratia, Providence, Streptococcus, and Diplococcus pneumoniae were resistant to concentrations of tobramycin which could be achieved in man. Tobramycin was effective against certain Pseudomonas strains resistant to gentamicin. The growth medium used to determine the inhibitory level of tobramycin had a significant effect upon the minimal inhibitory concentration. Calcium and magnesium ions inhibited the bactericidal effect of tobramycin. Tobramycin and carbenicillin acted in a synergistic manner. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid did not act in a synergistic manner with tobramycin. Broth-dilution susceptibility tests and disc-diffusion tests in agar (10-μg discs) showed excellent correlation except with Proteus strains.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R., Davies J. Enzymatic acetylation of aminoglycoside antibiotics by Escherichia coli carrying an R factor. Biochemistry. 1971 May 11;10(10):1787–1796. doi: 10.1021/bi00786a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black H. R., Griffith R. S. Preliminary studies with nebramycin factor 6. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1970;10:314–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. E., Kastner R. E. Nebramycin, a new broad-spectrum antibiotic complex. II. Description of Streptomyces tenebrarius. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1967;7:324–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Swarz H. Resistance of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium to carbenicillin. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Nov;58(3):301–305. doi: 10.1099/00221287-58-3-301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston D. A., Wick W. E. Preclinical assessment of the antibacterial activity of nebramycin factor 6. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1970;10:322–327. doi: 10.1128/AAC.10.2.322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. B., Dans P. E., Wilfert J. N., Finland M. Use of gentamicin in combinations with other antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1969 Apr-May;119(4):370–377. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.4-5.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick W. E., Welles J. S. Nebramycin, a new broad-spectrum antibiotic complex. IV. In vitro and in vivo laboratory evaluation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1967;7:341–348. doi: 10.1128/AAC.7.3.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


