Abstract
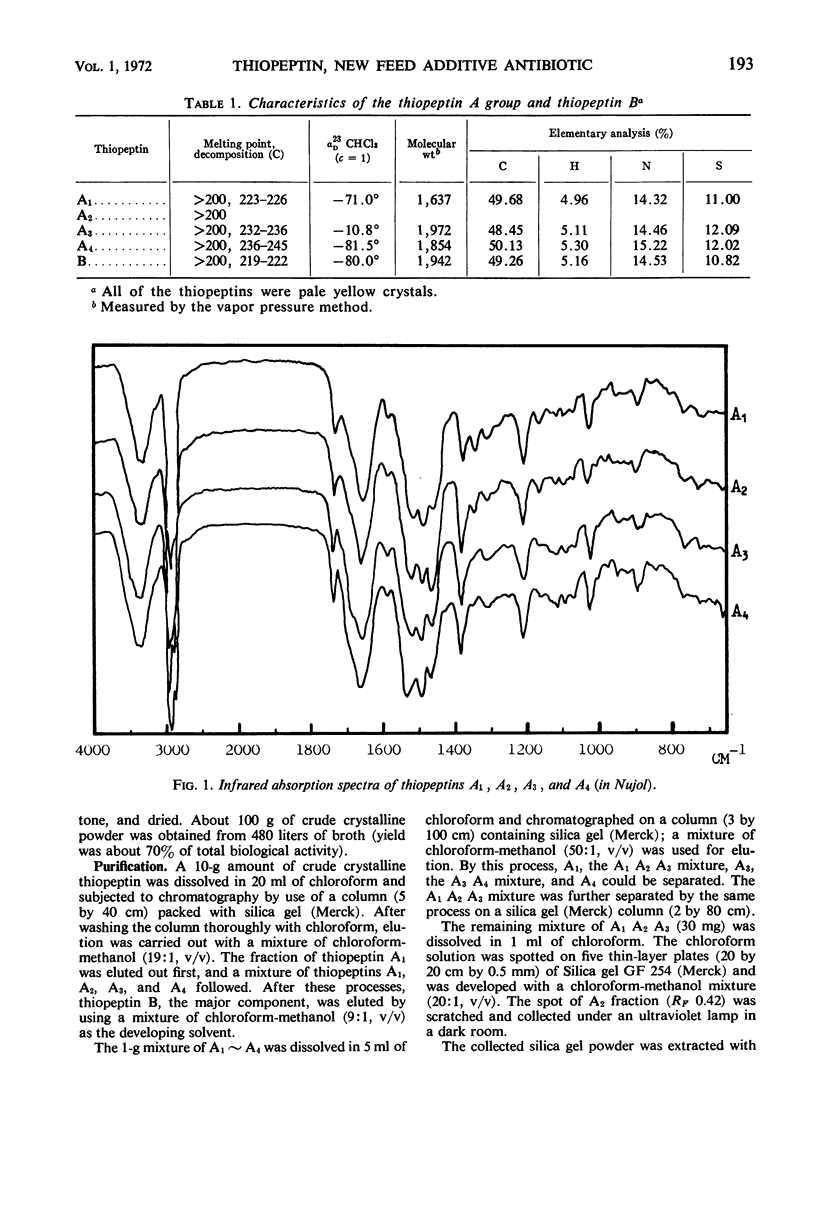
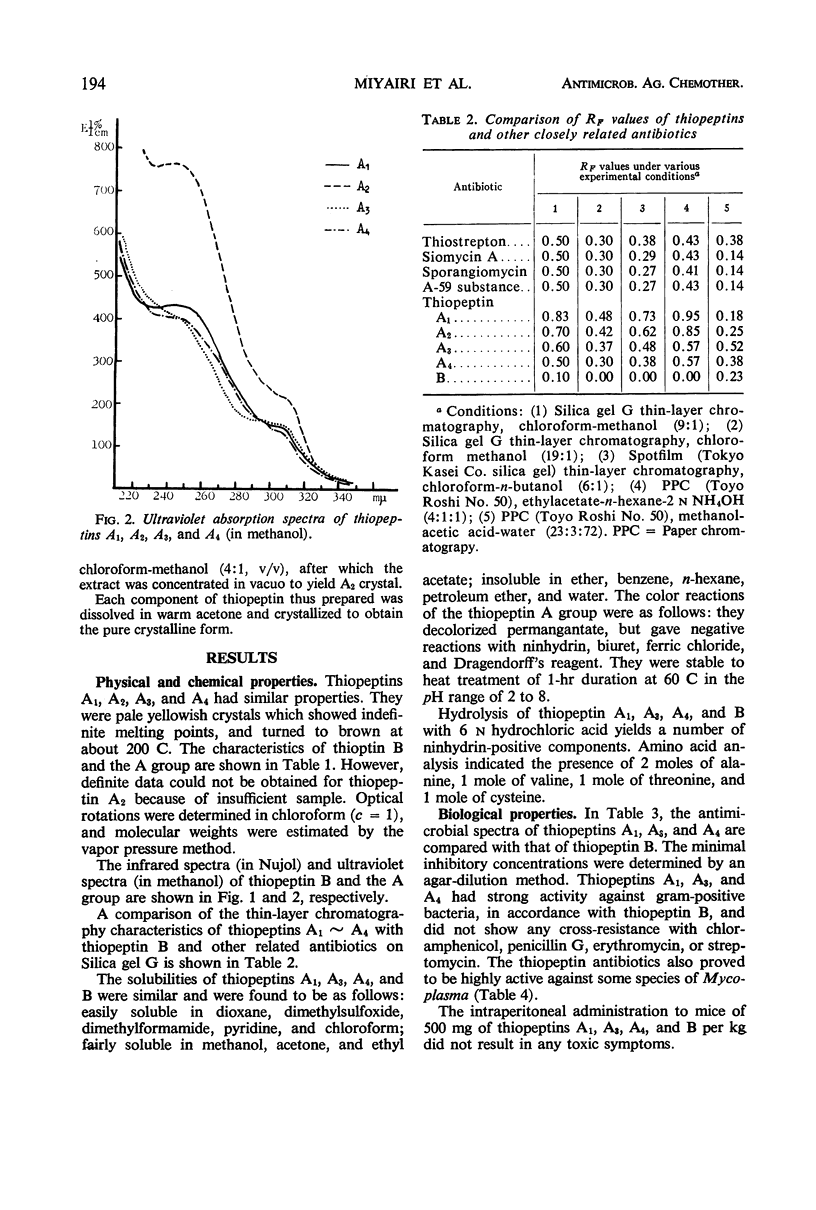
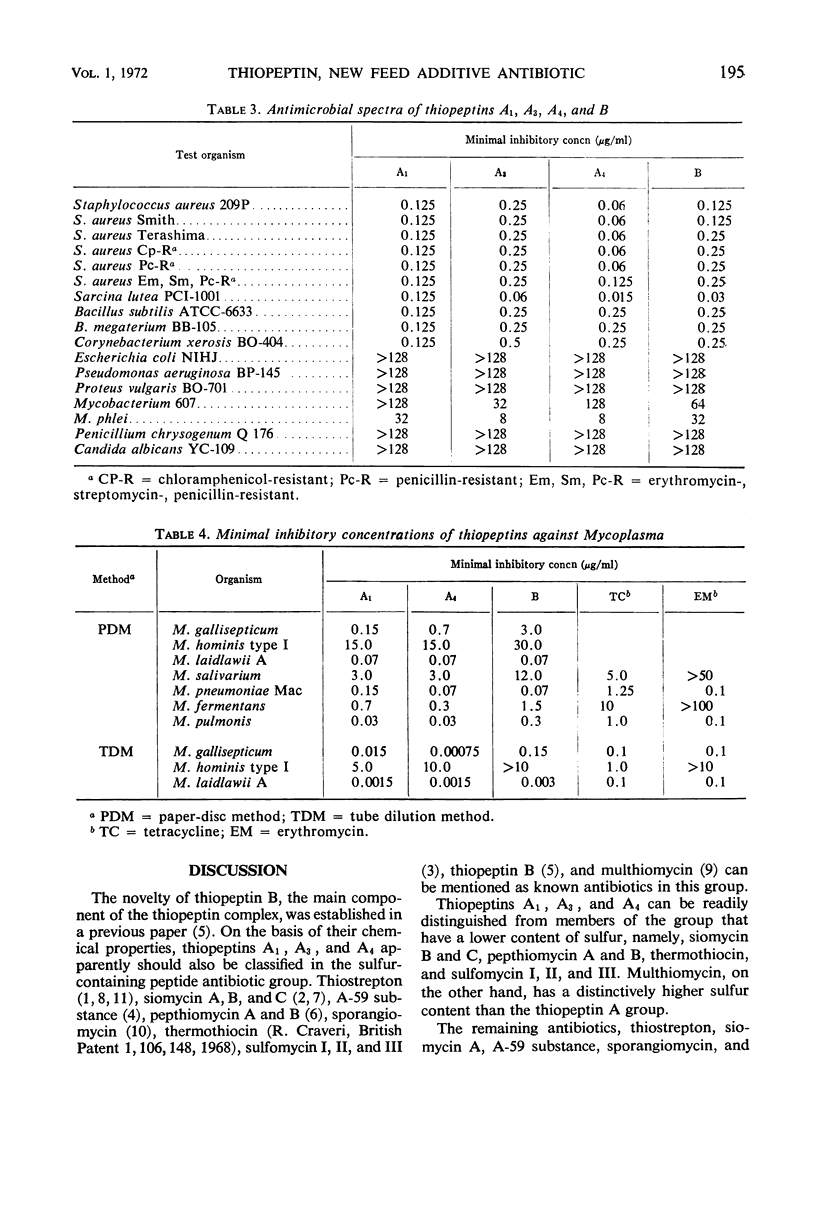
The thiopeptins are a new group of sulfur-containing peptide antibiotics produced by Streptomyces tateyamensis. The antibiotic consists of a major component (designated as thiopeptin B) and four minor ones (thiopeptins A1 to A4). These components were isolated by solvent extraction from mycelium followed by chromatography on silica gel with various ratios of chloroform and methanol as elution solvents. Acid hydrolysis of each of the thiopeptin components yielded 1 mole of valine, 1 of threonine, 1 of cysteine, and 2 of alanine as amino acids. Each component of the thiopeptin A group has chemical and biological properties closely similar to those of thiopeptin B, but detailed characterization has established that thiopeptins A1, A3, and A4 are new antibiotics. We could not obtain accurate data for determination of the uniqueness of A2 because of insufficient sample. Thiopeptin has strong antibacterial activity against gram-positive bacteria and Mycoplasma, and exhibits no cross-resistance to major human-use antibiotics.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DONOVICK R., PAGANO J. F., STOUT H. A., WEINSTEIN M. J. Thiostrepton, a new antibiotic. I. In vitro studies. Antibiot Annu. 1955;3:554–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTCHER J. D., VANDEPUTTE J. Thiostrepton, a new antibiotic. II. Isolation and chemical characterization. Antibiot Annu. 1955;3:560–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebata M., Miyazaki K., Otsuka H. Studies on siomycin. I. Physicochemical properties of siomycins A, B and C. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1969 Aug;22(8):364–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONDO S., AKITA E., SAKAMOTO J. M., OGASAWARA M., NIIDA T., HATAKEYAMA T. Studies on a new antibiotic produced by Streptomyces sp. A-59. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1961 Jul;14:194–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyairi N., Miyoshi T., Aoki H., Kosaka M., Ikushima H. Studies on thiopeptin antibiotics. I. Characteristics of thiopeptin B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Mar;23(3):113–119. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno K., Hamada M., Maeda K., Umezawa H. Pepthiomycin, a new peptide antibiotic mixture. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Jun;21(6):429–431. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Endo T., Shimazu A., Yoshida R., Suzuki Y. A new antibiotic, multhiomycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 May;23(5):231–237. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemann J. E., Coronelli C., Pagani H., Beretta G., Tamoni G. Antibiotic production by new form-genera of the Actinomycetales. I. Sporangiomycin, an antibacterial agent isolated from Planomonospora parontospora var. antibiotica var. nov. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Sep;21(9):525–531. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


