Abstract
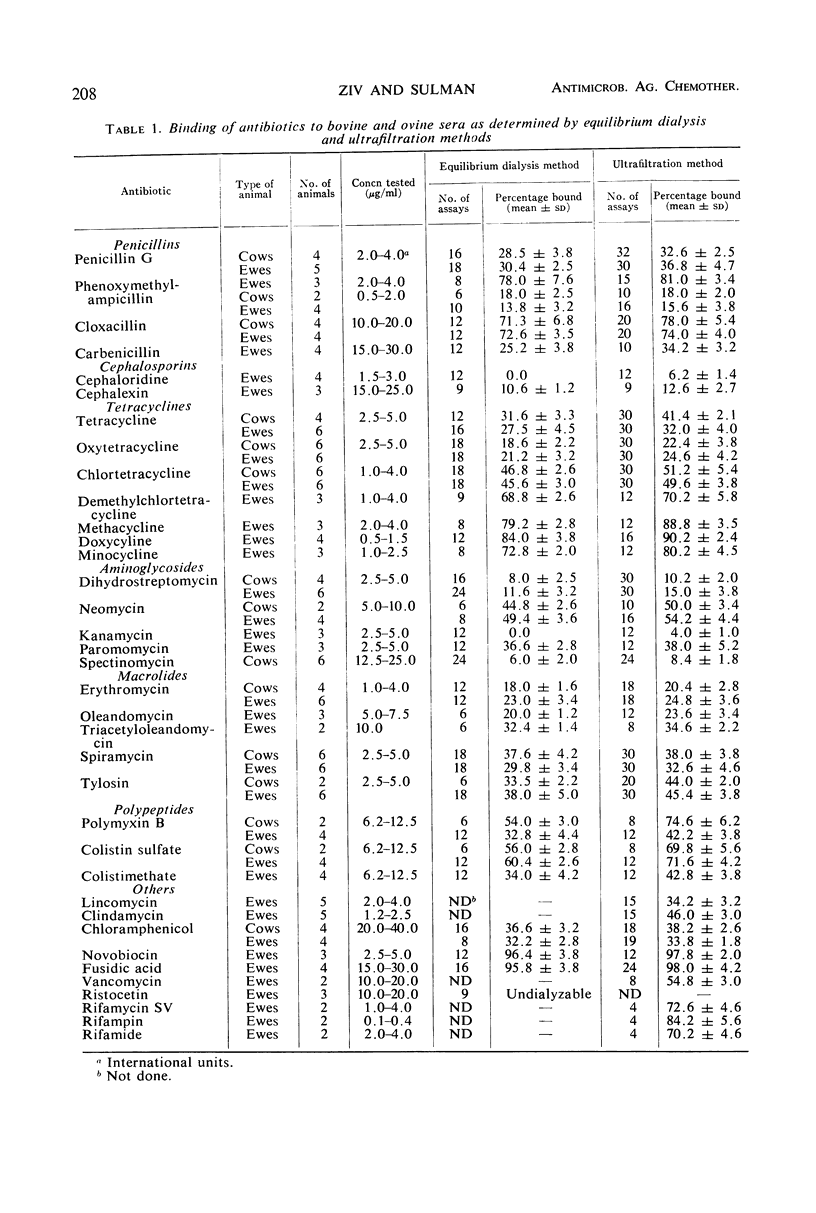
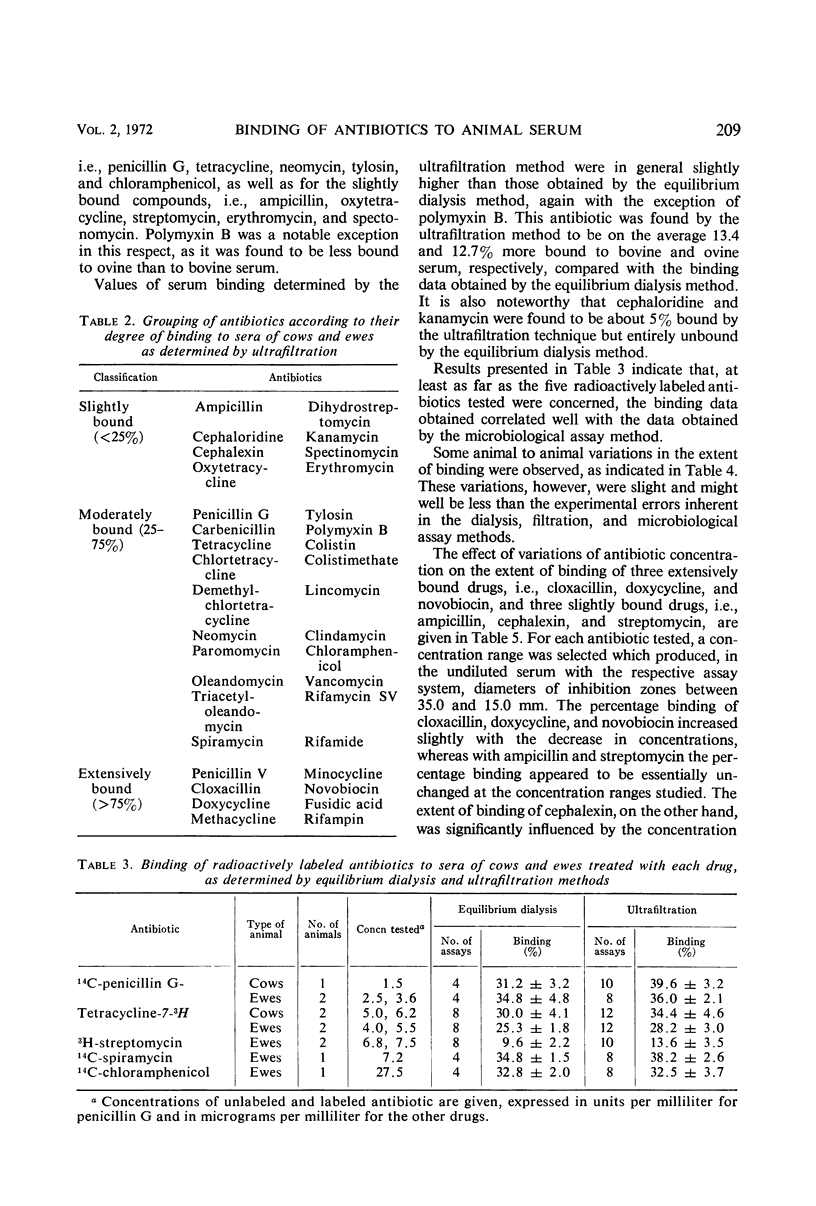
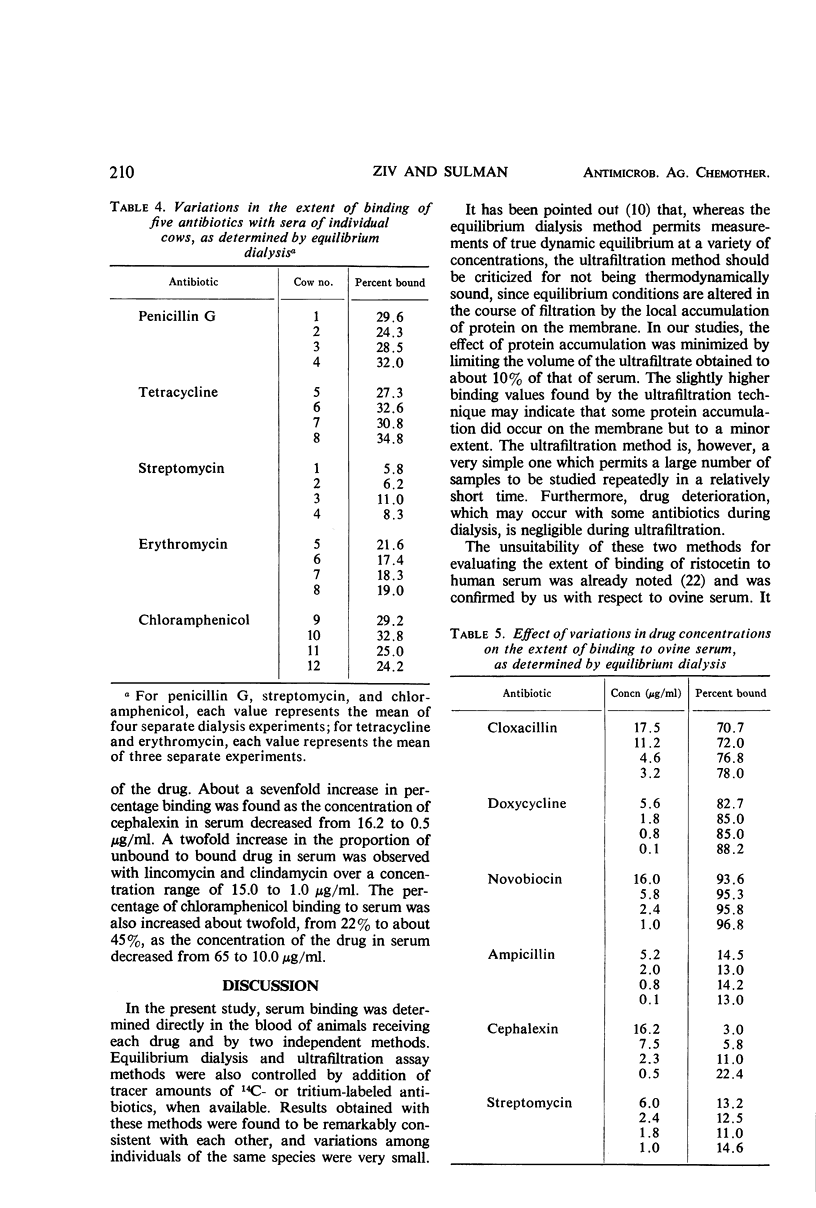
The degree of binding of 37 antibiotics to bovine and ovine serum, after treatment at therapeutic doses, was determined by equilibrium dialysis and ultrafiltration methods. In general, binding values obtained by the two methods were comparable. The extent of binding varied from 0% for cephaloridine and kanamycin to >95% for novobiocin and fusidic acid. Of the 37 drugs studied, one-fourth were less than 25% bound, one-fourth were more than 75% bound, and the percentage binding of about half of the antibiotics ranged from 25 to 75%. Animal to animal variations in the extent of binding of a particular antibiotic were very small. The capacity of bovine or ovine serum to bind antibiotics was, with a few exceptions, similar to the reported capacity of human serum. At drug concentration ranges usually achieved during therapy, variations in drug levels in serum did not influence the degree of binding except with cephalexin, lincomycin, clindamycin, and chloramphenicol. With these antibiotics, the extent of binding increased two- to sevenfold with the decrease in drug concentration in serum.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTON A. H. A drug-induced change in the distribution and renal excretion of sulfonamides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1961 Dec;134:291–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arret B., Johnson D. P., Kirshbaum A. Outline of details for microbiological assays of antibiotics: second revision. J Pharm Sci. 1971 Nov;60(11):1689–1694. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600601122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUER R. W., PESSOTTI R. L. The removal of bromsulphthalein from blood plasma by the liver of the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1949 Nov;97(3):358–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRODIE B. B., HOGBEN C. A. Some physico-chemical factors in drug action. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1957 Jun;9(6):345–380. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1957.tb12289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. V., Mickelwait J. S., Barrett J. E., Brodie J. L., Kirby W. M. Comparative serum binding of four tetracyclines under simulated in vivo conditions. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1965;5:180–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. E., Marshall A. C. Correlation of serum binding of penicillins with partition coefficients. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Dec;16(12):2275–2290. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90215-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie B. B. Displacement of one drug by another from carrier or receptor sites. Proc R Soc Med. 1965 Nov;58(11 Pt 2):946–955. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colaizzi J. L., Klink P. R. pH-Partition behavior of tetracyclines. J Pharm Sci. 1969 Oct;58(10):1184–1189. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600581003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS J. F., BRADSHAW W. H., LUDWIG B. J., POWERS D. INTERACTION OF PLASMA PROTEIN WITH RELATED 1,3-PROPANEDIOL DICARBAMATES. Biochem Pharmacol. 1964 Mar;13:537–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(64)90177-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. D. THE BINDING OF SULFONAMIDE DRUGS BY PLASMA PROTEINS. A FACTOR IN DETERMINING THE DISTRIBUTION OF DRUGS IN THE BODY. J Clin Invest. 1943 Sep;22(5):753–762. doi: 10.1172/JCI101448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDY W. E., SINCLAIR A. C., THERIAULT R. J., GOLDSTEIN A. W., RICKHER C. J., WARREN H. B., Jr, OLIVER T. J., SYLVESTER J. C. Ristocetin, microbiologic properties. Antibiot Annu. 1956:687–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith R. S., Black H. R. Cephalexin. Med Clin North Am. 1970 Sep;54(5):1229–1244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güttler F., Tybring L., Engberg-Pedersen H. Interaction of albumin and fusidic acid. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Sep;43(1):151–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSCH C., STEWARD A. R. THE USE OF SUBSTITUENT CONSTANTS IN THE ANALYSIS OF THE STRUCTURE--ACTIVITY RELATIONSHIP IN PENICILLIN DERIVATIVES. J Med Chem. 1964 Nov;7:691–694. doi: 10.1021/jm00336a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES T. R., KLOTZ I. M. Analysis of metal-protein complexes. Methods Biochem Anal. 1956;3:265–299. doi: 10.1002/9780470110195.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HWANG K., PRIMACK N., STEIN R. J., RICHARDS R. K. Pharmacological and toxicological properties of ristocetins A and B. Antibiot Annu. 1957;5:163–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M. Comparative serum binding, distribution and excretion of tetracycline and a new analogue, methacycline. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Jun;110:311–315. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M., DORNBUSH A. C., FINLAND M. Distribution and excretion of four tetracycline analogues in normal young men. J Clin Invest. 1959 Nov;38:1950–1963. doi: 10.1172/JCI103974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M. EFFECT OF SERUM BINDING ON THE DISTRIBUTION OF PENICILLINS IN THE RABBIT. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Mar;65:406–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M. INHIBITORS OF PENICILLIN BINDING TO SERUM PROTEINS. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Mar;65:416–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M. Serum binding, distribution and excretion of four penicillin analogues following intravenous injection in man. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Jun;107:337–341. doi: 10.3181/00379727-107-26618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J. L., Bullock F. J. The binding of salicylate to plasma protein from several animal species. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1969 May;21(5):293–296. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1969.tb08252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M. Clinical pharmacology of the new penicillins. 1. The importance of serum protein binding in determining antimicrobial activity and concentration in serum. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1966 Mar-Apr;7(2):166–179. doi: 10.1002/cpt196672166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M. Clinical significance of protein binding of the penicillins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Sep 27;145(2):282–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb50225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE C. C., ANDERSON R. C., CHEN K. K. Vancomycin, a new antibiotic. V. Distribution, excretion, and renal clearance. Antibiot Annu. 1956:82–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. K. Potential effect of the plasma on drug distribution. Nature. 1965 Jul 17;207(994):274–276. doi: 10.1038/207274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M. C., Guttman D. E. The binding of drugs by plasma proteins. J Pharm Sci. 1968 Jun;57(6):895–918. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600570601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON B. A. The properties and mode of action of the polymyxins. Bacteriol Rev. 1956 Mar;20(1):14–27. doi: 10.1128/br.20.1.14-27.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ODELL G. B. Studies in kernicterus. I. The protein binding of bilirubin. J Clin Invest. 1959 May;38(5):823–833. doi: 10.1172/JCI103864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen F. Mammary excretion of lincomycin in cows. Acta Vet Scand. 1966;7(1):97–98. doi: 10.1186/BF03547100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolinson G. N., Sutherland R. The binding of antibiotics to serum proteins. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1965 Dec;25(3):638–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1965.tb01788.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHANKER L. S. Passage of drugs across body membranes. Pharmacol Rev. 1962 Dec;14:501–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOLTAN W., SCHMID J. [The binding of penicillins on the proteins of the blood and tissues]. Arzneimittelforschung. 1962 Aug;12:741–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SENSI P., GRECO A. M., BALLOTTA R. Rifomycin. I. Isolation and properties of rifomycin B and rifomycin complex. Antibiot Annu. 1959;7:262–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERESI J. D., LUCK J. M. The combination of organic anions with serum albumin. VIII. Fatty acid salts. J Biol Chem. 1952 Feb;194(2):823–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UMEZAWA H. Kanamycin: its discovery. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Sep 30;76(2):20–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb54688.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von WITTENAU M., YEARY R. The excretion and distribution in body fluids of tetracyclines after intravenous administration to dogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 May;140:258–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


