Abstract
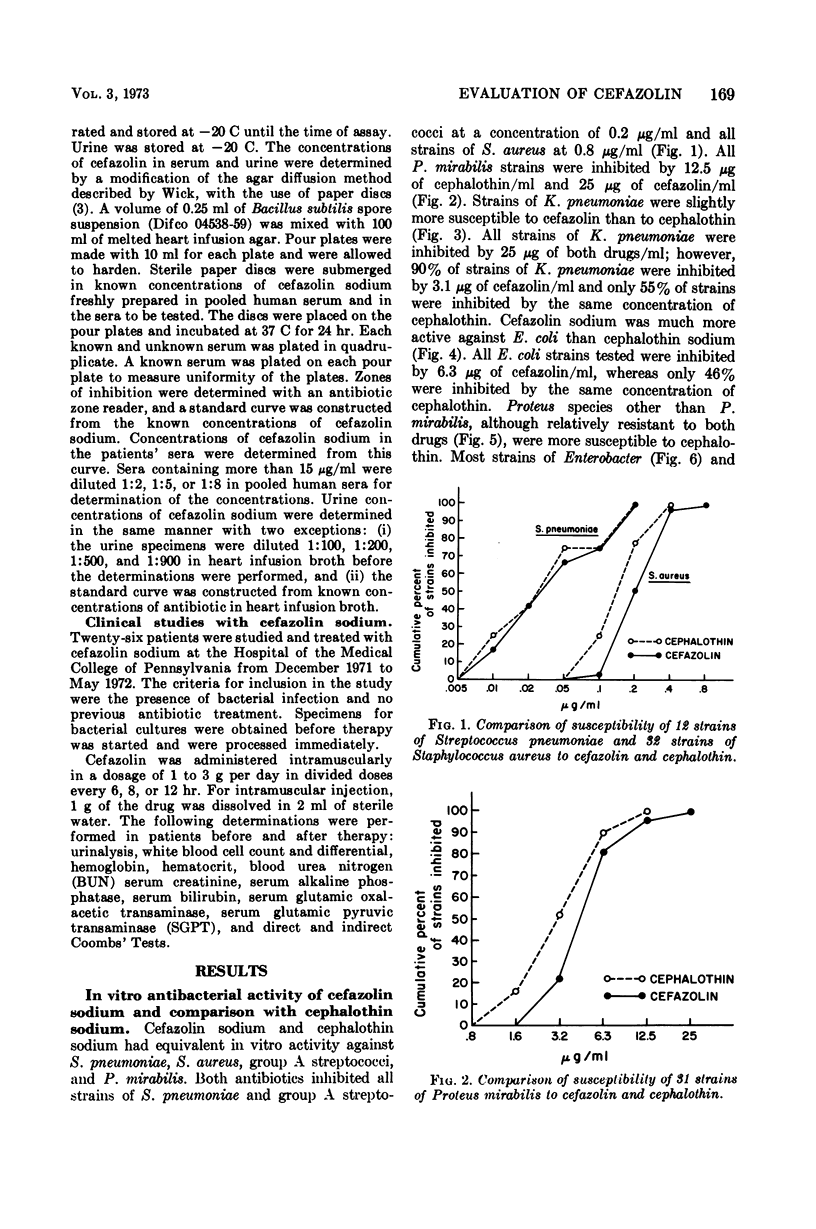
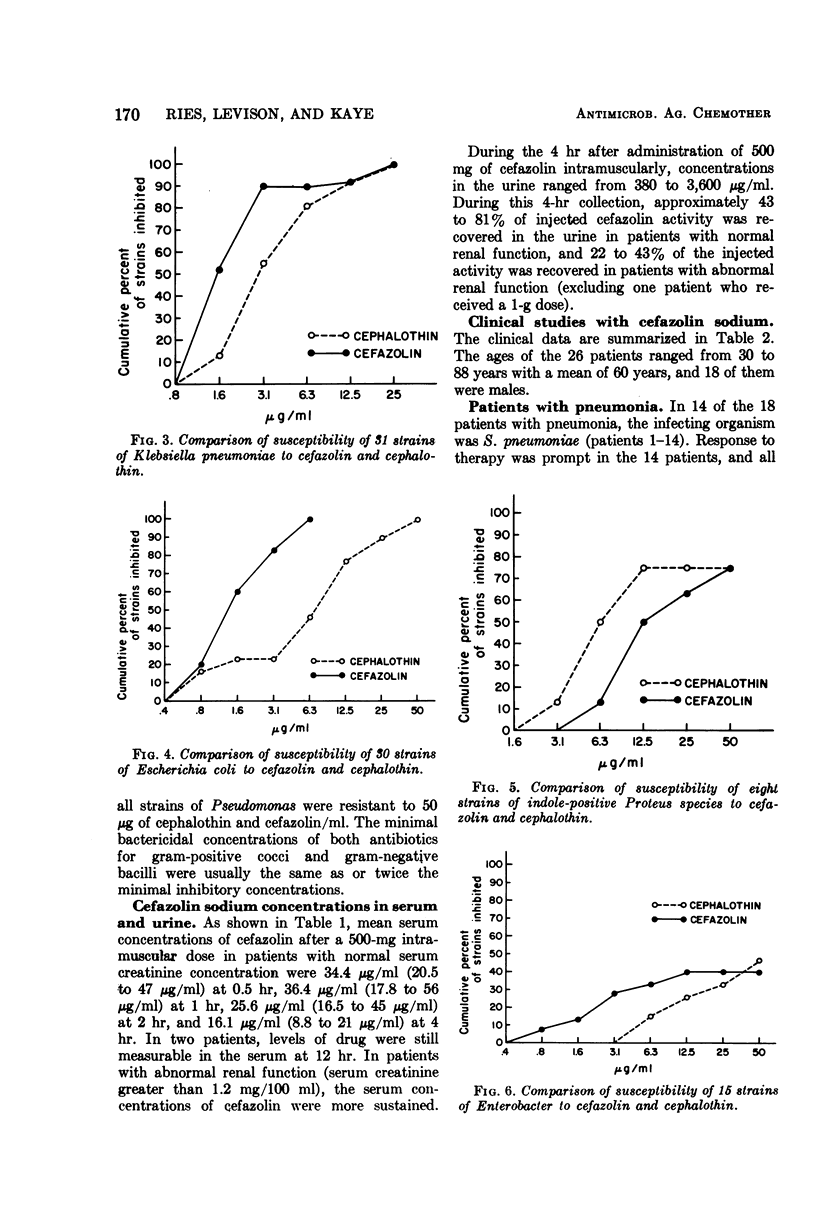
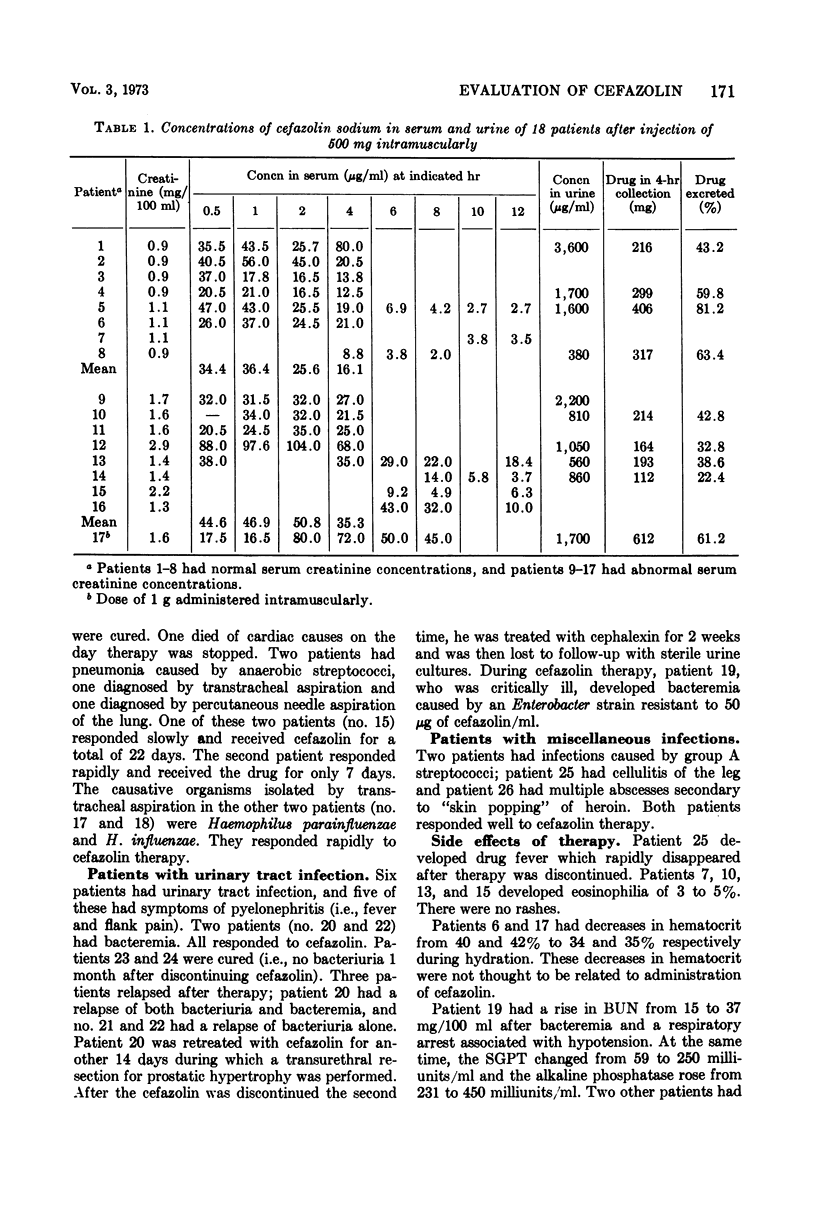
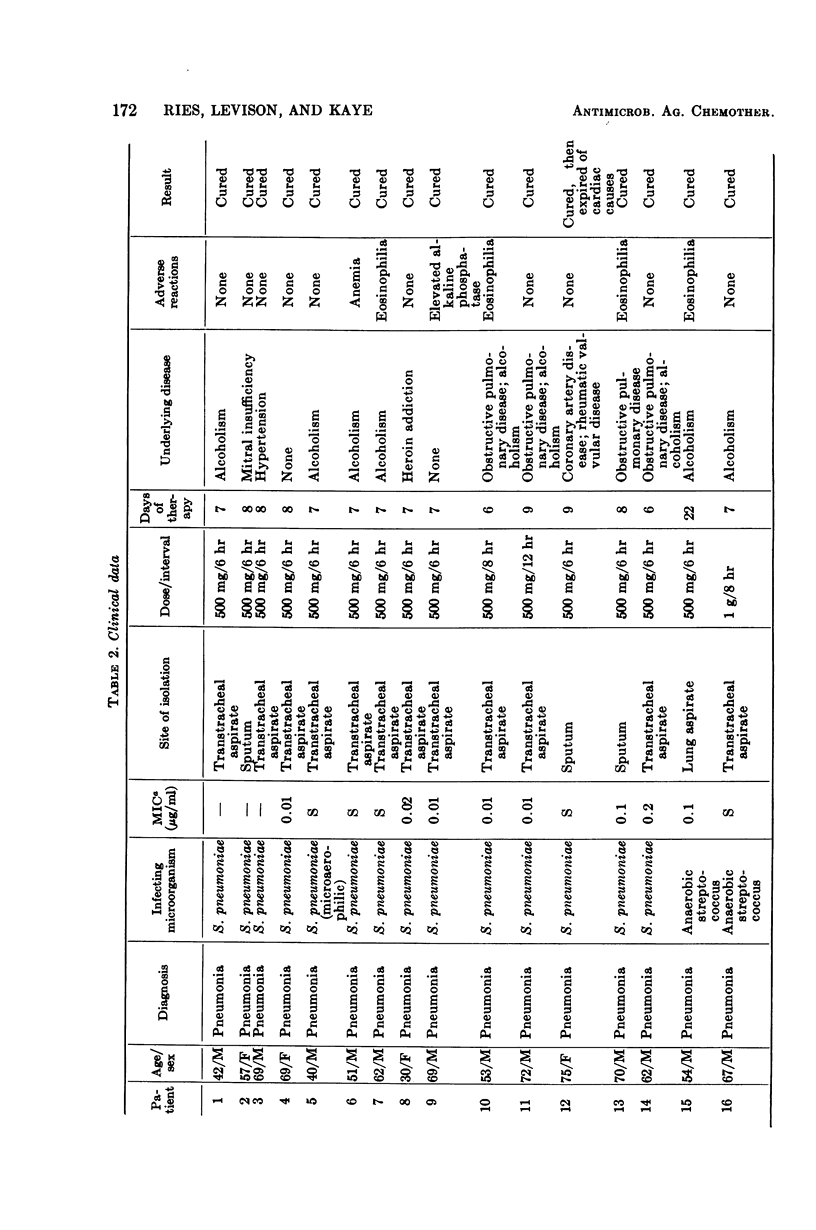
Cefazolin sodium, a cephalosporin for parenteral use, was evaluated in vitro and in 26 patients. Cefazolin had activity equivalent to cephalothin against Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, group A streptococci, and Proteus mirabilis. Cefazolin was four- to eightfold more active against Escherichia coli and slightly more active against Klebsiella pneumoniae, whereas cephalothin was slightly more active against indole-positive Proteus species. After a 500-mg dose of cefazolin intramuscularly, peak concentrations in the serum were high enough to inhibit all strains of S. pneumoniae, S. aureus, group A streptococci, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, and P. mirabilis, as well as 60% of strains of Proteus species other than P. mirabilis. All of 26 patients (18 with pneumonia, 6 with urinary tract infection, and 2 with skin infections) responded clinically and bacteriologically to cefazolin therapy. There were no major side effects of therapy, and no patient complained of pain at the site of intramuscular injection. Cefazolin is an effective cephalosporin which can be used intramuscularly for therapy of serious bacterial infections. Its major advantages over other cephalosporins are higher, more sustained concentrations in the blood and apparent lack of pain on intramuscular injection.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Griffith R. S., Black H. R. Blood, urine and tissue concentrations of the cephalosporin antibiotics in normal subjects. Postgrad Med J. 1971 Feb;47(Suppl):32–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiyama S., Nakayama I., Iwamoto H., Iwai S., Okui M. Absorption, tissue concentration, and organ distribution of cefazolin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1970;10:476–480. doi: 10.1128/AAC.10.3.476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WICK W. E., BONIECE W. S. IN VITRO AND IN VIVO LABORATORY EVALUATION OF CEPHALOGLYCIN AND CEPHALORIDINE. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:248–253. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.248-253.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


