Abstract
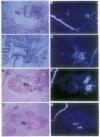
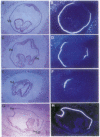
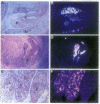
The expression of HNF-4 (hepatocyte nuclear factor 4) mRNA in postimplantation mouse embryos was analyzed by in situ hybridization. Expression was found in the primary endoderm at embryonic day 4.5 and was restricted to the columnar visceral endoderm cells of the yolk sac from day 5.5 to day 8.5. HNF-4 mRNA was first detected in embryonic tissues at day 8.5, in the liver diverticulum and the hindgut. At later times HNF-4 transcripts were observed in the mesonephric tubules, pancreas, stomach, and intestine and, still later, in the metanephric tubules of the developing kidney. This expression pattern suggests that HNF-4 has a role in the earliest stages of murine postimplantation development as well as in organogenesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ang S. L., Wierda A., Wong D., Stevens K. A., Cascio S., Rossant J., Zaret K. S. The formation and maintenance of the definitive endoderm lineage in the mouse: involvement of HNF3/forkhead proteins. Development. 1993 Dec;119(4):1301–1315. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.4.1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cascio S., Zaret K. S. Hepatocyte differentiation initiates during endodermal-mesenchymal interactions prior to liver formation. Development. 1991 Sep;113(1):217–225. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.1.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Ott M. O., Power S., Maury M. Expression patterns of vHNF1 and HNF1 homeoproteins in early postimplantation embryos suggest distinct and sequential developmental roles. Development. 1992 Nov;116(3):783–797. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.3.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGregori J., Russ A., von Melchner H., Rayburn H., Priyaranjan P., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Ruley H. E. A murine homolog of the yeast RNA1 gene is required for postimplantation development. Genes Dev. 1994 Feb 1;8(3):265–276. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.3.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douarin N. M. An experimental analysis of liver development. Med Biol. 1975 Dec;53(6):427–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziadek M., Adamson E. Localization and synthesis of alphafoetoprotein in post-implantation mouse embryos. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1978 Feb;43:289–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Episkopou V., Maeda S., Nishiguchi S., Shimada K., Gaitanaris G. A., Gottesman M. E., Robertson E. J. Disruption of the transthyretin gene results in mice with depressed levels of plasma retinol and thyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2375–2379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath J. K., Deller M. J. Serum-free culture of PC13 murine embryonal carcinoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Jun;115(3):225–230. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041150302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssaint E. Differentiation of the mouse hepatic primordium. I. An analysis of tissue interactions in hepatocyte differentiation. Cell Differ. 1980 Oct;9(5):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(80)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jollie W. P. Development, morphology, and function of the yolk-sac placenta of laboratory rodents. Teratology. 1990 Apr;41(4):361–381. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420410403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labosky P. A., Weir M. P., Grabel L. B. Homeobox-containing genes in teratocarcinoma embryoid bodies: a possible role for Hox-D12 (Hox-4.7) in establishing the extraembryonic endoderm lineage in the mouse. Dev Biol. 1993 Sep;159(1):232–244. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. J., Radice G., Perkins C. P., Costantini F. Identification and characterization of a novel, evolutionarily conserved gene disrupted by the murine H beta 58 embryonic lethal transgene insertion. Development. 1992 May;115(1):277–288. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.1.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. B. Cell physiology of the rat visceral yolk sac: a study of pinocytosis and lysosome function. Teratology. 1990 Apr;41(4):383–393. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420410404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makover A., Soprano D. R., Wyatt M. L., Goodman D. S. An in situ-hybridization study of the localization of retinol-binding protein and transthyretin messenger RNAs during fetal development in the rat. Differentiation. 1989 Mar;40(1):17–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1989.tb00809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Krumlauf R. Homeobox genes and axial patterning. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):283–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90471-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meehan R. R., Barlow D. P., Hill R. E., Hogan B. L., Hastie N. D. Pattern of serum protein gene expression in mouse visceral yolk sac and foetal liver. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1881–1885. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02062.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietus-Snyder M., Sladek F. M., Ginsburg G. S., Kuo C. F., Ladias J. A., Darnell J. E., Jr, Karathanasis S. K. Antagonism between apolipoprotein AI regulatory protein 1, Ear3/COUP-TF, and hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 modulates apolipoprotein CIII gene expression in liver and intestinal cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1708–1718. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan A. P., Kaestner K. H., Grau E., Schütz G. Postimplantation expression patterns indicate a role for the mouse forkhead/HNF-3 alpha, beta and gamma genes in determination of the definitive endoderm, chordamesoderm and neuroectoderm. Development. 1993 Nov;119(3):567–578. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.3.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Klein W. H. bHLH factors in muscle development: dead lines and commitments, what to leave in and what to leave out. Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(1):1–8. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padykula H. A., Deren J. J., Wilson T. H. Development of structure and function in the mammalian yolk sac. I. Developmental morphology and vitamin B12 uptake of the rat yolk sac. Dev Biol. 1966 Jun;13(3):311–348. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(66)90053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel N. H., Martin-Blanco E., Coleman K. G., Poole S. J., Ellis M. C., Kornberg T. B., Goodman C. S. Expression of engrailed proteins in arthropods, annelids, and chordates. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):955–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90947-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz i Altaba A., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jessell T. M. Sequential expression of HNF-3 beta and HNF-3 alpha by embryonic organizing centers: the dorsal lip/node, notochord and floor plate. Mech Dev. 1993 Dec;44(2-3):91–108. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90060-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Hogan B. L. Differential expression of multiple fork head related genes during gastrulation and axial pattern formation in the mouse embryo. Development. 1993 May;118(1):47–59. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Hogan B. L. HNF-3 beta as a regulator of floor plate development. Cell. 1994 Jan 14;76(1):103–115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi W. K., Heath J. K. Apolipoprotein expression by murine visceral yolk sac endoderm. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1984 Jun;81:143–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladek F. M., Darnell J. E. Mechanisms of liver-specific gene expression. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Apr;2(2):256–259. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80282-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladek F. M., Zhong W. M., Lai E., Darnell J. E., Jr Liver-enriched transcription factor HNF-4 is a novel member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2353–2365. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vranckx R., Savu L., Maya M., Nunez E. A. Characterization of a major development-regulated serum thyroxine-binding globulin in the euthyroid mouse. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 15;271(2):373–379. doi: 10.1042/bj2710373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bailes J. A., McMahon A. P. Expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 is restricted to specific neural cells in the developing mouse embryo. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90664-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong W., Sladek F. M., Darnell J. E., Jr The expression pattern of a Drosophila homolog to the mouse transcription factor HNF-4 suggests a determinative role in gut formation. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):537–544. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05685.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]