Abstract
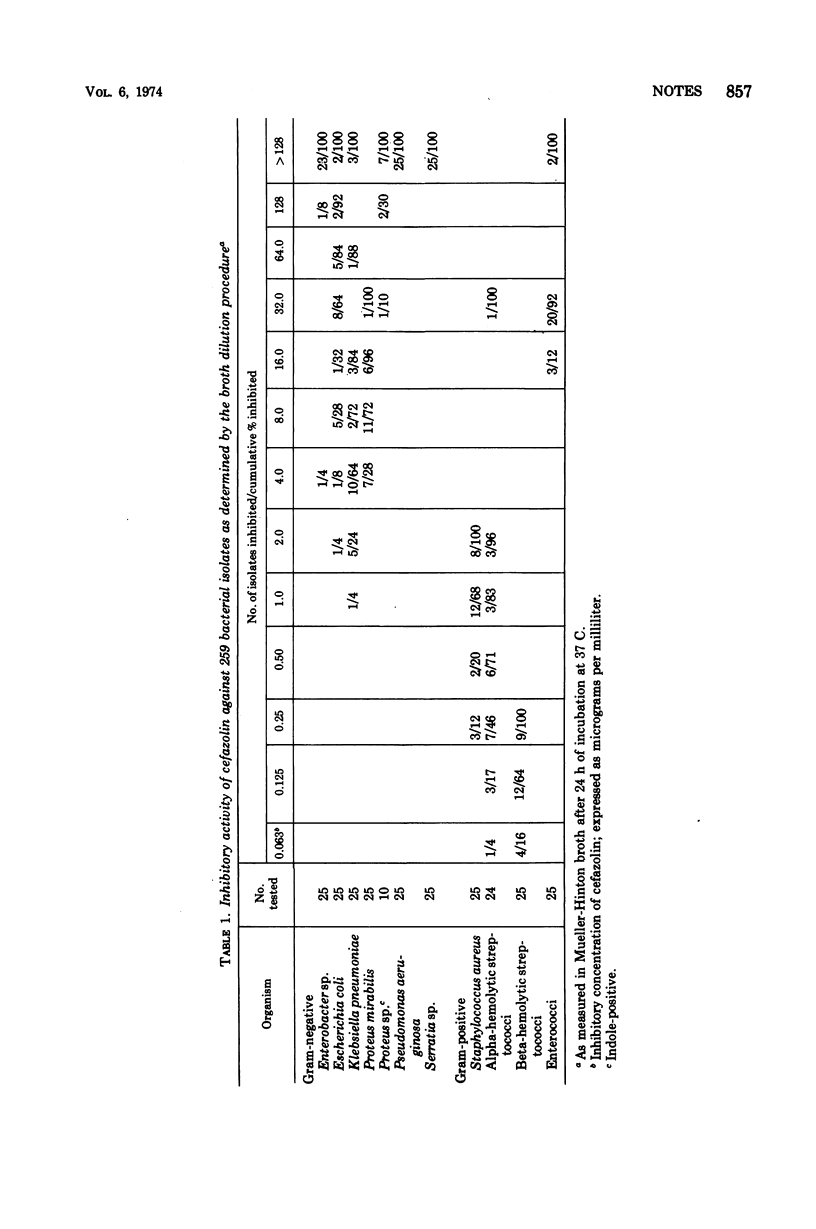
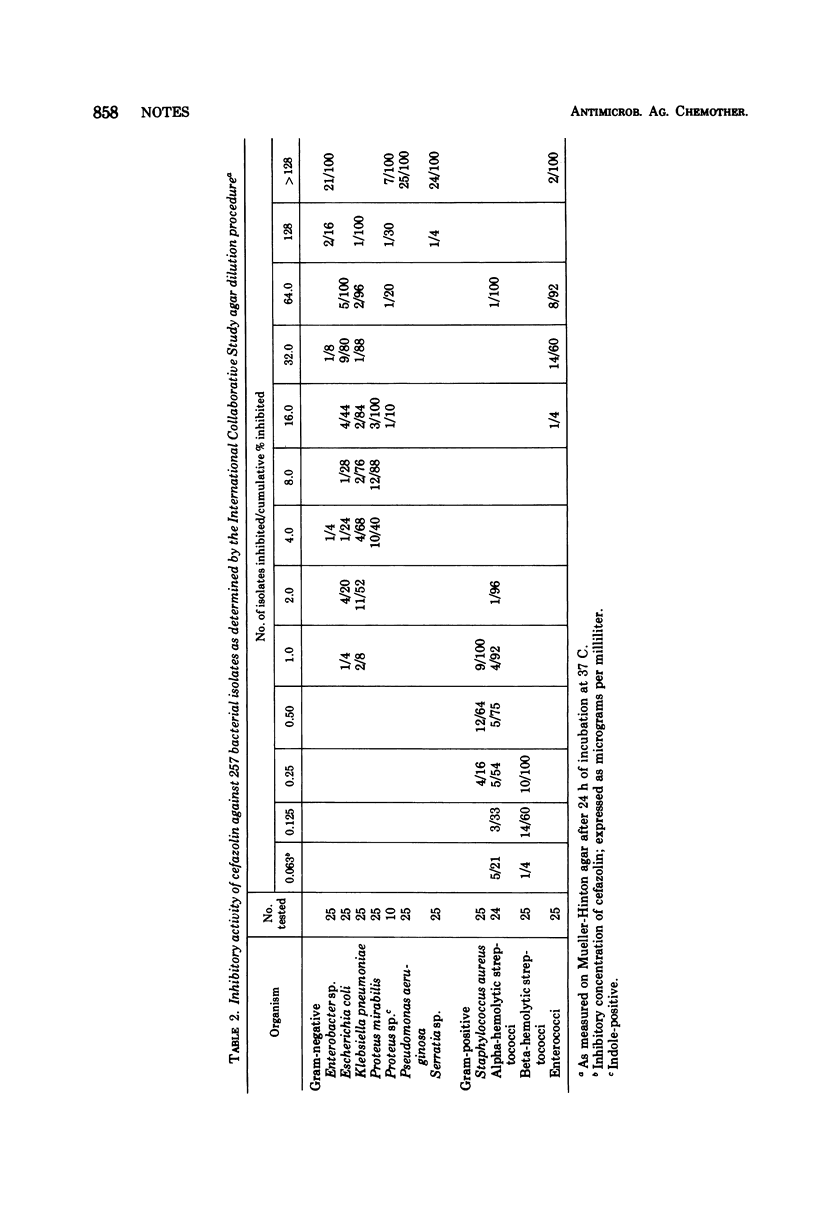
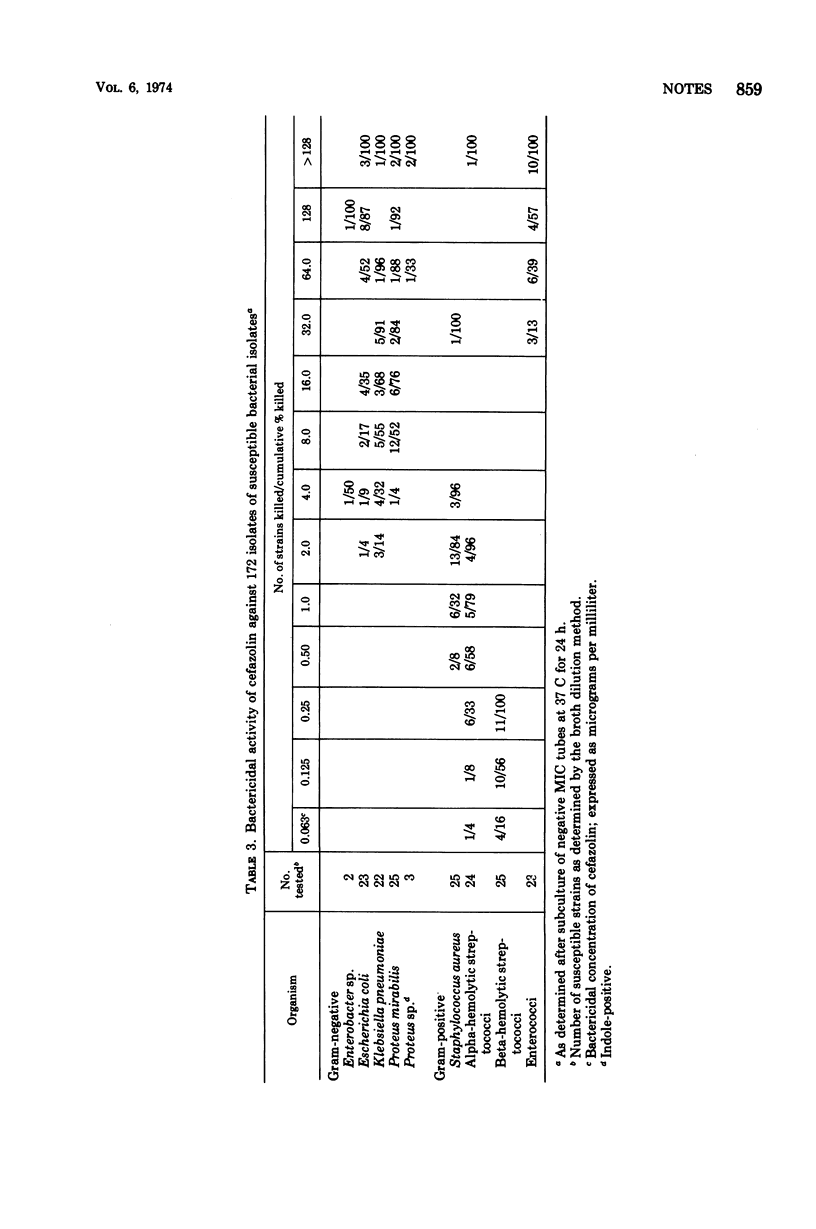
Susceptibilities of 259 isolates of pathogenic bacteria to cefazolin were measured by broth and agar dilution procedures. Beta-hemolytic streptococci were inhibited by 0.25 μg/ml, whereas Staphylococcus aureus and alphahemolytic streptococci were inhibited by 2.0 μg/ml. Enterococci were resistant to less than 32 μg/ml. Wide variation was seen with gram-negative species. Most isolates of Klebsiella species and Proteus mirabilis were inhibited by 4.0 or 8.0 μg/ml. Escherichia coli were less susceptible, and most isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Serratia species, and Enterobacter species were resistant to 128 μg/ml.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergeron M. G., Brusch J. L., Barza M., Weinstein L. Bactericidal activity and pharmacology of cefazolin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Oct;4(4):396–401. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.4.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller L. B., Karney W. W., Beaty H. N., Holmes K. K., Turck M. Evaluation of cefazolin, a new cephalosporin antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Apr;3(4):488–497. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.4.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ries K., Levison M. E., Kaye D. Clinical and in vitro evaluation of cefazolin, a new cephalosporin antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):168–174. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


