Abstract
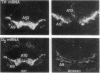
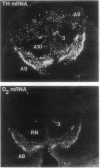
The tone and regulation of the brain dopaminergic projections are, in part, determined by the presence or absence of dopamine (DA) autoreceptors: rate of DA synthesis and turnover, as well as both pattern and rate of neuronal firing, are modulated by the expression and activity of these autoreceptors. The expression of dopaminergic receptors in the midbrain DA cell groups, presumably reflecting DA autoreceptors, was determined in the brains of the rat, Old World monkey, and human. In the rat, both the substantia nigra (A9) and the ventral tegmental area (A10) appear to express DA autoreceptors. In the monkey and human, however, only the projections arising from the substantia nigra express these receptors; the limbic projections originating in the ventral tegmental area lack this substrate for DA autoregulation. These results indicate that in the human, the nigrostriatal and mesocorticolimbic dopamine systems may be differentially autoregulated.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altar C. A., Boyar W. C., Oei E., Wood P. L. Dopamine autoreceptors modulate the in vivo release of dopamine in the frontal, cingulate and entorhinal cortices. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Jul;242(1):115–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannon M. J., Bunney E. B., Roth R. H. Mesocortical dopamine neurons: rapid transmitter turnover compared to other brain catecholamine systems. Brain Res. 1981 Aug 10;218(1-2):376–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannon M. J., Roth R. H. Pharmacology of mesocortical dopamine neurons. Pharmacol Rev. 1983 Mar;35(1):53–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckstead R. M., Domesick V. B., Nauta W. J. Efferent connections of the substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area in the rat. Brain Res. 1979 Oct 19;175(2):191–217. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)91001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouthenet M. L., Martres M. P., Sales N., Schwartz J. C. A detailed mapping of dopamine D-2 receptors in rat central nervous system by autoradiography with [125I]iodosulpride. Neuroscience. 1987 Jan;20(1):117–155. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouthenet M. L., Souil E., Martres M. P., Sokoloff P., Giros B., Schwartz J. C. Localization of dopamine D3 receptor mRNA in the rat brain using in situ hybridization histochemistry: comparison with dopamine D2 receptor mRNA. Brain Res. 1991 Nov 15;564(2):203–219. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91456-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunzow J. R., Van Tol H. H., Grandy D. K., Albert P., Salon J., Christie M., Machida C. A., Neve K. A., Civelli O. Cloning and expression of a rat D2 dopamine receptor cDNA. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):783–787. doi: 10.1038/336783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesselet M. F. Presynaptic regulation of neurotransmitter release in the brain: facts and hypothesis. Neuroscience. 1984 Jun;12(2):347–375. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodo L. A., Bannon M. J., Grace A. A., Roth R. H., Bunney B. S. Evidence for the absence of impulse-regulating somatodendritic and synthesis-modulating nerve terminal autoreceptors on subpopulations of mesocortical dopamine neurons. Neuroscience. 1984 May;12(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodo L. A., Bunney B. S. Typical and atypical neuroleptics: differential effects of chronic administration on the activity of A9 and A10 midbrain dopaminergic neurons. J Neurosci. 1983 Aug;3(8):1607–1619. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-08-01607.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese I., Burt D. R., Snyder S. H. Dopamine receptor binding predicts clinical and pharmacological potencies of antischizophrenic drugs. Science. 1976 Apr 30;192(4238):481–483. doi: 10.1126/science.3854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dearry A., Gingrich J. A., Falardeau P., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Bates M. D., Caron M. G. Molecular cloning and expression of the gene for a human D1 dopamine receptor. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):72–76. doi: 10.1038/347072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fadda F., Gessa G. L., Marcou M., Mosca E., Rossetti Z. Evidence for dopamine autoreceptors in mesocortical dopamine neurons. Brain Res. 1984 Feb 13;293(1):67–72. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91453-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon J. H., Moore R. Y. Catecholamine innervation of the basal forebrain. IV. Topography of the dopamine projection to the basal forebrain and neostriatum. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Aug 1;180(3):545–580. doi: 10.1002/cne.901800310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnebo L. O., Hamberger B. Drug-induced changes in the release of ( 3 H)-noradrenaline from field stimulated rat iris. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Sep;43(1):97–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07160.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedele E., Andrioli G. C., Ruelle A., Raiteri M. Release-regulating dopamine autoreceptors in human cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;110(1):20–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13765.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway M. P., Wolf M. E., Roth R. H. Regulation of dopamine synthesis in the medial prefrontal cortex is mediated by release modulating autoreceptors: studies in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Mar;236(3):689–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariano R. F., Tepper J. M., Sawyer S. F., Young S. J., Groves P. M. Mesocortical dopaminergic neurons. 1. Electrophysiological properties and evidence for soma-dendritic autoreceptors. Brain Res Bull. 1989 Mar;22(3):511–516. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(89)90103-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giros B., Martres M. P., Sokoloff P., Schwartz J. C. Clonage du gène du récepteur dopaminergique D3 humain et identification de son chromosome. C R Acad Sci III. 1990;311(13):501–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandy D. K., Marchionni M. A., Makam H., Stofko R. E., Alfano M., Frothingham L., Fischer J. B., Burke-Howie K. J., Bunzow J. R., Server A. C. Cloning of the cDNA and gene for a human D2 dopamine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9762–9766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetey L., Schwitzkowsky R., Ott T., Barz H. Diminished synaptosomal dopamine (DA) release and DA autoreceptor supersensitivity in schizophrenia. J Neural Transm Gen Sect. 1991;83(1-2):25–35. doi: 10.1007/BF01244449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann I. S., Talmaciu R. K., Ferro C. P., Cubeddu L. X. Sustained high release at rapid stimulation rates and reduced functional autoreceptors characterize prefrontal cortex dopamine terminals. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Jun;245(3):761–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehr W., Carlsson A., Lindqvist M., Magnusson T., Atack C. Evidence for a receptor-mediated feedback control of striatal tyrosine hydroxylase activity. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1972 Sep;24(9):744–747. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1972.tb09104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Puig M. Effect of flow-stop on noradrenaline release from normal spleens and spleens treated with cocaine, phentolamine or phenoxybenzamine. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Oct;43(2):359–369. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida C. A., Searles R. P., Nipper V., Brown J. A., Kozell L. B., Neve K. A. Molecular cloning and expression of the rhesus macaque D1 dopamine receptor gene. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;41(4):652–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meador-Woodruff J. H., Little K. Y., Damask S. P., Mansour A., Watson S. J. Effects of cocaine on dopamine receptor gene expression: a study in the postmortem human brain. Biol Psychiatry. 1993 Sep 15;34(6):348–355. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(93)90178-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meador-Woodruff J. H., Mansour A. A. E. Bennett Award paper. Expression of the dopamine D2 receptor gene in brain. Biol Psychiatry. 1991 Nov 15;30(10):985–1007. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(91)90120-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meador-Woodruff J. H., Mansour A., Bunzow J. R., Van Tol H. H., Watson S. J., Jr, Civelli O. Distribution of D2 dopamine receptor mRNA in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7625–7628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meador-Woodruff J. H., Mansour A., Civelli O., Watson S. J. Distribution of D2 dopamine receptor mRNA in the primate brain. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1991;15(6):885–893. doi: 10.1016/0278-5846(91)90016-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer H. Y. Relevance of dopamine autoreceptors for psychiatry: preclinical and clinical studies. Schizophr Bull. 1980;6(3):456–475. doi: 10.1093/schbul/6.3.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengod G., Martinez-Mir M. I., Vilaró M. T., Palacios J. M. Localization of the mRNA for the dopamine D2 receptor in the rat brain by in situ hybridization histochemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8560–8564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsma F. J., Jr, Mahan L. C., McVittie L. D., Gerfen C. R., Sibley D. R. Molecular cloning and expression of a D1 dopamine receptor linked to adenylyl cyclase activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6723–6727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. Y., Bloom F. E. Central catecholamine neuron systems: anatomy and physiology of the dopamine systems. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1978;1:129–169. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.01.030178.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Najlerahim A., Barton A. J., Harrison P. J., Heffernan J., Pearson R. C. Messenger RNA encoding the D2 dopaminergic receptor detected by in situ hybridization histochemistry in rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1989 Sep 25;255(2):335–339. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81116-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauta W. J., Smith G. P., Faull R. L., Domesick V. B. Efferent connections and nigral afferents of the nucleus accumbens septi in the rat. Neuroscience. 1978;3(4-5):385–401. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley K. L., Harmon S., Tang L., Todd R. D. The rat dopamine D4 receptor: sequence, gene structure, and demonstration of expression in the cardiovascular system. New Biol. 1992 Feb;4(2):137–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plantjé J. F., Schipper J., Verheijden P. F., Stoof J. C. D2-dopamine receptors regulate the release of [3H]dopamine in rat basal hypothalamus and neurointermediate lobe of the pituitary gland. Brain Res. 1987 Jun 16;413(2):205–212. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plantjé J. F., Steinbusch H. W., Schipper J., Dijcks F. A., Verheijden P. F., Stoof J. C. D-2 dopamine-receptors regulate the release of [3H]dopamine in rat cortical regions showing dopamine immunoreactive fibers. Neuroscience. 1987 Jan;20(1):157–168. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak R. L. Stimulating action of atropine on the release of acetylcholine by rat cerebral cortex in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Apr;41(4):600–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07068.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scatton B. Differential regional development of tolerance to increase in dopamine turnover upon repeated neuroleptic administration. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Dec 15;46(4):363–369. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90230-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P., Lee T., Chau-Wong M., Wong K. Antipsychotic drug doses and neuroleptic/dopamine receptors. Nature. 1976 Jun 24;261(5562):717–719. doi: 10.1038/261717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H. The dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia: focus on the dopamine receptor. Am J Psychiatry. 1976 Feb;133(2):197–202. doi: 10.1176/ajp.133.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff P., Giros B., Martres M. P., Bouthenet M. L., Schwartz J. C. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):146–151. doi: 10.1038/347146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Influence of -receptor stimulants on noradrenaline release. Naturwissenschaften. 1971 Aug;58(8):420–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00591535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Presynaptic alpha-autoreceptors. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;107:73–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;77:1–124. doi: 10.1007/BFb0050157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoof J. C., Verheijden P. F., Leysen J. E. Stimulation of D2-receptors in rat nucleus accumbens slices inhibits dopamine and acetylcholine release but not cyclic AMP formation. Brain Res. 1987 Oct 13;423(1-2):364–368. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90864-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunahara R. K., Guan H. C., O'Dowd B. F., Seeman P., Laurier L. G., Ng G., George S. R., Torchia J., Van Tol H. H., Niznik H. B. Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D5 receptor with higher affinity for dopamine than D1. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):614–619. doi: 10.1038/350614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunahara R. K., Niznik H. B., Weiner D. M., Stormann T. M., Brann M. R., Kennedy J. L., Gelernter J. E., Rozmahel R., Yang Y. L., Israel Y. Human dopamine D1 receptor encoded by an intronless gene on chromosome 5. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):80–83. doi: 10.1038/347080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo J. Organization of the ascending striatal afferents in monkeys. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Jan 15;189(2):307–321. doi: 10.1002/cne.901890207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmaciu R. K., Hoffmann I. S., Cubeddu L. X. Dopamine autoreceptors modulate dopamine release from the prefrontal cortex. J Neurochem. 1986 Sep;47(3):865–870. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb00691.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiberi M., Jarvie K. R., Silvia C., Falardeau P., Gingrich J. A., Godinot N., Bertrand L., Yang-Feng T. L., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Caron M. G. Cloning, molecular characterization, and chromosomal assignment of a gene encoding a second D1 dopamine receptor subtype: differential expression pattern in rat brain compared with the D1A receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7491–7495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tol H. H., Bunzow J. R., Guan H. C., Sunahara R. K., Seeman P., Niznik H. B., Civelli O. Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D4 receptor with high affinity for the antipsychotic clozapine. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):610–614. doi: 10.1038/350610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner D. M., Brann M. R. The distribution of a dopamine D2 receptor mRNA in rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1989 Aug 14;253(1-2):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80960-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M. E., Roth R. H. Dopamine neurons projecting to the medial prefrontal cortex possess release-modulating autoreceptors. Neuropharmacology. 1987 Aug;26(8):1053–1059. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(87)90248-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q. Y., Grandy D. K., Thambi L., Kushner J. A., Van Tol H. H., Cone R., Pribnow D., Salon J., Bunzow J. R., Civelli O. Cloning and expression of human and rat D1 dopamine receptors. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):76–80. doi: 10.1038/347076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]