Abstract
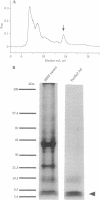
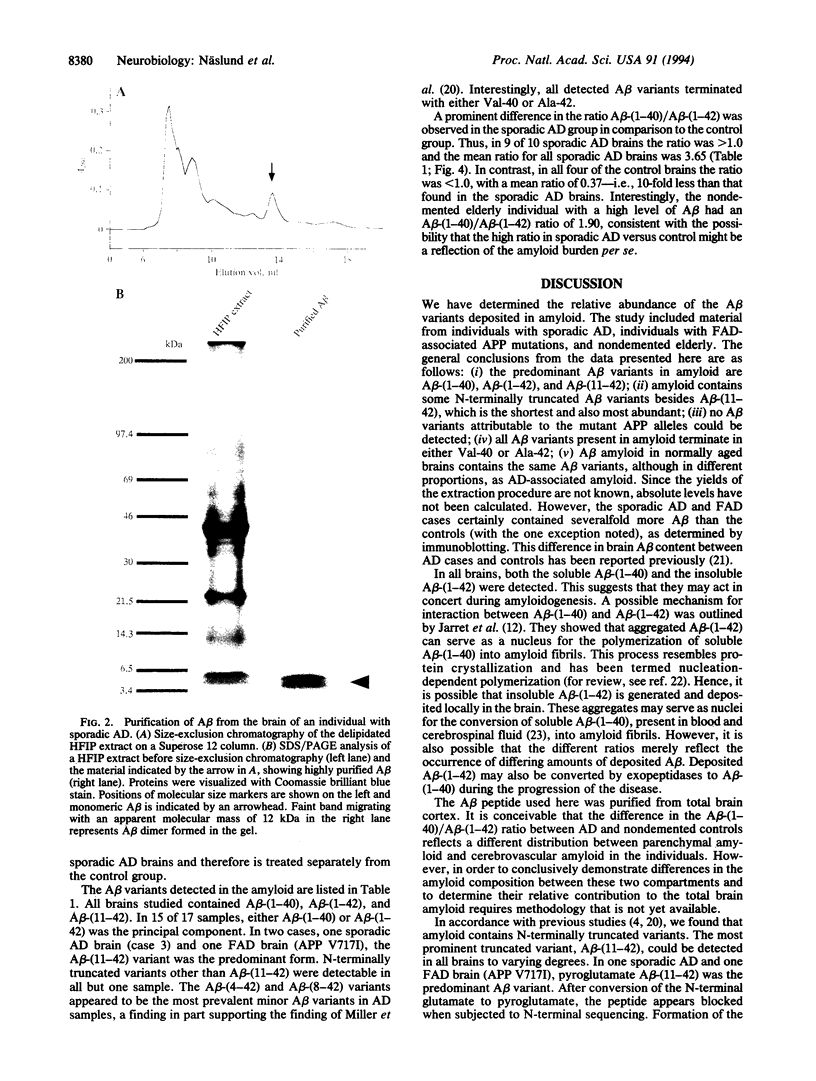
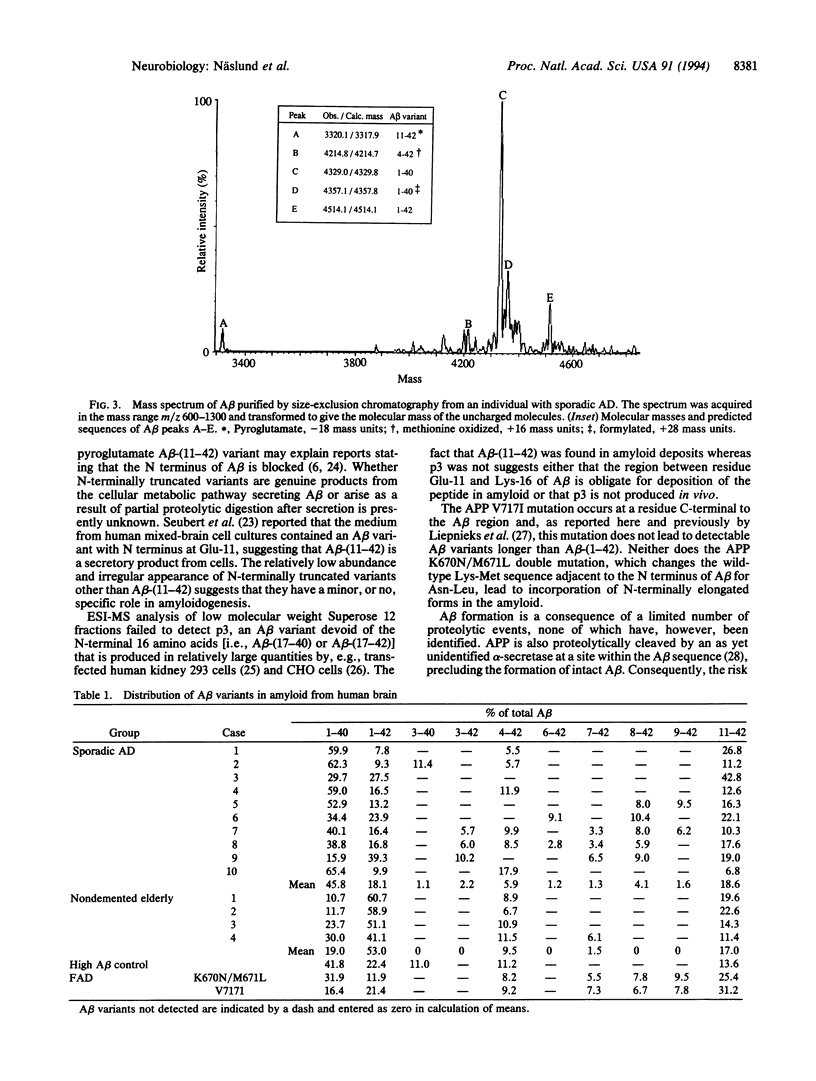
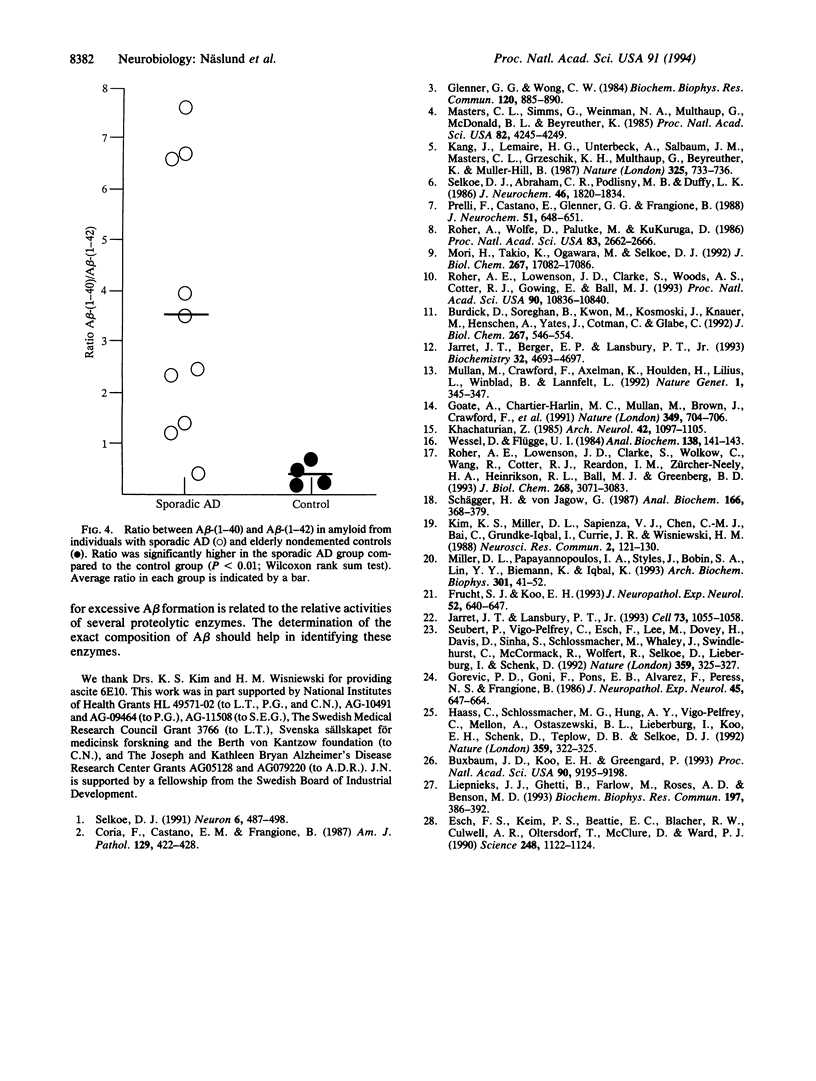
The Alzheimer A beta amyloid peptide (A beta) is the principal proteinaceous component of amyloid associated with Alzheimer disease (AD). We have determined the relative abundance of A beta structural variants present in amyloid from brains of 10 individuals with sporadic AD, 2 individuals with familial AD carrying specific mutations in the Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein gene, and 5 nondemented elderly controls. A procedure of isolation based on the extreme insolubility of A beta amyloid was used. The purified, nondigested A beta was analyzed by N-terminal sequencing and electrospray-ionization mass spectrometry. Three principal A beta variants were detected--A beta-(1-40), A beta-(1-42), and A beta-(11-42)--in all brains analyzed. The predominant variant in sporadic AD was A beta-(1-40), whereas the principal A beta variant in nondemented elderly controls was A beta-(1-42). The ratio A beta-(1-40)/A beta-(1-42) differed by 10-fold between brains from nondemented controls and those with sporadic AD.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burdick D., Soreghan B., Kwon M., Kosmoski J., Knauer M., Henschen A., Yates J., Cotman C., Glabe C. Assembly and aggregation properties of synthetic Alzheimer's A4/beta amyloid peptide analogs. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):546–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxbaum J. D., Koo E. H., Greengard P. Protein phosphorylation inhibits production of Alzheimer amyloid beta/A4 peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):9195–9198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coria F., Castaño E. M., Frangione B. Brain amyloid in normal aging and cerebral amyloid angiopathy is antigenically related to Alzheimer's disease beta-protein. Am J Pathol. 1987 Dec;129(3):422–428. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F. S., Keim P. S., Beattie E. C., Blacher R. W., Culwell A. R., Oltersdorf T., McClure D., Ward P. J. Cleavage of amyloid beta peptide during constitutive processing of its precursor. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1122–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.2111583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frucht S. J., Koo E. H. beta-Amyloid protein is higher in Alzheimer's disease brains: description of a quantitative biochemical assay. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1993 Nov;52(6):640–647. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199311000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goate A., Chartier-Harlin M. C., Mullan M., Brown J., Crawford F., Fidani L., Giuffra L., Haynes A., Irving N., James L. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):704–706. doi: 10.1038/349704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorevic P. D., Goñi F., Pons-Estel B., Alvarez F., Peress N. S., Frangione B. Isolation and partial characterization of neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid plaque core in Alzheimer's disease: immunohistological studies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1986 Nov;45(6):647–664. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198611000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haass C., Schlossmacher M. G., Hung A. Y., Vigo-Pelfrey C., Mellon A., Ostaszewski B. L., Lieberburg I., Koo E. H., Schenk D., Teplow D. B. Amyloid beta-peptide is produced by cultured cells during normal metabolism. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):322–325. doi: 10.1038/359322a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett J. T., Berger E. P., Lansbury P. T., Jr The carboxy terminus of the beta amyloid protein is critical for the seeding of amyloid formation: implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Biochemistry. 1993 May 11;32(18):4693–4697. doi: 10.1021/bi00069a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett J. T., Lansbury P. T., Jr Seeding "one-dimensional crystallization" of amyloid: a pathogenic mechanism in Alzheimer's disease and scrapie? Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1055–1058. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90635-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachaturian Z. S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1985 Nov;42(11):1097–1105. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060100083029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liepnieks J. J., Ghetti B., Farlow M., Roses A. D., Benson M. D. Characterization of amyloid fibril beta-peptide in familial Alzheimer's disease with APP717 mutations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Dec 15;197(2):386–392. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Papayannopoulos I. A., Styles J., Bobin S. A., Lin Y. Y., Biemann K., Iqbal K. Peptide compositions of the cerebrovascular and senile plaque core amyloid deposits of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Feb 15;301(1):41–52. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Takio K., Ogawara M., Selkoe D. J. Mass spectrometry of purified amyloid beta protein in Alzheimer's disease. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17082–17086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullan M., Crawford F., Axelman K., Houlden H., Lilius L., Winblad B., Lannfelt L. A pathogenic mutation for probable Alzheimer's disease in the APP gene at the N-terminus of beta-amyloid. Nat Genet. 1992 Aug;1(5):345–347. doi: 10.1038/ng0892-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelli F., Castaño E., Glenner G. G., Frangione B. Differences between vascular and plaque core amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 1988 Aug;51(2):648–651. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roher A. E., Lowenson J. D., Clarke S., Wolkow C., Wang R., Cotter R. J., Reardon I. M., Zürcher-Neely H. A., Heinrikson R. L., Ball M. J. Structural alterations in the peptide backbone of beta-amyloid core protein may account for its deposition and stability in Alzheimer's disease. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3072–3083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roher A. E., Lowenson J. D., Clarke S., Woods A. S., Cotter R. J., Gowing E., Ball M. J. beta-Amyloid-(1-42) is a major component of cerebrovascular amyloid deposits: implications for the pathology of Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10836–10840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roher A., Wolfe D., Palutke M., KuKuruga D. Purification, ultrastructure, and chemical analysis of Alzheimer disease amyloid plaque core protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2662–2666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Abraham C. R., Podlisny M. B., Duffy L. K. Isolation of low-molecular-weight proteins from amyloid plaque fibers in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 1986 Jun;46(6):1820–1834. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb08501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J. The molecular pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 1991 Apr;6(4):487–498. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seubert P., Vigo-Pelfrey C., Esch F., Lee M., Dovey H., Davis D., Sinha S., Schlossmacher M., Whaley J., Swindlehurst C. Isolation and quantification of soluble Alzheimer's beta-peptide from biological fluids. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):325–327. doi: 10.1038/359325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel D., Flügge U. I. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]