Abstract
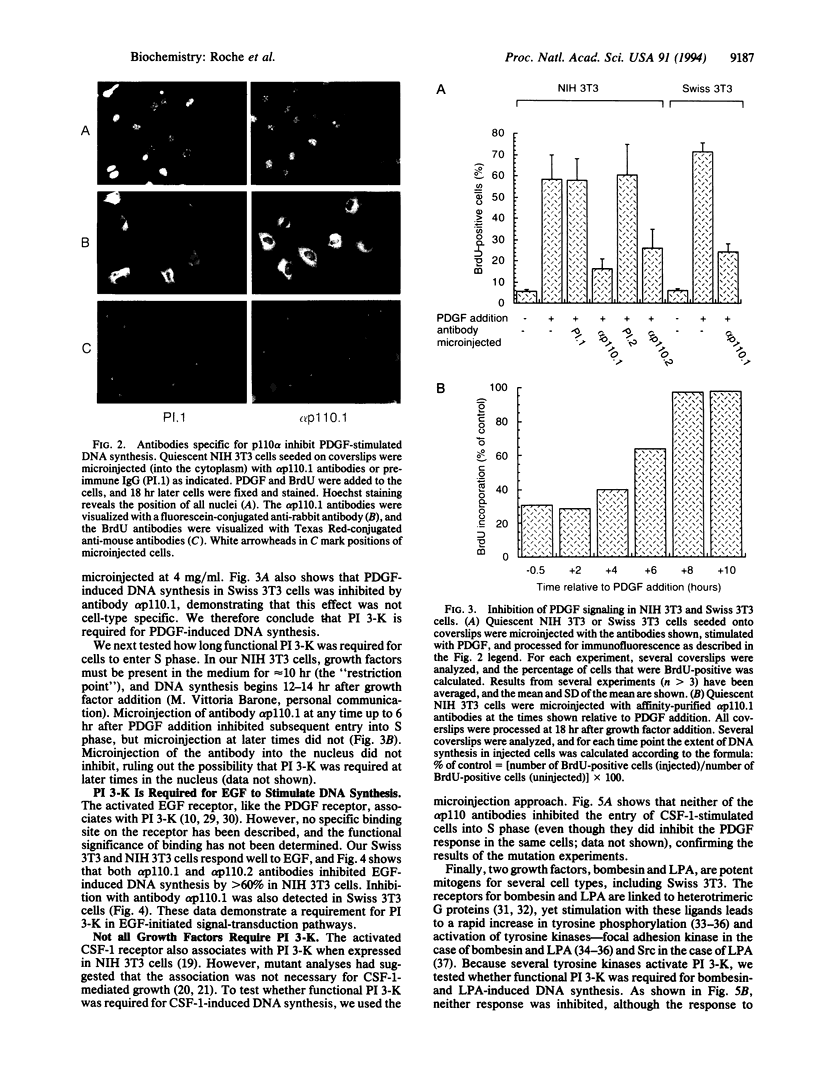
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-K) becomes activated when quiescent cells are stimulated with a variety of growth factors. We have microinjected antibodies specific for the p110 alpha subunit of the PI 3-K into quiescent fibroblasts and tested their effect on the ability of growth factors to stimulate exit from quiescence and entry into S phase. The antibodies inhibited platelet-derived growth factor-induced DNA synthesis, a result in keeping with previous studies using mutant platelet-derived growth factor receptors. Interestingly, functional PI 3-K was required for the first 6 hr of G1--i.e., until approximately 4 hr before the point at which the cells were committed to make DNA. A second tyrosine kinase receptor, the epidermal growth factor receptor, also required the PI 3-K for efficient signaling. However, colony-stimulating factor 1 (whose receptor is highly related to the platelet-derived growth factor receptor) could induce DNA synthesis in the absence of active PI 3-K, as could two growth factors (bombesin and lysophosphatidic acid) whose receptors are functionally coupled to G proteins. These data, therefore, demonstrate that some, but not all, growth factors require functional PI 3-K.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansorge W., Pepperkok R. Performance of an automated system for capillary microinjection into living cells. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1988 Aug;16(4):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(88)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auger K. R., Serunian L. A., Soltoff S. P., Libby P., Cantley L. C. PDGF-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation stimulates production of novel polyphosphoinositides in intact cells. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backer J. M., Myers M. G., Jr, Shoelson S. E., Chin D. J., Sun X. J., Miralpeix M., Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Schlessinger J. Phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase is activated by association with IRS-1 during insulin stimulation. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3469–3479. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battey J. F., Way J. M., Corjay M. H., Shapira H., Kusano K., Harkins R., Wu J. M., Slattery T., Mann E., Feldman R. I. Molecular cloning of the bombesin/gastrin-releasing peptide receptor from Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):395–399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berra E., Diaz-Meco M. T., Dominguez I., Municio M. M., Sanz L., Lozano J., Chapkin R. S., Moscat J. Protein kinase C zeta isoform is critical for mitogenic signal transduction. Cell. 1993 Aug 13;74(3):555–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80056-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorge J. D., Chan T. O., Antczak M., Kung H. J., Fujita D. J. Activated type I phosphatidylinositol kinase is associated with the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor following EGF stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3816–3820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. L., Auger K. R., Chanudhuri M., Yoakim M., Schaffhausen B., Shoelson S., Cantley L. C. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase is activated by phosphopeptides that bind to the SH2 domains of the 85-kDa subunit. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9478–9483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Escobedo J. A., Martin G. A., Turck C. W., del Rosario M., McCormick F., Williams L. T. Distinct phosphotyrosines on a growth factor receptor bind to specific molecules that mediate different signaling pathways. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90444-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh N., Tojo A., Muroya K., Hashimoto Y., Hattori S., Nakamura S., Takenawa T., Yazaki Y., Shibuya M. Epidermal growth factor-receptor mutant lacking the autophosphorylation sites induces phosphorylation of Shc protein and Shc-Grb2/ASH association and retains mitogenic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):167–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman P. K., Emr S. D. Characterization of VPS34, a gene required for vacuolar protein sorting and vacuole segregation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6742–6754. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiles I. D., Otsu M., Volinia S., Fry M. J., Gout I., Dhand R., Panayotou G., Ruiz-Larrea F., Thompson A., Totty N. F. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: structure and expression of the 110 kd catalytic subunit. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):419–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90166-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hordijk P. L., Verlaan I., van Corven E. J., Moolenaar W. H. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation induced by lysophosphatidic acid in Rat-1 fibroblasts. Evidence that phosphorylation of map kinase is mediated by the Gi-p21ras pathway. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):645–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Interaction of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-associated p85 with epidermal growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):981–990. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P., Mondino A., Skolnik E. Y., Schlessinger J. Cloning of a novel, ubiquitously expressed human phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and identification of its binding site on p85. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7677–7688. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson T. R., Stephens L. R., Hawkins P. T. Receptor specificity of growth factor-stimulated synthesis of 3-phosphorylated inositol lipids in Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16627–16636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalink K., Eichholtz T., Postma F. R., van Corven E. J., Moolenaar W. H. Lysophosphatidic acid induces neuronal shape changes via a novel, receptor-mediated signaling pathway: similarity to thrombin action. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Apr;4(4):247–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Kashishian A., Cooper J. A., Valius M. GTPase-activating protein and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase bind to distinct regions of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta subunit. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2534–2544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klippel A., Escobedo J. A., Fantl W. J., Williams L. T. The C-terminal SH2 domain of p85 accounts for the high affinity and specificity of the binding of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to phosphorylated platelet-derived growth factor beta receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1451–1459. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai N., Morii N., Fujisawa K., Yoshimasa T., Nakao K., Narumiya S. Lysophosphatidic acid induces tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of MAP-kinase and focal adhesion kinase in cultured Swiss 3T3 cells. FEBS Lett. 1993 Aug 30;329(3):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80236-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Song X. H. Bradykinin and bombesin rapidly stimulate tyrosine phosphorylation of a 120-kDa group of proteins in Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7746–7749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lips D. L., Majerus P. W., Gorga F. R., Young A. T., Benjamin T. L. Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate is present in normal and transformed fibroblasts and is resistant to hydrolysis by bovine brain phospholipase C II. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8759–8763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlade C. J., Ellis C., Reedijk M., Anderson D., Mbamalu G., Reith A. D., Panayotou G., End P., Bernstein A., Kazlauskas A. SH2 domains of the p85 alpha subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulate binding to growth factor receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):991–997. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi H., Brewer K. A., Exton J. H. Activation of the zeta isozyme of protein kinase C by phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):13–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura R., Li W., Kashishian A., Mondino A., Zhou M., Cooper J., Schlessinger J. Two signaling molecules share a phosphotyrosine-containing binding site in the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6889–6896. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotou G., Waterfield M. D. Phosphatidyl-inositol 3-kinase: a key enzyme in diverse signalling processes. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;2(12):358–360. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90042-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raffioni S., Bradshaw R. A. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by epidermal growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor, and nerve growth factor in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9121–9125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedijk M., Liu X. Q., Pawson T. Interactions of phosphatidylinositol kinase, GTPase-activating protein (GAP), and GAP-associated proteins with the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5601–5608. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche S., Dhand R., Waterfield M. D., Courtneidge S. A. The catalytic subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is a substrate for the activated platelet-derived growth factor receptor, but not for middle-T antigen-pp60c-src complexes. Biochem J. 1994 Aug 1;301(Pt 3):703–711. doi: 10.1042/bj3010703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serunian L. A., Haber M. T., Fukui T., Kim J. W., Rhee S. G., Lowenstein J. M., Cantley L. C. Polyphosphoinositides produced by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase are poor substrates for phospholipases C from rat liver and bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17809–17815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shurtleff S. A., Downing J. R., Rock C. O., Hawkins S. A., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Structural features of the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor that affect its association with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2415–2421. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07417.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., Chaudhuri M., Gish G., Pawson T., Haser W. G., King F., Roberts T., Ratnofsky S., Lechleider R. J. SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90404-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G. R., Reedijk M., Rothwell V., Rohrschneider L., Pawson T. The unique insert of cellular and viral fms protein tyrosine kinase domains is dispensable for enzymatic and transforming activities. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2029–2037. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03611.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twamley-Stein G. M., Pepperkok R., Ansorge W., Courtneidge S. A. The Src family tyrosine kinases are required for platelet-derived growth factor-mediated signal transduction in NIH 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7696–7700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valius M., Kazlauskas A. Phospholipase C-gamma 1 and phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase are the downstream mediators of the PDGF receptor's mitogenic signal. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):321–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90232-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varticovski L., Druker B., Morrison D., Cantley L., Roberts T. The colony stimulating factor-1 receptor associates with and activates phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):699–702. doi: 10.1038/342699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennström S., Siegbahn A., Yokote K., Arvidsson A. K., Heldin C. H., Mori S., Claesson-Welsh L. Membrane ruffling and chemotaxis transduced by the PDGF beta-receptor require the binding site for phosphatidylinositol 3' kinase. Oncogene. 1994 Feb;9(2):651–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Downes C. P., Keeler M., Keller T., Cantley L. Type I phosphatidylinositol kinase makes a novel inositol phospholipid, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):644–646. doi: 10.1038/332644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi K., Holt K., Pessin J. E. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase functions upstream of Ras and Raf in mediating insulin stimulation of c-fos transcription. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14597–14600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoakim M., Hou W., Liu Y., Carpenter C. L., Kapeller R., Schaffhausen B. S. Interactions of polyomavirus middle T with the SH2 domains of the pp85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5485–5491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5485-5491.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J. C., Heidaran M. A., Pierce J. H., Gutkind J. S., Lombardi D., Ruggiero M., Aaronson S. A. Tyrosine mutations within the alpha platelet-derived growth factor receptor kinase insert domain abrogate receptor-associated phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase activity without affecting mitogenic or chemotactic signal transduction. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3780–3785. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary I., Gil J., Lehmann W., Sinnett-Smith J., Rozengurt E. Bombesin, vasopressin, and endothelin rapidly stimulate tyrosine phosphorylation in intact Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4577–4581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Corven E. J., Groenink A., Jalink K., Eichholtz T., Moolenaar W. H. Lysophosphatidate-induced cell proliferation: identification and dissection of signaling pathways mediated by G proteins. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90868-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Geer P., Hunter T. Mutation of Tyr697, a GRB2-binding site, and Tyr721, a PI 3-kinase binding site, abrogates signal transduction by the murine CSF-1 receptor expressed in Rat-2 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5161–5172. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]