Abstract
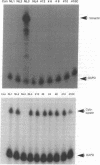
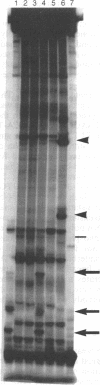
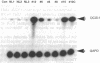
Histopathologic study of human breast biopsy samples has identified specific lesions which are associated with a high risk of development of invasive breast cancer. Presumably, these lesions (collectively termed premalignant breast disease) represent the earliest recognizable morphologic expression of fundamental molecular events that lead to the development of invasive breast cancer. To study molecular events underlying premalignant breast disease, we have developed a method for isolating RNA from histologically identified lesions from frozen human breast tissue. This method specifically obtains mRNA from breast epithelial cells and has identified three genes which are differentially expressed in premalignant breast epithelial lesions. One gene identified by this method is overexpressed in four of five noncomedo ductal carcinoma in situ lesions and appears to be the human homologue of the gene encoding the M2 subunit of ribonucleotide reductase, an enzyme involved in DNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF
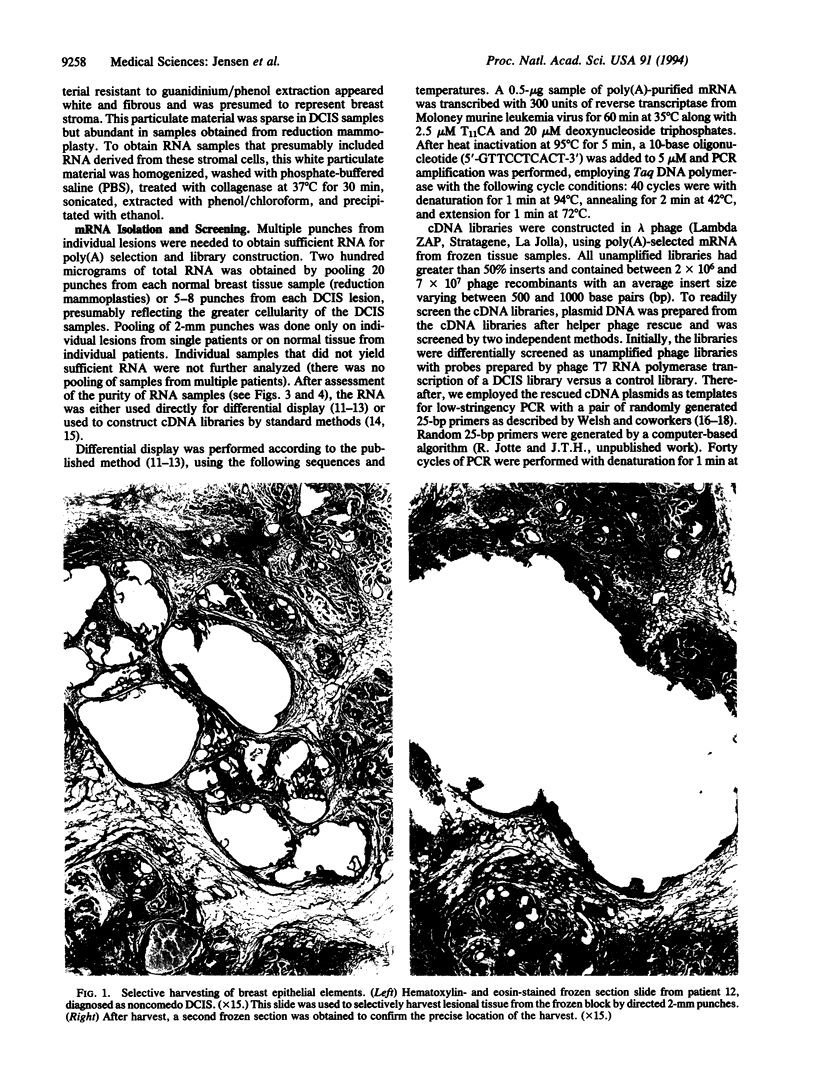


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert D. A., Rozengurt E. Synergistic and coordinate expression of the genes encoding ribonucleotide reductase subunits in Swiss 3T3 cells: effect of multiple signal-transduction pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1597–1601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacus S. S., Ruby S. G., Weinberg D. S., Chin D., Ortiz R., Bacus J. W. HER-2/neu oncogene expression and proliferation in breast cancers. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jul;137(1):103–111. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betsill W. L., Jr, Rosen P. P., Lieberman P. H., Robbins G. F. Intraductal carcinoma. Long-term follow-up after treatment by biopsy alone. JAMA. 1978 May 5;239(18):1863–1867. doi: 10.1001/jama.239.18.1863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri M. M., Tonin P. N., Srinivasan P. R. cDNA sequence of the small subunit of the hamster ribonucleotide reductase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Nov 15;1171(1):117–121. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90151-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff A. M., Herndon J. E., 2nd, Glover N. S., Kerns B. J., Pence J. C., Iglehart J. D., Marks J. R. Relation between p53 overexpression and established prognostic factors in breast cancer. Surgery. 1991 Aug;110(2):259–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. T. Antisense rescue defines specialized and generalized functional domains for c-Fos protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3821–3830. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurta R. A., Samuel S. K., Greenberg A. H., Wright J. A. Early induction of ribonucleotide reductase gene expression by transforming growth factor beta 1 in malignant H-ras transformed cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):24097–24100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurta R. A., Wright J. A. Alterations in the activity and regulation of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase by chlorambucil, a DNA damaging agent. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):7066–7071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulesh D. A., Ceceña G., Darmon Y. M., Vasseur M., Oshima R. G. Posttranslational regulation of keratins: degradation of mouse and human keratins 18 and 8. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1553–1565. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang P., Averboukh L., Keyomarsi K., Sager R., Pardee A. B. Differential display and cloning of messenger RNAs from human breast cancer versus mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 15;52(24):6966–6968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang P., Averboukh L., Pardee A. B. Distribution and cloning of eukaryotic mRNAs by means of differential display: refinements and optimization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3269–3275. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang P., Pardee A. B. Differential display of eukaryotic messenger RNA by means of the polymerase chain reaction. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):967–971. doi: 10.1126/science.1354393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodato R. F., Maguire H. C., Jr, Greene M. I., Weiner D. B., LiVolsi V. A. Immunohistochemical evaluation of c-erbB-2 oncogene expression in ductal carcinoma in situ and atypical ductal hyperplasia of the breast. Mod Pathol. 1990 Jul;3(4):449–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London S. J., Connolly J. L., Schnitt S. J., Colditz G. A. A prospective study of benign breast disease and the risk of breast cancer. JAMA. 1992 Feb 19;267(7):941–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. L., Dupont W. D. Anatomic markers of human premalignancy and risk of breast cancer. Cancer. 1990 Sep 15;66(6 Suppl):1326–1335. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19900915)66:14+<1326::aid-cncr2820661405>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. L., Dupont W. D., Rogers L. W., Landenberger M. Intraductal carcinoma of the breast: follow-up after biopsy only. Cancer. 1982 Feb 15;49(4):751–758. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19820215)49:4<751::aid-cncr2820490426>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. L., Rogers L. W. Combined histologic and cytologic criteria for the diagnosis of mammary atypical ductal hyperplasia. Hum Pathol. 1992 Oct;23(10):1095–1097. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(92)90026-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavloff N., Rivard D., Masson S., Shen S. H., Mes-Masson A. M. Sequence analysis of the large and small subunits of human ribonucleotide reductase. DNA Seq. 1992;2(4):227–234. doi: 10.3109/10425179209020807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perreau J., Lilienbaum A., Vasseur M., Paulin D. Nucleotide sequence of the human vimentin gene and regulation of its transcription in tissues and cultured cells. Gene. 1988;62(1):7–16. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90575-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poller D. N., Roberts E. C., Bell J. A., Elston C. W., Blamey R. W., Ellis I. O. p53 protein expression in mammary ductal carcinoma in situ: relationship to immunohistochemical expression of estrogen receptor and c-erbB-2 protein. Hum Pathol. 1993 May;24(5):463–468. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(93)90157-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Sorge J. A. In vivo excision properties of bacteriophage lambda ZAP expression vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1992;216:495–508. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)16045-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda J., Yano H., Eng S., Zeng Y., Bell G. I. A molecular inventory of human pancreatic islets: sequence analysis of 1000 cDNA clones. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Nov;2(11):1793–1798. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.11.1793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thor A. D., Moore DH I. I., Edgerton S. M., Kawasaki E. S., Reihsaus E., Lynch H. T., Marcus J. N., Schwartz L., Chen L. C., Mayall B. H. Accumulation of p53 tumor suppressor gene protein: an independent marker of prognosis in breast cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Jun 3;84(11):845–855. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.11.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., Chada K., Dalal S. S., Cheng R., Ralph D., McClelland M. Arbitrarily primed PCR fingerprinting of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 11;20(19):4965–4970. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.19.4965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., McClelland M. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7213–7218. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., McClelland M. Genomic fingerprinting using arbitrarily primed PCR and a matrix of pairwise combinations of primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5275–5279. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]