Abstract
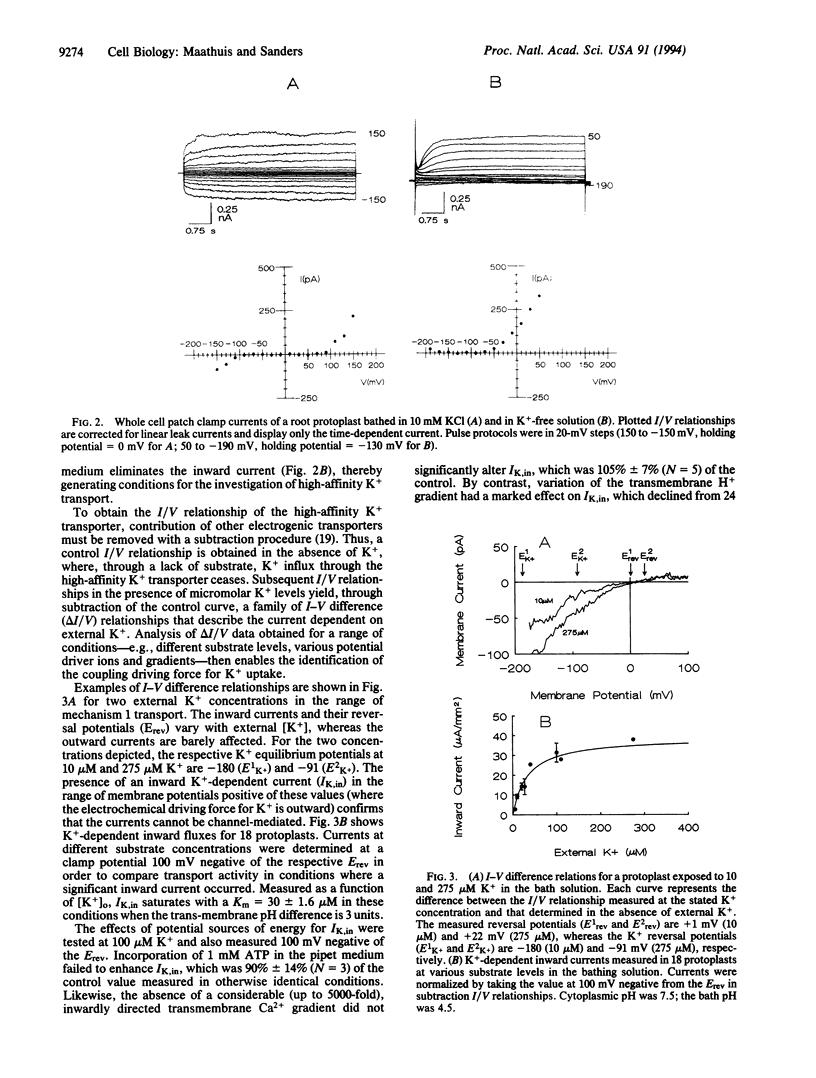
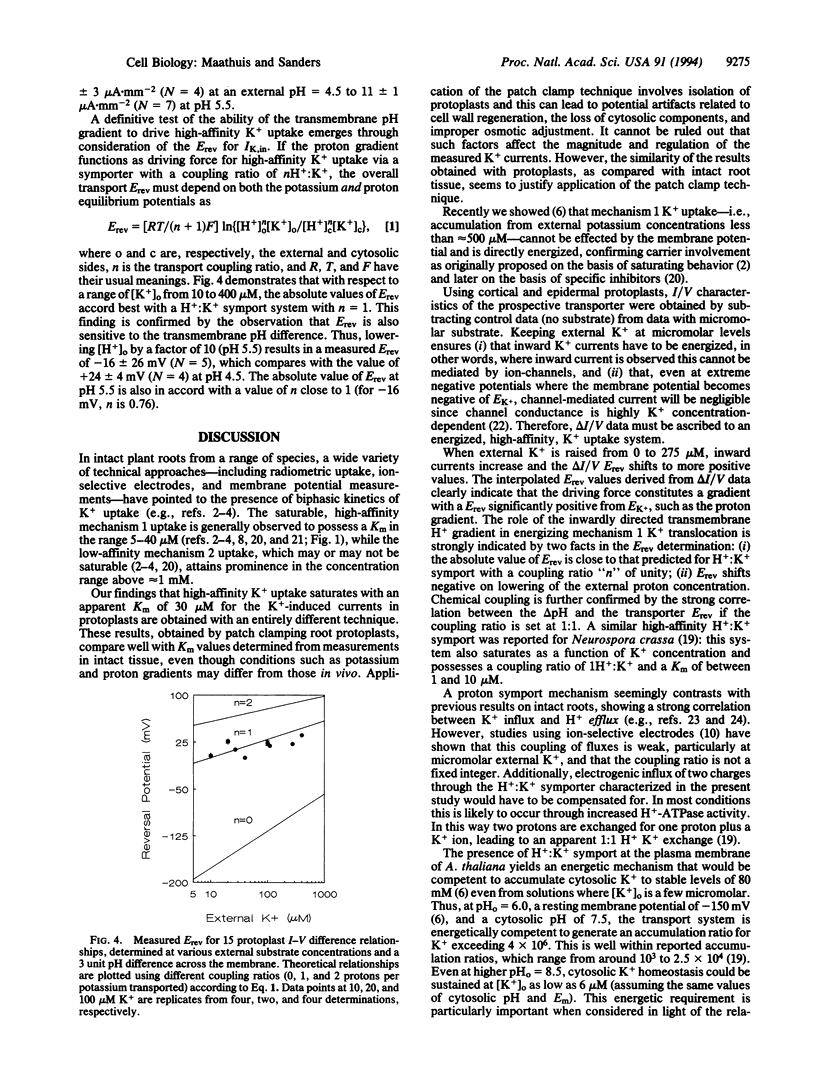
Potassium is a major nutrient in higher plants, where it plays a role in turgor regulation, charge balance, leaf movement, and protein synthesis. Terrestrial plants are able to sustain growth at micromolar external K+ concentrations, at which K+ uptake across the plasma membrane of root cells must be energized despite the presence of a highly negative membrane potential. However, the mechanism of energization has long remained obscure. Therefore, whole-cell mode patch clamping has been applied to root protoplasts from Arabidopsis thaliana to characterize membrane currents resulting from the application of micromolar K+. Analysis of whole cell current/voltage relationships in the presence and absence of micromolar K+ enabled direct testing of K+ transport for possible energization by cytoplasmic ATP and the respective trans-membrane gradients of Na+, Ca2+, and H+. Subtracted current/voltage relations for K(+)-dependent membrane currents are independent of ATP and reverse at potentials that imply H(+)-coupled K+ transport with a ratio of 1 H+:K+. Furthermore, the reversal potential of the K+ current shifts negative as external H+ activity is decreased. K(+)-dependent currents saturate in the micromolar concentration range with an apparent Km of 30 microM, a value in close agreement with previously reported Km values for high-affinity K+ uptake. We conclude that our results are consistent with the view that high-affinity K+ uptake in higher plants is mediated by a H+:K+ symport mechanism, competent in driving K+ accumulation to equilibrium ratios in excess of 10(6)-fold.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blatt M. R., Slayman C. L. Role of "active" potassium transport in the regulation of cytoplasmic pH by nonanimal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2737–2741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush D. R., Jacobson L. Potassium transport in suspension culture cells and protoplasts of carrot. Plant Physiol. 1986 Aug;81(4):1022–1026. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.4.1022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheeseman J. M., Hanson J. B. Energy-linked Potassium Influx as Related to Cell Potential in Corn Roots. Plant Physiol. 1979 Nov;64(5):842–845. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.5.842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. M., Poole R. J., Rea P. A., Sanders D. Potassium transport into plant vacuoles energized directly by a proton-pumping inorganic pyrophosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11701–11705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E. Microorganisms and ion absorption by roots. Experientia. 1968 Jun 15;24(6):616–617. doi: 10.1007/BF02153809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E., Rains D. W., Elzam O. E. RESOLUTION OF DUAL MECHANISMS OF POTASSIUM ABSORPTION BY BARLEY ROOTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 May;49(5):684–692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.5.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochian L. V., Lucas W. J. Potassium transport in corn roots : I. Resolution of kinetics into a saturable and linear component. Plant Physiol. 1982 Dec;70(6):1723–1731. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.6.1723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochian L. V., Shaff J. E., Lucas W. J. High affinity k uptake in maize roots: a lack of coupling with h efflux. Plant Physiol. 1989 Nov;91(3):1202–1211. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.3.1202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman I. A., Kochian L. V., Grusak M. A., Lucas W. J. Fluxes of h and k in corn roots : characterization and stoichiometries using ion-selective microelectrodes. Plant Physiol. 1987 Aug;84(4):1177–1184. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.4.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Navarro A., Blatt M. R., Slayman C. L. A potassium-proton symport in Neurospora crassa. J Gen Physiol. 1986 May;87(5):649–674. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.5.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders D. Generalized kinetic analysis of ion-driven cotransport systems: II. Random ligand binding as a simple explanation for non-michaelian kinetics. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(1):67–87. doi: 10.1007/BF01869687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. I., Fang H. H. Inward-rectifying K+ channels in guard cells provide a mechanism for low-affinity K+ uptake. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11583–11587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibaud J. B., Soler A., Grignon C. H and k electrogenic exchanges in corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jul;81(3):847–853. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.3.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



