Abstract
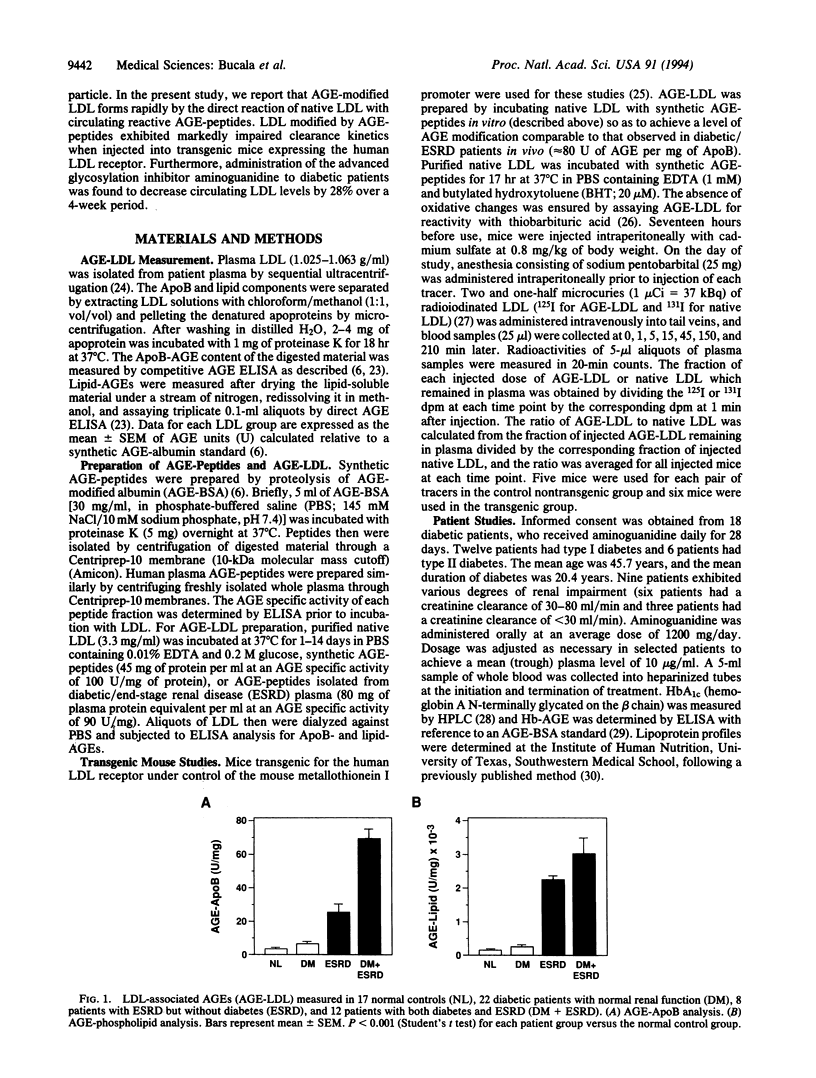
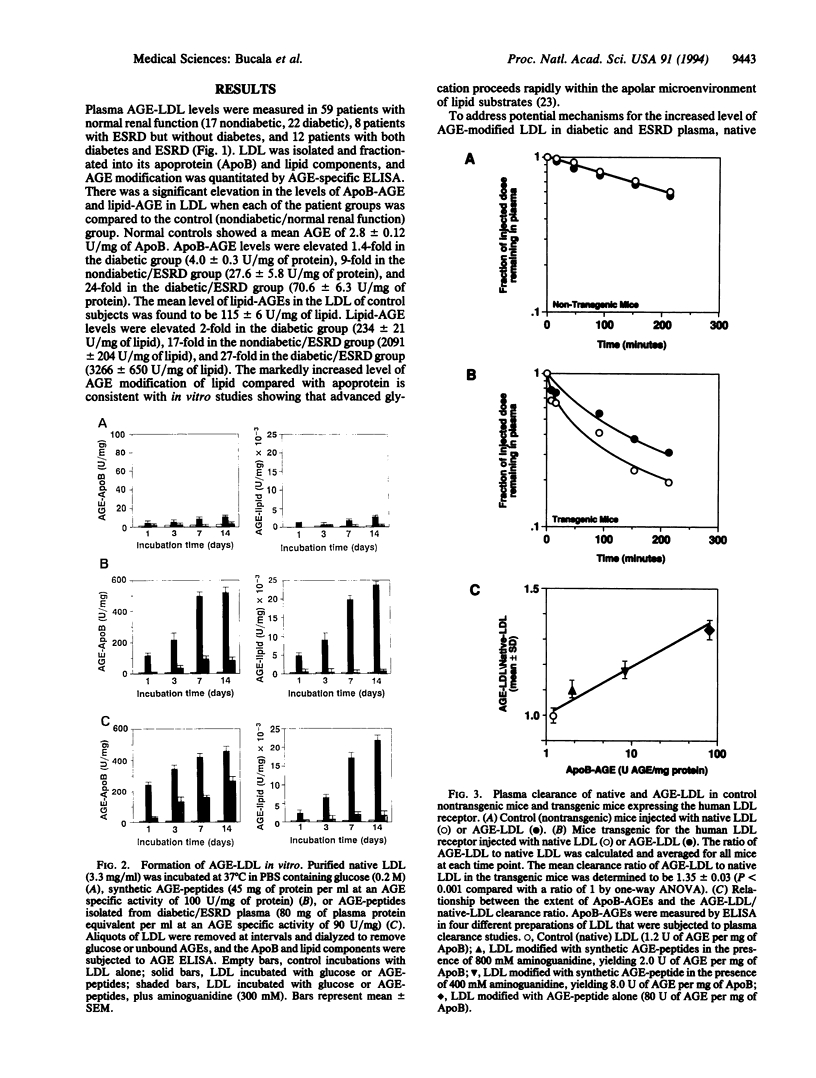
Atherosclerosis develops rapidly in patients with diabetes or renal insufficiency. Plasma lipoprotein profiles are frequently abnormal in these conditions and reflect an elevation in the level of the apoprotein B (ApoB)-containing components very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) and low density lipoprotein (LDL). High levels of circulating advanced glycation end products (AGEs) also occur in diabetes and end-stage renal disease (ESRD). These products arise from glucose-derived Amadori products and include AGE-modified peptides (AGE-peptides) which result from the catabolism of AGE-modified tissue proteins. AGE-peptides have been shown to crosslink protein amino groups and to accumulate in plasma as a consequence of renal insufficiency. To address potential mechanisms for the dyslipidemia of diabetes and ESRD, we investigated the possibility that circulating AGEs react directly with plasma lipoproteins to prevent their recognition by tissue LDL receptors. AGE-specific ELISA showed a significantly increased level of AGE-modified LDL in the plasma of diabetic or ESRD patients compared with normal controls. AGE-LDL formed readily in vitro when native LDL was incubated with either synthetic AGE-peptides or AGE-peptides isolated directly from patient plasma. LDL which had been modified by AGE-peptides in vitro to the same level of modification as that present in the plasma of diabetics with renal insufficiency exhibited markedly impaired clearance kinetics when injected into transgenic mice expressing the human LDL receptor. These data indicate that AGE modification significantly impairs LDL-receptor-mediated clearance mechanisms and may contribute to elevated LDL levels in patients with diabetes or renal insufficiency. This hypothesis was further supported by the observation that the administration of the advanced glycation inhibitor aminoguanidine to diabetic patients decreased circulating LDL levels by 28%.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown W. V. Lipoprotein disorders in diabetes mellitus. Med Clin North Am. 1994 Jan;78(1):143–161. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)30180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M., Cerami A., Vlassara H. Advanced glycosylation end products in tissue and the biochemical basis of diabetic complications. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 19;318(20):1315–1321. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805193182007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M., Vlassara H., Kooney A., Ulrich P., Cerami A. Aminoguanidine prevents diabetes-induced arterial wall protein cross-linking. Science. 1986 Jun 27;232(4758):1629–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.3487117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucala R., Cerami A. Advanced glycosylation: chemistry, biology, and implications for diabetes and aging. Adv Pharmacol. 1992;23:1–34. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60961-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucala R., Makita Z., Koschinsky T., Cerami A., Vlassara H. Lipid advanced glycosylation: pathway for lipid oxidation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6434–6438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucala R., Tracey K. J., Cerami A. Advanced glycosylation products quench nitric oxide and mediate defective endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in experimental diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):432–438. doi: 10.1172/JCI115014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito C., Gerlach H., Brett J., Stern D., Vlassara H. Endothelial receptor-mediated binding of glucose-modified albumin is associated with increased monolayer permeability and modulation of cell surface coagulant properties. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1387–1407. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The low-density lipoprotein pathway and its relation to atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiramatsu K., Bierman E. L., Chait A. Metabolism of low-density lipoprotein from patients with diabetic hypertriglyceridemia by cultured human skin fibroblasts. Diabetes. 1985 Jan;34(1):8–14. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann S. L., Russell D. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Hammer R. E. Overexpression of low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor eliminates LDL from plasma in transgenic mice. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1277–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.3344433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan M., Cerami A., Bucala R. Advanced glycosylation endproducts block the antiproliferative effect of nitric oxide. Role in the vascular and renal complications of diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):1110–1115. doi: 10.1172/JCI115928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Pitas R. E., Mahley R. W. Lipoprotein-receptor interactions. Methods Enzymol. 1986;129:542–565. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)29091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen T., Stender S., Deckert T. Abnormalities in plasmas concentrations of lipoproteins and fibrinogen in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients with increased urinary albumin excretion. Diabetologia. 1988 Mar;31(3):142–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00276846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannel W. B., McGee D. L. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The Framingham study. JAMA. 1979 May 11;241(19):2035–2038. doi: 10.1001/jama.241.19.2035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesaniemi Y. A., Witztum J. L., Steinbrecher U. P. Receptor-mediated catabolism of low density lipoprotein in man. Quantitation using glucosylated low density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1983 Apr;71(4):950–959. doi: 10.1172/JCI110849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikugawa K., Kojima T., Yamaki S., Kosugi H. Interpretation of the thiobarbituric acid reactivity of rat liver and brain homogenates in the presence of ferric ion and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. Anal Biochem. 1992 May 1;202(2):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90102-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn R. R., Cerami A., Monnier V. M. Collagen aging in vitro by nonenzymatic glycosylation and browning. Diabetes. 1984 Jan;33(1):57–59. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes-Virella M. F., Sherer G. K., Lees A. M., Wohltmann H., Mayfield R., Sagel J., LeRoy E. C., Colwell J. A. Surface binding, internalization and degradation by cultured human fibroblasts of low density lipoproteins isolated from type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients: changes with metabolic control. Diabetologia. 1982 Jun;22(6):430–436. doi: 10.1007/BF00282585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Pitas R. E., Weisgraber K. H., Brown J. H., Gross E. Inhibition of lipoprotein binding to cell surface receptors of fibroblasts following selective modification of arginyl residues in arginine-rich and B apoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7279–7287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Weisgraber K. B., Oh S. Y. Altered metabolism (in vivo and in vitro) of plasma lipoproteins after selective chemical modification of lysine residues of the apoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1979 Sep;64(3):743–750. doi: 10.1172/JCI109518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makita Z., Bucala R., Rayfield E. J., Friedman E. A., Kaufman A. M., Korbet S. M., Barth R. H., Winston J. A., Fuh H., Manogue K. R. Reactive glycosylation endproducts in diabetic uraemia and treatment of renal failure. Lancet. 1994 Jun 18;343(8912):1519–1522. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92935-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makita Z., Radoff S., Rayfield E. J., Yang Z., Skolnik E., Delaney V., Friedman E. A., Cerami A., Vlassara H. Advanced glycosylation end products in patients with diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 1991 Sep 19;325(12):836–842. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199109193251202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makita Z., Vlassara H., Cerami A., Bucala R. Immunochemical detection of advanced glycosylation end products in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5133–5138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makita Z., Vlassara H., Rayfield E., Cartwright K., Friedman E., Rodby R., Cerami A., Bucala R. Hemoglobin-AGE: a circulating marker of advanced glycosylation. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):651–653. doi: 10.1126/science.1411574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnier V. M., Kohn R. R., Cerami A. Accelerated age-related browning of human collagen in diabetes mellitus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):583–587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Njoroge F. G., Monnier V. M. The chemistry of the Maillard reaction under physiological conditions: a review. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;304:85–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock I. Glycosylated haemoglobin: measurement and clinical use. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Aug;37(8):841–851. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.8.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis--an update. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 20;314(8):488–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602203140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Haudenschild C. Diabetes as an atherogenic factor. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;26(5):373–412. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(84)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnider S. L., Kohn R. R. Effects of age and diabetes mellitus on the solubility and nonenzymatic glucosylation of human skin collagen. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;67(6):1630–1635. doi: 10.1172/JCI110198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Khoo J. C., Witztum J. L. Beyond cholesterol. Modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 6;320(14):915–924. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904063201407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlassara H., Brownlee M., Cerami A. High-affinity-receptor-mediated uptake and degradation of glucose-modified proteins: a potential mechanism for the removal of senescent macromolecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5588–5592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlassara H., Brownlee M., Manogue K. R., Dinarello C. A., Pasagian A. Cachectin/TNF and IL-1 induced by glucose-modified proteins: role in normal tissue remodeling. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1546–1548. doi: 10.1126/science.3259727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witztum J. L., Mahoney E. M., Branks M. J., Fisher M., Elam R., Steinberg D. Nonenzymatic glucosylation of low-density lipoprotein alters its biologic activity. Diabetes. 1982 Apr;31(4 Pt 1):283–291. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.4.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]