Abstract
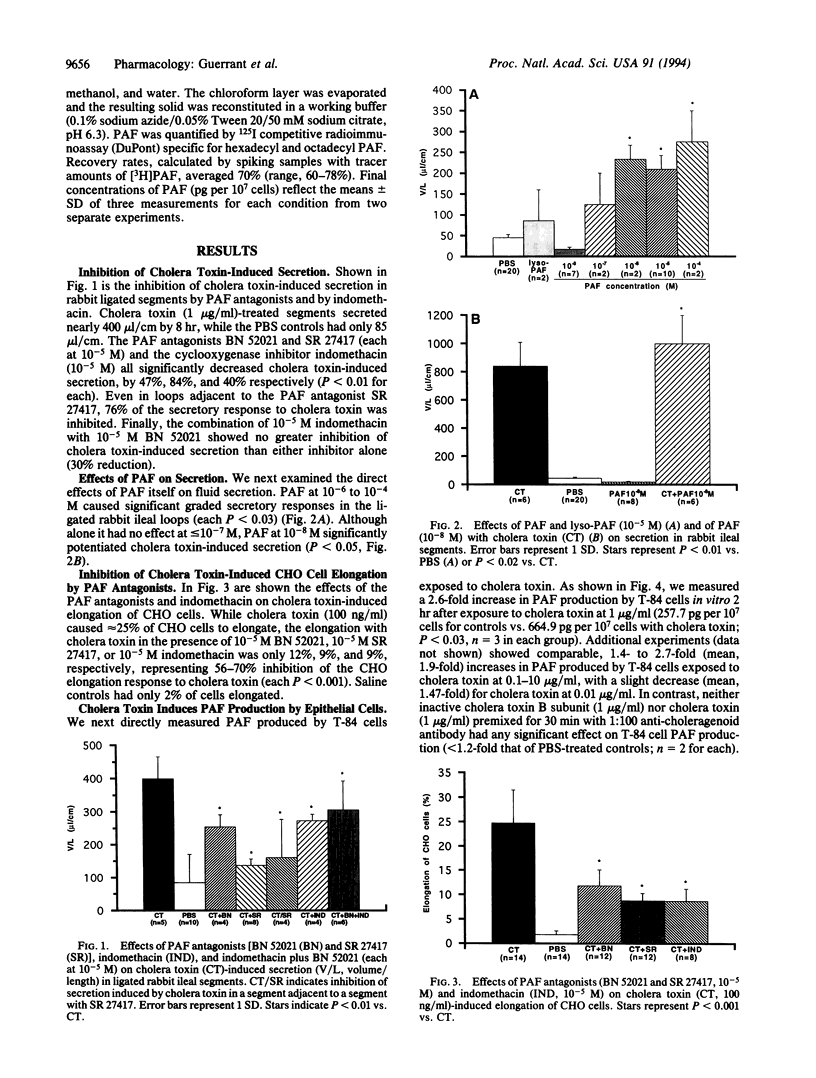
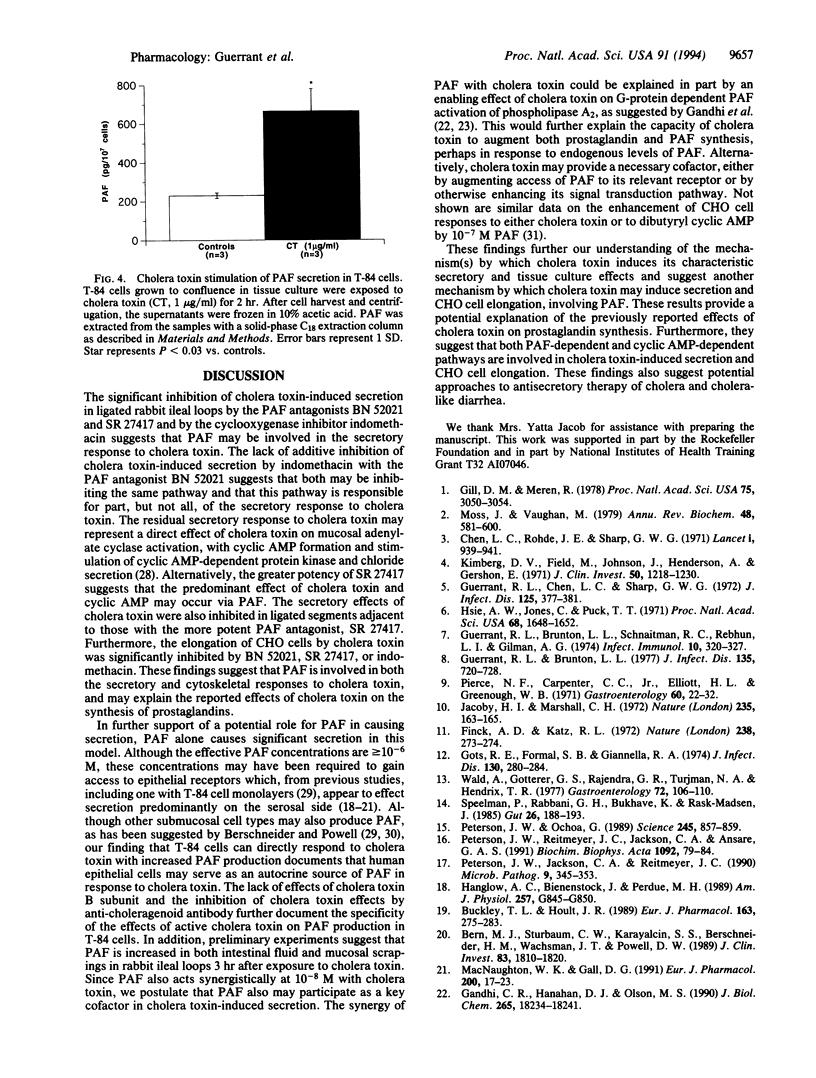
With the recent heightened concern about cholera around the world come new questions about the mechanism by which cholera toxin causes diarrhea. Peterson and Ochoa have suggested that prostaglandin synthesis is key to both the intestinal epithelial secretory and the CHO cell responses to cholera toxin [Peterson, J. W. and Ochoa, G. (1989) Science 245, 857-859]. Because platelet activating factor (PAF) can be a potent stimulus for prostaglandin synthesis, we examined its role in the intestinal and tissue culture effects of cholera toxin. We report that the specific PAF receptor antagonists BN 52021 and SR 27417 inhibit the effects of cholera toxin on intestinal secretion in rabbit ileal loops in vivo and on the cytoskeleton of Chinese hamster ovary cells in vitro. We also show that PAF itself can cause net fluid secretion in the rabbit model and that PAF potentiates the effects of cholera toxin on intestinal secretion. Finally, we demonstrate that cholera toxin stimulates significant PAF production (2.6-fold) in isolated T-84 intestinal epithelial cells. We conclude that cholera toxin stimulates PAF production and that PAF is involved in both the secretory and cytoskeletal responses to cholera toxin. These findings further support the involvement of additional mediators of cholera toxin effects other than mucosal cell cyclic AMP and help explain the effects of cholera toxin on prostaglandin synthesis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bern M. J., Sturbaum C. W., Karayalcin S. S., Berschneider H. M., Wachsman J. T., Powell D. W. Immune system control of rat and rabbit colonic electrolyte transport. Role of prostaglandins and enteric nervous system. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jun;83(6):1810–1820. doi: 10.1172/JCI114086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berschneider H. M., Powell D. W. Fibroblasts modulate intestinal secretory responses to inflammatory mediators. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):484–489. doi: 10.1172/JCI115610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley T. L., Hoult J. R. Platelet activating factor is a potent colonic secretagogue with actions independent of specific PAF receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Apr 25;163(2-3):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90196-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. C., Rohde J. E., Sharp G. W. Intestinal adenyl-cyclase activity in human cholera. Lancet. 1971 May 8;1(7706):939–941. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91443-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., McRoberts J. A., Mandel K. G., Tisdale L. D., Masui H. A human colonic tumor cell line that maintains vectorial electrolyte transport. Am J Physiol. 1984 Feb;246(2 Pt 1):G204–G208. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.2.G204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finck A. D., Katz R. L. Prevention of cholera-induced intestinal secretion in the cat by aspirin. Nature. 1972 Aug 4;238(5362):273–274. doi: 10.1038/238273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi C. R., DeBuysere M. S., Olson M. S. Platelet-activating factor-mediated synthesis of prostaglandins in rat Kupffer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jul 22;1136(1):68–74. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90086-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi C. R., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Two distinct pathways of platelet-activating factor-induced hydrolysis of phosphoinositides in primary cultures of rat Kupffer cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18234–18241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Meren R. ADP-ribosylation of membrane proteins catalyzed by cholera toxin: basis of the activation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3050–3054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gots R. E., Formal S. B., Giannella R. A. Indomethacin inhibition of Salmonella typhimurium, Shigella flexneri, and cholera-mediated rabbit ileal secretion. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):280–284. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L. Characterization of the Chinese hamster ovary cell assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli and for specific antisera, and toxoid. J Infect Dis. 1977 May;135(5):720–728. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.5.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Chen L. C., Sharp G. W. Intestinal adenyl-cyclase activity in canine cholera: correlation with fluid accumulation. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):377–381. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanglow A. C., Bienenstock J., Perdue M. H. Effects of platelet-activating factor on ion transport in isolated rat jejunum. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 1):G845–G850. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.257.5.G845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert J. M., Bernat A., Valette G., Gigo V., Lale A., LaPlace M. C., Lespy L., Savi P., Maffrand J. P., Le Fur G. Biochemical and pharmacological activities of SR 27417, a highly potent, long-acting platelet-activating factor receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Oct;259(1):44–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsie A. W., Jones C., Puck T. T. Further changes in differentiation state accompanying the conversion of Chinese hamster cells of fibroblastic form by dibutyryl adenosine cyclic 3':5'-monophosphate and hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby H. I., Marshall C. H. Antagonism of cholera enterotoxin by anti-inflammatory agents in the rat. Nature. 1972 Jan 21;235(5334):163–165. doi: 10.1038/235163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Johnson J., Henderson A., Gershon E. Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI106599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lencer W. I., Delp C., Neutra M. R., Madara J. L. Mechanism of cholera toxin action on a polarized human intestinal epithelial cell line: role of vesicular traffic. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(6):1197–1209. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.6.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNaughton W. K., Gall D. G. Mechanisms of platelet-activating factor-induced electrolyte transport in the rat jejunum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 23;200(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90660-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. Activation of adenylate cyclase by choleragen. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:581–600. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.003053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. W., Jackson C. A., Reitmeyer J. C. Synthesis of prostaglandins in cholera toxin-treated Chinese hamster ovary cells. Microb Pathog. 1990 Nov;9(5):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. W., Ochoa L. G. Role of prostaglandins and cAMP in the secretory effects of cholera toxin. Science. 1989 Aug 25;245(4920):857–859. doi: 10.1126/science.2549637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. W., Reitmeyer J. C., Jackson C. A., Ansari G. A. Protein synthesis is required for cholera toxin-induced stimulation of arachidonic acid metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 19;1092(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Carpenter C. C., Jr, Elliott H. L., Greenough W. B., 3rd Effects of prostaglandins, theophylline, and cholera exotoxin upon transmucosal water and electrolyte movement in the canine jejunum. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jan;60(1):22–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. W. Epithelial secretory responses to inflammation. Platelet activating factor and reactive oxygen metabolites. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992;664:232–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb39764.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speelman P., Rabbani G. H., Bukhave K., Rask-Madsen J. Increased jejunal prostaglandin E2 concentrations in patients with acute cholera. Gut. 1985 Feb;26(2):188–193. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.2.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald A., Gotterer G. S., Rajendra G. R., Turjman N. A., Hendrix T. R. Effect of indomethacin on cholera-induced fluid movement, unidirectional sodium fluxes, and intestinal cAMP. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jan;72(1):106–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jonge H. R., Lohmann S. M. Mechanisms by which cyclic nucleotides and other intracellular mediators regulate secretion. Ciba Found Symp. 1985;112:116–138. doi: 10.1002/9780470720936.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


