Abstract
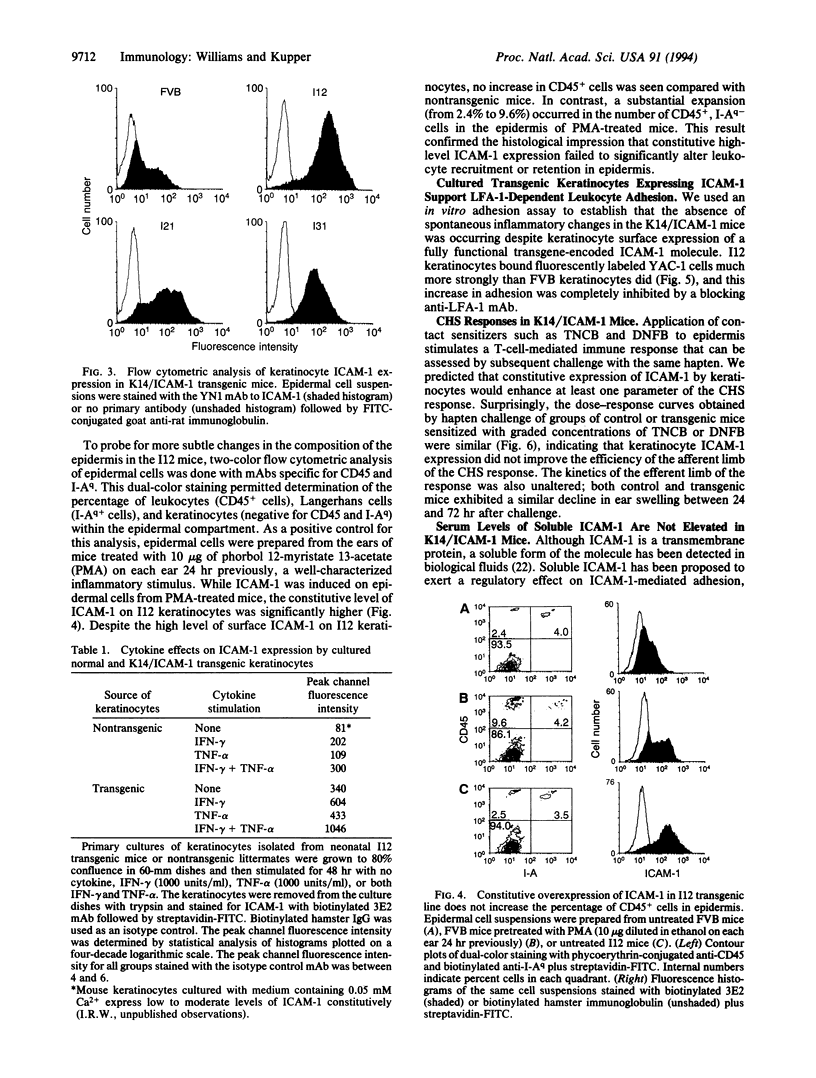
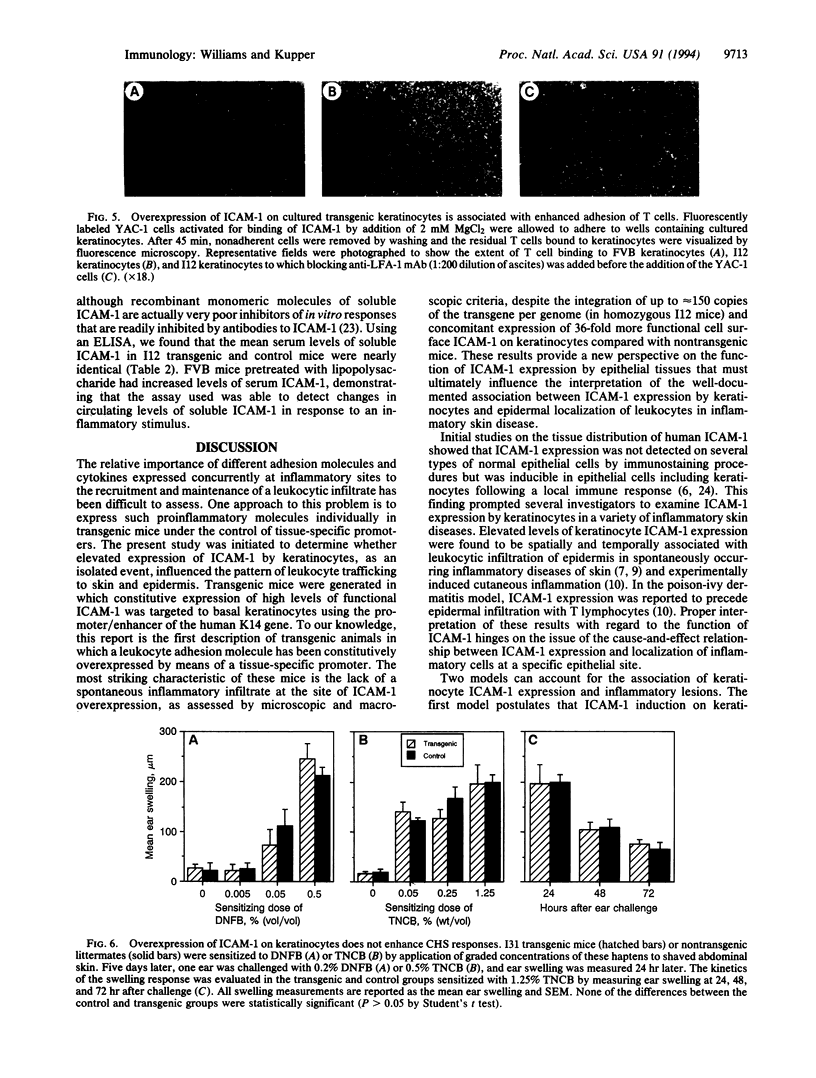
Keratinocytes at sites of cutaneous inflammation have increased expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), a cytokine-inducible adhesion molecule which binds the leukocyte integrins LFA-1 and Mac-1. Transgenic mice were prepared in which the expression of mouse ICAM-1 was targeted to basal keratinocytes by using the human K14 keratin promoter. The level of constitutive expression attained in the transgenic mice exceeded the peak level of ICAM-1 expression induced on nontransgenic mouse keratinocytes in vitro by optimal combinations of interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha or in vivo by proinflammatory stimuli such as phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. In vitro adhesion assays demonstrated that cultured transgenic keratinocytes were superior to normal keratinocytes as a substrate for the LFA-1-dependent binding of mouse T cells, confirming that the transgene-encoded ICAM-1 was expressed in a functional form. However, the high level of constitutive ICAM-1 expression achieved on keratinocytes in vivo in these transgenic mice did not result in additional recruitment of CD45+ leukocytes into transgenic epidermis, nor did it elicit dermal inflammation. Keratinocyte ICAM-1 expression also did not potentiate contact-hypersensitivity reactions to epicutaneous application of haptens. The absence of a spontaneous phenotype in these transgenic mice was not the result of increased levels of soluble ICAM-1, since serum levels of soluble ICAM-1 were equal in transgenic mice and controls. We conclude that elevated ICAM-1 expression on keratinocytes cannot act independently to influence leukocyte trafficking and elicit cutaneous inflammation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballantyne C. M., O'Brien W. E., Beaudet A. L. Nucleotide sequence of the cDNA for murine intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5853–5853. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. Z., Evans G. A. A simple screening method for transgenic mice using the polymerase chain reaction. Biotechniques. 1990 Jan;8(1):32–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Panfilis G., Manara G. C., Ferrari C., Torresani C., Lonati A. Adhesion molecules on the plasma membrane of epidermal cells. IV. Immunolocalization of the intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1, CD54) on the cell surface of a small subpopulation of keratinocytes freshly isolated from normal human epidermis. Reg Immunol. 1992 May-Jun;4(3):119–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. S., Staunton D. E., de Fougerolles A. R., Stacker S. A., Garcia-Aguilar J., Hibbs M. L., Springer T. A. ICAM-1 (CD54): a counter-receptor for Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18). J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3129–3139. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Rothlein R., Bhan A. K., Dinarello C. A., Springer T. A. Induction by IL 1 and interferon-gamma: tissue distribution, biochemistry, and function of a natural adherence molecule (ICAM-1). J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):245–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Singer K. H., Tuck D. T., Springer T. A. Adhesion of T lymphoblasts to epidermal keratinocytes is regulated by interferon gamma and is mediated by intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1). J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1323–1340. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths C. E., Nickoloff B. J. Keratinocyte intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) expression precedes dermal T lymphocytic infiltration in allergic contact dermatitis (Rhus dermatitis). Am J Pathol. 1989 Dec;135(6):1045–1053. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths C. E., Voorhees J. J., Nickoloff B. J. Characterization of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and HLA-DR expression in normal and inflamed skin: modulation by recombinant gamma interferon and tumor necrosis factor. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989 Apr;20(4):617–629. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennings H., Michael D., Cheng C., Steinert P., Holbrook K., Yuspa S. H. Calcium regulation of growth and differentiation of mouse epidermal cells in culture. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90406-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilgus O., Payer E., Schreiber S., Elbe A., Strohal R., Stingl G. In vivo cytokine expression in normal and perturbed murine skin--analysis by competitive quantitative polymerase chain reaction. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 May;100(5):674–680. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12472339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupper T. S. Immune and inflammatory processes in cutaneous tissues. Mechanisms and speculations. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1783–1789. doi: 10.1172/JCI114907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothlein R., Dustin M. L., Marlin S. D., Springer T. A. A human intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM-1) distinct from LFA-1. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1270–1274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothlein R., Mainolfi E. A., Czajkowski M., Marlin S. D. A form of circulating ICAM-1 in human serum. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3788–3793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheynius A., Camp R. L., Puré E. Reduced contact sensitivity reactions in mice treated with monoclonal antibodies to leukocyte function-associated molecule-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):655–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sligh J. E., Jr, Ballantyne C. M., Rich S. S., Hawkins H. K., Smith C. W., Bradley A., Beaudet A. L. Inflammatory and immune responses are impaired in mice deficient in intercellular adhesion molecule 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8529–8533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. Functional cloning of ICAM-2, a cell adhesion ligand for LFA-1 homologous to ICAM-1. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):61–64. doi: 10.1038/339061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan S., Bergstresser P. R., Tigelaar R. E., Streilein J. W. FACS purification of bone marrow-derived epidermal populations in mice: Langerhans cells and Thy-1+ dendritic cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Jun;84(6):491–495. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12273454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takei F. Inhibition of mixed lymphocyte response by a rat monoclonal antibody to a novel murine lymphocyte activation antigen (MALA-2). J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1403–1407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassar R., Fuchs E. Transgenic mice provide new insights into the role of TGF-alpha during epidermal development and differentiation. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):714–727. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassar R., Rosenberg M., Ross S., Tyner A., Fuchs E. Tissue-specific and differentiation-specific expression of a human K14 keratin gene in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1563–1567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vejlsgaard G. L., Ralfkiaer E., Avnstorp C., Czajkowski M., Marlin S. D., Rothlein R. Kinetics and characterization of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) expression on keratinocytes in various inflammatory skin lesions and malignant cutaneous lymphomas. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989 May;20(5 Pt 1):782–790. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welder C. A., Lee D. H., Takei F. Inhibition of cell adhesion by microspheres coated with recombinant soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2203–2210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H., Gonzalo J. A., St Pierre Y., Williams I. R., Kupper T. S., Cotran R. S., Springer T. A., Gutierrez-Ramos J. C. Leukocytosis and resistance to septic shock in intercellular adhesion molecule 1-deficient mice. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):95–109. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuspa S. H., Kilkenny A. E., Steinert P. M., Roop D. R. Expression of murine epidermal differentiation markers is tightly regulated by restricted extracellular calcium concentrations in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1207–1217. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Fougerolles A. R., Springer T. A. Intercellular adhesion molecule 3, a third adhesion counter-receptor for lymphocyte function-associated molecule 1 on resting lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):185–190. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]