Abstract
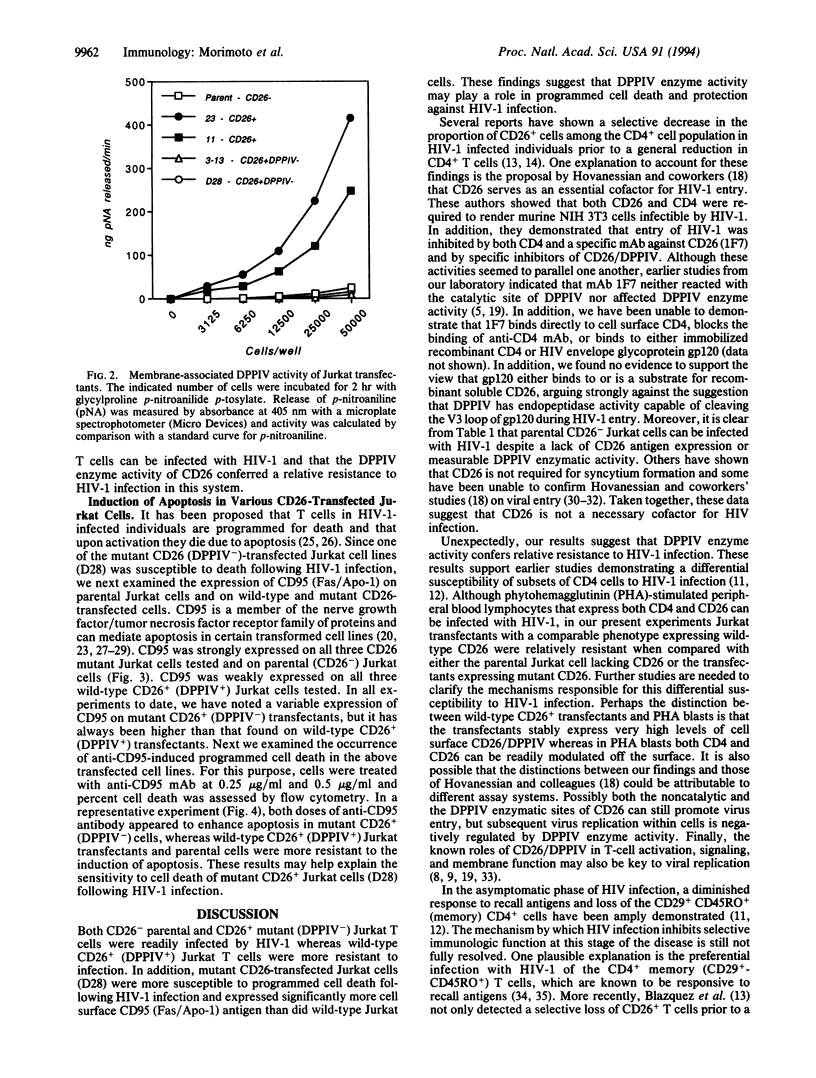
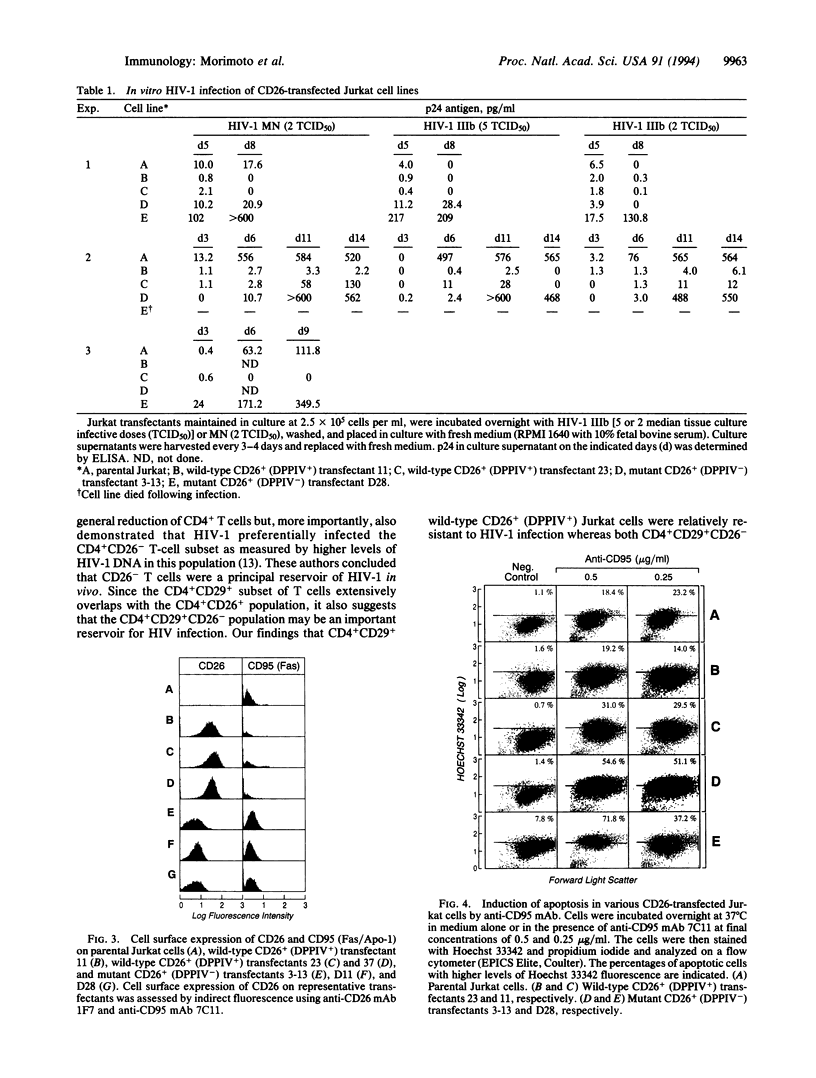
To examine the role of CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV; EC 3.4.14.5) in infection by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), we utilized CD26 cDNA-transfected Jurkat T-cell lines. Both CD26- parental Jurkat cells and mutant CD26+ (DPPIV-) transfected Jurkat cells were readily infected with HIV-1, whereas wild-type CD26+ (DPPIV+) transfected Jurkat cells were more resistant to HIV-1 infection. Our results suggest that CD26 is not essential for HIV-1 infectivity as suggested by others but that DPPIV enzyme activity may decrease the efficiency of HIV-1 infection. Of great interest, we found that mutant CD26+ (DPPIV-) transfectants and CD26- parental Jurkat cells strongly expressed CD95 (Fas/Apo-1) and were more sensitive than wild-type CD26+ (DPPIV+) transfectants to the induction of apoptosis by anti-CD95 monoclonal antibody. These results suggest that CD26 may play a role in HIV-1-associated loss of -CD4+ cells through the process of programmed cell death.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ameisen J. C., Capron A. Cell dysfunction and depletion in AIDS: the programmed cell death hypothesis. Immunol Today. 1991 Apr;12(4):102–105. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banda N. K., Bernier J., Kurahara D. K., Kurrle R., Haigwood N., Sekaly R. P., Finkel T. H. Crosslinking CD4 by human immunodeficiency virus gp120 primes T cells for activation-induced apoptosis. J Exp Med. 1992 Oct 1;176(4):1099–1106. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.4.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., van Huffel C. Unraveling function in the TNF ligand and receptor families. Science. 1994 Apr 29;264(5159):667–668. doi: 10.1126/science.8171316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazquez M. V., Madueño J. A., Gonzalez R., Jurado R., Bachovchin W. W., Peña J., Muñoz E. Selective decrease of CD26 expression in T cells from HIV-1-infected individuals. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 1;149(9):3073–3077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder C. C., Nussbaum O., Gutheil W. G., Bachovchin W. W., Berger E. A. CD26 antigen and HIV fusion? Science. 1994 May 20;264(5162):1156–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.7909959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callebaut C., Krust B., Jacotot E., Hovanessian A. G. T cell activation antigen, CD26, as a cofactor for entry of HIV in CD4+ cells. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):2045–2050. doi: 10.1126/science.7903479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini D., Planelles V., Chen I. S. CD26 antigen and HIV fusion? Science. 1994 May 20;264(5162):1160–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.7909961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Does HIV-1 Tat induce a change in viral initiation rights? Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90126-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang N. H., Torimoto Y., Deusch K., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Comitogenic effect of solid-phase immobilized anti-1F7 on human CD4 T cell activation via CD3 and CD2 pathways. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4092–4100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang N. H., Torimoto Y., Sugita K., Daley J. F., Schow P., Prado C., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Cell surface modulation of CD26 by anti-1F7 monoclonal antibody. Analysis of surface expression and human T cell activation. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):3963–3971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debatin K. M., Fahrig-Faissner A., Enenkel-Stoodt S., Kreuz W., Benner A., Krammer P. H. High expression of APO-1 (CD95) on T lymphocytes from human immunodeficiency virus-1-infected children. Blood. 1994 May 15;83(10):3101–3103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox D. A., Hussey R. E., Fitzgerald K. A., Acuto O., Poole C., Palley L., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Ta1, a novel 105 KD human T cell activation antigen defined by a monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1250–1256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gougeon M. L., Garcia S., Heeney J., Tschopp R., Lecoeur H., Guetard D., Rame V., Dauguet C., Montagnier L. Programmed cell death in AIDS-related HIV and SIV infections. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993 Jun;9(6):553–563. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gougeon M. L., Montagnier L. Apoptosis in AIDS. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1269–1270. doi: 10.1126/science.8098552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groux H., Torpier G., Monté D., Mouton Y., Capron A., Ameisen J. C. Activation-induced death by apoptosis in CD4+ T cells from human immunodeficiency virus-infected asymptomatic individuals. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):331–340. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutheil W. G., Subramanyam M., Flentke G. R., Sanford D. G., Munoz E., Huber B. T., Bachovchin W. W. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 Tat binds to dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV (CD26): a possible mechanism for Tat's immunosuppressive activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6594–6598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegen M., Niedobitek G., Klein C. E., Stein H., Fleischer B. The T cell triggering molecule Tp103 is associated with dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV activity. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):2908–2914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heike M., Möbius U., Knuth A., Meuer S., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Tissue distribution of the T cell activation antigen Ta1. Serological, immunohistochemical and biochemical investigations. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Dec;74(3):431–434. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh N., Yonehara S., Ishii A., Yonehara M., Mizushima S., Sameshima M., Hase A., Seto Y., Nagata S. The polypeptide encoded by the cDNA for human cell surface antigen Fas can mediate apoptosis. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90614-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameoka J., Tanaka T., Nojima Y., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Direct association of adenosine deaminase with a T cell activation antigen, CD26. Science. 1993 Jul 23;261(5120):466–469. doi: 10.1126/science.8101391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Booth A. G., George S. G., Ingram J., Kershaw D., Wood E. J., Young A. R. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV, a kidney brush-border serine peptidase. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):169–182. doi: 10.1042/bj1570169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Depper J. M., Greene W. C., Whalen G., Waldmann T. A., Fauci A. S. Qualitative analysis of immune function in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Evidence for a selective defect in soluble antigen recognition. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jul 11;313(2):79–84. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198507113130204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Yamada A., Kay J., Yamada K. M., Akiyama S. K., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Activation of CD4 cells by fibronectin and anti-CD3 antibody. A synergistic effect mediated by the VLA-5 fibronectin receptor complex. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1133–1148. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyaard L., Otto S. A., Jonker R. R., Mijnster M. J., Keet R. P., Miedema F. Programmed death of T cells in HIV-1 infection. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):217–219. doi: 10.1126/science.1352911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyawaki T., Uehara T., Nibu R., Tsuji T., Yachie A., Yonehara S., Taniguchi N. Differential expression of apoptosis-related Fas antigen on lymphocyte subpopulations in human peripheral blood. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 1;149(11):3753–3758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Letvin N. L., Boyd A. W., Hagan M., Brown H. M., Kornacki M. M., Schlossman S. F. The isolation and characterization of the human helper inducer T cell subset. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3762–3769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Torimoto Y., Levinson G., Rudd C. E., Schrieber M., Dang N. H., Letvin N. L., Schlossman S. F. 1F7, a novel cell surface molecule, involved in helper function of CD4 cells. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3430–3439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patience C., McKnight A., Clapham P. R., Boyd M. T., Weiss R. A., Schulz T. F. CD26 antigen and HIV fusion? Science. 1994 May 20;264(5162):1159–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.7909960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S. M., Lane H. C., Greenhouse J., Justement J. S., Baseler M., Fauci A. S. Preferential infection of CD4+ memory T cells by human immunodeficiency virus type 1: evidence for a role in the selective T-cell functional defects observed in infected individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6058–6062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Farrah T., Goodwin R. G. The TNF receptor superfamily of cellular and viral proteins: activation, costimulation, and death. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):959–962. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. M., Snowden R. T., Skilleter D. N., Dinsdale D., Ormerod M. G., Cohen G. M. A flow-cytometric method for the separation and quantitation of normal and apoptotic thymocytes. Anal Biochem. 1992 Aug 1;204(2):351–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90251-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Camerini D., Seed B., Torimoto Y., Dang N. H., Kameoka J., Dahlberg H. N., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Cloning and functional expression of the T cell activation antigen CD26. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 15;149(2):481–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Kameoka J., Yaron A., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. The costimulatory activity of the CD26 antigen requires dipeptidyl peptidase IV enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4586–4590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torimoto Y., Dang N. H., Tanaka T., Prado C., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Biochemical characterization of CD26 (dipeptidyl peptidase IV): functional comparison of distinct epitopes recognized by various anti-CD26 monoclonal antibodies. Mol Immunol. 1992 Feb;29(2):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(92)90099-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torimoto Y., Dang N. H., Vivier E., Tanaka T., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Coassociation of CD26 (dipeptidyl peptidase IV) with CD45 on the surface of human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;147(8):2514–2517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trauth B. C., Klas C., Peters A. M., Matzku S., Möller P., Falk W., Debatin K. M., Krammer P. H. Monoclonal antibody-mediated tumor regression by induction of apoptosis. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):301–305. doi: 10.1126/science.2787530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanham G., Kestens L., De Meester I., Vingerhoets J., Penne G., Vanhoof G., Scharpé S., Heyligen H., Bosmans E., Ceuppens J. L. Decreased expression of the memory marker CD26 on both CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes of HIV-infected subjects. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1993 Jul;6(7):749–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viscidi R. P., Mayur K., Lederman H. M., Frankel A. D. Inhibition of antigen-induced lymphocyte proliferation by Tat protein from HIV-1. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1606–1608. doi: 10.1126/science.2556795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Noesel C. J., Gruters R. A., Terpstra F. G., Schellekens P. T., van Lier R. A., Miedema F. Functional and phenotypic evidence for a selective loss of memory T cells in asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus-infected men. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):293–299. doi: 10.1172/JCI114698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


