Abstract
Cells in the neuroectoderm of Drosophila become either neural or epidermal progenitors. A critical threshold concentration of proneural gene products in a given cell causes it to develop as a neuroblast. The proteins encoded by the genes Delta (Dl) and Notch (N) act as the source and the receptor, respectively, of inhibitory signals sent by the neuroblast to neighboring cells that prevent these cells from also adopting the neural fate. We show here that proneural gene products activate transcription of Delta in the neuroectoderm by binding to specific sites in its promoter. This transcriptional activation enhances lateral inhibition and thus helps ensure that cells in the vicinity of prospective neuroblasts will themselves become epidermoblasts.
Full text
PDF
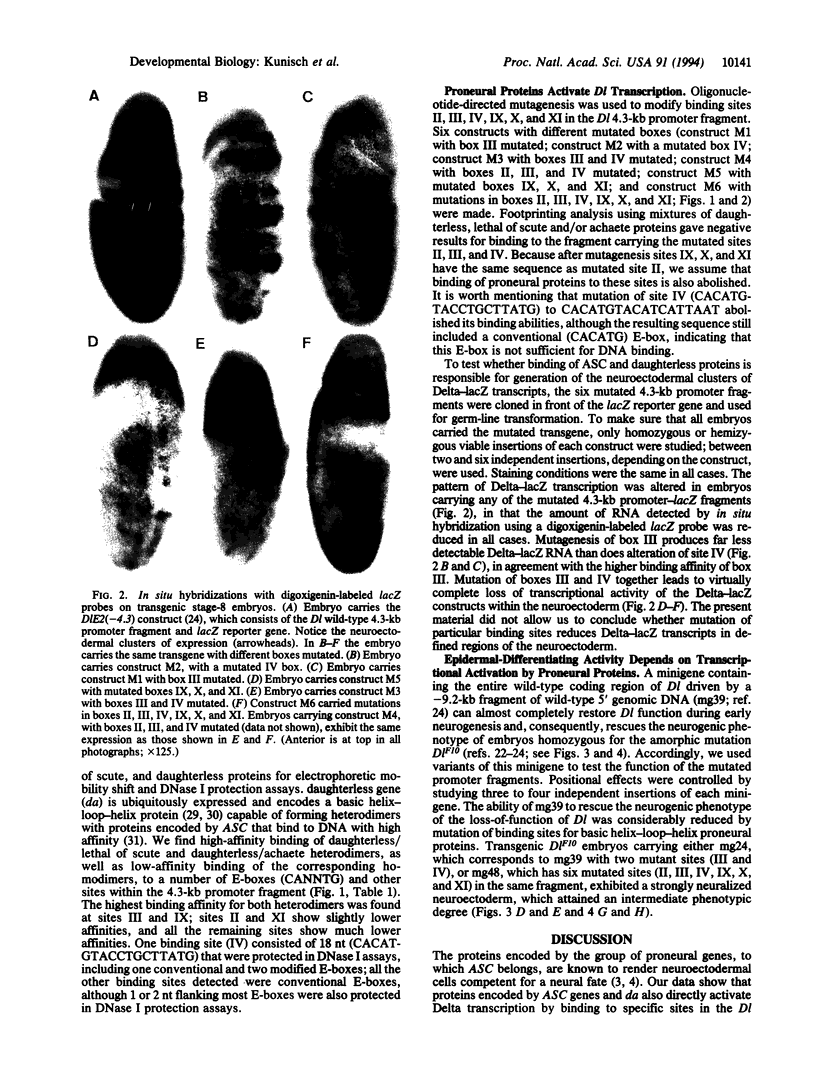
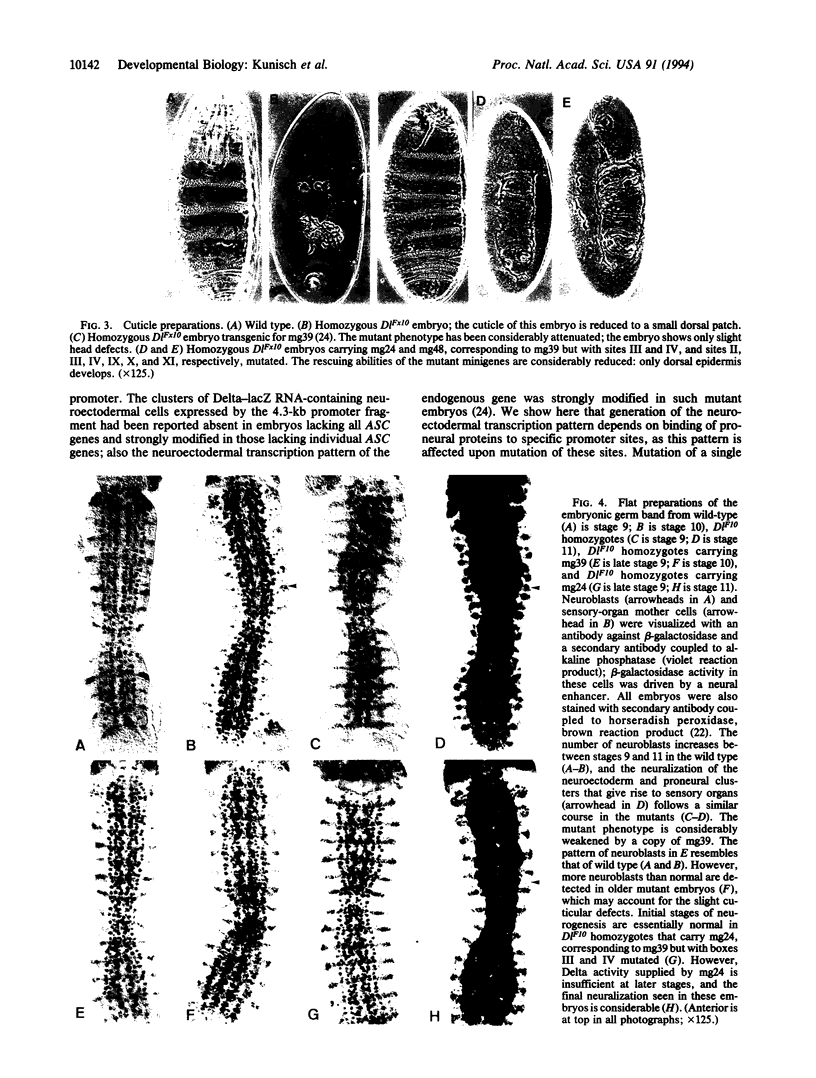

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso M. C., Cabrera C. V. The achaete-scute gene complex of Drosophila melanogaster comprises four homologous genes. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2585–2591. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03108.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caudy M., Vässin H., Brand M., Tuma R., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. daughterless, a Drosophila gene essential for both neurogenesis and sex determination, has sequence similarities to myc and the achaete-scute complex. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1061–1067. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90250-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronmiller C., Schedl P., Cline T. W. Molecular characterization of daughterless, a Drosophila sex determination gene with multiple roles in development. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1666–1676. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubas P., de Celis J. F., Campuzano S., Modolell J. Proneural clusters of achaete-scute expression and the generation of sensory organs in the Drosophila imaginal wing disc. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):996–1008. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delidakis C., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. The Enhancer of split [E(spl)] locus of Drosophila encodes seven independent helix-loop-helix proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8731–8735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doe C. Q., Goodman C. S. Early events in insect neurogenesis. II. The role of cell interactions and cell lineage in the determination of neuronal precursor cells. Dev Biol. 1985 Sep;111(1):206–219. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90446-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehon R. G., Kooh P. J., Rebay I., Regan C. L., Xu T., Muskavitch M. A., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Molecular interactions between the protein products of the neurogenic loci Notch and Delta, two EGF-homologous genes in Drosophila. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):523–534. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90534-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghysen A., Dambly-Chaudière C., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Cell interactions and gene interactions in peripheral neurogenesis. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):723–733. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haenlin M., Kramatschek B., Campos-Ortega J. A. The pattern of transcription of the neurogenic gene Delta of Drosophila melanogaster. Development. 1990 Nov;110(3):905–914. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.3.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haenlin M., Kunisch M., Kramatschek B., Campos-Ortega J. A. Genomic regions regulating early embryonic expression of the Drosophila neurogenic gene Delta. Mech Dev. 1994 Jul;47(1):99–110. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(94)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitzler P., Simpson P. Altered epidermal growth factor-like sequences provide evidence for a role of Notch as a receptor in cell fate decisions. Development. 1993 Mar;117(3):1113–1123. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.3.1113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitzler P., Simpson P. The choice of cell fate in the epidermis of Drosophila. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1083–1092. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90263-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klämbt C., Knust E., Tietze K., Campos-Ortega J. A. Closely related transcripts encoded by the neurogenic gene complex enhancer of split of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):203–210. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03365.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knust E., Schrons H., Grawe F., Campos-Ortega J. A. Seven genes of the Enhancer of split complex of Drosophila melanogaster encode helix-loop-helix proteins. Genetics. 1992 Oct;132(2):505–518. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber T., Kidd S., Alcamo E., Corbin V., Young M. W. Antineurogenic phenotypes induced by truncated Notch proteins indicate a role in signal transduction and may point to a novel function for Notch in nuclei. Genes Dev. 1993 Oct;7(10):1949–1965. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.10.1949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber T., Wesley C. S., Alcamo E., Hassel B., Krane J. F., Campos-Ortega J. A., Young M. W. Single amino acid substitutions in EGF-like elements of Notch and Delta modify Drosophila development and affect cell adhesion in vitro. Neuron. 1992 Nov;9(5):847–859. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90238-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez C., Modolell J. Cross-regulatory interactions between the proneural achaete and scute genes of Drosophila. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1485–1487. doi: 10.1126/science.1900954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oellers N., Dehio M., Knust E. bHLH proteins encoded by the Enhancer of split complex of Drosophila negatively interfere with transcriptional activation mediated by proneural genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1994 Sep 1;244(5):465–473. doi: 10.1007/BF00583897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeath J. B., Carroll S. B. Regulation of achaete-scute gene expression and sensory organ pattern formation in the Drosophila wing. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):984–995. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl G., Fitzgerald K., Greenwald I. Intrinsic activity of the Lin-12 and Notch intracellular domains in vivo. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90424-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stüttem I., Campos-Ortega J. A. Cell commitment and cell interactions in the ectoderm of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Suppl. 1991;Suppl 2:39–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taghert P. H., Doe C. Q., Goodman C. S. Cell determination and regulation during development of neuroblasts and neurones in grasshopper embryo. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):163–165. doi: 10.1038/307163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Technau G. M., Campos-Ortega J. A. Cell autonomy of expression of neurogenic genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4500–4504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thisse C., Perrin-Schmitt F., Stoetzel C., Thisse B. Sequence-specific transactivation of the Drosophila twist gene by the dorsal gene product. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1191–1201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90014-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Doren M., Powell P. A., Pasternak D., Singson A., Posakony J. W. Spatial regulation of proneural gene activity: auto- and cross-activation of achaete is antagonized by extramacrochaetae. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2592–2605. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villares R., Cabrera C. V. The achaete-scute gene complex of D. melanogaster: conserved domains in a subset of genes required for neurogenesis and their homology to myc. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):415–424. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90495-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]