Abstract
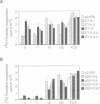
The exchange of nerve growth factor receptor/Trk and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) phospholipase C gamma (PLC gamma) binding sites resulted in the transfer of their distinct affinities for this Src homology 2 domain-containing protein. Relative to wild-type EGFR, the PLC gamma affinity increase of the EGFR switch mutant EGFR.X enhanced its inositol trisphosphate (IP3) and calcium signals and resulted in a more sustained mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase activation and accelerated receptor dephosphorylation. In parallel, EGFR.X exhibited a significantly decreased mitogenic and transforming potential in NIH 3T3 cells. Conversely, the transfer of the EGFR PLC gamma binding site into the Trk cytoplasmic domain context impaired the IP3/calcium signal and attenuated the MAP kinase activation and receptor dephosphorylation, but resulted in an enhancement of the ETR.X exchange mutant mitogenic and oncogenic capacity. Our findings establish the significance of PLC gamma affinity for signal definition, the role of this receptor tyrosine kinase substrate as a negative feedback regulator and the importance of this regulatory function for mitogenesis and its disturbance in oncogenic aberrations.
Full text
PDF
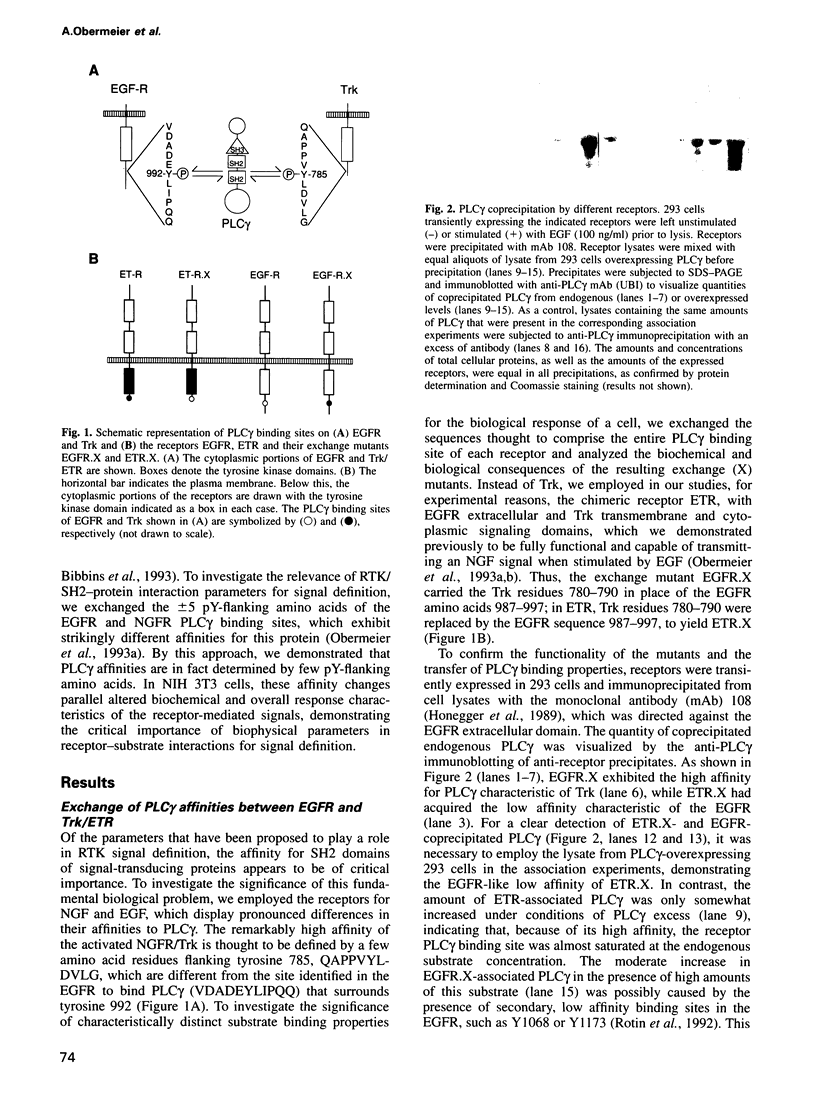





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronheim A., Engelberg D., Li N., al-Alawi N., Schlessinger J., Karin M. Membrane targeting of the nucleotide exchange factor Sos is sufficient for activating the Ras signaling pathway. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):949–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backer J. M., Myers M. G., Jr, Shoelson S. E., Chin D. J., Sun X. J., Miralpeix M., Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Schlessinger J. Phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase is activated by association with IRS-1 during insulin stimulation. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3469–3479. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibbins K. B., Boeuf H., Varmus H. E. Binding of the Src SH2 domain to phosphopeptides is determined by residues in both the SH2 domain and the phosphopeptides. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7278–7287. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgering B. M., de Vries-Smits A. M., Medema R. H., van Weeren P. C., Tertoolen L. G., Bos J. L. Epidermal growth factor induces phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 via multiple pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7248–7256. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao T. S., Foster D. A., Rapp U. R., Rosner M. R. Differential Raf requirement for activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by growth factors, phorbol esters, and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7337–7341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordon-Cardo C., Tapley P., Jing S. Q., Nanduri V., O'Rourke E., Lamballe F., Kovary K., Klein R., Jones K. R., Reichardt L. F. The trk tyrosine protein kinase mediates the mitogenic properties of nerve growth factor and neurotrophin-3. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):173–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90149-s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countaway J. L., McQuilkin P., Gironès N., Davis R. J. Multisite phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Use of site-directed mutagenesis to examine the role of serine/threonine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3407–3416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowley S., Paterson H., Kemp P., Marshall C. J. Activation of MAP kinase kinase is necessary and sufficient for PC12 differentiation and for transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):841–852. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dikic I., Schlessinger J., Lax I. PC12 cells overexpressing the insulin receptor undergo insulin-dependent neuronal differentiation. Curr Biol. 1994 Aug 1;4(8):702–708. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00155-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder S., Zhou M., Hu P., Ureña J., Ullrich A., Chaudhuri M., White M., Shoelson S. E., Schlessinger J. SH2 domains exhibit high-affinity binding to tyrosine-phosphorylated peptides yet also exhibit rapid dissociation and exchange. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1449–1455. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fendly B. M., Winget M., Hudziak R. M., Lipari M. T., Napier M. A., Ullrich A. Characterization of murine monoclonal antibodies reactive to either the human epidermal growth factor receptor or HER2/neu gene product. Cancer Res. 1990 Mar 1;50(5):1550–1558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G. A., Clementi E., Raichman M., Südhof T., Ullrich A., Meldolesi J. Stable expression of truncated inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor subunits in 3T3 fibroblasts. Coordinate signaling changes and differential suppression of cell growth and transformation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 29;269(30):19216–19224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandino L., Munaron L., Naldini L., Ferracini R., Magni M., Comoglio P. M. Intracellular calcium regulates the tyrosine kinase receptor encoded by the MET oncogene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16098–16104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. J., Nye S. H., Hantzopoulos P., Macchi M. J., Squinto S. P., Goldfarb M., Yancopoulos G. D. TrkB mediates BDNF/NT-3-dependent survival and proliferation in fibroblasts lacking the low affinity NGF receptor. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90629-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Kim J. W., Machesky L. M., Rhee S. G., Pollard T. D. Regulation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by profilin and tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1231–1233. doi: 10.1126/science.1848725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajnóczky G., Thomas A. P. The inositol trisphosphate calcium channel is inactivated by inositol trisphosphate. Nature. 1994 Aug 11;370(6489):474–477. doi: 10.1038/370474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson P. I., Schulman H. Neuronal Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:559–601. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisermann G. J., Wiley H. S., Walsh B. J., Ingraham H. A., Fiol C. J., Gill G. N. Mutational removal of the Thr669 and Ser671 phosphorylation sites alters substrate specificity and ligand-induced internalization of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12820–12827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameshita I., Fujisawa H. A sensitive method for detection of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activity in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 15;183(1):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. K., Kim J. W., Zilberstein A., Margolis B., Kim J. G., Schlessinger J., Rhee S. G. PDGF stimulation of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis requires PLC-gamma 1 phosphorylation on tyrosine residues 783 and 1254. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):435–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90461-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krook A., Rapoport M. J., Anderson S., Pross H., Zhou Y. C., Denhardt D. T., Delovitch T. L., Haliotis T. p21ras and protein kinase C function in distinct and interdependent signaling pathways in C3H 10T1/2 fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1471–1479. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H., Ghose-Dastidar J., Winawer S., Friedman E. Signal transduction through extracellular signal-regulated kinase-like pp57 blocked in differentiated cells having low protein kinase C beta activity. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):5255–5263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maly K., Doppler W., Oberhuber H., Meusburger H., Hofmann J., Jaggi R., Grunicke H. H. Desensitization of the Ca2+-mobilizing system to serum growth factors by Ha-ras and v-mos. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4212–4216. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. J., Matten W. T., Hermann A. S., Candia J. M., Rong S., Fukasawa K., Vande Woude G. F., Ahn N. G. Transformation of mammalian cells by constitutively active MAP kinase kinase. Science. 1994 Aug 12;265(5174):966–970. doi: 10.1126/science.8052857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx J. Forging a path to the nucleus. Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1588–1590. doi: 10.1126/science.8503004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Hernández-Sotomayor S. M., Tonks N. K., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Increase of the catalytic activity of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1253–1256. doi: 10.1126/science.1700866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Intracellular signaling by hydrolysis of phospholipids and activation of protein kinase C. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):607–614. doi: 10.1126/science.1411571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obermeier A., Bradshaw R. A., Seedorf K., Choidas A., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Neuronal differentiation signals are controlled by nerve growth factor receptor/Trk binding sites for SHC and PLC gamma. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 1;13(7):1585–1590. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06421.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obermeier A., Halfter H., Wiesmüller K. H., Jung G., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Tyrosine 785 is a major determinant of Trk--substrate interaction. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):933–941. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05734.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obermeier A., Lammers R., Wiesmüller K. H., Jung G., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Identification of Trk binding sites for SHC and phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase and formation of a multimeric signaling complex. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):22963–22966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotou G., Gish G., End P., Truong O., Gout I., Dhand R., Fry M. J., Hiles I., Pawson T., Waterfield M. D. Interactions between SH2 domains and tyrosine-phosphorylated platelet-derived growth factor beta-receptor sequences: analysis of kinetic parameters by a novel biosensor-based approach. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3567–3576. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qui M. S., Green S. H. PC12 cell neuronal differentiation is associated with prolonged p21ras activity and consequent prolonged ERK activity. Neuron. 1992 Oct;9(4):705–717. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90033-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redemann N., Holzmann B., von Rüden T., Wagner E. F., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Anti-oncogenic activity of signalling-defective epidermal growth factor receptor mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):491–498. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotin D., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Daly R. J., Daum G., Li N., Fischer E. H., Burgess W. H., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. SH2 domains prevent tyrosine dephosphorylation of the EGF receptor: identification of Tyr992 as the high-affinity binding site for SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):559–567. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Growth factor signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90177-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shariff A., Luna E. J. Diacylglycerol-stimulated formation of actin nucleation sites at plasma membranes. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):245–247. doi: 10.1126/science.1373523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takishima K., Griswold-Prenner I., Ingebritsen T., Rosner M. R. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor T669 peptide kinase from 3T3-L1 cells is an EGF-stimulated "MAP" kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2520–2524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traverse S., Gomez N., Paterson H., Marshall C., Cohen P. Sustained activation of the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade may be required for differentiation of PC12 cells. Comparison of the effects of nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 1;288(Pt 2):351–355. doi: 10.1042/bj2880351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traverse S., Seedorf K., Paterson H., Marshall C. J., Cohen P., Ullrich A. EGF triggers neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells that overexpress the EGF receptor. Curr Biol. 1994 Aug 1;4(8):694–701. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valius M., Kazlauskas A. Phospholipase C-gamma 1 and phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase are the downstream mediators of the PDGF receptor's mitogenic signal. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):321–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90232-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Horn D. J., Myers M. G., Jr, Backer J. M. Direct activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase by the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):29–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L. J., Rhee S. G., Williamson J. R. Epidermal growth factor-induced activation and translocation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 to the cytoskeleton in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7156–7162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]