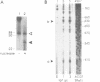
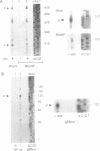
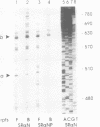
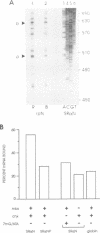
Abstract
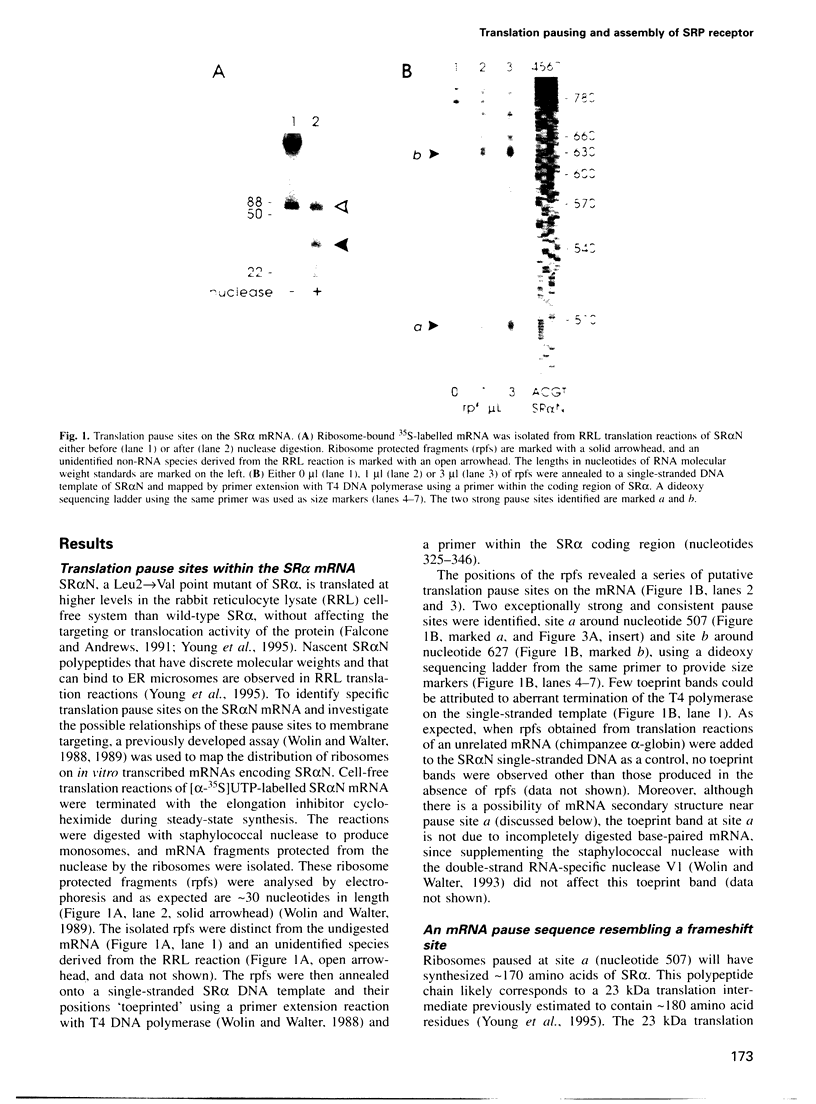
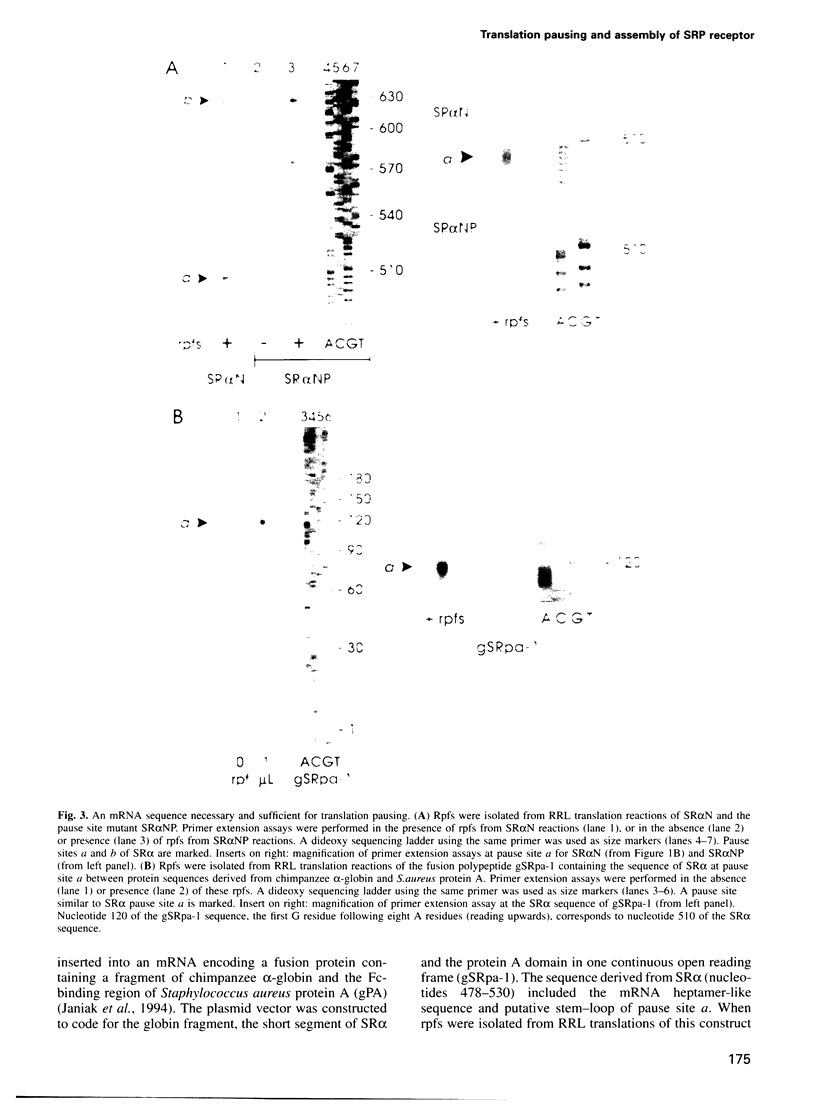
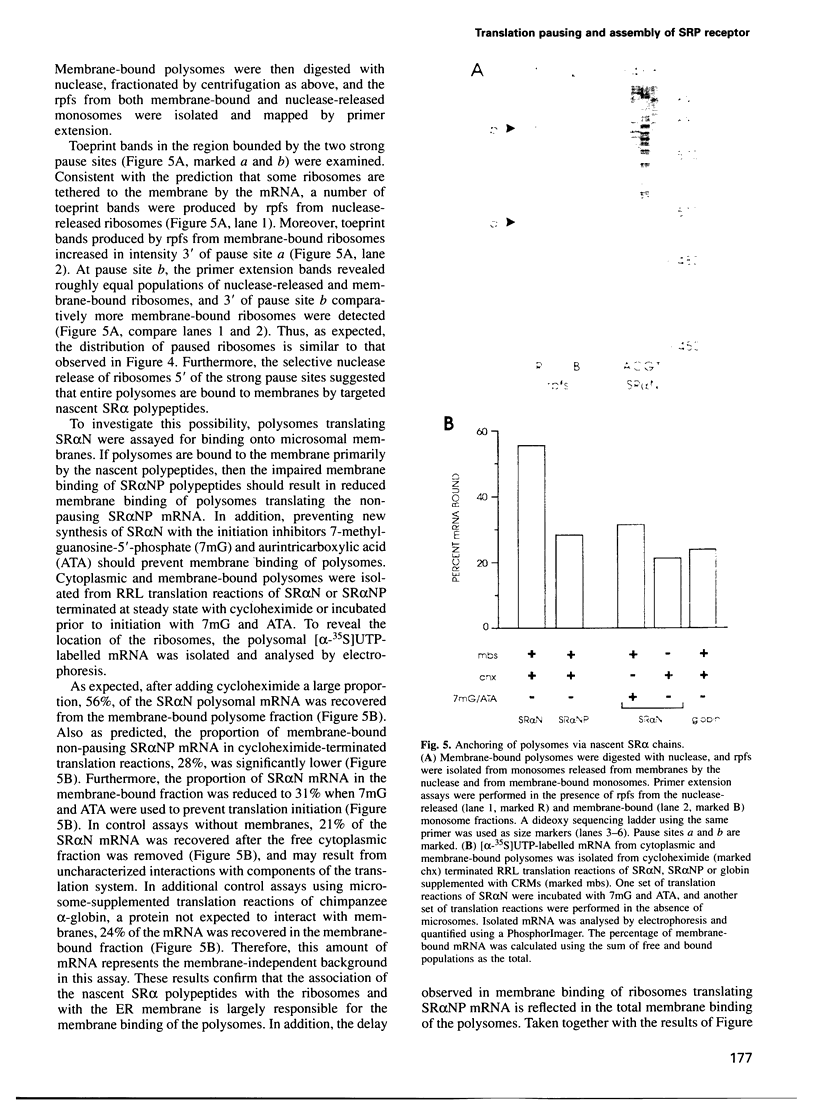
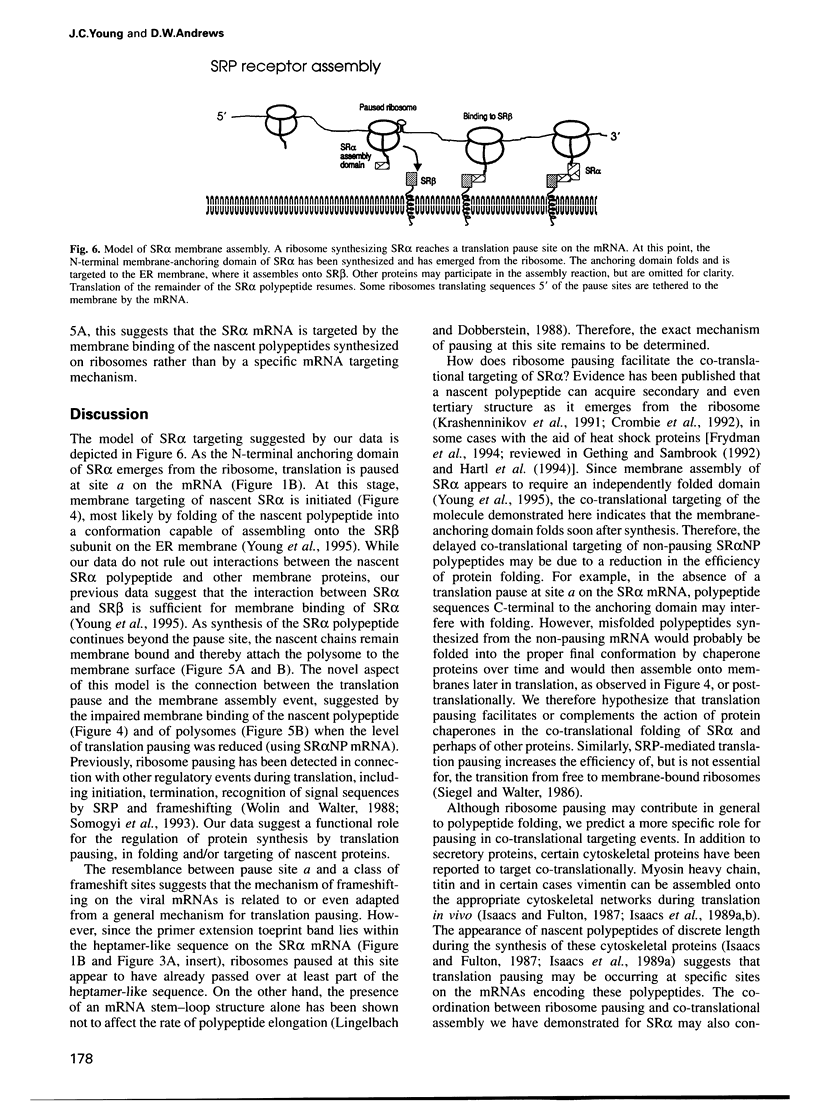
Many proteins, including the alpha subunit of the signal recognition particle receptor (SR alpha), are targeted within the cell by poorly defined mechanisms. A 140 residue N-terminal domain of SR alpha targets and anchors the polypeptide to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane by a mechanism independent of the pathway involving the signal recognition particle. To investigate the mechanism of membrane anchoring, translation pause sites on the SR alpha mRNA were used to examine the targeting of translation intermediates. A strong pause site at nucleotide 507 of the mRNA open reading frame corresponded with the shortest nascent SR alpha polypeptide able to assemble on membranes. An mRNA sequence at this pause site that resembles a class of viral -1 frameshift sequences caused translation pausing when transferred into another mRNA context. Site-directed mutagenesis of the mRNA greatly reduced translation pausing without altering the polypeptide sequence, demonstrating unambiguously a role for this mRNA sequence in translation pausing. SR alpha polypeptides synthesized from the non-pausing mRNA were impaired in co-translational membrane anchoring. Furthermore, co-translational membrane assembly of SR alpha appears to anchor polysomes translating SR alpha to membranes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews D. W., Lauffer L., Walter P., Lingappa V. R. Evidence for a two-step mechanism involved in assembly of functional signal recognition particle receptor. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):797–810. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinkowa A. L., Walker J. R. Programmed ribosomal frameshifting generates the Escherichia coli DNA polymerase III gamma subunit from within the tau subunit reading frame. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1725–1729. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley I., Jenner A. J., Inglis S. C. Mutational analysis of the "slippery-sequence" component of a coronavirus ribosomal frameshifting signal. J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 20;227(2):463–479. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90901-U. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamorro M., Parkin N., Varmus H. E. An RNA pseudoknot and an optimal heptameric shift site are required for highly efficient ribosomal frameshifting on a retroviral messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):713–717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X., Chamorro M., Lee S. I., Shen L. X., Hines J. V., Tinoco I., Jr, Varmus H. E. Structural and functional studies of retroviral RNA pseudoknots involved in ribosomal frameshifting: nucleotides at the junction of the two stems are important for efficient ribosomal frameshifting. EMBO J. 1995 Feb 15;14(4):842–852. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07062.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crombie T., Swaffield J. C., Brown A. J. Protein folding within the cell is influenced by controlled rates of polypeptide elongation. J Mol Biol. 1992 Nov 5;228(1):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90486-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doohan J. P., Samuel C. E. Biosynthesis of reovirus-specified polypeptides: ribosome pausing during the translation of reovirus S1 mRNA. Virology. 1992 Feb;186(2):409–425. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90006-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcone D., Andrews D. W. Both the 5' untranslated region and the sequences surrounding the start site contribute to efficient initiation of translation in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2656–2664. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk H., Mador N., Udi R., Panet A., Honigman A. Two cis-acting signals control ribosomal frameshift between human T-cell leukemia virus type II gag and pro genes. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):6273–6277. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.6273-6277.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower A. M., McHenry C. S. The gamma subunit of DNA polymerase III holoenzyme of Escherichia coli is produced by ribosomal frameshifting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3713–3717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Kierzek R., Jaeger J. A., Sugimoto N., Caruthers M. H., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydman J., Nimmesgern E., Ohtsuka K., Hartl F. U. Folding of nascent polypeptide chains in a high molecular mass assembly with molecular chaperones. Nature. 1994 Jul 14;370(6485):111–117. doi: 10.1038/370111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia A., van Duin J., Pleij C. W. Differential response to frameshift signals in eukaryotic and prokaryotic translational systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):401–406. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Blobel G., Walter P. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. I. Detection in the microsomal membrane of a receptor for the signal recognition particle. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):463–469. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurevich V. V., Pokrovskaya I. D., Obukhova T. A., Zozulya S. A. Preparative in vitro mRNA synthesis using SP6 and T7 RNA polymerases. Anal Biochem. 1991 Jun;195(2):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90318-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. U., Hlodan R., Langer T. Molecular chaperones in protein folding: the art of avoiding sticky situations. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jan;19(1):20–25. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield D. L., Levin J. G., Rein A., Oroszlan S. Translational suppression in retroviral gene expression. Adv Virus Res. 1992;41:193–239. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60037-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hortsch M., Avossa D., Meyer D. I. A structural and functional analysis of the docking protein. Characterization of active domains by proteolysis and specific antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9137–9145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs W. B., Cook R. K., Van Atta J. C., Redmond C. M., Fulton A. B. Assembly of vimentin in cultured cells varies with cell type. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17953–17960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs W. B., Fulton A. B. Cotranslational assembly of myosin heavy chain in developing cultured skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6174–6178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs W. B., Kim I. S., Struve A., Fulton A. B. Biosynthesis of titin in cultured skeletal muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2189–2195. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Hunt T. Preparation and use of nuclease-treated rabbit reticulocyte lysates for the translation of eukaryotic messenger RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:50–74. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janiak F., Glover J. R., Leber B., Rachubinski R. A., Andrews D. W. Targeting of passenger protein domains to multiple intracellular membranes. Biochem J. 1994 May 15;300(Pt 1):191–199. doi: 10.1042/bj3000191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. K., Hollingsworth M. J. Localization of in vivo ribosome pause sites. Anal Biochem. 1992 Oct;206(1):183–188. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(05)80031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Klein P. G., Mullet J. E. Ribosomes pause at specific sites during synthesis of membrane-bound chloroplast reaction center protein D1. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):14931–14938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasheninnikov I. A., Komar A. A., Adzhubei I. A. Nonuniform size distribution of nascent globin peptides, evidence for pause localization sites, and a contranslational protein-folding model. J Protein Chem. 1991 Oct;10(5):445–453. doi: 10.1007/BF01025472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauffer L., Garcia P. D., Harkins R. N., Coussens L., Ullrich A., Walter P. Topology of signal recognition particle receptor in endoplasmic reticulum membrane. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):334–338. doi: 10.1038/318334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingelbach K., Dobberstein B. An extended RNA/RNA duplex structure within the coding region of mRNA does not block translational elongation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3405–3414. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. D., Tajima S., Lauffer L., Walter P. The beta subunit of the signal recognition particle receptor is a transmembrane GTPase that anchors the alpha subunit, a peripheral membrane GTPase, to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;128(3):273–282. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.3.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Lerman L. S., Maniatis T. A general method for saturation mutagenesis of cloned DNA fragments. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):242–247. doi: 10.1126/science.2990046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perara E., Lingappa V. R. A former amino terminal signal sequence engineered to an internal location directs translocation of both flanking protein domains. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2292–2301. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polard P., Prère M. F., Chandler M., Fayet O. Programmed translational frameshifting and initiation at an AUU codon in gene expression of bacterial insertion sequence IS911. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 5;222(3):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90490-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel V., Walter P. Removal of the Alu structural domain from signal recognition particle leaves its protein translocation activity intact. Nature. 1986 Mar 6;320(6057):81–84. doi: 10.1038/320081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Jenner A. J., Brierley I., Inglis S. C. Ribosomal pausing during translation of an RNA pseudoknot. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6931–6940. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima S., Lauffer L., Rath V. L., Walter P. The signal recognition particle receptor is a complex that contains two distinct polypeptide chains. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1167–1178. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchihashi Z., Kornberg A. Translational frameshifting generates the gamma subunit of DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2516–2520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verner K., Schatz G. Protein translocation across membranes. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1307–1313. doi: 10.1126/science.2842866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vögele K., Schwartz E., Welz C., Schiltz E., Rak B. High-level ribosomal frameshifting directs the synthesis of IS150 gene products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4377–4385. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Preparation of microsomal membranes for cotranslational protein translocation. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:84–93. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm J. E., Vale R. D. RNA on the move: the mRNA localization pathway. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(2):269–274. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Walter P. Discrete nascent chain lengths are required for the insertion of presecretory proteins into microsomal membranes. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;121(6):1211–1219. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.6.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Walter P. Ribosome pausing and stacking during translation of a eukaryotic mRNA. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3559–3569. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03233.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Walter P. Signal recognition particle mediates a transient elongation arrest of preprolactin in reticulocyte lysate. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2617–2622. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. C., Ursini J., Legate K. R., Miller J. D., Walter P., Andrews D. W. An amino-terminal domain containing hydrophobic and hydrophilic sequences binds the signal recognition particle receptor alpha subunit to the beta subunit on the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 30;270(26):15650–15657. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.26.15650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]