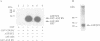Abstract
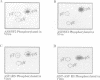
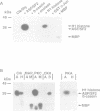
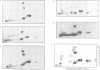
Mammalian Clk/Sty is the prototype for a family of dual specificity kinases (termed LAMMER kinases) that have been conserved in evolution, but whose physiological substrates are unknown. In a yeast two-hybrid screen, the Clk/Sty kinase specifically interacted with RNA binding proteins, particularly members of the serine/arginine-rich (SR) family of splicing factors. Clk/Sty itself has an serine/arginine-rich non-catalytic N-terminal region which is important for its association with SR splicing factors. In vitro, Clk/Sty efficiently phosphorylated the SR family member ASF/SF2 on serine residues located within its serine/arginine-rich region (the RS domain). Tryptic phosphopeptide mapping demonstrated that the sites on ASF/SF2 phosphorylated in vitro overlap with those phosphorylated in vivo. Immunofluorescence studies showed that a catalytically inactive form of Clk/Sty co-localized with SR proteins in nuclear speckles. Overexpression of the active Clk/Sty kinase caused a redistribution of SR proteins within the nucleus. These results suggest that Clk/Sty kinase directly regulates the activity and compartmentalization of SR splicing factors.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amrein H., Hedley M. L., Maniatis T. The role of specific protein-RNA and protein-protein interactions in positive and negative control of pre-mRNA splicing by Transformer 2. Cell. 1994 Feb 25;76(4):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90512-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayane M., Preuss U., Köhler G., Nielsen P. J. A differentially expressed murine RNA encoding a protein with similarities to two types of nucleic acid binding motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 25;19(6):1273–1278. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.6.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-David Y., Letwin K., Tannock L., Bernstein A., Pawson T. A mammalian protein kinase with potential for serine/threonine and tyrosine phosphorylation is related to cell cycle regulators. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):317–325. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07952.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender J., Fink G. R. AFC1, a LAMMER kinase from Arabidopsis thaliana, activates STE12-dependent processes in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):12105–12109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.12105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
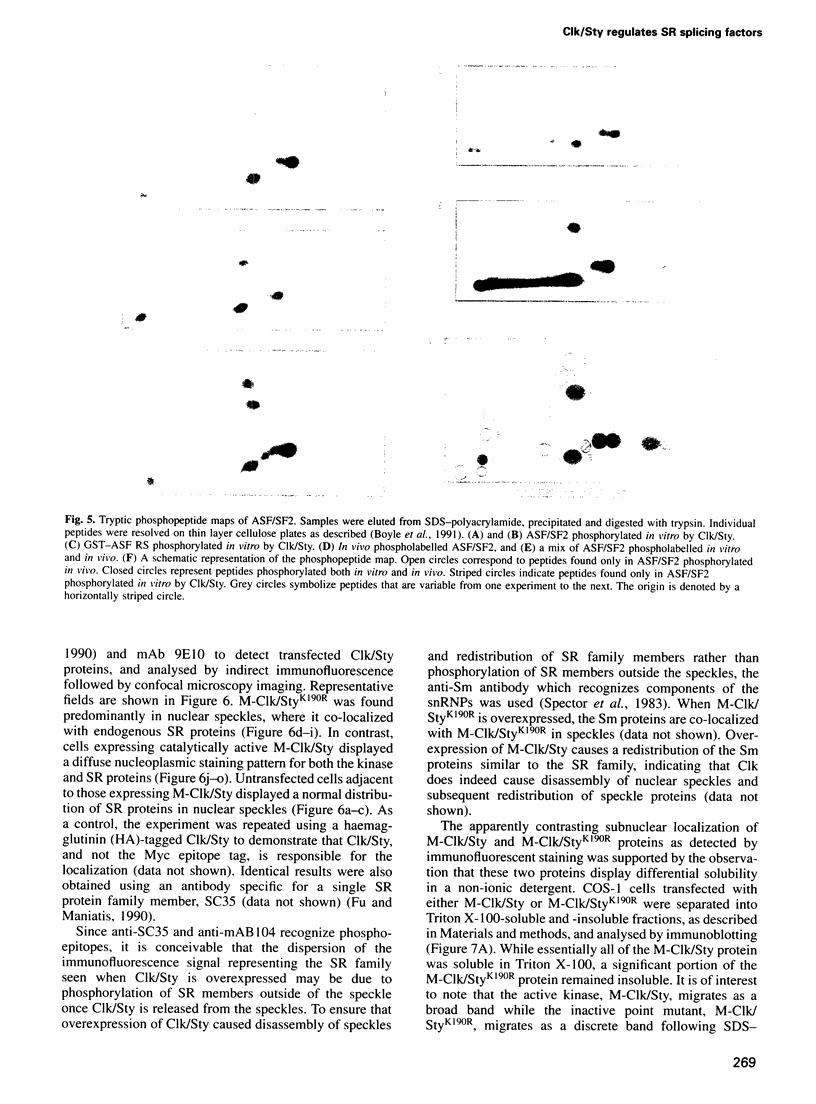
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd C. G., Dreyfuss G. Conserved structures and diversity of functions of RNA-binding proteins. Science. 1994 Jul 29;265(5172):615–621. doi: 10.1126/science.8036511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardinali B., Cohen P. T., Lamond A. I. Protein phosphatase 1 can modulate alternative 5' splice site selection in a HeLa splicing extract. FEBS Lett. 1994 Oct 3;352(3):276–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00973-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cáceres J. F., Krainer A. R. Functional analysis of pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2/ASF structural domains. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4715–4726. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06160.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douville E., Duncan P., Abraham N., Bell J. C. Dual specificity kinases--a new family of signal transducers. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1994 Mar;13(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00690414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Matunis M. J., Piñol-Roma S., Burd C. G. hnRNP proteins and the biogenesis of mRNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:289–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan P. I., Howell B. W., Marius R. M., Drmanic S., Douville E. M., Bell J. C. Alternative splicing of STY, a nuclear dual specificity kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 15;270(37):21524–21531. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.37.21524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durfee T., Becherer K., Chen P. L., Yeh S. H., Yang Y., Kilburn A. E., Lee W. H., Elledge S. J. The retinoblastoma protein associates with the protein phosphatase type 1 catalytic subunit. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):555–569. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Leser G., Martin T. E. Ultrastructural distribution of nuclear ribonucleoproteins as visualized by immunocytochemistry on thin sections. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):358–363. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Factor required for mammalian spliceosome assembly is localized to discrete regions in the nucleus. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):437–441. doi: 10.1038/343437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D. Specific commitment of different pre-mRNAs to splicing by single SR proteins. Nature. 1993 Sep 2;365(6441):82–85. doi: 10.1038/365082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Manley J. L. A protein factor, ASF, controls cell-specific alternative splicing of SV40 early pre-mRNA in vitro. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Zuo P., Manley J. L. Primary structure of the human splicing factor ASF reveals similarities with Drosophila regulators. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90626-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Moriyama K., Matsuda S., Okumura E., Kishimoto T., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K., Yahara I., Sakai H., Nishida E. Xenopus M phase MAP kinase: isolation of its cDNA and activation by MPF. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2661–2668. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gui J. F., Lane W. S., Fu X. D. A serine kinase regulates intracellular localization of splicing factors in the cell cycle. Nature. 1994 Jun 23;369(6482):678–682. doi: 10.1038/369678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gui J. F., Tronchère H., Chandler S. D., Fu X. D. Purification and characterization of a kinase specific for the serine- and arginine-rich pre-mRNA splicing factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):10824–10828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.10824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanes J., von der Kammer H., Klaudiny J., Scheit K. H. Characterization by cDNA cloning of two new human protein kinases. Evidence by sequence comparison of a new family of mammalian protein kinases. J Mol Biol. 1994 Dec 16;244(5):665–672. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M. Protein kinase catalytic domain sequence database: identification of conserved features of primary structure and classification of family members. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:38–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00126-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell B. W., Afar D. E., Lew J., Douville E. M., Icely P. L., Gray D. A., Bell J. C. STY, a tyrosine-phosphorylating enzyme with sequence homology to serine/threonine kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):568–572. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Deerinck T. J., Ellisman M. H., Spector D. L. In vivo analysis of the stability and transport of nuclear poly(A)+ RNA. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(4):877–899. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.4.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. W., Smith K. A. Molecular cloning of a novel human cdc2/CDC28-like protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3402–3407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenan D. J., Query C. C., Keene J. D. RNA recognition: towards identifying determinants of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90088-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Structure of a peptide inhibitor bound to the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):414–420. doi: 10.1126/science.1862343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohtz J. D., Jamison S. F., Will C. L., Zuo P., Lührmann R., Garcia-Blanco M. A., Manley J. L. Protein-protein interactions and 5'-splice-site recognition in mammalian mRNA precursors. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):119–124. doi: 10.1038/368119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. The essential pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 influences 5' splice site selection by activating proximal sites. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Mayeda A., Kozak D., Binns G. Functional expression of cloned human splicing factor SF2: homology to RNA-binding proteins, U1 70K, and Drosophila splicing regulators. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):383–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90627-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Bingham P. M. Arginine/serine-rich domains of the su(wa) and tra RNA processing regulators target proteins to a subnuclear compartment implicated in splicing. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg R. A., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. Dual-specificity protein kinases: will any hydroxyl do? Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Mar;17(3):114–119. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermoud J. E., Cohen P. T., Lamond A. I. Regulation of mammalian spliceosome assembly by a protein phosphorylation mechanism. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 1;13(23):5679–5688. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06906.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermoud J. E., Cohen P., Lamond A. I. Ser/Thr-specific protein phosphatases are required for both catalytic steps of pre-mRNA splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 25;20(20):5263–5269. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.20.5263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. P., Murphy M. B., Landreth G. The dual-specificity CLK kinase induces neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6954–6961. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabha R., Gehrung S., Snyder M. The KNS1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a nonessential protein kinase homologue that is distantly related to members of the CDC28/cdc2 gene family. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Sep;229(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00264206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. B., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase phosphorylation site sequences and consensus specificity motifs: tabulations. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:62–81. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00127-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinow L., Birchler J. A. A dosage-sensitive modifier of retrotransposon-induced alleles of the Drosophila white locus. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):879–889. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03449.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith A. D., Ellis C., Lyman S. D., Anderson D. M., Williams D. E., Bernstein A., Pawson T. Signal transduction by normal isoforms and W mutant variants of the Kit receptor tyrosine kinase. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2451–2459. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07784.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romac J. M., Keene J. D. Overexpression of the arginine-rich carboxy-terminal region of U1 snRNP 70K inhibits both splicing and nucleocytoplasmic transport of mRNA. Genes Dev. 1995 Jun 1;9(11):1400–1410. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.11.1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. B., Murphy C., Gall J. G. A monoclonal antibody that recognizes a phosphorylated epitope stains lampbrush chromosome loops and small granules in the amphibian germinal vesicle. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2217–2223. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Pawson T. Catalytic and non-catalytic domains of the Fujinami sarcoma virus P130gag-fps protein-tyrosine kinase distinguished by the expression of v-fps polypeptides in Escherichia coli. Oncogene. 1987 May;1(2):181–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt G., Werner D. Sequence of a complete murine cDNA reflecting an S phase-prevalent transcript encoding a protein with two types of nucleic acid binding motifs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Nov 16;1216(2):317–320. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Screaton G. R., Cáceres J. F., Mayeda A., Bell M. V., Plebanski M., Jackson D. G., Bell J. I., Krainer A. R. Identification and characterization of three members of the human SR family of pre-mRNA splicing factors. EMBO J. 1995 Sep 1;14(17):4336–4349. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00108.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soulard M., Della Valle V., Siomi M. C., Piñol-Roma S., Codogno P., Bauvy C., Bellini M., Lacroix J. C., Monod G., Dreyfuss G. hnRNP G: sequence and characterization of a glycosylated RNA-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 11;21(18):4210–4217. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.18.4210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L. Macromolecular domains within the cell nucleus. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:265–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L., Schrier W. H., Busch H. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of snRNPs. Biol Cell. 1983;49(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1984.tb00215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacke R., Boned A., Goridis C. ASF alternative transcripts are highly conserved between mouse and man. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 25;20(20):5482–5482. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.20.5482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi M., Yanagida M. A mitotic role for a novel fission yeast protein kinase dsk1 with cell cycle stage dependent phosphorylation and localization. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Mar;4(3):247–260. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.3.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang Z., Coleman T. R., Dunphy W. G. Two distinct mechanisms for negative regulation of the Wee1 protein kinase. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3427–3436. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06017.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Daugeron M. C., Cathala G., Brunel C., Jeanteur P. Adenosine phosphorothioates (ATP alpha S and ATP tau S) differentially affect the two steps of mammalian pre-mRNA splicing. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4322–4326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomis D. C., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action: evidence for intermolecular autophosphorylation and autoactivation of the interferon-induced, RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7695–7700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7695-7700.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen R., Kuijpers H., Vooijs P., Van Venrooij W., Ramaekers F. Distribution of the 70K U1 RNA-associated protein during interphase and mitosis. Correlation with other U RNP particles and proteins of the nuclear matrix. J Cell Sci. 1986 Dec;86:173–190. doi: 10.1242/jcs.86.1.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R., Ainscough R., Anderson K., Baynes C., Berks M., Bonfield J., Burton J., Connell M., Copsey T., Cooper J. 2.2 Mb of contiguous nucleotide sequence from chromosome III of C. elegans. Nature. 1994 Mar 3;368(6466):32–38. doi: 10.1038/368032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woppmann A., Will C. L., Kornstädt U., Zuo P., Manley J. L., Lührmann R. Identification of an snRNP-associated kinase activity that phosphorylates arginine/serine rich domains typical of splicing factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 25;21(12):2815–2822. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.12.2815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y., Maniatis T. Specific interactions between proteins implicated in splice site selection and regulated alternative splicing. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1061–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90316-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun B., Farkas R., Lee K., Rabinow L. The Doa locus encodes a member of a new protein kinase family and is essential for eye and embryonic development in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1994 May 15;8(10):1160–1173. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.10.1160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Lane W. S., Stolk J. A., Roth M. B. SR proteins: a conserved family of pre-mRNA splicing factors. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):837–847. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Neugebauer K. M., Lane W. S., Roth M. B. Distinct functions of SR proteins in alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Science. 1993 Apr 9;260(5105):219–222. doi: 10.1126/science.8385799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Neugebauer K. M., Stolk J. A., Roth M. B. Human SR proteins and isolation of a cDNA encoding SRp75. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4023–4028. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F., Strand A., Robbins D., Cobb M. H., Goldsmith E. J. Atomic structure of the MAP kinase ERK2 at 2.3 A resolution. Nature. 1994 Feb 24;367(6465):704–711. doi: 10.1038/367704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang G., Taneja K. L., Singer R. H., Green M. R. Localization of pre-mRNA splicing in mammalian nuclei. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):809–812. doi: 10.1038/372809a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuo P., Manley J. L. Functional domains of the human splicing factor ASF/SF2. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4727–4737. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06161.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]