Abstract
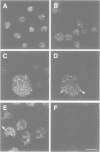
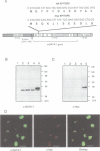
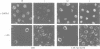
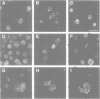
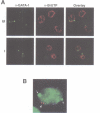
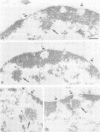
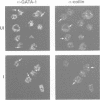
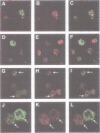
The nuclear distribution of GATA transcription factors in murine haemopoietic cells was examined by indirect immunofluorescence. Specific bright foci of GATA-1 fluorescence were observed in erythroleukaemia cells and primary murine erythroblasts and megakaryocytes, in addition to diffuse nucleoplasmic localization. These foci, which were preferentially found adjacent to nucleoli or at the nuclear periphery, did not represent sites of active transcription or binding of GATA-1 to consensus sites in the beta-globin loci. Immunoelectron microscopy demonstrated the presence of intensely labelled structures likely to represent the GATA-1 foci seen by immunofluorescence. The GATA-1 nuclear bodies differed from previously described nuclear structures and there was no co-localization with nuclear antigens involved in RNA processing or other ubiquitous (Spl, c-Jun and TBP) or haemopoietic (NF-E2) transcription factors. Interestingly, GATA-2 and GATA-3 proteins also localized to the same nuclear bodies in cell lines co-expressing GATA-1 and -2 or GATA-1 and -3 gene products. This pattern of distribution is, thus far, unique to the GATA transcription factors and suggests a protein-protein interaction with other components of the nuclear bodies via the GATA zinc finger domain.
Full text
PDF
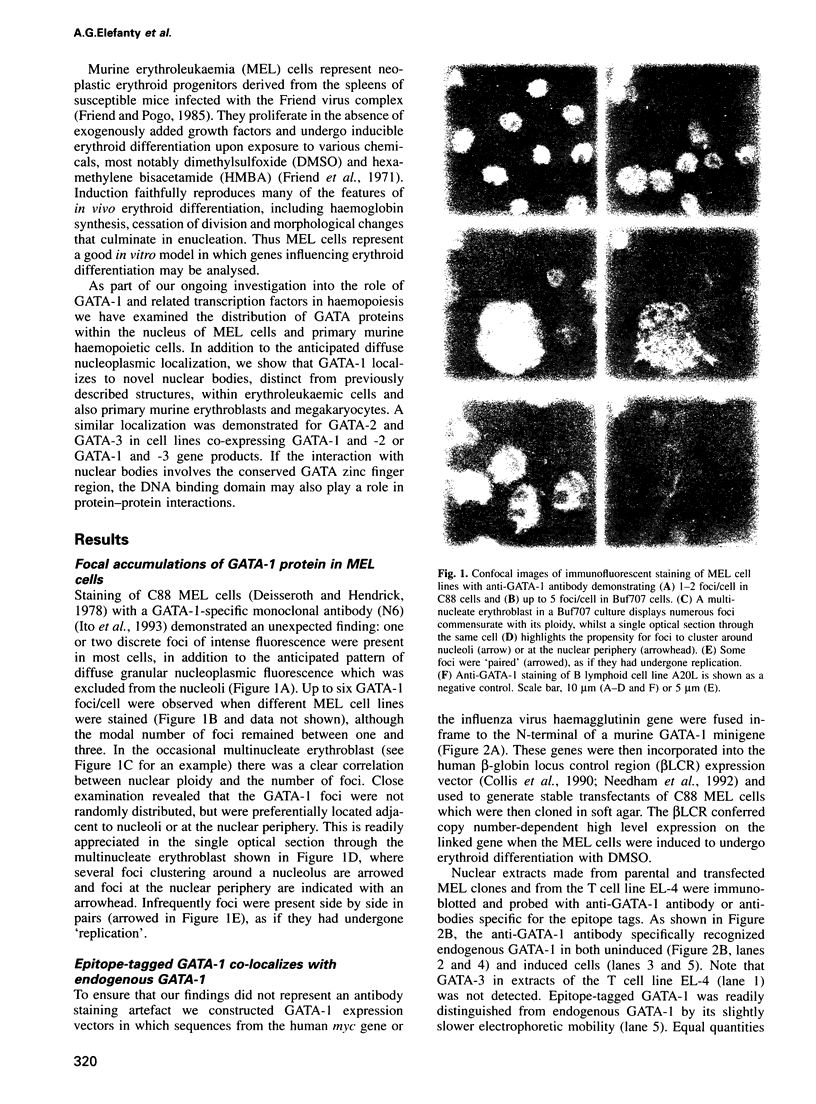
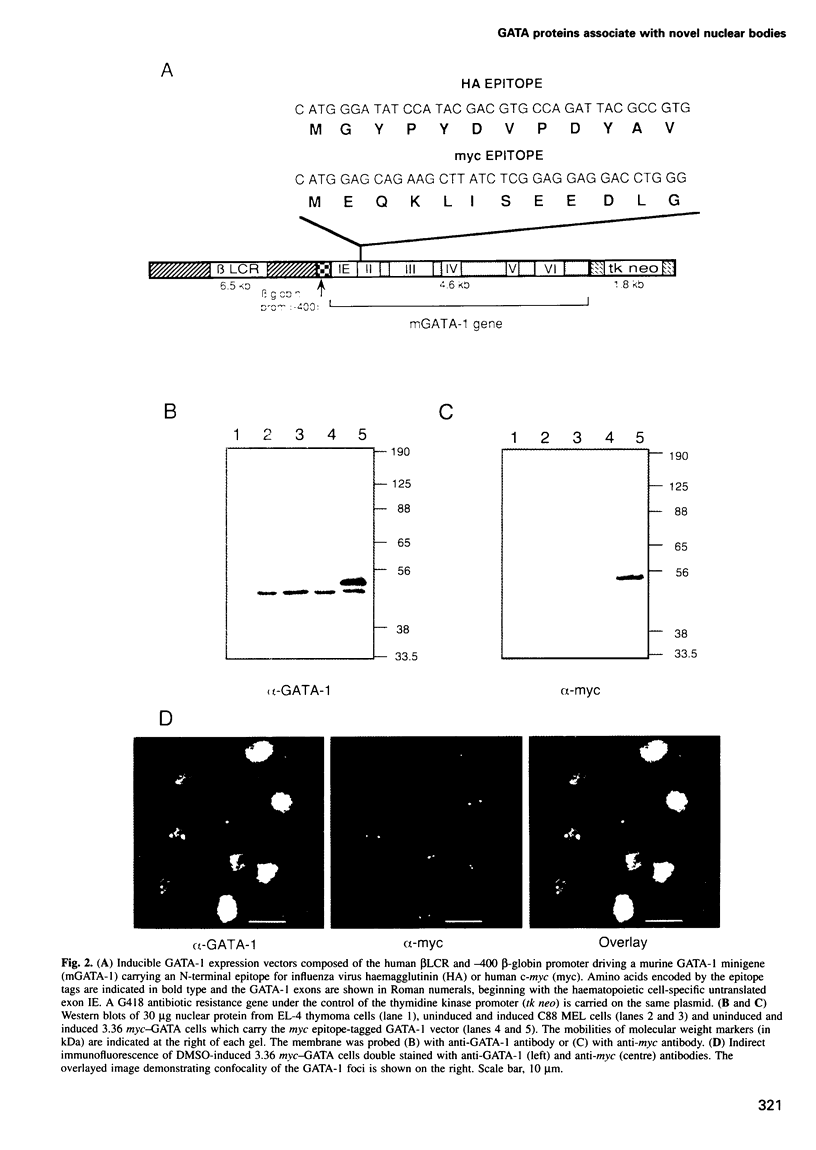






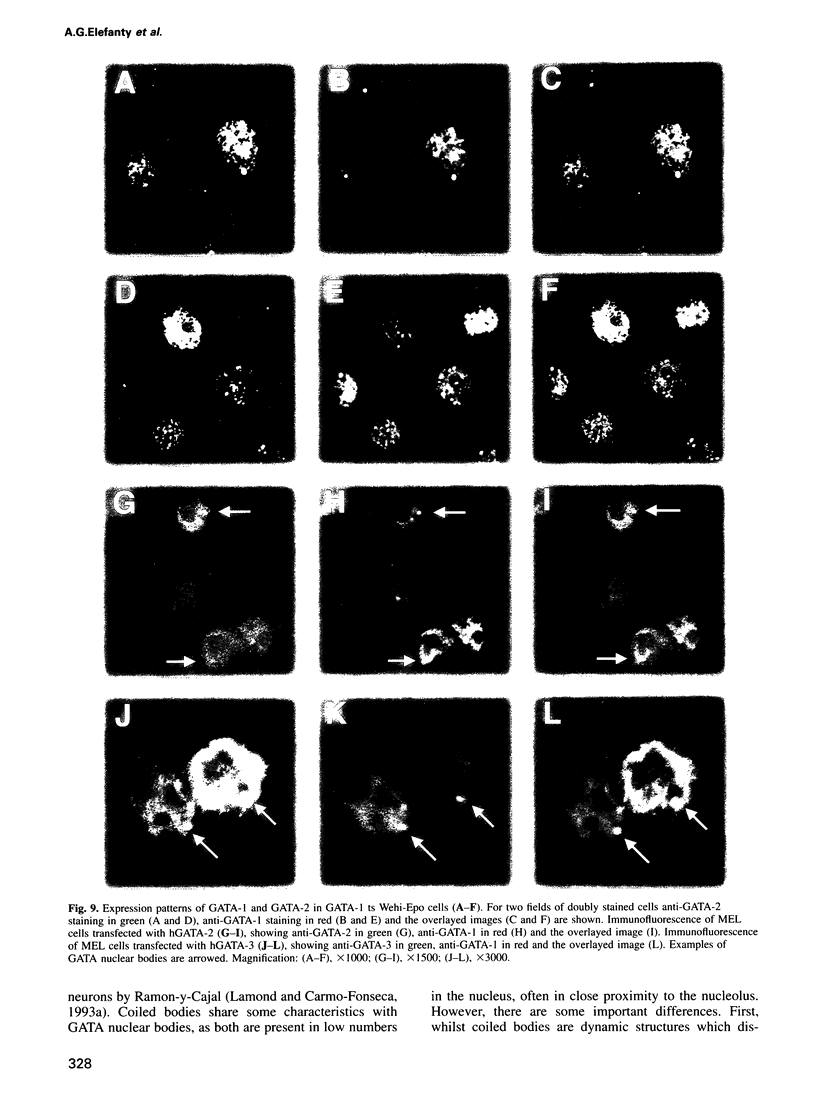





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abel T., Michelson A. M., Maniatis T. A Drosophila GATA family member that binds to Adh regulatory sequences is expressed in the developing fat body. Development. 1993 Nov;119(3):623–633. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.3.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade L. E., Tan E. M., Chan E. K. Immunocytochemical analysis of the coiled body in the cell cycle and during cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1947–1951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. C., Erdjument-Bromage H., Davidson M. B., Tempst P., Orkin S. H. Erythroid transcription factor NF-E2 is a haematopoietic-specific basic-leucine zipper protein. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):722–728. doi: 10.1038/362722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniou M., Carmo-Fonseca M., Ferreira J., Lamond A. I. Nuclear organization of splicing snRNPs during differentiation of murine erythroleukemia cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(5):1055–1068. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.5.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascoli C. A., Maul G. G. Identification of a novel nuclear domain. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):785–795. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. A., Simon M. C., Orkin S. H. Rescue of GATA-1-deficient embryonic stem cells by heterologous GATA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;15(2):626–633. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.2.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borden K. L., Boddy M. N., Lally J., O'Reilly N. J., Martin S., Howe K., Solomon E., Freemont P. S. The solution structure of the RING finger domain from the acute promyelocytic leukaemia proto-oncoprotein PML. EMBO J. 1995 Apr 3;14(7):1532–1541. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07139.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmo-Fonseca M., Ferreira J., Lamond A. I. Assembly of snRNP-containing coiled bodies is regulated in interphase and mitosis--evidence that the coiled body is a kinetic nuclear structure. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(4):841–852. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.4.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmo-Fonseca M., Pepperkok R., Carvalho M. T., Lamond A. I. Transcription-dependent colocalization of the U1, U2, U4/U6, and U5 snRNPs in coiled bodies. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):1–14. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis P., Antoniou M., Grosveld F. Definition of the minimal requirements within the human beta-globin gene and the dominant control region for high level expression. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):233–240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08100.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley M., Merika M., Orkin S. H. Self-association of the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 mediated by its zinc finger domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2448–2456. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crotta S., Nicolis S., Ronchi A., Ottolenghi S., Ruzzi L., Shimada Y., Migliaccio A. R., Migliaccio G. Progressive inactivation of the expression of an erythroid transcriptional factor in GM- and G-CSF-dependent myeloid cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6863–6869. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham T. S., Cooper T. G. Expression of the DAL80 gene, whose product is homologous to the GATA factors and is a negative regulator of multiple nitrogen catabolic genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is sensitive to nitrogen catabolite repression. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6205–6215. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisseroth A., Hendrick D. Human alpha-globin gene expression following chromosomal dependent gene transfer into mouse erythroleukemia cells. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorfman D. M., Wilson D. B., Bruns G. A., Orkin S. H. Human transcription factor GATA-2. Evidence for regulation of preproendothelin-1 gene expression in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1279–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck J. A., Maul G. G., Miller W. H., Jr, Chen J. D., Kakizuka A., Evans R. M. A novel macromolecular structure is a target of the promyelocyte-retinoic acid receptor oncoprotein. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):333–343. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Felsenfeld G. The erythroid-specific transcription factor Eryf1: a new finger protein. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):877–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90940-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D., Maul G. G. HSV-1 IE protein Vmw110 causes redistribution of PML. EMBO J. 1994 Nov 1;13(21):5062–5069. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06835.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira J. A., Carmo-Fonseca M., Lamond A. I. Differential interaction of splicing snRNPs with coiled bodies and interchromatin granules during mitosis and assembly of daughter cell nuclei. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):11–23. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerstein R., Wang X., Song D., Cooke N. E., Liebhaber S. A. The LIM/double zinc-finger motif functions as a protein dimerization domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10655–10659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Nikawa J., Broek D., MacDonald B., Rodgers L., Wilson I. A., Lerner R. A., Wigler M. Purification of a RAS-responsive adenylyl cyclase complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by use of an epitope addition method. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2159–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed E., Symons M., Macdonald S. G., McCormick F., Ruggieri R. Binding of 14-3-3 proteins to the protein kinase Raf and effects on its activation. Science. 1994 Sep 16;265(5179):1713–1716. doi: 10.1126/science.8085158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend C., Pogo B. G. The molecular pathology of Friend erythroleukemia virus strains. An overview. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985;780(3):181–195. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(85)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend C., Scher W., Holland J. G., Sato T. Hemoglobin synthesis in murine virus-induced leukemic cells in vitro: stimulation of erythroid differentiation by dimethyl sulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):378–382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORER P. A. Studies in antibody response of mice to tumour inoculation. Br J Cancer. 1950 Dec;4(4):372–379. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1950.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisberg J. V., Lee W. S., Berk A. J., Ricciardi R. P. The zinc finger region of the adenovirus E1A transactivating domain complexes with the TATA box binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2488–2492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., Antoniou M., Berry M., de Boer E., Dillon N., Ellis J., Fraser P., Hurst J., Imam A., Meijer D. Regulation of human globin gene switching. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1993;58:7–13. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1993.058.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho I. C., Vorhees P., Marin N., Oakley B. K., Tsai S. F., Orkin S. H., Leiden J. M. Human GATA-3: a lineage-restricted transcription factor that regulates the expression of the T cell receptor alpha gene. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1187–1192. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08059.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta T., Kan Y. W. In vivo protein-DNA interactions at the beta-globin gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10188–10192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irie K., Gotoh Y., Yashar B. M., Errede B., Nishida E., Matsumoto K. Stimulatory effects of yeast and mammalian 14-3-3 proteins on the Raf protein kinase. Science. 1994 Sep 16;265(5179):1716–1719. doi: 10.1126/science.8085159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito E., Toki T., Ishihara H., Ohtani H., Gu L., Yokoyama M., Engel J. D., Yamamoto M. Erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 is abundantly transcribed in mouse testis. Nature. 1993 Apr 1;362(6419):466–468. doi: 10.1038/362466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang W. Q., Szekely L., Wendel-Hansen V., Ringertz N., Klein G., Rosén A. Co-localization of the retinoblastoma protein and the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen EBNA-5. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Dec;197(2):314–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90438-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joulin V., Bories D., Eléouet J. F., Labastie M. C., Chrétien S., Mattéi M. G., Roméo P. H. A T-cell specific TCR delta DNA binding protein is a member of the human GATA family. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1809–1816. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07706.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastner P., Perez A., Lutz Y., Rochette-Egly C., Gaub M. P., Durand B., Lanotte M., Berger R., Chambon P. Structure, localization and transcriptional properties of two classes of retinoic acid receptor alpha fusion proteins in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL): structural similarities with a new family of oncoproteins. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):629–642. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05095.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley C., Blumberg H., Zon L. I., Evans T. GATA-4 is a novel transcription factor expressed in endocardium of the developing heart. Development. 1993 Jul;118(3):817–827. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.3.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. J., Kanellopoulos-Langevin C., Merwin R. M., Sachs D. H., Asofsky R. Establishment and characterization of BALB/c lymphoma lines with B cell properties. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):549–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko L. J., Yamamoto M., Leonard M. W., George K. M., Ting P., Engel J. D. Murine and human T-lymphocyte GATA-3 factors mediate transcription through a cis-regulatory element within the human T-cell receptor delta gene enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2778–2784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koken M. H., Puvion-Dutilleul F., Guillemin M. C., Viron A., Linares-Cruz G., Stuurman N., de Jong L., Szostecki C., Calvo F., Chomienne C. The t(15;17) translocation alters a nuclear body in a retinoic acid-reversible fashion. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 1;13(5):1073–1083. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06356.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudla B., Caddick M. X., Langdon T., Martinez-Rossi N. M., Bennett C. F., Sibley S., Davies R. W., Arst H. N., Jr The regulatory gene areA mediating nitrogen metabolite repression in Aspergillus nidulans. Mutations affecting specificity of gene activation alter a loop residue of a putative zinc finger. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1355–1364. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08250.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Carmo-Fonseca M. Localisation of splicing snRNPs in mammalian cells. Mol Biol Rep. 1993 Aug;18(2):127–133. doi: 10.1007/BF00986767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Carmo-Fonseca M. The coiled body. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;3(6):198–204. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90214-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laverriere A. C., MacNeill C., Mueller C., Poelmann R. E., Burch J. B., Evans T. GATA-4/5/6, a subfamily of three transcription factors transcribed in developing heart and gut. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 16;269(37):23177–23184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Galvin K. M., Shi Y. Evidence for physical interaction between the zinc-finger transcription factors YY1 and Sp1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6145–6149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. E., Temizer D. H., Clifford J. A., Quertermous T. Cloning of the GATA-binding protein that regulates endothelin-1 gene expression in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16188–16192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisi B. F., Xu W. X., Otwinowski Z., Freedman L. P., Yamamoto K. R., Sigler P. B. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):497–505. doi: 10.1038/352497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. I., Zon L. I., Mutter G., Orkin S. H. Expression of an erythroid transcription factor in megakaryocytic and mast cell lineages. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):444–447. doi: 10.1038/344444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merika M., Orkin S. H. Functional synergy and physical interactions of the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 with the Krüppel family proteins Sp1 and EKLF. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2437–2447. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murrell A. M., Green A. R. Regulation of lineage restricted haemopoietic transcription factors in cell hybrids. Oncogene. 1995 Feb 16;10(4):631–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needham M., Gooding C., Hudson K., Antoniou M., Grosveld F., Hollis M. LCR/MEL: a versatile system for high-level expression of heterologous proteins in erythroid cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 11;20(5):997–1003. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.5.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omichinski J. G., Clore G. M., Schaad O., Felsenfeld G., Trainor C., Appella E., Stahl S. J., Gronenborn A. M. NMR structure of a specific DNA complex of Zn-containing DNA binding domain of GATA-1. Science. 1993 Jul 23;261(5120):438–446. doi: 10.1126/science.8332909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. GATA-binding transcription factors in hematopoietic cells. Blood. 1992 Aug 1;80(3):575–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandolfi P. P., Roth M. E., Karis A., Leonard M. W., Dzierzak E., Grosveld F. G., Engel J. D., Lindenbaum M. H. Targeted disruption of the GATA3 gene causes severe abnormalities in the nervous system and in fetal liver haematopoiesis. Nat Genet. 1995 Sep;11(1):40–44. doi: 10.1038/ng0995-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevny L., Lin C. S., D'Agati V., Simon M. C., Orkin S. H., Costantini F. Development of hematopoietic cells lacking transcription factor GATA-1. Development. 1995 Jan;121(1):163–172. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.1.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevny L., Simon M. C., Robertson E., Klein W. H., Tsai S. F., D'Agati V., Orkin S. H., Costantini F. Erythroid differentiation in chimaeric mice blocked by a targeted mutation in the gene for transcription factor GATA-1. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):257–260. doi: 10.1038/349257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Alvarado G. C., Miles C., Michelsen J. W., Louis H. A., Winge D. R., Beckerle M. C., Summers M. F. Structure of the carboxy-terminal LIM domain from the cysteine rich protein CRP. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Jun;1(6):388–398. doi: 10.1038/nsb0694-388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastinejad F., Perlmann T., Evans R. M., Sigler P. B. Structural determinants of nuclear receptor assembly on DNA direct repeats. Nature. 1995 May 18;375(6528):203–211. doi: 10.1038/375203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer G., Pollard K. M., Penning C. A., Ochs R. L., Lischwe M. A., Busch H., Tan E. M. Monoclonal autoantibody from a (New Zealand black x New Zealand white)F1 mouse and some human scleroderma sera target an Mr 34,000 nucleolar protein of the U3 RNP particle. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jul;30(7):793–800. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Lewis B., Shenk T. Interaction between transcription factors Sp1 and YY1. Nature. 1993 Sep 30;365(6445):462–464. doi: 10.1038/365462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollerbrant K., Akusjärvi G., Linder S., Svensson C. The DNA binding domains of the yeast Gal4 and human c-Jun transcription factors interact through the zinc-finger and bZIP motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Feb 25;23(4):588–594. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.4.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spieth J., Shim Y. H., Lea K., Conrad R., Blumenthal T. elt-1, an embryonically expressed Caenorhabditis elegans gene homologous to the GATA transcription factor family. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4651–4659. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sposi N. M., Zon L. I., Carè A., Valtieri M., Testa U., Gabbianelli M., Mariani G., Bottero L., Mather C., Orkin S. H. Cell cycle-dependent initiation and lineage-dependent abrogation of GATA-1 expression in pure differentiating hematopoietic progenitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6353–6357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuurman N., de Graaf A., Floore A., Josso A., Humbel B., de Jong L., van Driel R. A monoclonal antibody recognizing nuclear matrix-associated nuclear bodies. J Cell Sci. 1992 Apr;101(Pt 4):773–784. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.4.773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostecki C., Guldner H. H., Netter H. J., Will H. Isolation and characterization of cDNA encoding a human nuclear antigen predominantly recognized by autoantibodies from patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4338–4347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. F., Martin D. I., Zon L. I., D'Andrea A. D., Wong G. G., Orkin S. H. Cloning of cDNA for the major DNA-binding protein of the erythroid lineage through expression in mammalian cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):446–451. doi: 10.1038/339446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. M., Franchi L. Identification of protein antigens associated with the nuclear matrix and with clusters of interchromatin granules in both interphase and mitotic cells. J Cell Sci. 1987 Mar;87(Pt 2):269–282. doi: 10.1242/jcs.87.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvader J. E., Crossley M., Hill J., Orkin S. H., Adams J. M. The C-terminal zinc finger of GATA-1 or GATA-2 is sufficient to induce megakaryocytic differentiation of an early myeloid cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;15(2):634–641. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.2.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvader J. E., Elefanty A. G., Strasser A., Adams J. M. GATA-1 but not SCL induces megakaryocytic differentiation in an early myeloid line. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4557–4564. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05557.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvader J., Adams J. M. Megakaryocytic differentiation induced in 416B myeloid cells by GATA-2 and GATA-3 transgenes or 5-azacytidine is tightly coupled to GATA-1 expression. Blood. 1993 Sep 1;82(5):1493–1501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadman I., Li J., Bash R. O., Forster A., Osada H., Rabbitts T. H., Baer R. Specific in vivo association between the bHLH and LIM proteins implicated in human T cell leukemia. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 17;13(20):4831–4839. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton T. H., Moen P. T., Jr, Fox E., Bodnar J. W. Interactions of minute virus of mice and adenovirus with host nucleoli. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3651–3660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3651-3660.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wansink D. G., Schul W., van der Kraan I., van Steensel B., van Driel R., de Jong L. Fluorescent labeling of nascent RNA reveals transcription by RNA polymerase II in domains scattered throughout the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(2):283–293. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.2.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis K., Rambaud S., Lavau C., Jansen J., Carvalho T., Carmo-Fonseca M., Lamond A., Dejean A. Retinoic acid regulates aberrant nuclear localization of PML-RAR alpha in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):345–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. J., Keller G., Orkin S. H. Novel insights into erythroid development revealed through in vitro differentiation of GATA-1 embryonic stem cells. Genes Dev. 1994 May 15;8(10):1184–1197. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.10.1184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. J., Orkin S. H. GATA transcription factors: key regulators of hematopoiesis. Exp Hematol. 1995 Feb;23(2):99–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie K., Lambie E. J., Snyder M. Nuclear dot antigens may specify transcriptional domains in the nucleus. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6170–6179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Ko L. J., Leonard M. W., Beug H., Orkin S. H., Engel J. D. Activity and tissue-specific expression of the transcription factor NF-E1 multigene family. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1650–1662. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Evans T. Homotypic interactions of chicken GATA-1 can mediate transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;15(3):1353–1363. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.3.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]