Abstract
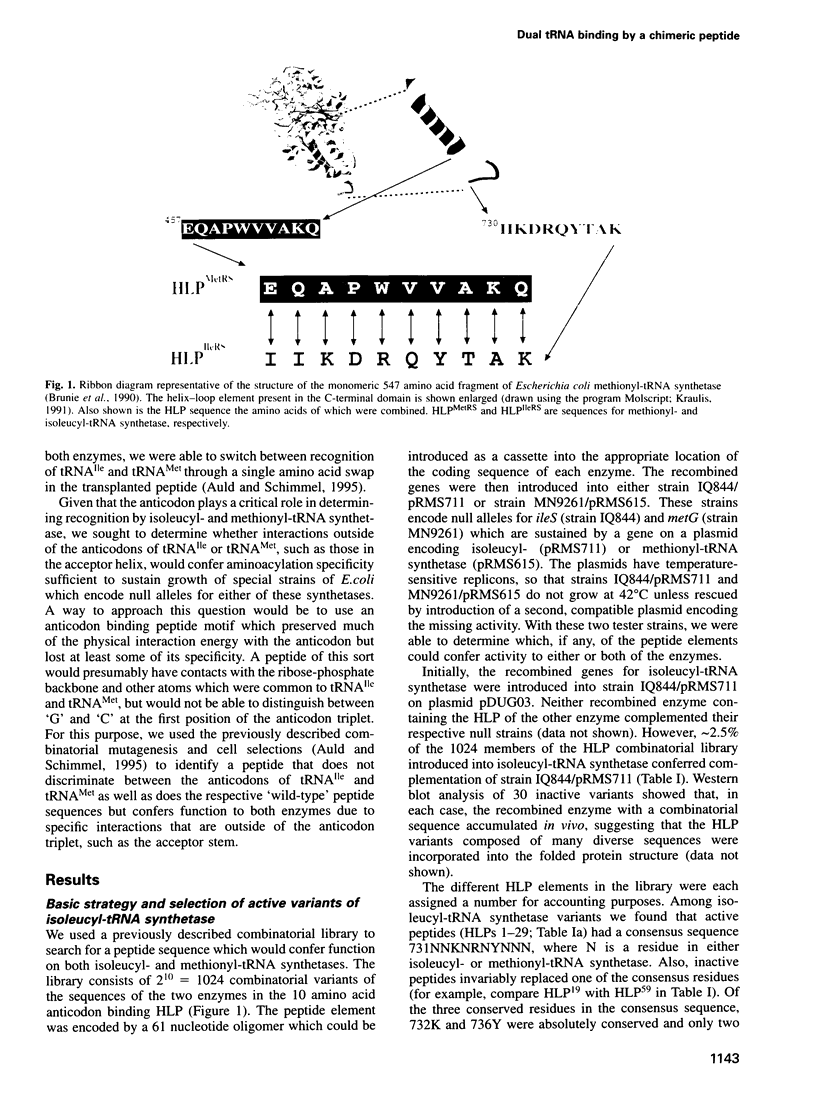
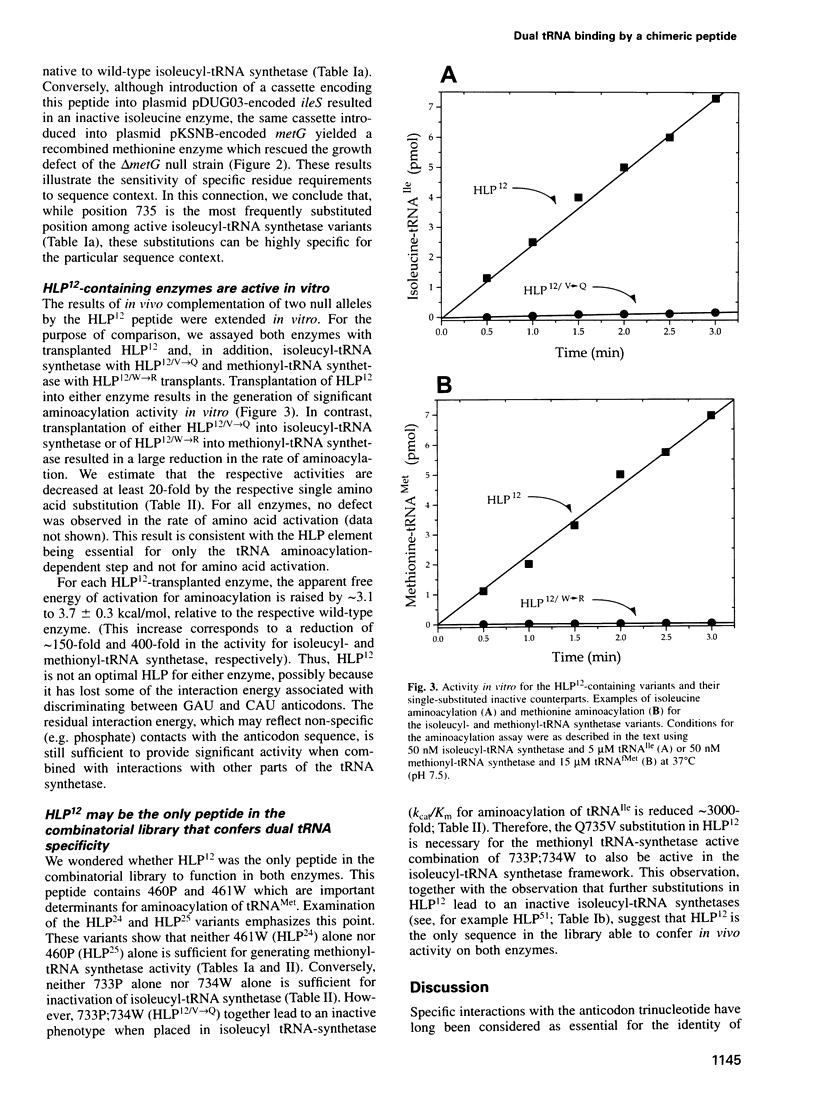
The specific aminoacylation of RNA oligonucleotides whose sequences are based on the acceptor stems of tRNAs can be viewed as an operational RNA code for amino acids that may be related to the development of the genetic code. Many synthetases also have direct interactions with tRNA anticodon triplets and, in some cases, these interactions are thought to be essential for aminoacylation specificity. In these instances, an unresolved question is whether interactions with parts of the tRNA outside of the anticodon are sufficient for decoding genetic information. Escherichia coli isoleucyl- and methionyl-tRNA synthetases are closely related enzymes that interact with their respective anticodons. We used binary combinatorial mutagenesis of a 10 amino acid anticodon binding peptide in these two enzymes to identify composite sequences that would confer function to both enzymes despite their recognizing different anticodons. A single peptide was found that confers function to both enzymes in vivo and in vitro. Thus, even in enzymes where anticodon interactions are normally important for distinguishing one tRNA from another, these interactions can be 'neutralized' without losing specificity of amino-acylation. We suggest that acceptor helix interactions may play a role in providing the needed specificity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auld D. S., Schimmel P. Switching recognition of two tRNA synthetases with an amino acid swap in a designed peptide. Science. 1995 Mar 31;267(5206):1994–1996. doi: 10.1126/science.7701322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. G., Ebel J. P., Jakes R., Bruton C. J. Methionyl-tRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli. Primary structure of the active crystallised tryptic fragment. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(3):449–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedouelle H., Guez V., Vidal-Cros A., Hermann M. Overproduction of tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase is toxic to Escherichia coli: a genetic analysis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3940–3945. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3940-3945.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biou V., Yaremchuk A., Tukalo M., Cusack S. The 2.9 A crystal structure of T. thermophilus seryl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Ser). Science. 1994 Mar 11;263(5152):1404–1410. doi: 10.1126/science.8128220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunie S., Zelwer C., Risler J. L. Crystallographic study at 2.5 A resolution of the interaction of methionyl-tRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli with ATP. J Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 20;216(2):411–424. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80331-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buechter D. D., Schimmel P. Aminoacylation of RNA minihelices: implications for tRNA synthetase structural design and evolution. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1993;28(4):309–322. doi: 10.3109/10409239309078438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbaum J. J., Schimmel P. Assembly of a class I tRNA synthetase from products of an artificially split gene. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 15;30(2):319–324. doi: 10.1021/bi00216a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calendar R., Berg P. The catalytic properties of tyrosyl ribonucleic acid synthetases from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Biochemistry. 1966 May;5(5):1690–1695. doi: 10.1021/bi00869a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Despons L., Walter P., Senger B., Ebel J. P., Fasiolo F. Identification of potential amino acid residues supporting anticodon recognition in yeast methionyl-tRNA synthetase. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 9;289(2):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81073-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frugier M., Florentz C., Giegé R. Efficient aminoacylation of resected RNA helices by class II aspartyl-tRNA synthetase dependent on a single nucleotide. EMBO J. 1994 May 1;13(9):2218–2226. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06499.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh G., Kim H. Y., Demaret J. P., Brunie S., Schulman L. H. Arginine-395 is required for efficient in vivo and in vitro aminoacylation of tRNAs by Escherichia coli methionyl-tRNA synthetase. Biochemistry. 1991 Dec 24;30(51):11767–11774. doi: 10.1021/bi00115a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh G., Pelka H., Schulman L. H. Identification of the tRNA anticodon recognition site of Escherichia coli methionyl-tRNA synthetase. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 6;29(9):2220–2225. doi: 10.1021/bi00461a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamann C. S., Hou Y. M. Enzymatic aminoacylation of tRNA acceptor stem helices with cysteine is dependent on a single nucleotide. Biochemistry. 1995 May 16;34(19):6527–6532. doi: 10.1021/bi00019a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou Y. M., Schimmel P. A simple structural feature is a major determinant of the identity of a transfer RNA. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):140–145. doi: 10.1038/333140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iaccarino M., Berg P. Isoleucine auxotrophy as a consequence of a mutationally altered isoleucyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1971 Feb;105(2):527–537. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.2.527-537.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Ribas de Pouplana L., Schimmel P. Diversified sequences of peptide epitope for same-RNA recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10046–10050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Schimmel P. Function independence of microhelix aminoacylation from anticodon binding in a class I tRNA synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15563–15567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landro J. A., Schimmel P. Metal-binding site in a class I tRNA synthetase localized to a cysteine cluster inserted into nucleotide-binding fold. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2261–2265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. P., Dyson M. R., Mandal N., Varshney U., Bahramian B., RajBhandary U. L. Striking effects of coupling mutations in the acceptor stem on recognition of tRNAs by Escherichia coli Met-tRNA synthetase and Met-tRNA transformylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9262–9266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinis S. A., Schimmel P. Enzymatic aminoacylation of sequence-specific RNA minihelices and hybrid duplexes with methionine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):65–69. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinis S. A., Schimmel P. Microhelix aminoacylation by a class I tRNA synthetase. Non-conserved base pairs required for specificity. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6069–6072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain W. H., Foss K. Changing the identity of a tRNA by introducing a G-U wobble pair near the 3' acceptor end. Science. 1988 May 6;240(4853):793–796. doi: 10.1126/science.2452483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinnel T., Mechulam Y., Lazennec C., Blanquet S., Fayat G. Critical role of the acceptor stem of tRNAs(Met) in their aminoacylation by Escherichia coli methionyl-tRNA synthetase. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jan 5;229(1):26–36. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moras D. Structural and functional relationships between aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Apr;17(4):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90326-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu T., Nishikawa K., Nemoto F., Kuchino Y., Nishimura S., Miyazawa T., Yokoyama S. Codon and amino-acid specificities of a transfer RNA are both converted by a single post-transcriptional modification. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):179–181. doi: 10.1038/336179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu T., Yokoyama S., Horie N., Matsuda A., Ueda T., Yamaizumi Z., Kuchino Y., Nishimura S., Miyazawa T. A novel lysine-substituted nucleoside in the first position of the anticodon of minor isoleucine tRNA from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9261–9267. doi: 10.1351/pac198961030573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normanly J., Ogden R. C., Horvath S. J., Abelson J. Changing the identity of a transfer RNA. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):213–219. doi: 10.1038/321213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nureki O., Niimi T., Muramatsu T., Kanno H., Kohno T., Florentz C., Giegé R., Yokoyama S. Molecular recognition of the identity-determinant set of isoleucine transfer RNA from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 25;236(3):710–724. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park S. J., Schimmel P. Evidence for interaction of an aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetase with a region important for the identity of its cognate transfer RNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16527–16530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perona J. J., Rould M. A., Steitz T. A., Risler J. L., Zelwer C., Brunie S. Structural similarities in glutaminyl- and methionyl-tRNA synthetases suggest a common overall orientation of tRNA binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2903–2907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidhaar-Olson J. F., Bowie J. U., Breyer R. M., Hu J. C., Knight K. L., Lim W. A., Mossing M. C., Parsell D. A., Shoemaker K. R., Sauer R. T. Random mutagenesis of protein sequences using oligonucleotide cassettes. Methods Enzymol. 1991;208:564–586. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)08029-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saks M. E., Sampson J. R., Abelson J. N. The transfer RNA identity problem: a search for rules. Science. 1994 Jan 14;263(5144):191–197. doi: 10.1126/science.7506844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J. R., Saks M. E. Contributions of discrete tRNA(Ser) domains to aminoacylation by E.coli seryl-tRNA synthetase: a kinetic analysis using model RNA substrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 25;21(19):4467–4475. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.19.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel P., Giegé R., Moras D., Yokoyama S. An operational RNA code for amino acids and possible relationship to genetic code. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8763–8768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel P., Ribas de Pouplana L. Transfer RNA: from minihelix to genetic code. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):983–986. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel P., Shepard A., Shiba K. Intron locations and functional deletions in relation to the design and evolution of a subgroup of class I tRNA synthetases. Protein Sci. 1992 Oct;1(10):1387–1391. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560011018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E., Schimmel P. Dominant lethality by expression of a catalytically inactive class I tRNA synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):6919–6923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.6919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E., Schimmel P. Mutational isolation of a sieve for editing in a transfer RNA synthetase. Science. 1994 Apr 8;264(5156):265–267. doi: 10.1126/science.8146659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman L. H., Pelka H. Anticodon switching changes the identity of methionine and valine transfer RNAs. Science. 1988 Nov 4;242(4879):765–768. doi: 10.1126/science.3055296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman L. H. Recognition of tRNAs by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;41:23–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard A., Shiba K., Schimmel P. RNA binding determinant in some class I tRNA synthetases identified by alignment-guided mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9964–9968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba K., Schimmel P. Functional assembly of a randomly cleaved protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1880–1884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzyk R. M., Burbaum J. J., Schimmel P. Insertion of new sequences into the catalytic domain of an enzyme. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8479–8484. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzyk R. M., Webster T. A., Schimmel P. Evidence for dispensable sequences inserted into a nucleotide fold. Science. 1987 Sep 25;237(4822):1614–1618. doi: 10.1126/science.3306924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshney U., Lee C. P., RajBhandary U. L. Direct analysis of aminoacylation levels of tRNAs in vivo. Application to studying recognition of Escherichia coli initiator tRNA mutants by glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24712–24718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal-Cros A., Bedouelle H. Role of residue Glu152 in the discrimination between transfer RNAs by tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 5;223(3):801–810. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90991-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster T., Tsai H., Kula M., Mackie G. A., Schimmel P. Specific sequence homology and three-dimensional structure of an aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetase. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1315–1317. doi: 10.1126/science.6390679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Maizels N. Molecular evolution. Unlocking the secrets of retroviral evolution. Curr Biol. 1994 Jun 1;4(6):560–563. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00126-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Maizels N. tRNA-like structures tag the 3' ends of genomic RNA molecules for replication: implications for the origin of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7383–7387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]