Abstract
The 'protein only' hypothesis postulates that the prion, the agent causing transmissible spongiform encephalopathies, is PrP(Sc), an isoform of the host protein PrP(C). Protease treatment of prion preparations cleaves off approximately 60 N-terminal residues of PrP(Sc) but does not abrogate infectivity. Disruption of the PrP gene in the mouse abolishes susceptibility to scrapie and prion replication. We have introduced into PrP knockout mice transgenes encoding wild-type PrP or PrP lacking 26 or 49 amino-proximal amino acids which are protease susceptible in PrP(Sc). Inoculation with prions led to fatal disease, prion propagation and accumulation of PrP(Sc) in mice expressing both wild-type and truncated PrPs. Within the framework of the 'protein only' hypothesis, this means that the amino-proximal segment of PrP(C) is not required either for its susceptibility to conversion into the pathogenic, infectious form of PrP or for the generation of PrP(Sc).
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry R. A., Kent S. B., McKinley M. P., Meyer R. K., DeArmond S. J., Hood L. E., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie and cellular prion proteins share polypeptide epitopes. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):848–854. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basler K., Oesch B., Scott M., Westaway D., Wälchli M., Groth D. F., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B., Weissmann C. Scrapie and cellular PrP isoforms are encoded by the same chromosomal gene. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):417–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90662-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Identification of a protein that purifies with the scrapie prion. Science. 1982 Dec 24;218(4579):1309–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.6815801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., Rudelli R. D., Currie J. R., Bendheim P. E. Copurification of Sp33-37 and scrapie agent from hamster brain prior to detectable histopathology and clinical disease. J Gen Virol. 1991 Dec;72(Pt 12):2905–2913. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-12-2905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandner S., Isenmann S., Raeber A., Fischer M., Sailer A., Kobayashi Y., Marino S., Weissmann C., Aguzzi A. Normal host prion protein necessary for scrapie-induced neurotoxicity. Nature. 1996 Jan 25;379(6563):339–343. doi: 10.1038/379339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Allen J. M., Behringer R. R., Gelinas R. E., Palmiter R. D. Introns increase transcriptional efficiency in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):836–840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M. E., Yagle M. K., Palmiter R. D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4438–4442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büeler H., Aguzzi A., Sailer A., Greiner R. A., Autenried P., Aguet M., Weissmann C. Mice devoid of PrP are resistant to scrapie. Cell. 1993 Jul 2;73(7):1339–1347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90360-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büeler H., Fischer M., Lang Y., Bluethmann H., Lipp H. P., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B., Aguet M., Weissmann C. Normal development and behaviour of mice lacking the neuronal cell-surface PrP protein. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):577–582. doi: 10.1038/356577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büeler H., Raeber A., Sailer A., Fischer M., Aguzzi A., Weissmann C. High prion and PrPSc levels but delayed onset of disease in scrapie-inoculated mice heterozygous for a disrupted PrP gene. Mol Med. 1994 Nov;1(1):19–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson G. A., Goodman P. A., Lovett M., Taylor B. A., Marshall S. T., Peterson-Torchia M., Westaway D., Prusiner S. B. Genetics and polymorphism of the mouse prion gene complex: control of scrapie incubation time. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5528–5540. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey B. W., Dong A., Bhat K. S., Ernst D., Hayes S. F., Caughey W. S. Secondary structure analysis of the scrapie-associated protein PrP 27-30 in water by infrared spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 6;30(31):7672–7680. doi: 10.1021/bi00245a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinge J., Palmer M. S., Sidle K. C., Gowland I., Medori R., Ironside J., Lantos P. Transmission of fatal familial insomnia to laboratory animals. Lancet. 1995 Aug 26;346(8974):569–570. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91405-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson A. G., Outram G. W. Genetic aspects of unconventional virus infections: the basis of the virino hypothesis. Ciba Found Symp. 1988;135:63–83. doi: 10.1002/9780470513613.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Beekes M., Oberdieck U. The nature of the scrapie agent: the virus theory. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994 Jun 6;724:246–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb38915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar C. F., Somerville R. A., Ritchie L. A. Post-mortem immunodiagnosis of scrapie and bovine spongiform encephalopathy. J Virol Methods. 1989 Apr-May;24(1-2):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(89)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabizon R., McKinley M. P., Groth D., Prusiner S. B. Immunoaffinity purification and neutralization of scrapie prion infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6617–6621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. S. Self-replication and scrapie. Nature. 1967 Sep 2;215(5105):1043–1044. doi: 10.1038/2151043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope J., Multhaup G., Reekie L. J., Kimberlin R. H., Beyreuther K. Molecular pathology of scrapie-associated fibril protein (PrP) in mouse brain affected by the ME7 strain of scrapie. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 1;172(2):271–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao K. K., Groth D., Scott M., Yang S. L., Serban H., Rapp D., Foster D., Torchia M., Dearmond S. J., Prusiner S. B. Serial transmission in rodents of neurodegeneration from transgenic mice expressing mutant prion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):9126–9130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.9126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao K. K., Scott M., Foster D., Groth D. F., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B. Spontaneous neurodegeneration in transgenic mice with mutant prion protein. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1587–1590. doi: 10.1126/science.1980379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellings K., Meyer N., Mirenda C., Prusiner S. B., Riesner D. Analysis of nucleic acids in purified scrapie prion preparations. Arch Virol Suppl. 1993;7:215–225. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-9300-6_17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Iizuka R., Tateishi J. An amber mutation of prion protein in Gerstmann-Sträussler syndrome with mutant PrP plaques. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Apr 30;192(2):525–531. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird P. W., Zijderveld A., Linders K., Rudnicki M. A., Jaenisch R., Berns A. Simplified mammalian DNA isolation procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4293–4293. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozano G., Levine A. J. Tissue-specific expression of p53 in transgenic mice is regulated by intron sequences. Mol Carcinog. 1991;4(1):3–9. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940040103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Sklaviadis T., Manuelidis E. E. Evidence suggesting that PrP is not the infectious agent in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):341–347. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley M. P., Bolton D. C., Prusiner S. B. A protease-resistant protein is a structural component of the scrapie prion. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90207-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. K., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Braunfeld M. B., Barry R. A., Prusiner S. B. Separation and properties of cellular and scrapie prion proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2310–2314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
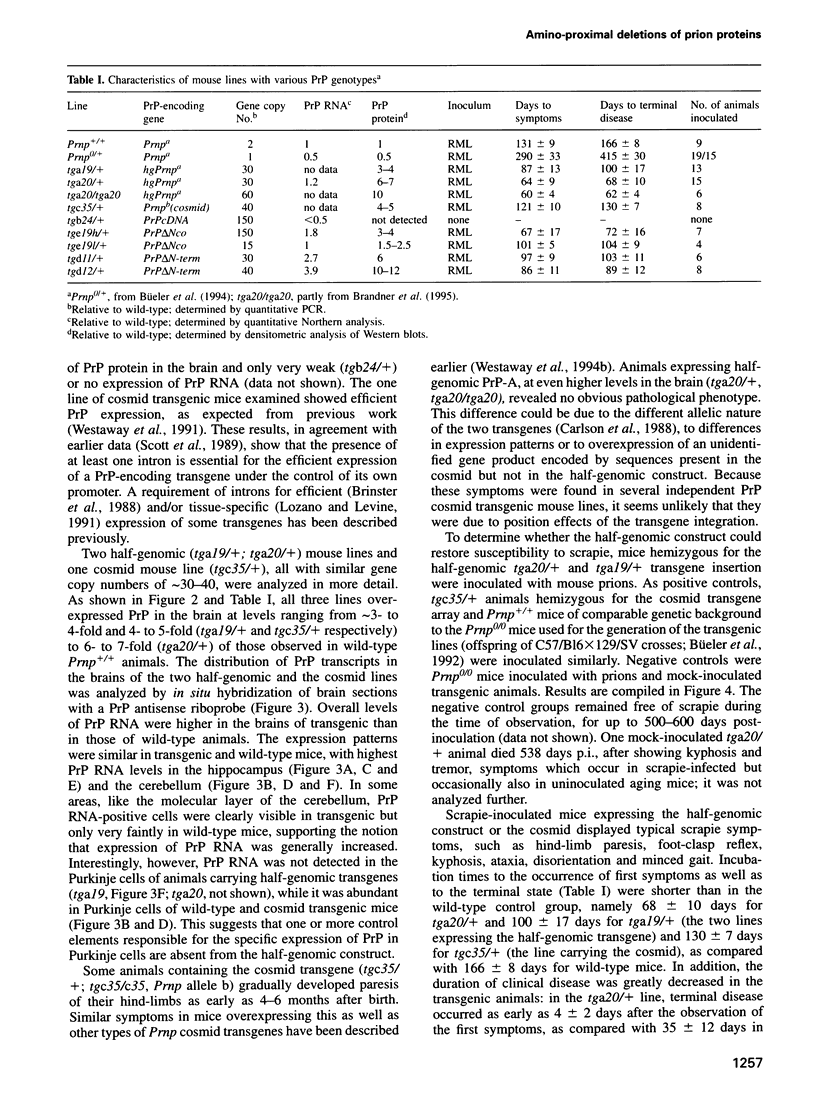
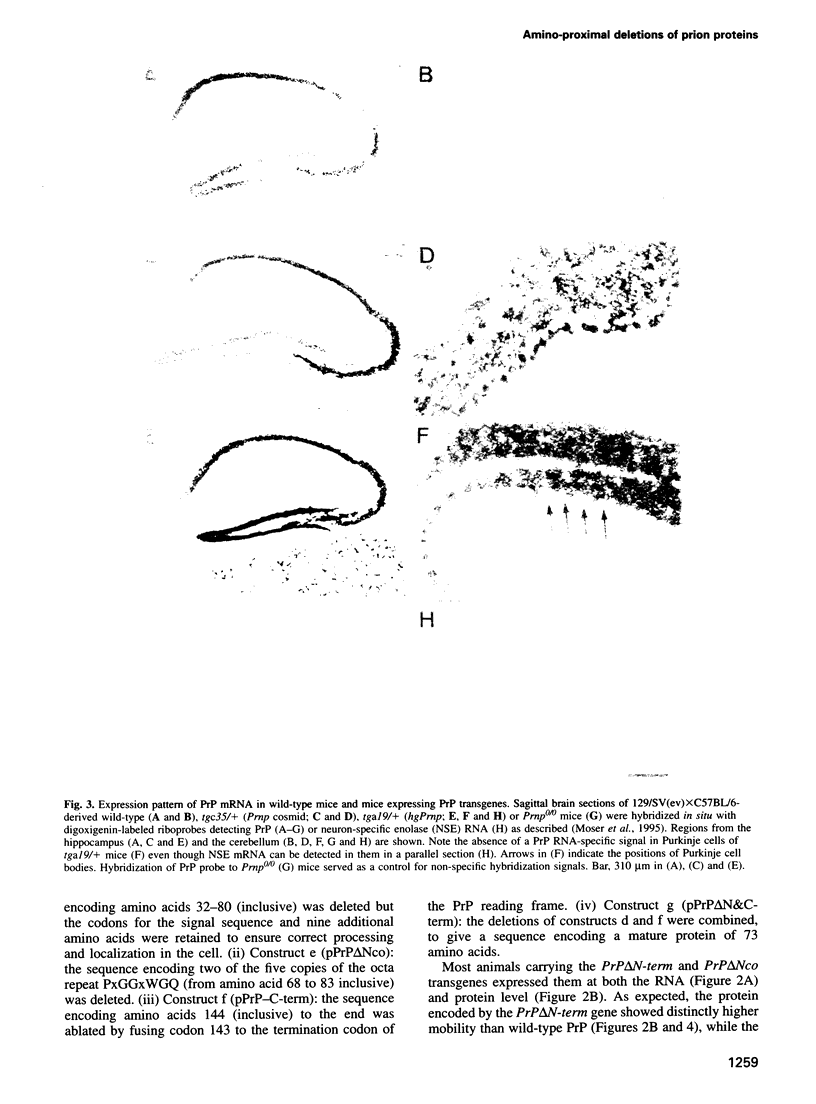
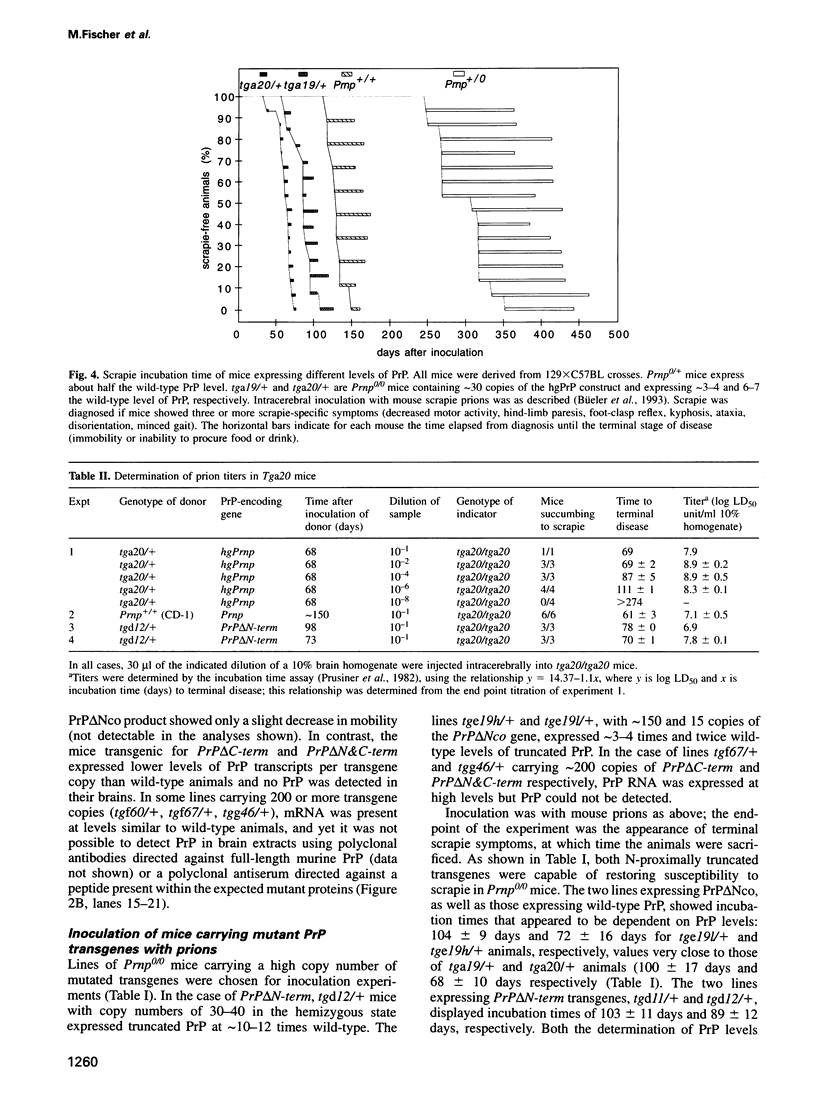
- Moser M., Colello R. J., Pott U., Oesch B. Developmental expression of the prion protein gene in glial cells. Neuron. 1995 Mar;14(3):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90307-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neary K., Caughey B., Ernst D., Race R. E., Chesebro B. Protease sensitivity and nuclease resistance of the scrapie agent propagated in vitro in neuroblastoma cells. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):1031–1034. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.1031-1034.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan K. M., Baldwin M., Nguyen J., Gasset M., Serban A., Groth D., Mehlhorn I., Huang Z., Fletterick R. J., Cohen F. E. Conversion of alpha-helices into beta-sheets features in the formation of the scrapie prion proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):10962–10966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.10962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocchiari M. Prions and related neurological diseases. Mol Aspects Med. 1994;15(3):195–291. doi: 10.1016/0098-2997(94)90042-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Cochran S. P., Groth D. F., Downey D. E., Bowman K. A., Martinez H. M. Measurement of the scrapie agent using an incubation time interval assay. Ann Neurol. 1982 Apr;11(4):353–358. doi: 10.1002/ana.410110406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Molecular biology of prion diseases. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1515–1522. doi: 10.1126/science.1675487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Scott M., Foster D., Pan K. M., Groth D., Mirenda C., Torchia M., Yang S. L., Serban D., Carlson G. A. Transgenetic studies implicate interactions between homologous PrP isoforms in scrapie prion replication. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):673–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90134-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M., Yehiely F., Scott M., Prusiner S. B. Conversion of truncated and elongated prion proteins into the scrapie isoform in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3182–3186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sailer A., Büeler H., Fischer M., Aguzzi A., Weissmann C. No propagation of prions in mice devoid of PrP. Cell. 1994 Jul 1;77(7):967–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M., Foster D., Mirenda C., Serban D., Coufal F., Wälchli M., Torchia M., Groth D., Carlson G., DeArmond S. J. Transgenic mice expressing hamster prion protein produce species-specific scrapie infectivity and amyloid plaques. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90608-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serban D., Taraboulos A., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B. Rapid detection of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and scrapie prion proteins. Neurology. 1990 Jan;40(1):110–117. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.1.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Baldwin M. A., Teplow D. B., Hood L., Gibson B. W., Burlingame A. L., Prusiner S. B. Structural studies of the scrapie prion protein using mass spectrometry and amino acid sequencing. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 2;32(8):1991–2002. doi: 10.1021/bi00059a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliavini F., Prelli F., Porro M., Rossi G., Giaccone G., Farlow M. R., Dlouhy S. R., Ghetti B., Bugiani O., Frangione B. Amyloid fibrils in Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease (Indiana and Swedish kindreds) express only PrP peptides encoded by the mutant allele. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90554-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann C. Spongiform encephalopathies. The prion's progress. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):569–571. doi: 10.1038/349569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway D., Cooper C., Turner S., Da Costa M., Carlson G. A., Prusiner S. B. Structure and polymorphism of the mouse prion protein gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6418–6422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway D., DeArmond S. J., Cayetano-Canlas J., Groth D., Foster D., Yang S. L., Torchia M., Carlson G. A., Prusiner S. B. Degeneration of skeletal muscle, peripheral nerves, and the central nervous system in transgenic mice overexpressing wild-type prion proteins. Cell. 1994 Jan 14;76(1):117–129. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway D., Mirenda C. A., Foster D., Zebarjadian Y., Scott M., Torchia M., Yang S. L., Serban H., DeArmond S. J., Ebeling C. Paradoxical shortening of scrapie incubation times by expression of prion protein transgenes derived from long incubation period mice. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90074-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilmut I., Hooper M. L., Simons J. P. Genetic manipulation of mammals and its application in reproductive biology. J Reprod Fertil. 1991 Jul;92(2):245–279. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0920245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xi Y. G., Ingrosso L., Ladogana A., Masullo C., Pocchiari M. Amphotericin B treatment dissociates in vivo replication of the scrapie agent from PrP accumulation. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):598–601. doi: 10.1038/356598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]