Abstract
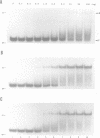
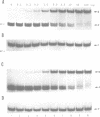
Ethylation interference and hydroxyl radical footprinting were used to identify substrate ribose-phosphate backbone sites that interact with the Escherichia coli RNA processing enzyme, ribonuclease III. Two RNase III mutants were employed, which bind substrate in vitro similarly as wild-type enzyme, but lack detectable phosphodiesterase activity. Specifically, altering glutamic acid at position 117 to lysine or alanine uncouples substrate binding from cleavage. The two substrates examined are based on the bacteriophage T7 R1.1 RNase III processing signal. One substrate, R1.1 RNA, undergoes accurate single cleavage at the canonical site, while a close variant, R1.1[WC-L] RNA, undergoes coordinate double cleavage. The interference and footprinting patterns for each substrate (i) overlap, (ii) exhibit symmetry and (iii) extend approximately one helical turn in each direction from the RNase III cleavage sites. Divalent metal ions (Mg2+, Ca2+) significantly enhance substrate binding, and confer stronger protection from hydroxyl radicals, but do not significantly affect the interference pattern. The footprinting and interference patterns indicate that (i) RNase III contacts the sugar-phosphate backbone; (ii) the RNase III-substrate interaction spans two turns of the A-form helix; and (iii) divalent metal ion does not play an essential role in binding specificity. These results rationalize the conserved two-turn helix motif seen in most RNase III processing signals, and which is necessary for optimal processing reactivity. In addition, the specific differences in the footprint and interference patterns of the two substrates suggest why RNase III catalyzes the coordinate double cleavage of R1.1[WC-L] RNA, and dsRNA in general, while catalyzing only single cleavage of R1.1 RNA and related substrates in which the scissle bond is within an asymmetric internal loop.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beese L. S., Steitz T. A. Structural basis for the 3'-5' exonuclease activity of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I: a two metal ion mechanism. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):25–33. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Young R. A., Steitz J. A. The ribonuclease III site flanking 23S sequences in the 30S ribosomal precursor RNA of E. coli. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90513-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bycroft M., Grünert S., Murzin A. G., Proctor M., St Johnston D. NMR solution structure of a dsRNA binding domain from Drosophila staufen protein reveals homology to the N-terminal domain of ribosomal protein S5. EMBO J. 1995 Jul 17;14(14):3563–3571. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07362.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey J., Cameron V., de Haseth P. L., Uhlenbeck O. C. Sequence-specific interaction of R17 coat protein with its ribonucleic acid binding site. Biochemistry. 1983 May 24;22(11):2601–2610. doi: 10.1021/bi00280a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelladurai B. S., Li H., Nicholson A. W. A conserved sequence element in ribonuclease III processing signals is not required for accurate in vitro enzymatic cleavage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1759–1766. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelladurai B., Li H., Zhang K., Nicholson A. W. Mutational analysis of a ribonuclease III processing signal. Biochemistry. 1993 Jul 27;32(29):7549–7558. doi: 10.1021/bi00080a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P. A., Mathews M. B. Interactions between the double-stranded RNA binding motif and RNA: definition of the binding site for the interferon-induced protein kinase DAI (PKR) on adenovirus VA RNA. RNA. 1995 Mar;1(1):7–20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage T7 DNA and the locations of T7 genetic elements. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):477–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gott J. M., Pan T., LeCuyer K. A., Uhlenbeck O. C. Using circular permutation analysis to redefine the R17 coat protein binding site. Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 14;32(49):13399–13404. doi: 10.1021/bi00212a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodberg J., Dunn J. J. ompT encodes the Escherichia coli outer membrane protease that cleaves T7 RNA polymerase during purification. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1245–1253. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1245-1253.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Cleavage of DNA with methidiumpropyl-EDTA-iron(II): reaction conditions and product analyses. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 14;23(17):3934–3945. doi: 10.1021/bi00312a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino Y., Sugimoto A., Yamamoto M. S. pombe pac1+, whose overexpression inhibits sexual development, encodes a ribonuclease III-like RNase. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):221–226. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07939.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inada T., Kawakami K., Chen S. M., Takiff H. E., Court D. L., Nakamura Y. Temperature-sensitive lethal mutant of era, a G protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5017–5024. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5017-5024.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayanagi K., Miyagawa M., Matsushima M., Ishikawa M., Kanaya S., Ikehara M., Matsuzaki T., Morikawa K. Three-dimensional structure of ribonuclease H from E. coli. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):306–309. doi: 10.1038/347306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharrat A., Macias M. J., Gibson T. J., Nilges M., Pastore A. Structure of the dsRNA binding domain of E. coli RNase III. EMBO J. 1995 Jul 17;14(14):3572–3584. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krinke L., Wulff D. L. The cleavage specificity of RNase III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4809–4815. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham J. A., Cech T. R. Defining the inside and outside of a catalytic RNA molecule. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):276–282. doi: 10.1126/science.2501870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. L., Chelladurai B. S., Zhang K., Nicholson A. W. Ribonuclease III cleavage of a bacteriophage T7 processing signal. Divalent cation specificity, and specific anion effects. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):1919–1925. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March P. E., Gonzalez M. A. Characterization of the biochemical properties of recombinant ribonuclease III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3293–3298. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meegan J. M., Marcus P. I. Double-stranded ribonuclease coinduced with interferon. Science. 1989 Jun 2;244(4908):1089–1091. doi: 10.1126/science.2471268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra S., Bechhofer D. H. Substrate specificity of an RNase III-like activity from Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31450–31456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano L., Cawley D., Herschman H. R. Disuccinimidyl suberate cross-linked ricin does not inhibit cell-free protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Nov 16;109(1):7–13. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91558-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson A. W. Accurate enzymatic cleavage in vitro of a 2'-deoxyribose-substituted ribonuclease III processing signal. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 11;1129(3):318–322. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90509-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson A. W., Niebling K. R., McOsker P. L., Robertson H. D. Accurate in vitro cleavage by RNase III of phosphorothioate-substituted RNA processing signals in bacteriophage T7 early mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1577–1591. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson A. W. Structure, reactivity, and biology of double-stranded RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1996;52:1–65. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60963-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin S., Gilliland G. Site-specific mutagenesis using asymmetric polymerase chain reaction and a single mutant primer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7433–7438. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. D. Escherichia coli ribonuclease III cleavage sites. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):669–672. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90270-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendahl G., Douthwaite S. Ribosomal proteins L11 and L10.(L12)4 and the antibiotic thiostrepton interact with overlapping regions of the 23 S rRNA backbone in the ribosomal GTPase centre. J Mol Biol. 1993 Dec 20;234(4):1013–1020. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweisguth D. C., Chelladurai B. S., Nicholson A. W., Moore P. B. Structural characterization of a ribonuclease III processing signal. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Feb 25;22(4):604–612. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.4.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. J., Capaldi R. A., Muchmore D., Dahlquist F. Cross-linking of ubiquinone cytochrome c reductase (complex III) with periodate-cleavable bifunctional reagents. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 5;17(18):3719–3723. doi: 10.1021/bi00611a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Brown N. H., Gall J. G., Jantsch M. A conserved double-stranded RNA-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10979–10983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlassov V. V., Giegé R., Ebel J. P. Tertiary structure of tRNAs in solution monitored by phosphodiester modification with ethylnitrosourea. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep;119(1):51–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. G., Simons R. W. Antisense RNA control in bacteria, phages, and plasmids. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1994;48:713–742. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.48.100194.003433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler F. K., Banner D. W., Oefner C., Tsernoglou D., Brown R. S., Heathman S. P., Bryan R. K., Martin P. D., Petratos K., Wilson K. S. The crystal structure of EcoRV endonuclease and of its complexes with cognate and non-cognate DNA fragments. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1781–1795. doi: 10.2210/pdb4rve/pdb. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang W., Hendrickson W. A., Crouch R. J., Satow Y. Structure of ribonuclease H phased at 2 A resolution by MAD analysis of the selenomethionyl protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1398–1405. doi: 10.1126/science.2169648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber M., Hoover T. A., Powell B. S., Court D. L. Analysis of the rnc locus of Coxiella burnetii. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Oct;14(2):291–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]