Abstract
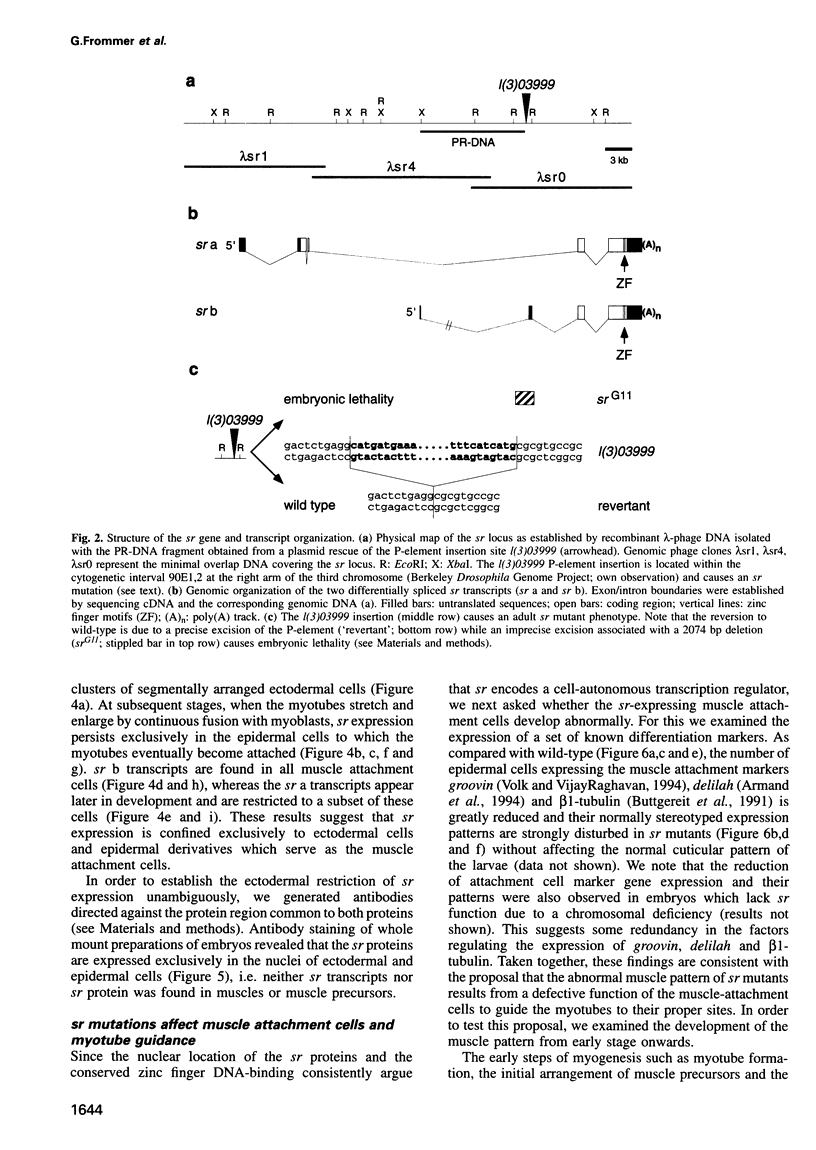
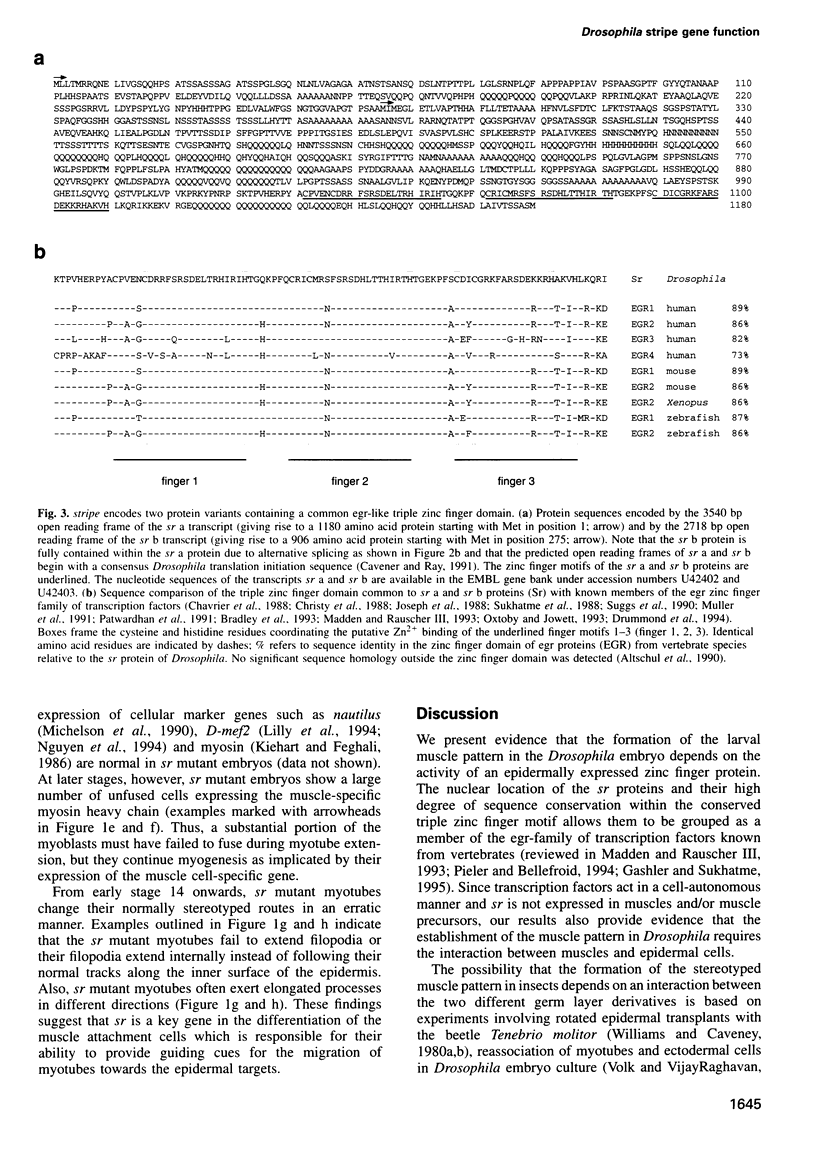
We have cloned and molecularly characterized the Drosophila gene stripe (sr) required for muscle-pattern formation in the embryo. Through differential splicing, sr encodes two nuclear protein variants which contain a zinc finger DNA-binding domain in common with the early growth response (egr) family of vertebrate transcription factors. The sr transcripts and their protein products are exclusively expressed in the epidermal muscle attachment cells and their ectodermal precursors, but not in muscles or muscle precursors. The results suggest that sr activity induces a subset of ectodermal cells to develop into muscle attachment sites and to provide spatial cues necessary to orient myotubes along the basal surface of the epidermis to their targeted attachment cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abmayr S. M., Erickson M. S., Bour B. A. Embryonic development of the larval body wall musculature of Drosophila melanogaster. Trends Genet. 1995 Apr;11(4):153–159. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)89030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armand P., Knapp A. C., Hirsch A. J., Wieschaus E. F., Cole M. D. A novel basic helix-loop-helix protein is expressed in muscle attachment sites of the Drosophila epidermis. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):4145–4154. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.4145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball E. E., Ho R. K., Goodman C. S. Muscle development in the grasshopper embryo. I. Muscles, nerves, and apodemes in the metathoracic leg. Dev Biol. 1985 Oct;111(2):383–398. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90492-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bate M. The embryonic development of larval muscles in Drosophila. Development. 1990 Nov;110(3):791–804. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.3.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellen H. J., O'Kane C. J., Wilson C., Grossniklaus U., Pearson R. K., Gehring W. J. P-element-mediated enhancer detection: a versatile method to study development in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1288–1300. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogaert T., Brown N., Wilcox M. The Drosophila PS2 antigen is an invertebrate integrin that, like the fibronectin receptor, becomes localized to muscle attachments. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):929–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90580-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley L. C., Snape A., Bhatt S., Wilkinson D. G. The structure and expression of the Xenopus Krox-20 gene: conserved and divergent patterns of expression in rhombomeres and neural crest. Mech Dev. 1993 Jan;40(1-2):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90089-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brower D. L., Bunch T. A., Mukai L., Adamson T. E., Wehrli M., Lam S., Friedlander E., Roote C. E., Zusman S. Nonequivalent requirements for PS1 and PS2 integrin at cell attachments in Drosophila: genetic analysis of the alpha PS1 integrin subunit. Development. 1995 May;121(5):1311–1320. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.5.1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. H. Null mutations in the alpha PS2 and beta PS integrin subunit genes have distinct phenotypes. Development. 1994 May;120(5):1221–1231. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.5.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttgereit D., Leiss D., Michiels F., Renkawitz-Pohl R. During Drosophila embryogenesis the beta 1 tubulin gene is specifically expressed in the nervous system and the apodemes. Mech Dev. 1991 Feb;33(2):107–118. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90077-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R., Ray S. C. Eukaryotic start and stop translation sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3185–3192. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Zerial M., Lemaire P., Almendral J., Bravo R., Charnay P. A gene encoding a protein with zinc fingers is activated during G0/G1 transition in cultured cells. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):29–35. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy B. A., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated in mouse 3T3 cells by serum growth factors encodes a protein with "zinc finger" sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7857–7861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello W. J., Wyman R. J. Development of an indirect flight muscle in a muscle-specific mutant of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1986 Nov;118(1):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue M. J., Sanes J. R. All muscles are not created equal. Trends Genet. 1994 Nov;10(11):396–401. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond I. A., Rohwer-Nutter P., Sukhatme V. P. The zebrafish egr1 gene encodes a highly conserved, zinc-finger transcriptional regulator. DNA Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;13(9):953–961. doi: 10.1089/dna.1994.13.953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogerty F. J., Fessler L. I., Bunch T. A., Yaron Y., Parker C. G., Nelson R. E., Brower D. L., Gullberg D., Fessler J. H. Tiggrin, a novel Drosophila extracellular matrix protein that functions as a ligand for Drosophila alpha PS2 beta PS integrins. Development. 1994 Jul;120(7):1747–1758. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.7.1747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch M. Induction of visceral and cardiac mesoderm by ectodermal Dpp in the early Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1995 Mar 30;374(6521):464–467. doi: 10.1038/374464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gashler A., Sukhatme V. P. Early growth response protein 1 (Egr-1): prototype of a zinc-finger family of transcription factors. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1995;50:191–224. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60815-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph L. J., Le Beau M. M., Jamieson G. A., Jr, Acharya S., Shows T. B., Rowley J. D., Sukhatme V. P. Molecular cloning, sequencing, and mapping of EGR2, a human early growth response gene encoding a protein with "zinc-binding finger" structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7164–7168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpen G. H., Spradling A. C. Analysis of subtelomeric heterochromatin in the Drosophila minichromosome Dp1187 by single P element insertional mutagenesis. Genetics. 1992 Nov;132(3):737–753. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehart D. P., Feghali R. Cytoplasmic myosin from Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1517–1525. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilly B., Galewsky S., Firulli A. B., Schulz R. A., Olson E. N. D-MEF2: a MADS box transcription factor expressed in differentiating mesoderm and muscle cell lineages during Drosophila embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5662–5666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. M., Ingham P., Struhl G. Isolation, structure, and expression of even-skipped: a second pair-rule gene of Drosophila containing a homeo box. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):721–734. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90515-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. M., Abmayr S. M., Bate M., Arias A. M., Maniatis T. Expression of a MyoD family member prefigures muscle pattern in Drosophila embryos. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2086–2097. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H. J., Skerka C., Bialonski A., Zipfel P. F. Clone pAT 133 identifies a gene that encodes another human member of a class of growth factor-induced genes with almost identical zinc-finger domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10079–10083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen H. T., Bodmer R., Abmayr S. M., McDermott J. C., Spoerel N. A. D-mef2: a Drosophila mesoderm-specific MADS box-containing gene with a biphasic expression profile during embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 2;91(16):7520–7524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.16.7520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Rosenthal N. Homeobox genes and muscle patterning. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):9–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90395-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxtoby E., Jowett T. Cloning of the zebrafish krox-20 gene (krx-20) and its expression during hindbrain development. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 11;21(5):1087–1095. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Bellefroid E. Perspectives on zinc finger protein function and evolution--an update. Mol Biol Rep. 1994 Jul;20(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00999848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehling-Hampton K., Hoffmann F. M., Baylies M. K., Rushton E., Bate M. dpp induces mesodermal gene expression in Drosophila. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):783–786. doi: 10.1038/372783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suggs S. V., Katzowitz J. L., Tsai-Morris C., Sukhatme V. P. cDNA sequence of the human cellular early growth response gene Egr-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4283–4283. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk T., VijayRaghavan K. A central role for epidermal segment border cells in the induction of muscle patterning in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1994 Jan;120(1):59–70. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. J., Caveney S. A gradient of morphogenetic information involved in muscle patterning. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1980 Aug;58:35–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. J., Caveney S. Changing muscle patterns in a segmental epidermal field. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1980 Aug;58:13–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Pearson R. K., Bellen H. J., O'Kane C. J., Grossniklaus U., Gehring W. J. P-element-mediated enhancer detection: an efficient method for isolating and characterizing developmentally regulated genes in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1301–1313. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Pompa J. L., Garcia J. R., Ferrús A. Genetic analysis of muscle development in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1989 Feb;131(2):439–454. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(89)80016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]