Abstract
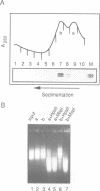
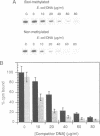
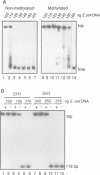
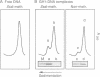
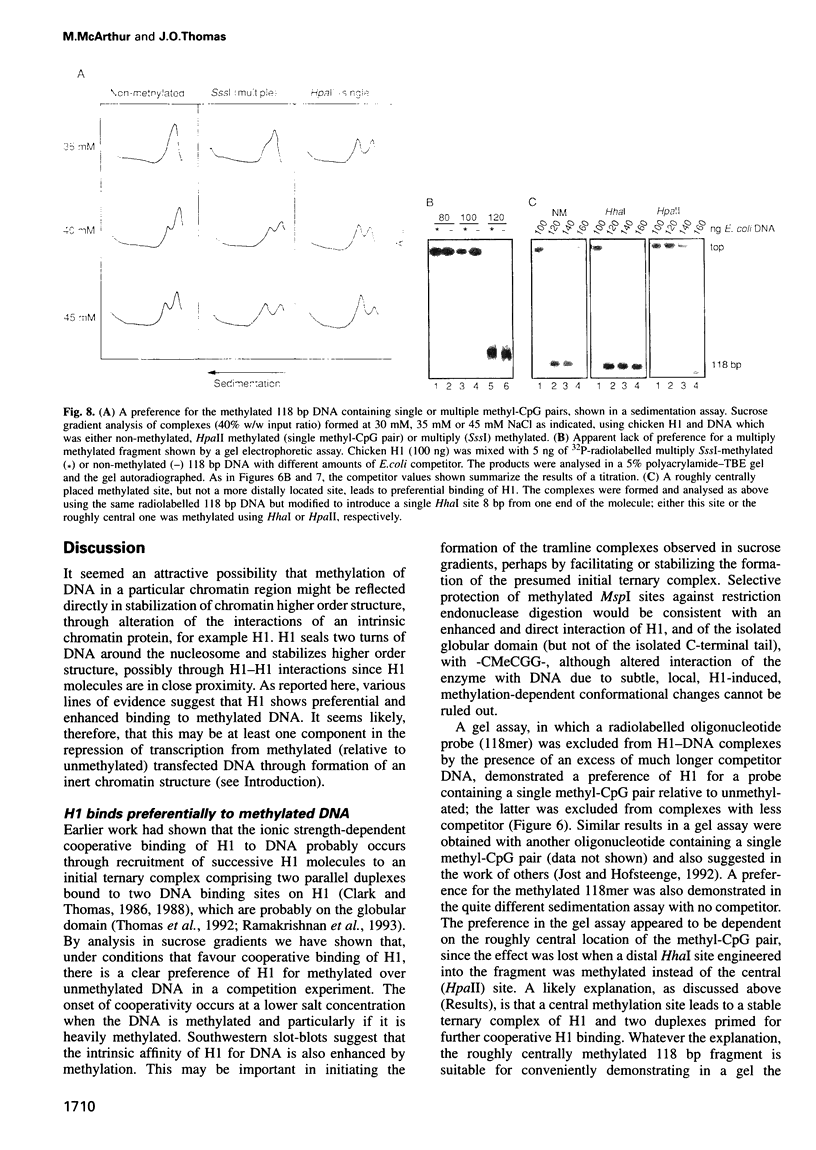
We have identified a clear preference of histone H1 for CpG-methylated DNA, irrespective of DNA sequence. The conditions under which this preference is observed allowed cooperative binding of H1; the H1-DNA complexes formed were shown earlier to be 'tramlines' of two DNA duplexes bridged by an array of H1 molecules, and multiples of these. The preference for methylated DNA is clear in sedimentation assays, which also show that the preference is greater with increased methylation level, and in gel retardation assays with an oligonucleotide containing a single methyl-CpG pair; it is shared by the globular domain which also binds cooperatively to DNA. A small intrinsic preference of H1 for methylated DNA is also apparent in Southwestern assays where the immobilized H1 presumably cannot bind cooperatively. Methylated DNA in H1-DNA complexes was partially protected (relative to unmethylated DNA) against digestion by MspI but not by enzymes whose cutting sites were not methylated, consistent with a direct interaction of H1 with methylated nucleotides; this was also true of GH1-DNA complexes. H1 variants (spH1 and H5) from transcriptionally repressed nuclei have a stronger preference than H1 for methylated DNA, suggesting that this may be relevant to the stabilization of chromatin higher order structure and transcriptional repression.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball D. J., Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. 5-methylcytosine is localized in nucleosomes that contain histone H1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5490–5494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates D. L., Butler P. J., Pearson E. C., Thomas J. O. Stability of the higher-order structure of chicken-erythrocyte chromatin in solution. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Oct;119(3):469–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P., Taggart M. H., Smith B. A. Methylated and unmethylated DNA compartments in the sea urchin genome. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):889–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90329-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschhausen G., Wittig B., Graessmann M., Graessmann A. Chromatin structure is required to block transcription of the methylated herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1177–1181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H. DNA methylation and gene activity. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90479-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerf C., Lippens G., Ramakrishnan V., Muyldermans S., Segers A., Wyns L., Wodak S. J., Hallenga K. Homo- and heteronuclear two-dimensional NMR studies of the globular domain of histone H1: full assignment, tertiary structure, and comparison with the globular domain of histone H5. Biochemistry. 1994 Sep 20;33(37):11079–11086. doi: 10.1021/bi00203a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. J., Hill C. S., Martin S. R., Thomas J. O. Alpha-helix in the carboxy-terminal domains of histones H1 and H5. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):69–75. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02784.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. J., Thomas J. O. Differences in the binding of H1 variants to DNA. Cooperativity and linker-length related distribution. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Dec 1;178(1):225–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. J., Thomas J. O. Salt-dependent co-operative interaction of histone H1 with linear DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 20;187(4):569–580. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90335-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draves P. H., Lowary P. T., Widom J. Co-operative binding of the globular domain of histone H5 to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 20;225(4):1105–1121. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90108-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. J., Pruss D., Wolffe A. P. Contacts of the globular domain of histone H5 and core histones with DNA in a "chromatosome". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 2;91(16):7817–7821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.16.7817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higurashi M., Cole R. D. The combination of DNA methylation and H1 histone binding inhibits the action of a restriction nuclease on plasmid DNA. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8619–8625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. S., Rimmer J. M., Green B. N., Finch J. T., Thomas J. O. Histone-DNA interactions and their modulation by phosphorylation of -Ser-Pro-X-Lys/Arg- motifs. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1939–1948. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07720.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. A., Goddard J. P., Adams R. L. The effect of histone H1 and DNA methylation on transcription. Biochem J. 1995 Feb 1;305(Pt 3):791–798. doi: 10.1042/bj3050791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Hofsteenge J. The repressor MDBP-2 is a member of the histone H1 family that binds preferentially in vitro and in vivo to methylated nonspecific DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9499–9503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamakaka R. T., Thomas J. O. Chromatin structure of transcriptionally competent and repressed genes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3997–4006. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07621.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet I., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Cedar H. DNA methylation affects the formation of active chromatin. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90263-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Zwieb C., Wu C., Adhya S. Bending of DNA by gene-regulatory proteins: construction and use of a DNA bending vector. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A., Yeivin A., Ben-Asher E., Aloni Y., Razin A. Histone H1-mediated inhibition of transcription initiation of methylated templates in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21754–21759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. D., Meehan R. R., Henzel W. J., Maurer-Fogy I., Jeppesen P., Klein F., Bird A. Purification, sequence, and cellular localization of a novel chromosomal protein that binds to methylated DNA. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):905–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90610-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meehan R. R., Lewis J. D., Bird A. P. Characterization of MeCP2, a vertebrate DNA binding protein with affinity for methylated DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 11;20(19):5085–5092. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.19.5085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meehan R. R., Lewis J. D., McKay S., Kleiner E. L., Bird A. P. Identification of a mammalian protein that binds specifically to DNA containing methylated CpGs. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):499–507. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90430-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskimins W. K., Roberts M. P., McClelland A., Ruddle F. H. Use of a protein-blotting procedure and a specific DNA probe to identify nuclear proteins that recognize the promoter region of the transferrin receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6741–6744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nightingale K., Wolffe A. P. Methylation at CpG sequences does not influence histone H1 binding to a nucleosome including a Xenopus borealis 5 S rRNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 3;270(9):4197–4200. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.9.4197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. Preparation of native chromatin and damage caused by shearing. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1203–1206. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4182.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan V., Finch J. T., Graziano V., Lee P. L., Sweet R. M. Crystal structure of globular domain of histone H5 and its implications for nucleosome binding. Nature. 1993 Mar 18;362(6417):219–223. doi: 10.1038/362219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renz M. Preferential and cooperative binding of histone I to chromosomal mammalian DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):733–736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supakar P. C., Weist D., Zhang D. L., Inamdar N., Zhang X. Y., Khan R., Ehrlich K. C., Ehrlich M. Methylated DNA-binding protein is present in various mammalian cell types. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):8029–8044. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.8029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Bird A. Alternative chromatin structure at CpG islands. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):909–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90339-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Koller T., Klug A. Involvement of histone H1 in the organization of the nucleosome and of the salt-dependent superstructures of chromatin. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):403–427. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. The study of histone--histone associations by chemical cross-linking. Methods Cell Biol. 1978;18:429–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Rees C., Butler P. J. Salt-induced folding of sea urchin sperm chromatin. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jan 15;154(2):343–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Rees C., Finch J. T. Cooperative binding of the globular domains of histones H1 and H5 to DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):187–194. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., LaMarco K. L., Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. In situ detection of sequence-specific DNA binding activity specified by a recombinant bacteriophage. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):801–806. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalwijk C., Flavell R. A. MspI, an isoschizomer of hpaII which cleaves both unmethylated and methylated hpaII sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3231–3236. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]