Abstract
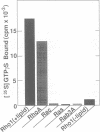
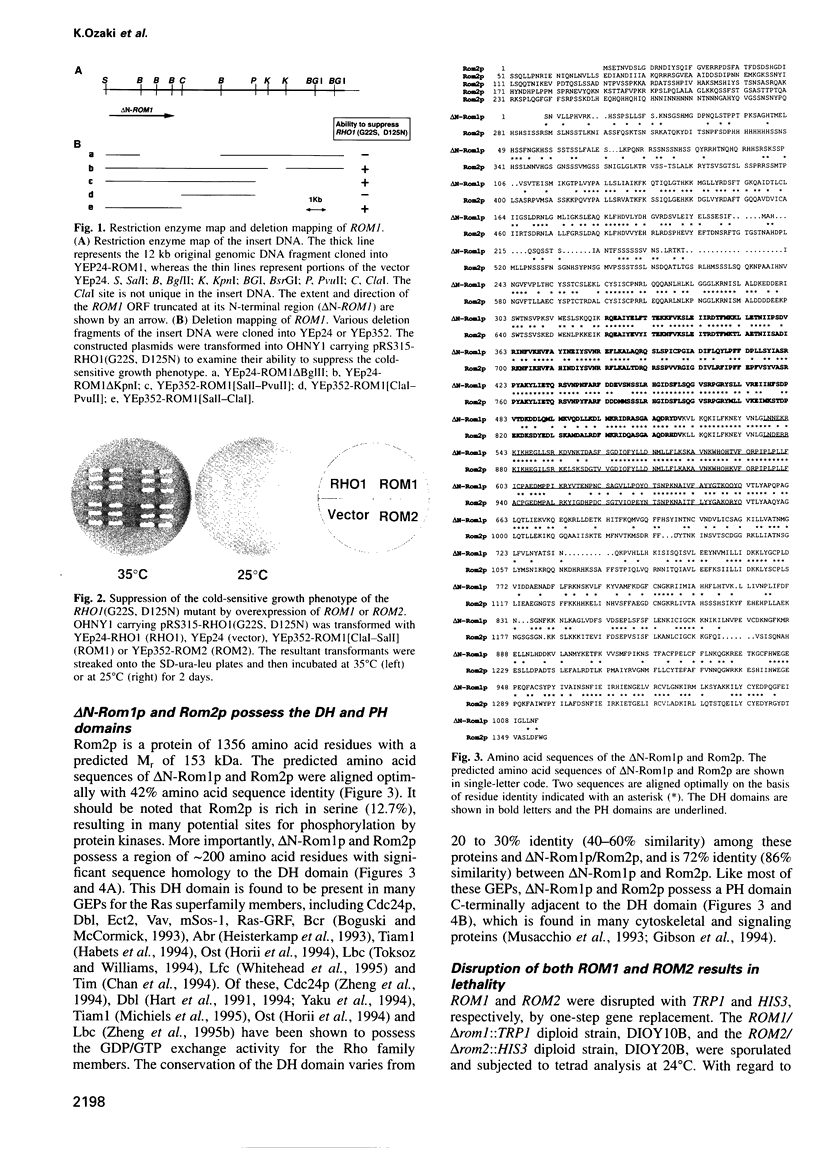
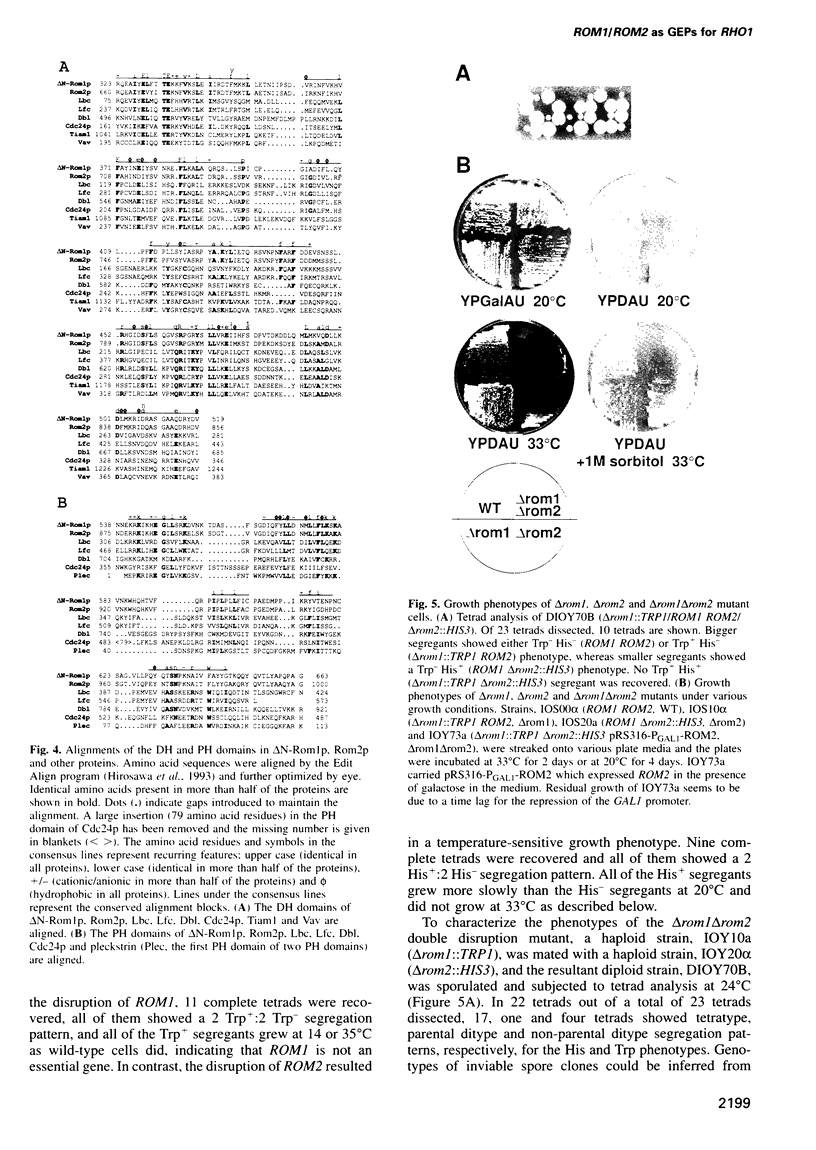
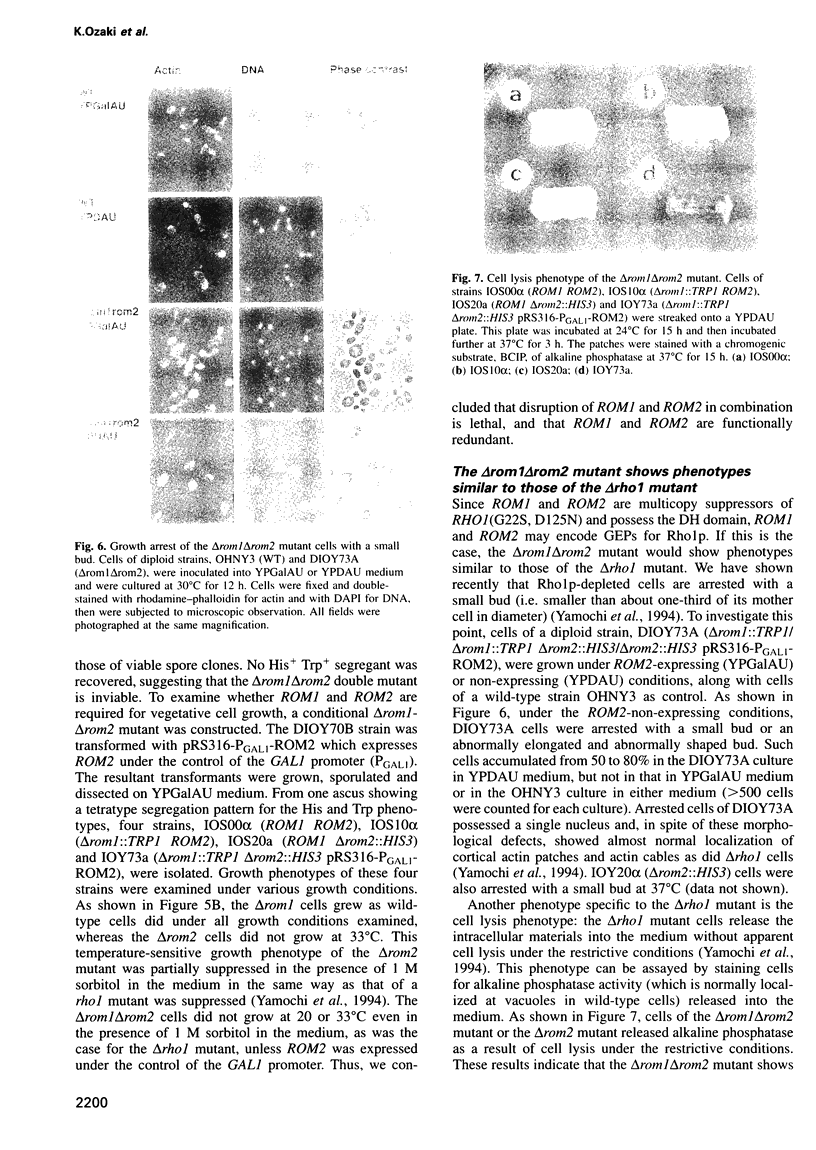
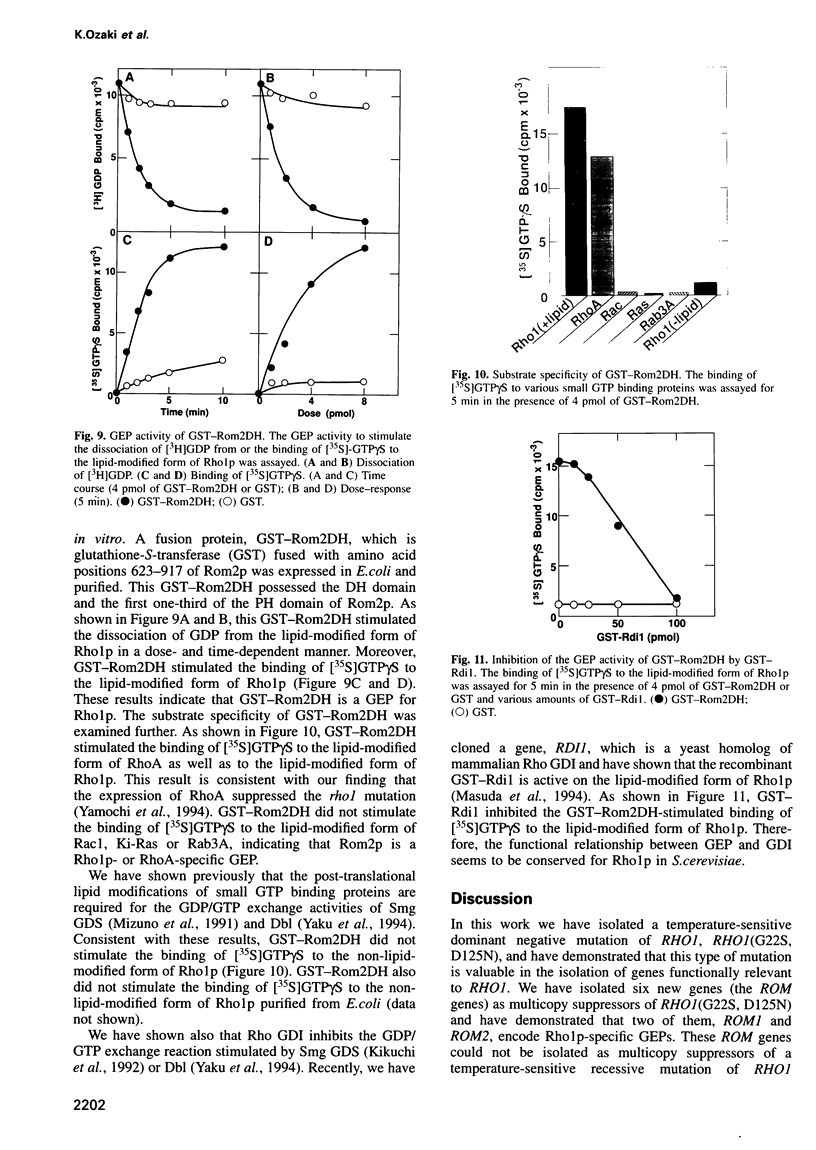
The RHO1 gene encodes a homolog of the mammalian RhoA small GTP binding protein in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Rho1p is localized at the growth site and is required for bud formation. Multicopy suppressors of a temperature-sensitive, dominant negative mutant allele of RHO1, RHO1(G22S, D125N), were isolated and named ROM (RHO1 multicopy suppressor). Rom1p and Rom2p were found to contain a DH (Dbl homologous) domain and a PH (pleckstrin homologous) domain, both of which are conserved among the GDP/GTP exchange proteins (GEPs) for the Rho family small GTP binding proteins. Disruption of ROM2 resulted in a temperature-sensitive growth phenotype, whereas disruption of both ROM1 and ROM2 resulted in lethality. The phenotypes of deltarom1deltarom2 cells were similar to those of deltarho1 cells, including growth arrest with a small bud and cell lysis. Moreover, the temperature-sensitive growth phenotype of deltarom2 was suppressed by overexpression of RHO1 or RHO2, but not of CDC42. The glutathione-S-transferase (GST) fusion protein containing the DH domain of Rom2p showed the lipid-modified Rholp-specific GDP/GTP exchange activity which was sensitive to Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor. These results indicate that Rom1p and Rom2p are GEPs that activate Rho1p in S.cerevisiae.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A. E., Johnson D. I., Longnecker R. M., Sloat B. F., Pringle J. R. CDC42 and CDC43, two additional genes involved in budding and the establishment of cell polarity in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;111(1):131–142. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando S., Kaibuchi K., Sasaki T., Hiraoka K., Nishiyama T., Mizuno T., Asada M., Nunoi H., Matsuda I., Matsuura Y. Post-translational processing of rac p21s is important both for their interaction with the GDP/GTP exchange proteins and for their activation of NADPH oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25709–25713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel P., Chien C. T., Sternglanz R., Fields S. Elimination of false positives that arise in using the two-hybrid system. Biotechniques. 1993 Jun;14(6):920–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguski M. S., McCormick F. Proteins regulating Ras and its relatives. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):643–654. doi: 10.1038/366643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Bohl B. P., Chuang T. H. Guanine nucleotide exchange regulates membrane translocation of Rac/Rho GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31674–31679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan A. M., McGovern E. S., Catalano G., Fleming T. P., Miki T. Expression cDNA cloning of a novel oncogene with sequence similarity to regulators of small GTP-binding proteins. Oncogene. 1994 Apr;9(4):1057–1063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chant J., Stowers L. GTPase cascades choreographing cellular behavior: movement, morphogenesis, and more. Cell. 1995 Apr 7;81(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90363-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. Y., Huff S. Y., Lai C. C., Der C. J., Powers S. Ras-15A protein shares highly similar dominant-negative biological properties with Ras-17N and forms a stable, guanine-nucleotide resistant complex with CDC25 exchange factor. Oncogene. 1994 Sep;9(9):2691–2698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G. Development of cell polarity in budding yeast. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1093–1096. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90001-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto Y., Kaibuchi K., Hori Y., Fujioka H., Araki S., Ueda T., Kikuchi A., Takai Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel type of regulatory protein (GDI) for the rho proteins, ras p21-like small GTP-binding proteins. Oncogene. 1990 Sep;5(9):1321–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T. J., Hyvönen M., Musacchio A., Saraste M., Birney E. PH domain: the first anniversary. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Sep;19(9):349–353. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz D., St Jean A., Woods R. A., Schiestl R. H. Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1425–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters and lacZ fusions designed to study expression of cloned genes in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:181–191. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habets G. G., Scholtes E. H., Zuydgeest D., van der Kammen R. A., Stam J. C., Berns A., Collard J. G. Identification of an invasion-inducing gene, Tiam-1, that encodes a protein with homology to GDP-GTP exchangers for Rho-like proteins. Cell. 1994 May 20;77(4):537–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90216-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. Small GTP-binding proteins and the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1994;10:31–54. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.10.110194.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. E., Hajduk P. J., Yoon H. S., Fesik S. W. Pleckstrin homology domains bind to phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate. Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):168–170. doi: 10.1038/371168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart M. J., Eva A., Evans T., Aaronson S. A., Cerione R. A. Catalysis of guanine nucleotide exchange on the CDC42Hs protein by the dbl oncogene product. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):311–314. doi: 10.1038/354311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart M. J., Eva A., Zangrilli D., Aaronson S. A., Evans T., Cerione R. A., Zheng Y. Cellular transformation and guanine nucleotide exchange activity are catalyzed by a common domain on the dbl oncogene product. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):62–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisterkamp N., Kaartinen V., van Soest S., Bokoch G. M., Groffen J. Human ABR encodes a protein with GAPrac activity and homology to the DBL nucleotide exchange factor domain. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):16903–16906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Koerner T. J., Tzagoloff A. Yeast/E. coli shuttle vectors with multiple unique restriction sites. Yeast. 1986 Sep;2(3):163–167. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horii Y., Beeler J. F., Sakaguchi K., Tachibana M., Miki T. A novel oncogene, ost, encodes a guanine nucleotide exchange factor that potentially links Rho and Rac signaling pathways. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 17;13(20):4776–4786. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06803.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. I., Pringle J. R. Molecular characterization of CDC42, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene involved in the development of cell polarity. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;111(1):143–152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Mizuno T., Fujioka H., Yamamoto T., Kishi K., Fukumoto Y., Hori Y., Takai Y. Molecular cloning of the cDNA for stimulatory GDP/GTP exchange protein for smg p21s (ras p21-like small GTP-binding proteins) and characterization of stimulatory GDP/GTP exchange protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2873–2880. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzav S., Cleveland J. L., Heslop H. E., Pulido D. Loss of the amino-terminal helix-loop-helix domain of the vav proto-oncogene activates its transforming potential. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1912–1920. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi A., Kuroda S., Sasaki T., Kotani K., Hirata K., Katayama M., Takai Y. Functional interactions of stimulatory and inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange proteins and their common substrate small GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14611–14615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi A., Yamashita T., Kawata M., Yamamoto K., Ikeda K., Tanimoto T., Takai Y. Purification and characterization of a novel GTP-binding protein with a molecular weight of 24,000 from bovine brain membranes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2897–2904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda S., Kikuchi A., Hirata K., Masuda T., Kishi K., Sasaki T., Takai Y. Cooperative function of rho GDS and rho GDI to regulate rho p21 activation in smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 29;185(1):473–480. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. C., Boguski M., Broek D., Powers S. Influence of guanine nucleotides on complex formation between Ras and CDC25 proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1345–1352. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lelias J. M., Adra C. N., Wulf G. M., Guillemot J. C., Khagad M., Caput D., Lim B. cDNA cloning of a human mRNA preferentially expressed in hematopoietic cells and with homology to a GDP-dissociation inhibitor for the rho GTP-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1479–1483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madaule P., Axel R., Myers A. M. Characterization of two members of the rho gene family from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):779–783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martegani E., Vanoni M., Zippel R., Coccetti P., Brambilla R., Ferrari C., Sturani E., Alberghina L. Cloning by functional complementation of a mouse cDNA encoding a homologue of CDC25, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAS activator. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2151–2157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05274.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda T., Tanaka K., Nonaka H., Yamochi W., Maeda A., Takai Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of yeast rho GDP dissociation inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 5;269(31):19713–19718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui Y., Toh-E A. Yeast RHO3 and RHO4 ras superfamily genes are necessary for bud growth, and their defect is suppressed by a high dose of bud formation genes CDC42 and BEM1. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5690–5699. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura Y., Possee R. D., Overton H. A., Bishop D. H. Baculovirus expression vectors: the requirements for high level expression of proteins, including glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1987 May;68(Pt 5):1233–1250. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-5-1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels F., Habets G. G., Stam J. C., van der Kammen R. A., Collard J. G. A role for Rac in Tiam1-induced membrane ruffling and invasion. Nature. 1995 May 25;375(6529):338–340. doi: 10.1038/375338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Kaibuchi K., Yamamoto T., Kawamura M., Sakoda T., Fujioka H., Matsuura Y., Takai Y. A stimulatory GDP/GTP exchange protein for smg p21 is active on the post-translationally processed form of c-Ki-ras p21 and rhoA p21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6442–6446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musacchio A., Gibson T., Rice P., Thompson J., Saraste M. The PH domain: a common piece in the structural patchwork of signalling proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Sep;18(9):343–348. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90071-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paravicini G., Cooper M., Friedli L., Smith D. J., Carpentier J. L., Klig L. S., Payton M. A. The osmotic integrity of the yeast cell requires a functional PKC1 gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4896–4905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J., Zheng Y., Bender L., Myers A., Cerione R., Bender A. Interactions between the bud emergence proteins Bem1p and Bem2p and Rho-type GTPases in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(5):1395–1406. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.5.1395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., O'Neill K., Wigler M. Dominant yeast and mammalian RAS mutants that interfere with the CDC25-dependent activation of wild-type RAS in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):390–395. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regazzi R., Kikuchi A., Takai Y., Wollheim C. B. The small GTP-binding proteins in the cytosol of insulin-secreting cells are complexed to GDP dissociation inhibitor proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17512–17519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Graziani G., Aaronson S. A., Eva A. The N-terminal region of proto-dbl down regulates its transforming activity. Oncogene. 1989 Sep;4(9):1067–1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Fink G. R. KAR1, a gene required for function of both intranuclear and extranuclear microtubules in yeast. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1047–1060. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90712-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherle P., Behrens T., Staudt L. M. Ly-GDI, a GDP-dissociation inhibitor of the RhoA GTP-binding protein, is expressed preferentially in lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7568–7572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Sasaki T., Tanaka K., Nakanishi H. Rho as a regulator of the cytoskeleton. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Jun;20(6):227–231. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)89022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toksoz D., Williams D. A. Novel human oncogene lbc detected by transfection with distinct homology regions to signal transduction products. Oncogene. 1994 Feb;9(2):621–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touhara K., Inglese J., Pitcher J. A., Shaw G., Lefkowitz R. J. Binding of G protein beta gamma-subunits to pleckstrin homology domains. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10217–10220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Kikuchi A., Ohga N., Yamamoto J., Takai Y. Purification and characterization from bovine brain cytosol of a novel regulatory protein inhibiting the dissociation of GDP from and the subsequent binding of GTP to rhoB p20, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9373–9380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtek A. B., Hollenberg S. M., Cooper J. A. Mammalian Ras interacts directly with the serine/threonine kinase Raf. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90307-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead I., Kirk H., Tognon C., Trigo-Gonzalez G., Kay R. Expression cloning of lfc, a novel oncogene with structural similarities to guanine nucleotide exchange factors and to the regulatory region of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 4;270(31):18388–18395. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.31.18388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaku H., Sasaki T., Takai Y. The Dbl oncogene product as a GDP/GTP exchange protein for the Rho family: its properties in comparison with those of Smg GDS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jan 28;198(2):811–817. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Kaibuchi K., Mizuno T., Hiroyoshi M., Shirataki H., Takai Y. Purification and characterization from bovine brain cytosol of proteins that regulate the GDP/GTP exchange reaction of smg p21s, ras p21-like GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16626–16634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamochi W., Tanaka K., Nonaka H., Maeda A., Musha T., Takai Y. Growth site localization of Rho1 small GTP-binding protein and its involvement in bud formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(5):1077–1093. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.5.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Y., Cerione R., Bender A. Control of the yeast bud-site assembly GTPase Cdc42. Catalysis of guanine nucleotide exchange by Cdc24 and stimulation of GTPase activity by Bem3. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2369–2372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Y., Olson M. F., Hall A., Cerione R. A., Toksoz D. Direct involvement of the small GTP-binding protein Rho in lbc oncogene function. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 21;270(16):9031–9034. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.16.9031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]