Abstract
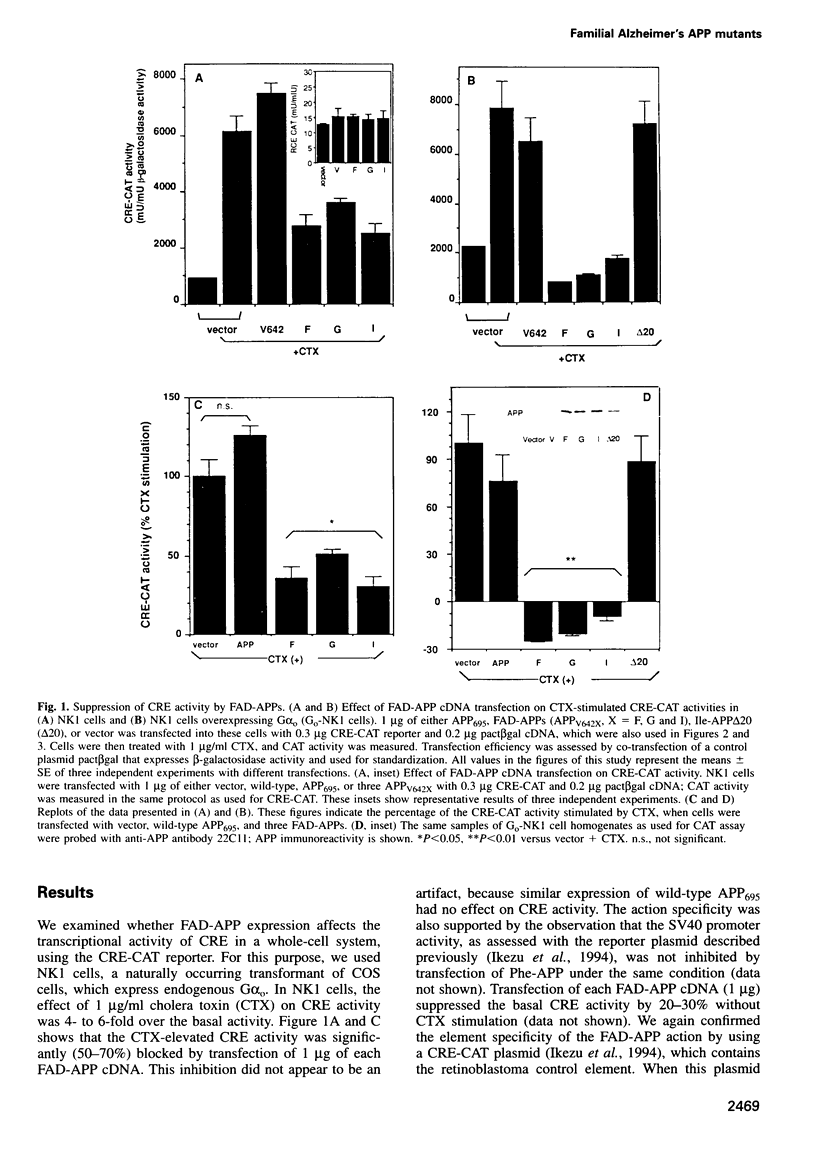
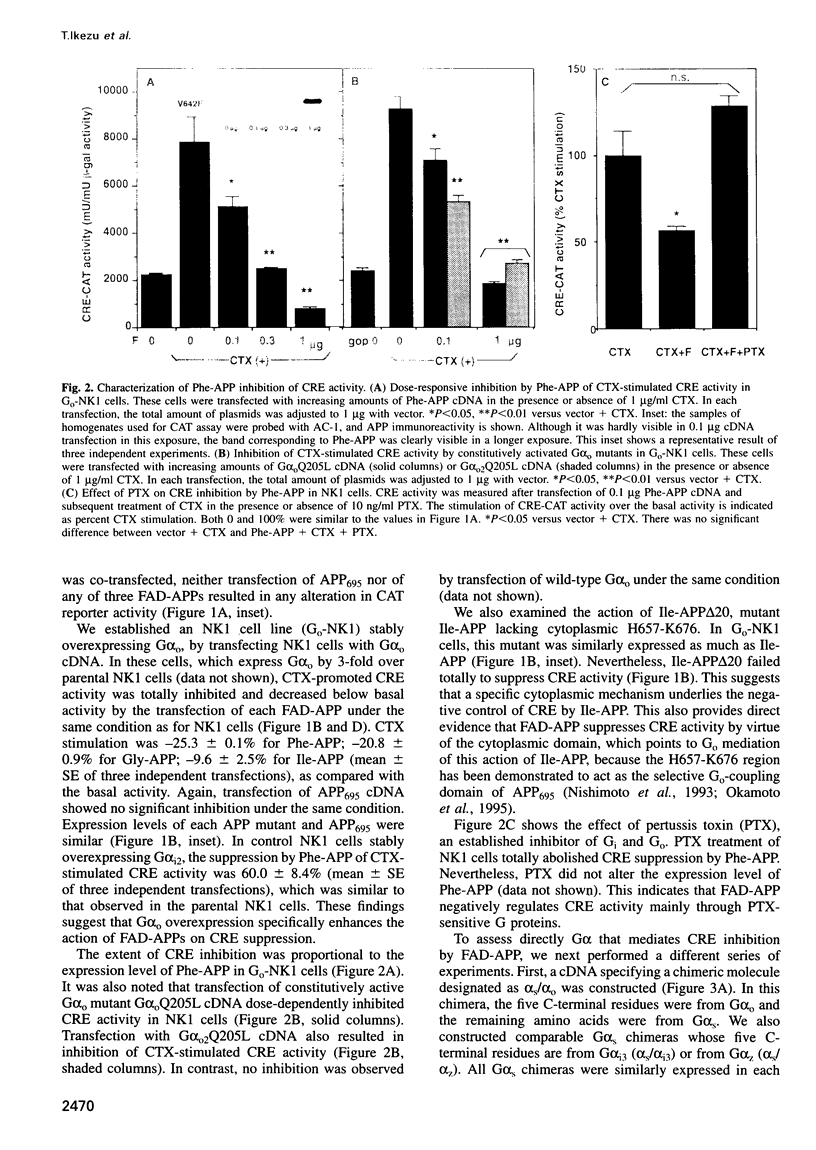
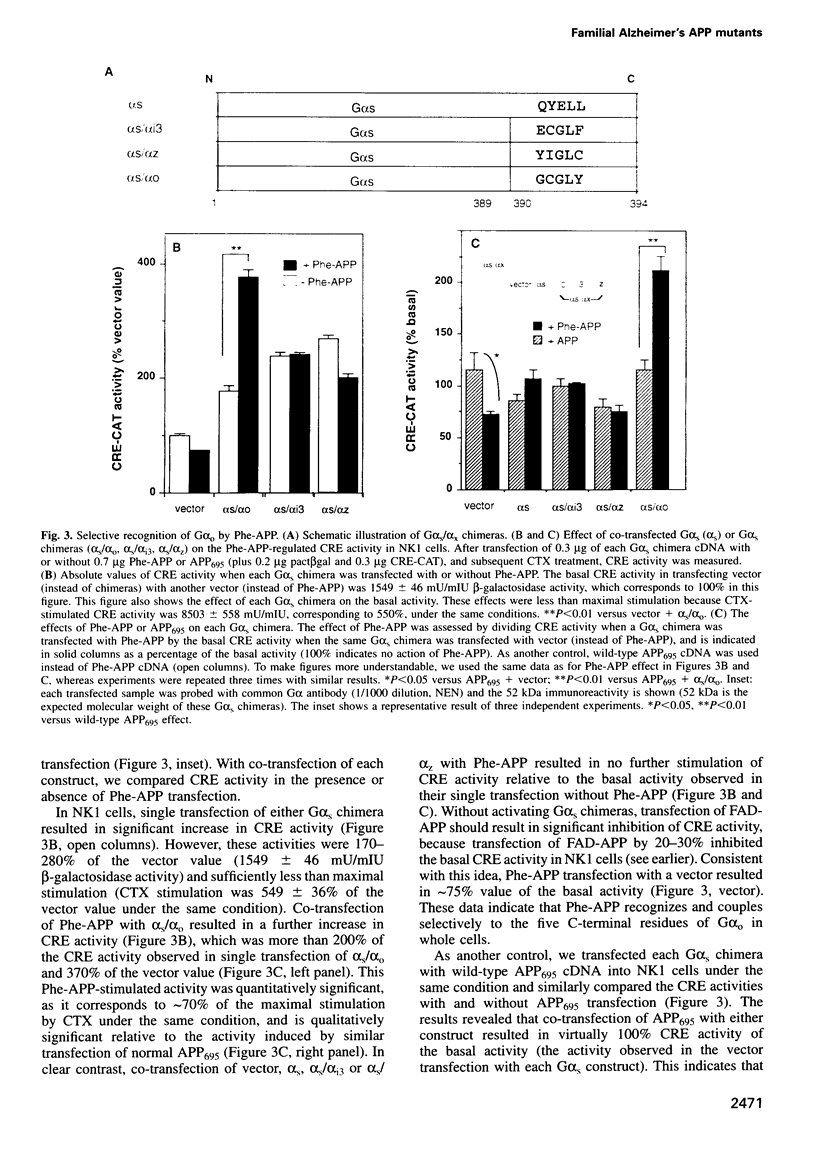
In familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD), missense point mutations V642I/F/G, which co-segregate with the disease phenotype, have been discovered in amyloid precursor APP695. Here, we report that three FAD mutants (FAD-APPs) negatively regulated the transcriptional activity of cAMP response element (CRE) by a G(o)-dependent mechanism, but expression of wildtype APP695 had no effect on CRE. Experiments with various Galpha(s) chimeras demonstrated that Phe-APP coupled selectively to the C-terminus of Galpha(0). Again, wild-type APP695 had no effect on its C-terminus. These data indicate that FAD-APPs are gain-of-function mutants of APP695 that negatively regulate the CRE activity through G(o). This negative transactivation of CRE is the first biochemically analyzed signal evoked by the three FAD-APPs, but not by wild-type APP695, in a whole-cell system. We discuss the significance of constitutive CRE suppression by FAD-APPs, which is potentially relevant to synaptic malplasticity or memory disorders.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberini C. M., Ghirardi M., Metz R., Kandel E. R. C/EBP is an immediate-early gene required for the consolidation of long-term facilitation in Aplysia. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1099–1114. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90386-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. Multiple independent activations of the neu oncogene by a point mutation altering the transmembrane domain of p185. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90779-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourtchuladze R., Frenguelli B., Blendy J., Cioffi D., Schutz G., Silva A. J. Deficient long-term memory in mice with a targeted mutation of the cAMP-responsive element-binding protein. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90400-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin B. R., Farfel Z., Lustig K. D., Julius D., Bourne H. R. Substitution of three amino acids switches receptor specificity of Gq alpha to that of Gi alpha. Nature. 1993 May 20;363(6426):274–276. doi: 10.1038/363274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dash P. K., Hochner B., Kandel E. R. Injection of the cAMP-responsive element into the nucleus of Aplysia sensory neurons blocks long-term facilitation. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):718–721. doi: 10.1038/345718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P., Ashton S. V., Moore S. E., Walsh F. S. Morphoregulatory activities of NCAM and N-cadherin can be accounted for by G protein-dependent activation of L- and N-type neuronal Ca2+ channels. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):21–33. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90569-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyrks T., Weidemann A., Multhaup G., Salbaum J. M., Lemaire H. G., Kang J., Müller-Hill B., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K. Identification, transmembrane orientation and biogenesis of the amyloid A4 precursor of Alzheimer's disease. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):949–957. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02900.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D. A., Greenberg M. E. CREB: a mediator of long-term memory from mollusks to mammals. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90394-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Games D., Adams D., Alessandrini R., Barbour R., Berthelette P., Blackwell C., Carr T., Clemens J., Donaldson T., Gillespie F. Alzheimer-type neuropathology in transgenic mice overexpressing V717F beta-amyloid precursor protein. Nature. 1995 Feb 9;373(6514):523–527. doi: 10.1038/373523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goate A., Chartier-Harlin M. C., Mullan M., Brown J., Crawford F., Fidani L., Giuffra L., Haynes A., Irving N., James L. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):704–706. doi: 10.1038/349704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh J. W., Pennefather P. S. A pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein in hippocampal long-term potentiation. Science. 1989 May 26;244(4907):980–983. doi: 10.1126/science.2543072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Montminy M. R. Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillén A., Jallon J. M., Fehrentz J. A., Pantaloni C., Bockaert J., Homburger V. A Go-like protein in Drosophila melanogaster and its expression in memory mutants. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1449–1455. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08261.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy J. Framing beta-amyloid. Nat Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):233–234. doi: 10.1038/ng0792-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. Y., Li X. C., Kandel E. R. cAMP contributes to mossy fiber LTP by initiating both a covalently mediated early phase and macromolecular synthesis-dependent late phase. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):69–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikezu T., Okamoto T., Murayama Y., Okamoto T., Homma Y., Ogata E., Nishimoto I. Bidirectional regulation of c-fos promoter by an oncogenic gip2 mutant of G alpha i2. A novel implication of retinoblastoma gene product. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31955–31961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaang B. K., Kandel E. R., Grant S. G. Activation of cAMP-responsive genes by stimuli that produce long-term facilitation in Aplysia sensory neurons. Neuron. 1993 Mar;10(3):427–435. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90331-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlinsky H., Vaula G., Haines J. L., Ridgley J., Bergeron C., Mortilla M., Tupler R. G., Percy M. E., Robitaille Y., Noldy N. E. Molecular and prospective phenotypic characterization of a pedigree with familial Alzheimer's disease and a missense mutation in codon 717 of the beta-amyloid precursor protein gene. Neurology. 1992 Aug;42(8):1445–1453. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.8.1445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman R. Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 1986 Apr 10;314(15):964–973. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198604103141506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel J. E., Korswagen H. C., Liu K. S., Hajdu-Cronin Y. M., Simon M. I., Plasterk R. H., Sternberg P. W. Participation of the protein Go in multiple aspects of behavior in C. elegans. Science. 1995 Mar 17;267(5204):1652–1655. doi: 10.1126/science.7886455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon J. C., Thomas S. L., Nathanson N. M. Regulation of cAMP-mediated gene transcription by wild type and mutated G-protein alpha subunits. Inhibition of adenylyl cyclase activity by muscarinic receptor-activated and constitutively activated G(o) alpha. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 18;269(46):29146–29152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milward E. A., Papadopoulos R., Fuller S. J., Moir R. D., Small D., Beyreuther K., Masters C. L. The amyloid protein precursor of Alzheimer's disease is a mediator of the effects of nerve growth factor on neurite outgrowth. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):129–137. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90228-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mönning U., König G., Banati R. B., Mechler H., Czech C., Gehrmann J., Schreiter-Gasser U., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K. Alzheimer beta A4-amyloid protein precursor in immunocompetent cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23950–23956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto I., Okamoto T., Matsuura Y., Takahashi S., Okamoto T., Murayama Y., Ogata E. Alzheimer amyloid protein precursor complexes with brain GTP-binding protein G(o) Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):75–79. doi: 10.1038/362075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Takeda S., Murayama Y., Ogata E., Nishimoto I. Ligand-dependent G protein coupling function of amyloid transmembrane precursor. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 3;270(9):4205–4208. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.9.4205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandbrink R., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K. Beta A4-amyloid protein precursor mRNA isoforms without exon 15 are ubiquitously expressed in rat tissues including brain, but not in neurons. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1510–1517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert W., Prior R., Weidemann A., Dircksen H., Multhaup G., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K. Localization of Alzheimer beta A4 amyloid precursor protein at central and peripheral synaptic sites. Brain Res. 1991 Nov 1;563(1-2):184–194. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91532-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuch U., Lohse M. J., Schachner M. Neural cell adhesion molecules influence second messenger systems. Neuron. 1989 Jul;3(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90111-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebok K., Woodside D., al-Aoukaty A., Ho A. D., Gluck S., Maghazachi A. A. IL-8 induces the locomotion of human IL-2-activated natural killer cells. Involvement of a guanine nucleotide binding (Go) protein. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 15;150(4):1524–1534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. H., Nurcombe V., Reed G., Clarris H., Moir R., Beyreuther K., Masters C. L. A heparin-binding domain in the amyloid protein precursor of Alzheimer's disease is involved in the regulation of neurite outgrowth. J Neurosci. 1994 Apr;14(4):2117–2127. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-04-02117.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter S. M., Fishman M. C., Zhu X. P. Activated mutants of the alpha subunit of G(o) promote an increased number of neurites per cell. J Neurosci. 1994 Apr;14(4):2327–2338. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-04-02327.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun P., Enslen H., Myung P. S., Maurer R. A. Differential activation of CREB by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases type II and type IV involves phosphorylation of a site that negatively regulates activity. Genes Dev. 1994 Nov 1;8(21):2527–2539. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.21.2527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ségalat L., Elkes D. A., Kaplan J. M. Modulation of serotonin-controlled behaviors by Go in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 1995 Mar 17;267(5204):1648–1651. doi: 10.1126/science.7886454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Murayama Y., Okamoto T., Yokota T., Ikezu T., Takahashi S., Giambarella U., Ogata E., Nishimoto I. Conversion of G-protein specificity of insulin-like growth factor II/mannose 6-phosphate receptor by exchanging of a short region with beta-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11772–11776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Yonezawa K., Nishimoto I. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor activated by a transmembrane mutation. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 11;270(32):19041–19045. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.32.19041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uéda K., Cole G., Sundsmo M., Katzman R., Saitoh T. Decreased adhesiveness of Alzheimer's disease fibroblasts: is amyloid beta-protein precursor involved? Ann Neurol. 1989 Mar;25(3):246–251. doi: 10.1002/ana.410250307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voyno-Yasenetskaya T., Conklin B. R., Gilbert R. L., Hooley R., Bourne H. R., Barber D. L. G alpha 13 stimulates Na-H exchange. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 18;269(7):4721–4724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamatsuji T., Okamoto T., Takeda S., Murayama Y., Tanaka N., Nishimoto I. Expression of V642 APP mutant causes cellular apoptosis as Alzheimer trait-linked phenotype. EMBO J. 1996 Feb 1;15(3):498–509. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin J. C., Wallach J. S., Del Vecchio M., Wilder E. L., Zhou H., Quinn W. G., Tully T. Induction of a dominant negative CREB transgene specifically blocks long-term memory in Drosophila. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):49–58. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90399-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng H., Jiang M., Trumbauer M. E., Sirinathsinghji D. J., Hopkins R., Smith D. W., Heavens R. P., Dawson G. R., Boyce S., Conner M. W. beta-Amyloid precursor protein-deficient mice show reactive gliosis and decreased locomotor activity. Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):525–531. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]