Abstract
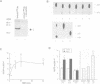
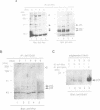
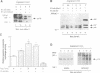
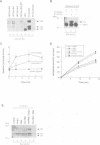
p21 ras plays as important role in cell proliferation, transformation and differentiation. Recently, the requirement of p21 ras has been suggested for cellular responses induced by stimulation of heterotrimeric G protein-coupled receptors. However, it remains to be determined how agonists for G protein-coupled receptors activate p21 ras in metazoans. We show here that stimulation of the G q protein-coupled angiotensin II (Ang II) receptor causes activation of p21 ras in cardiac myocytes. The p21 ras activation by Ang II is mediated by an increase in the guanine nucleotide exchange activity, but not by an inhibition of the GTPase-activating protein. Ang II causes rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of Shc and its association with Grb2 and mSos-1, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor of p21 ras. This leads to translocation of mSos-1 to the membrane fraction. Shc associates with the SH3 domain of Fyn whose tyrosine kinase activity is activated by Ang II with a similar time course as that of tyrosine phosphorylation of Shc. Ang II-induced increase in the guanine nucleotide exchange activity was inhibited by a peptide ligand specific to the SH3 domain of the Src family tyrosine kinases. These results suggest that an agonist for a pertussis toxin-insensitive G protein-coupled receptor may initiate the cross-talk with non-receptor-type tyrosine kinases, thereby activating p21 ras using a similar mechanism as receptor tyrosine kinase-induced p21 ras activation.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdellatif M., MacLellan W. R., Schneider M. D. p21 Ras as a governor of global gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 3;269(22):15423–15426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alblas J., van Corven E. J., Hordijk P. L., Milligan G., Moolenaar W. H. Gi-mediated activation of the p21ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by alpha 2-adrenergic receptors expressed in fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22235–22238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Zhang X. F., Kyriakis J. M. Raf meets Ras: completing the framework of a signal transduction pathway. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jul;19(7):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J. Signal transduction via the MAP kinases: proceed at your own RSK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5889–5892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguski M. S., McCormick F. Proteins regulating Ras and its relatives. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):643–654. doi: 10.1038/366643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buday L., Downward J. Epidermal growth factor regulates p21ras through the formation of a complex of receptor, Grb2 adapter protein, and Sos nucleotide exchange factor. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):611–620. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90146-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buday L., Downward J. Epidermal growth factor regulates the exchange rate of guanine nucleotides on p21ras in fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1903–1910. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgering B. M., Bos J. L. Regulation of Ras-mediated signalling: more than one way to skin a cat. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Jan;20(1):18–22. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)88944-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazaubon S. M., Ramos-Morales F., Fischer S., Schweighoffer F., Strosberg A. D., Couraud P. O. Endothelin induces tyrosine phosphorylation and GRB2 association of Shc in astrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):24805–24809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. J., Rubinfeld B., Albert I., McCormick F. RapV12 antagonizes Ras-dependent activation of ERK1 and ERK2 by LPA and EGF in Rat-1 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3475–3485. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06022.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Howell B. The when and how of Src regulation. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1051–1054. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90634-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crespo P., Xu N., Simonds W. F., Gutkind J. S. Ras-dependent activation of MAP kinase pathway mediated by G-protein beta gamma subunits. Nature. 1994 Jun 2;369(6479):418–420. doi: 10.1038/369418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Graves J. D., Warne P. H., Rayter S., Cantrell D. A. Stimulation of p21ras upon T-cell activation. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):719–723. doi: 10.1038/346719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan S. E., Giddings B. W., Brooks M. W., Buday L., Sizeland A. M., Weinberg R. A. Association of Sos Ras exchange protein with Grb2 is implicated in tyrosine kinase signal transduction and transformation. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):45–51. doi: 10.1038/363045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Davis L. J., Fleurdelys B., Scolnick E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to the p21 products of the transforming gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus and of the cellular ras gene family. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):294–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.294-304.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutowski S., Smrcka A., Nowak L., Wu D. G., Simon M., Sternweis P. C. Antibodies to the alpha q subfamily of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein alpha subunits attenuate activation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis by hormones. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20519–20524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H. Dimerization of cell surface receptors in signal transduction. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90404-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. MAP kinase pathways in yeast: for mating and more. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):187–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90402-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hordijk P. L., Verlaan I., van Corven E. J., Moolenaar W. H. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation induced by lysophosphatidic acid in Rat-1 fibroblasts. Evidence that phosphorylation of map kinase is mediated by the Gi-p21ras pathway. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):645–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Protein kinases and phosphatases: the yin and yang of protein phosphorylation and signaling. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90405-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kai H., Griendling K. K., Lassègue B., Ollerenshaw J. D., Runge M. S., Alexander R. W. Agonist-induced phosphorylation of the vascular type 1 angiotensin II receptor. Hypertension. 1994 Oct;24(4):523–527. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.24.4.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W. J., Hawes B. E., Allen L. F., Lefkowitz R. J. Direct evidence that Gi-coupled receptor stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase is mediated by G beta gamma activation of p21ras. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12706–12710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Goldberg Y., Ulug E. T., Courtneidge S. A. Association between the PDGF receptor and members of the src family of tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMorte V. J., Kennedy E. D., Collins L. R., Goldstein D., Harootunian A. T., Brown J. H., Feramisco J. R. A requirement for Ras protein function in thrombin-stimulated mitogenesis in astrocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19411–19415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langhans-Rajasekaran S. A., Wan Y., Huang X. Y. Activation of Tsk and Btk tyrosine kinases by G protein beta gamma subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 12;92(19):8601–8605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev S., Moreno H., Martinez R., Canoll P., Peles E., Musacchio J. M., Plowman G. D., Rudy B., Schlessinger J. Protein tyrosine kinase PYK2 involved in Ca(2+)-induced regulation of ion channel and MAP kinase functions. Nature. 1995 Aug 31;376(6543):737–745. doi: 10.1038/376737a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrero M. B., Schieffer B., Paxton W. G., Heerdt L., Berk B. C., Delafontaine P., Bernstein K. E. Direct stimulation of Jak/STAT pathway by the angiotensin II AT1 receptor. Nature. 1995 May 18;375(6528):247–250. doi: 10.1038/375247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F. Activators and effectors of ras p21 proteins. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Feb;4(1):71–76. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlade J., Cheng A., Pelicci G., Pelicci P. G., Pawson T. Shc proteins are phosphorylated and regulated by the v-Src and v-Fps protein-tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8869–8873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medema R. H., de Vries-Smits A. M., van der Zon G. C., Maassen J. A., Bos J. L. Ras activation by insulin and epidermal growth factor through enhanced exchange of guanine nucleotides on p21ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):155–162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J. Heterotrimeric G proteins: organizers of transmembrane signals. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90407-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmichi M., Sawada T., Kanda Y., Koike K., Hirota K., Miyake A., Saltiel A. R. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone stimulates MAP kinase activity in GH3 cells by divergent pathways. Evidence of a role for early tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3783–3788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paxton W. G., Marrero M. B., Klein J. D., Delafontaine P., Berk B. C., Bernstein K. E. The angiotensin II AT1 receptor is tyrosine and serine phosphorylated and can serve as a substrate for the src family of tyrosine kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Apr 15;200(1):260–267. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelicci G., Lanfrancone L., Grignani F., McGlade J., Cavallo F., Forni G., Nicoletti I., Grignani F., Pawson T., Pelicci P. G. A novel transforming protein (SHC) with an SH2 domain is implicated in mitogenic signal transduction. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90536-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravichandran K. S., Lorenz U., Shoelson S. E., Burakoff S. J. Interaction of Shc with Grb2 regulates association of Grb2 with mSOS. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;15(2):593–600. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.2.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickles R. J., Botfield M. C., Weng Z., Taylor J. A., Green O. M., Brugge J. S., Zoller M. J. Identification of Src, Fyn, Lyn, PI3K and Abl SH3 domain ligands using phage display libraries. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 1;13(23):5598–5604. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06897.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Viciana P., Warne P. H., Dhand R., Vanhaesebroeck B., Gout I., Fry M. J., Waterfield M. D., Downward J. Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase as a direct target of Ras. Nature. 1994 Aug 18;370(6490):527–532. doi: 10.1038/370527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozakis-Adcock M., McGlade J., Mbamalu G., Pelicci G., Daly R., Li W., Batzer A., Thomas S., Brugge J., Pelicci P. G. Association of the Shc and Grb2/Sem5 SH2-containing proteins is implicated in activation of the Ras pathway by tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):689–692. doi: 10.1038/360689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoshima J., Izumo S. Mechanical stretch rapidly activates multiple signal transduction pathways in cardiac myocytes: potential involvement of an autocrine/paracrine mechanism. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1681–1692. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05813.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoshima J., Izumo S. Molecular characterization of angiotensin II--induced hypertrophy of cardiac myocytes and hyperplasia of cardiac fibroblasts. Critical role of the AT1 receptor subtype. Circ Res. 1993 Sep;73(3):413–423. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.3.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoshima J., Izumo S. Signal transduction pathways of angiotensin II--induced c-fos gene expression in cardiac myocytes in vitro. Roles of phospholipid-derived second messengers. Circ Res. 1993 Sep;73(3):424–438. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.3.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoshima J., Jahn L., Takahashi T., Kulik T. J., Izumo S. Molecular characterization of the stretch-induced adaptation of cultured cardiac cells. An in vitro model of load-induced cardiac hypertrophy. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10551–10560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoshima J., Qiu Z., Morgan J. P., Izumo S. Angiotensin II and other hypertrophic stimuli mediated by G protein-coupled receptors activate tyrosine kinase, mitogen-activated protein kinase, and 90-kD S6 kinase in cardiac myocytes. The critical role of Ca(2+)-dependent signaling. Circ Res. 1995 Jan;76(1):1–15. doi: 10.1161/01.res.76.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoshima J., Xu Y., Slayter H. S., Izumo S. Autocrine release of angiotensin II mediates stretch-induced hypertrophy of cardiac myocytes in vitro. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):977–984. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90541-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Nakafuku M., Kaziro Y. Function of Ras as a molecular switch in signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24149–24152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorb W., Peeler T. C., Madigan N. N., Conrad K. M., Baker K. M. Angiotensin II-induced protein tyrosine phosphorylation in neonatal rat cardiac fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 29;269(30):19626–19632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shou C., Wurmser A., Suen K. L., Barbacid M., Feig L. A., Ling K. Differential response of the Ras exchange factor, Ras-GRF to tyrosine kinase and G protein mediated signals. Oncogene. 1995 May 18;10(10):1887–1893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., McGlade J., Olivier P., Pawson T., Bustelo X. R., Barbacid M., Sabe H., Hanafusa H., Yi T. Specific motifs recognized by the SH2 domains of Csk, 3BP2, fps/fes, GRB-2, HCP, SHC, Syk, and Vav. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2777–2785. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P. L., Lee H. M., Rich S., Soriano P. pp59fyn mutant mice display differential signaling in thymocytes and peripheral T cells. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):741–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90308-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T. Cytokine signaling through nonreceptor protein tyrosine kinases. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):251–255. doi: 10.1126/science.7716517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorburn A., Thorburn J., Chen S. Y., Powers S., Shubeita H. E., Feramisco J. R., Chien K. R. HRas-dependent pathways can activate morphological and genetic markers of cardiac muscle cell hypertrophy. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):2244–2249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtek A. B., Hollenberg S. M., Cooper J. A. Mammalian Ras interacts directly with the serine/threonine kinase Raf. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90307-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Littman D. R. Signal transduction by lymphocyte antigen receptors. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weng Z., Thomas S. M., Rickles R. J., Taylor J. A., Brauer A. W., Seidel-Dugan C., Michael W. M., Dreyfuss G., Brugge J. S. Identification of Src, Fyn, and Lyn SH3-binding proteins: implications for a function of SH3 domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4509–4521. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winitz S., Russell M., Qian N. X., Gardner A., Dwyer L., Johnson G. L. Involvement of Ras and Raf in the Gi-coupled acetylcholine muscarinic m2 receptor activation of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase and MAP kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19196–19199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu H., Rosen M. K., Shin T. B., Seidel-Dugan C., Brugge J. S., Schreiber S. L. Solution structure of the SH3 domain of Src and identification of its ligand-binding site. Science. 1992 Dec 4;258(5088):1665–1668. doi: 10.1126/science.1280858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Alawi N., Rose D. W., Buckmaster C., Ahn N., Rapp U., Meinkoth J., Feramisco J. R. Thyrotropin-induced mitogenesis is Ras dependent but appears to bypass the Raf-dependent cytoplasmic kinase cascade. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;15(3):1162–1168. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.3.1162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Biesen T., Hawes B. E., Luttrell D. K., Krueger K. M., Touhara K., Porfiri E., Sakaue M., Luttrell L. M., Lefkowitz R. J. Receptor-tyrosine-kinase- and G beta gamma-mediated MAP kinase activation by a common signalling pathway. Nature. 1995 Aug 31;376(6543):781–784. doi: 10.1038/376781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Corven E. J., Hordijk P. L., Medema R. H., Bos J. L., Moolenaar W. H. Pertussis toxin-sensitive activation of p21ras by G protein-coupled receptor agonists in fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1257–1261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Geer P., Wiley S., Lai V. K., Olivier J. P., Gish G. D., Stephens R., Kaplan D., Shoelson S., Pawson T. A conserved amino-terminal Shc domain binds to phosphotyrosine motifs in activated receptors and phosphopeptides. Curr Biol. 1995 Apr 1;5(4):404–412. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]