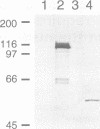
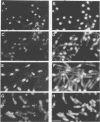
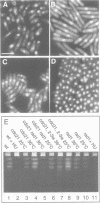
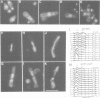
Abstract
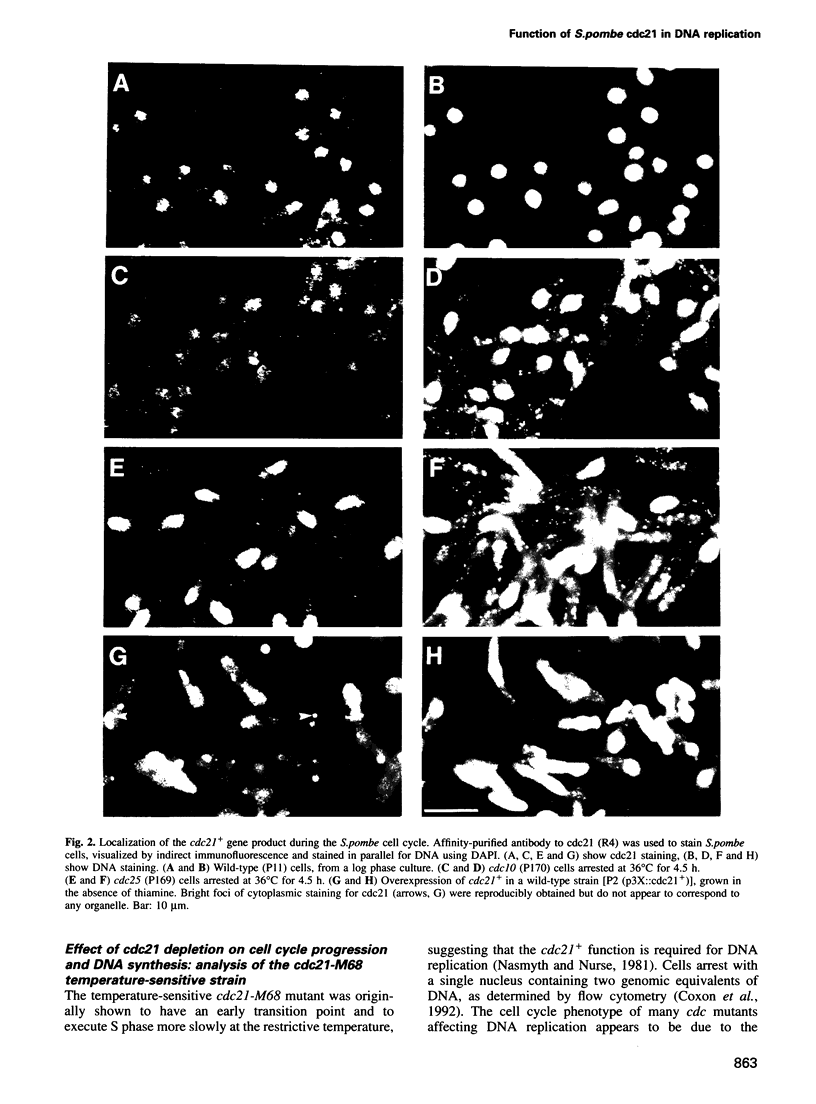
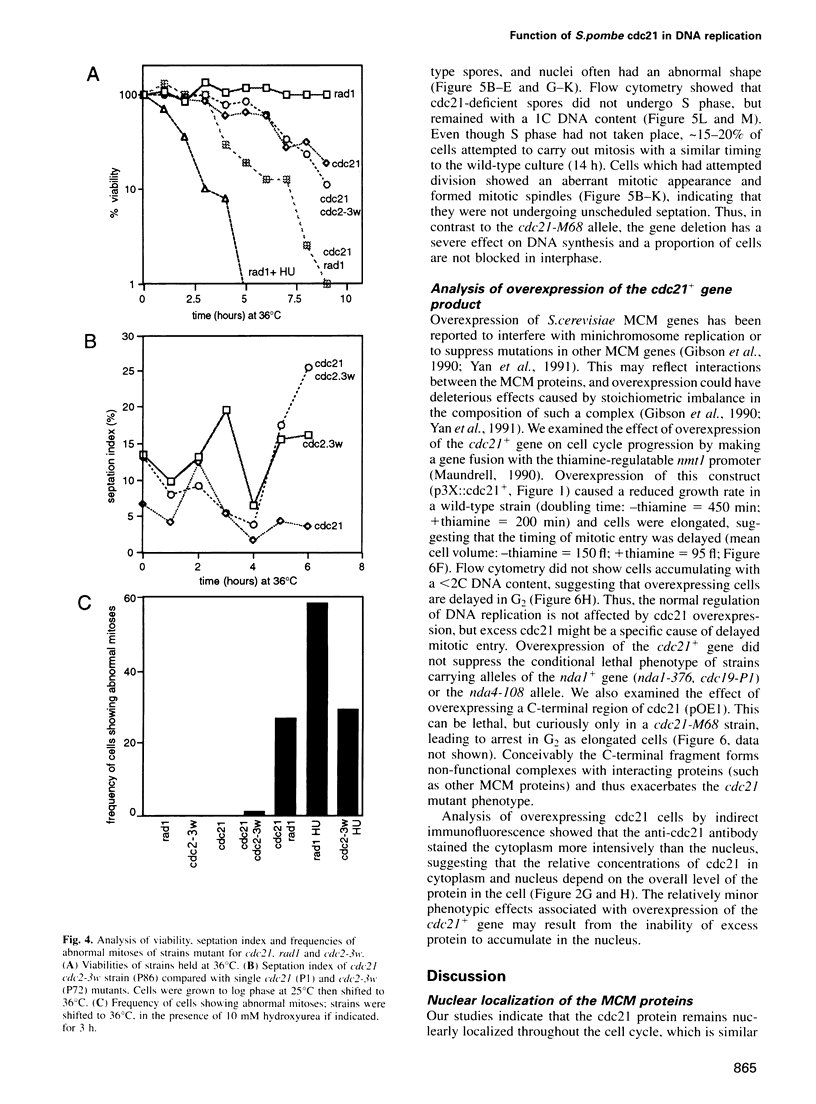
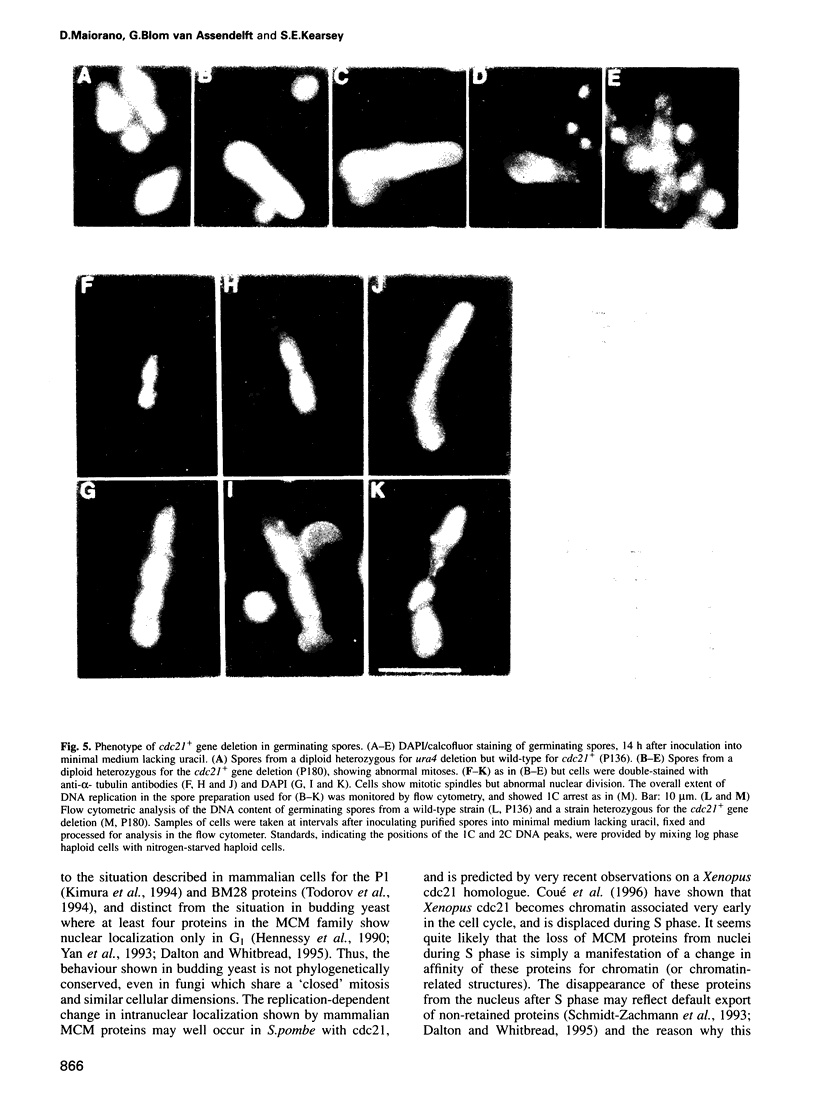
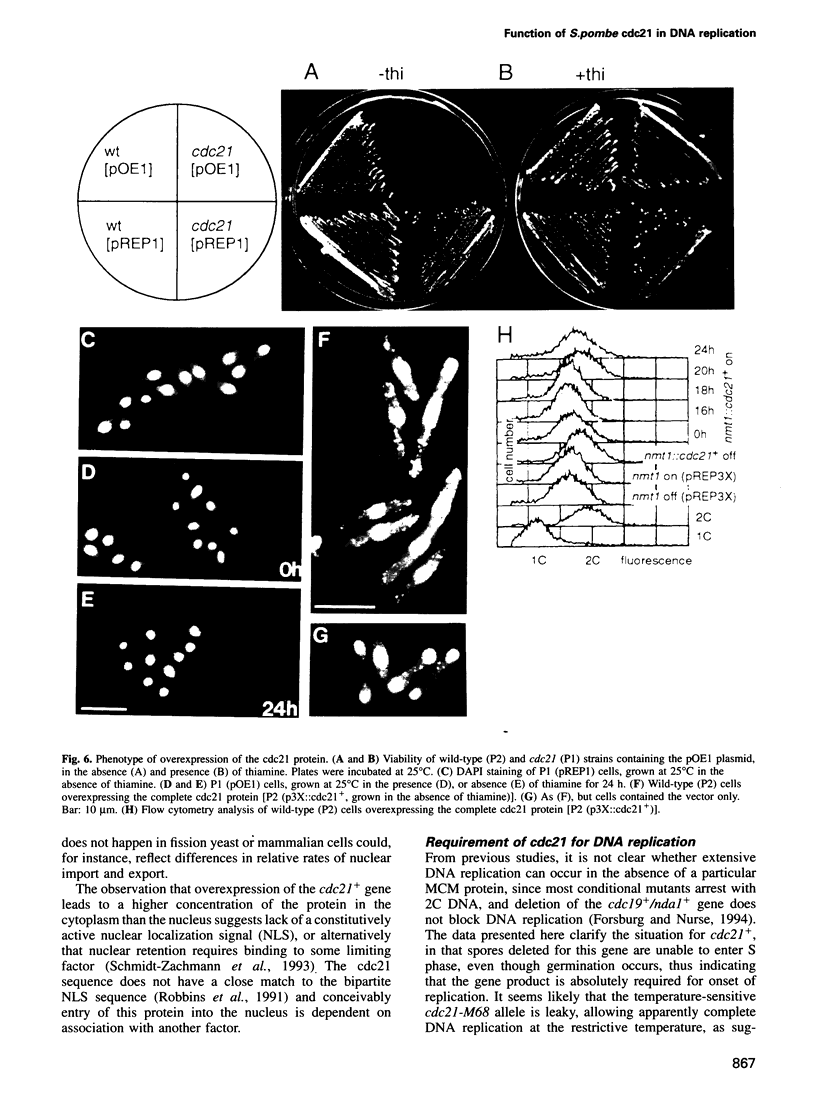
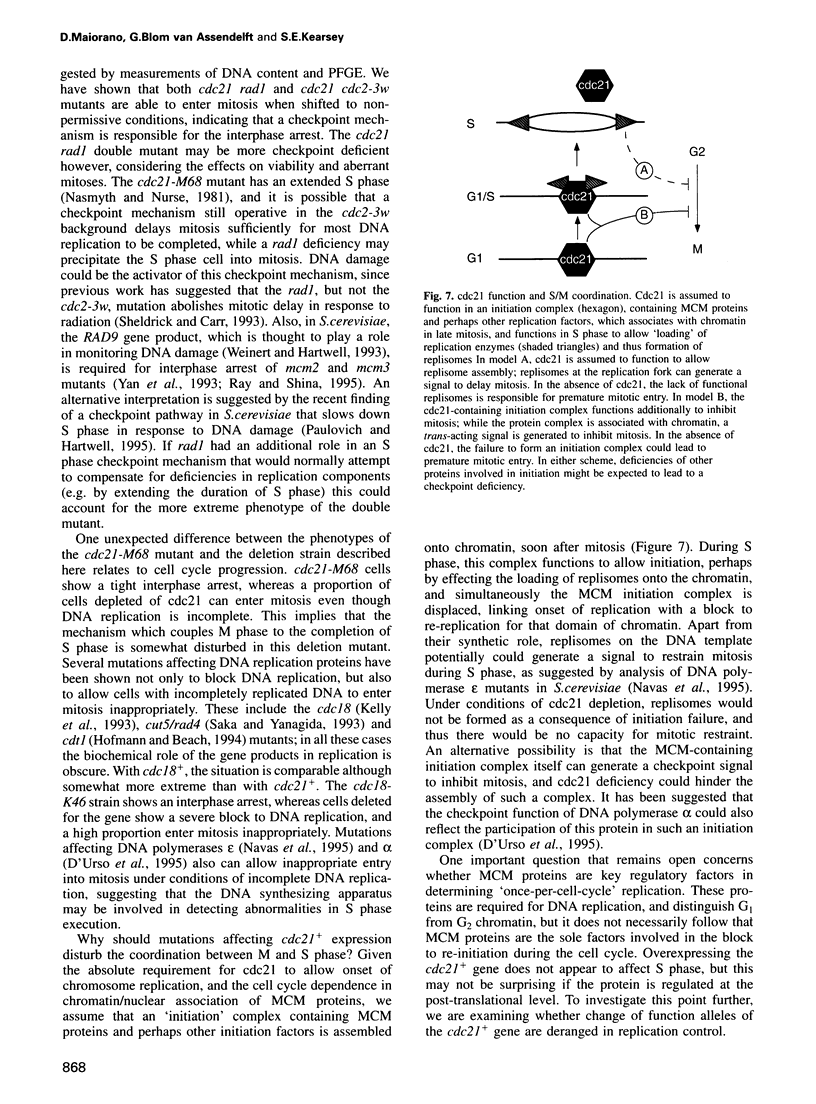
The fission yeast cdc21 protein belongs to the MCM family, implicated in the once per cell cycle regulation of chromosome replication. In budding yeast, proteins in this family are eliminated from the nucleus during S phase, which has led to the suggestion that they may serve to distinguish unreplicated from replicated DNA, as in the licensing factor model. We show here that, in contrast to the situation in budding yeast, cdc21 remains in the nucleus after S phase, as is found for related proteins in mammalian cells. We suggest that regulation of nuclear import of these proteins may not be an essential aspect of their function in chromosome replication. To determine the function of cdc21+, we have analysed the phenotype of a gene deletion. cdc21+ is required for entry into S phase and, unexpectedly, a proportion of cells depleted of the gene product are able to enter mitosis in the absence of DNA replication. These results are consistent with the view that individual proteins in the MCM family are required for all initiation events, and defective initiation may impair the coordination between mitosis and S phase.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell S. P., Kobayashi R., Stillman B. Yeast origin recognition complex functions in transcription silencing and DNA replication. Science. 1993 Dec 17;262(5141):1844–1849. doi: 10.1126/science.8266072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow J. J., Laskey R. A. A role for the nuclear envelope in controlling DNA replication within the cell cycle. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):546–548. doi: 10.1038/332546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal A. B., Kriegstein H. J., Hogness D. S. The units of DNA replication in Drosophila melanogaster chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:205–223. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Hennessy K. M., Botstein D., Tye B. K. CDC46/MCM5, a yeast protein whose subcellular localization is cell cycle-regulated, is involved in DNA replication at autonomously replicating sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10459–10463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong J. P., Mahbubani H. M., Khoo C. Y., Blow J. J. Purification of an MCM-containing complex as a component of the DNA replication licensing system. Nature. 1995 Jun 1;375(6530):418–421. doi: 10.1038/375418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coverley D., Downes C. S., Romanowski P., Laskey R. A. Reversible effects of nuclear membrane permeabilization on DNA replication: evidence for a positive licensing factor. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(5):985–992. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coxon A., Maundrell K., Kearsey S. E. Fission yeast cdc21+ belongs to a family of proteins involved in an early step of chromosome replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5571–5577. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crevel G., Cotterill S. DNA replication in cell-free extracts from Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4361–4369. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05014.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Urso G., Grallert B., Nurse P. DNA polymerase alpha, a component of the replication initiation complex, is essential for the checkpoint coupling S phase to mitosis in fission yeast. J Cell Sci. 1995 Sep;108(Pt 9):3109–3118. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.9.3109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Whitbread L. Cell cycle-regulated nuclear import and export of Cdc47, a protein essential for initiation of DNA replication in budding yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2514–2518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Cocker J. H. Protein-DNA interactions at a yeast replication origin. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):169–172. doi: 10.1038/357169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Nurse P. Mutation of fission yeast cell cycle control genes abolishes dependence of mitosis on DNA replication. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):665–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90669-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsburg S. L. Comparison of Schizosaccharomyces pombe expression systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 25;21(12):2955–2956. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.12.2955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsburg S. L., Nurse P. The fission yeast cdc19+ gene encodes a member of the MCM family of replication proteins. J Cell Sci. 1994 Oct;107(Pt 10):2779–2788. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.10.2779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson S. I., Surosky R. T., Tye B. K. The phenotype of the minichromosome maintenance mutant mcm3 is characteristic of mutants defective in DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5707–5720. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttes S., Guttes E. Regulation of DNA replication in the nuclei of the slime mold Physarum polycephalum. Transplantation of nuclei by plasmodial coalescence. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jun;37(3):761–772. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.3.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagan I. M., Hyams J. S. The use of cell division cycle mutants to investigate the control of microtubule distribution in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Cell Sci. 1988 Mar;89(Pt 3):343–357. doi: 10.1242/jcs.89.3.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Weinert T. A. Checkpoints: controls that ensure the order of cell cycle events. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):629–634. doi: 10.1126/science.2683079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K. M., Clark C. D., Botstein D. Subcellular localization of yeast CDC46 varies with the cell cycle. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2252–2263. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K. M., Lee A., Chen E., Botstein D. A group of interacting yeast DNA replication genes. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):958–969. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann J. F., Beach D. cdt1 is an essential target of the Cdc10/Sct1 transcription factor: requirement for DNA replication and inhibition of mitosis. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 15;13(2):425–434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06277.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu B., Burkhart R., Schulte D., Musahl C., Knippers R. The P1 family: a new class of nuclear mammalian proteins related to the yeast Mcm replication proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 25;21(23):5289–5293. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.23.5289-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J., Martin G. S., Forsburg S. L., Stephen R. J., Russo A., Nurse P. The fission yeast cdc18+ gene product couples S phase to START and mitosis. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):371–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90427-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilmartin J. V., Adams A. E. Structural rearrangements of tubulin and actin during the cell cycle of the yeast Saccharomyces. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):922–933. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., Nozaki N., Sugimoto K. DNA polymerase alpha associated protein P1, a murine homolog of yeast MCM3, changes its intranuclear distribution during the DNA synthetic period. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 15;13(18):4311–4320. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06751.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koonin E. V. A common set of conserved motifs in a vast variety of putative nucleic acid-dependent ATPases including MCM proteins involved in the initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 11;21(11):2541–2547. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.11.2541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota Y., Mimura S., Nishimoto S., Takisawa H., Nojima H. Identification of the yeast MCM3-related protein as a component of Xenopus DNA replication licensing factor. Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):601–609. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leno G. H., Downes C. S., Laskey R. A. The nuclear membrane prevents replication of human G2 nuclei but not G1 nuclei in Xenopus egg extract. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90126-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Herskowitz I. Isolation of ORC6, a component of the yeast origin recognition complex by a one-hybrid system. Science. 1993 Dec 17;262(5141):1870–1874. doi: 10.1126/science.8266075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madine M. A., Khoo C. Y., Mills A. D., Laskey R. A. MCM3 complex required for cell cycle regulation of DNA replication in vertebrate cells. Nature. 1995 Jun 1;375(6530):421–424. doi: 10.1038/375421a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maundrell K. Thiamine-repressible expression vectors pREP and pRIP for fission yeast. Gene. 1993 Jan 15;123(1):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90551-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maundrell K. nmt1 of fission yeast. A highly transcribed gene completely repressed by thiamine. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10857–10864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake S., Okishio N., Samejima I., Hiraoka Y., Toda T., Saitoh I., Yanagida M. Fission yeast genes nda1+ and nda4+, mutations of which lead to S-phase block, chromatin alteration and Ca2+ suppression, are members of the CDC46/MCM2 family. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Oct;4(10):1003–1015. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.10.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Hayles J., Nurse P. Regulation of p34cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):361–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90850-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Klar A., Nurse P. Molecular genetic analysis of fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:795–823. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94059-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musahl C., Schulte D., Burkhart R., Knippers R. A human homologue of the yeast replication protein Cdc21. Interactions with other Mcm proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Jun 15;230(3):1096–1101. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K., Nurse P. Cell division cycle mutants altered in DNA replication and mitosis in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(1):119–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00422777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navas T. A., Zhou Z., Elledge S. J. DNA polymerase epsilon links the DNA replication machinery to the S phase checkpoint. Cell. 1995 Jan 13;80(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90448-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulovich A. G., Hartwell L. H. A checkpoint regulates the rate of progression through S phase in S. cerevisiae in response to DNA damage. Cell. 1995 Sep 8;82(5):841–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90481-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao P. N., Johnson R. T. Mammalian cell fusion: studies on the regulation of DNA synthesis and mitosis. Nature. 1970 Jan 10;225(5228):159–164. doi: 10.1038/225159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray A., Sinha P. The mcm2-1 mutation of yeast causes DNA damage with a RAD9 requirement for repair. Curr Genet. 1995 Jan;27(2):95–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00313422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Two interdependent basic domains in nucleoplasmin nuclear targeting sequence: identification of a class of bipartite nuclear targeting sequence. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):615–623. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90245-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley R., Subramani S., Young P. G. Checkpoint controls in Schizosaccharomyces pombe: rad1. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1335–1342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05178.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saka Y., Yanagida M. Fission yeast cut5+, required for S phase onset and M phase restraint, is identical to the radiation-damage repair gene rad4+. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):383–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90428-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sazer S., Sherwood S. W. Mitochondrial growth and DNA synthesis occur in the absence of nuclear DNA replication in fission yeast. J Cell Sci. 1990 Nov;97(Pt 3):509–516. doi: 10.1242/jcs.97.3.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Zachmann M. S., Dargemont C., Kühn L. C., Nigg E. A. Nuclear export of proteins: the role of nuclear retention. Cell. 1993 Aug 13;74(3):493–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80051-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulte D., Burkhart R., Musahl C., Hu B., Schlatterer C., Hameister H., Knippers R. Expression, phosphorylation and nuclear localization of the human P1 protein, a homologue of the yeast Mcm 3 replication protein. J Cell Sci. 1995 Apr;108(Pt 4):1381–1389. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.4.1381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick K. S., Carr A. M. Feedback controls and G2 checkpoints: fission yeast as a model system. Bioessays. 1993 Dec;15(12):775–782. doi: 10.1002/bies.950151202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Yamada H., Yanagida M. Fission yeast minichromosome loss mutants mis cause lethal aneuploidy and replication abnormality. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Oct;5(10):1145–1158. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.10.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todorov I. T., Attaran A., Kearsey S. E. BM28, a human member of the MCM2-3-5 family, is displaced from chromatin during DNA replication. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;129(6):1433–1445. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todorov I. T., Pepperkok R., Philipova R. N., Kearsey S. E., Ansorge W., Werner D. A human nuclear protein with sequence homology to a family of early S phase proteins is required for entry into S phase and for cell division. J Cell Sci. 1994 Jan;107(Pt 1):253–265. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.1.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tye B. K. The MCM2-3-5 proteins: are they replication licensing factors? Trends Cell Biol. 1994 May;4(5):160–166. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waseem N. H., Labib K., Nurse P., Lane D. P. Isolation and analysis of the fission yeast gene encoding polymerase delta accessory protein PCNA. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5111–5120. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05618.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinert T. A., Hartwell L. H. Cell cycle arrest of cdc mutants and specificity of the RAD9 checkpoint. Genetics. 1993 May;134(1):63–80. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitebread L. A., Dalton S. Cdc54 belongs to the Cdc46/Mcm3 family of proteins which are essential for initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication. Gene. 1995 Mar 21;155(1):113–117. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)00925-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., Sherwin T., Sasse R., MacRae T. H., Baines A. J., Gull K. Definition of individual components within the cytoskeleton of Trypanosoma brucei by a library of monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Sci. 1989 Jul;93(Pt 3):491–500. doi: 10.1242/jcs.93.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan H., Gibson S., Tye B. K. Mcm2 and Mcm3, two proteins important for ARS activity, are related in structure and function. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):944–957. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan H., Merchant A. M., Tye B. K. Cell cycle-regulated nuclear localization of MCM2 and MCM3, which are required for the initiation of DNA synthesis at chromosomal replication origins in yeast. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2149–2160. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Khodairy F., Carr A. M. DNA repair mutants defining G2 checkpoint pathways in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1343–1350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]