Abstract
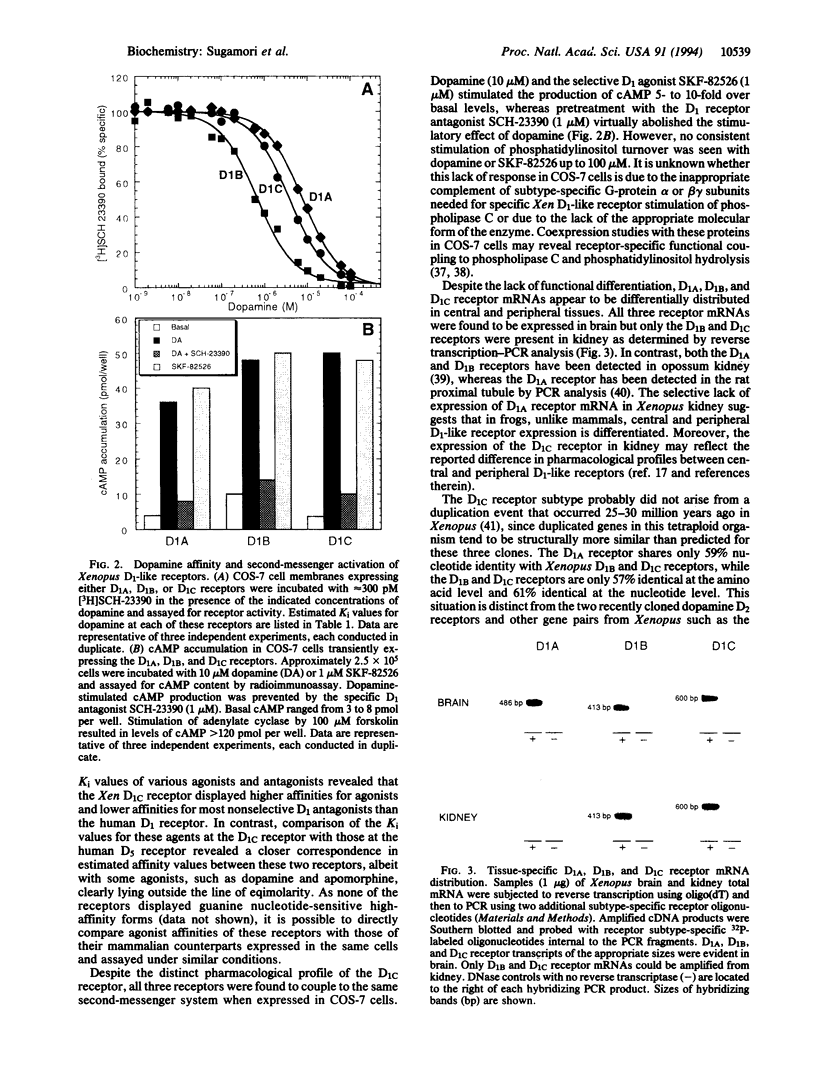
Three distinct genes encoding members of the D1 dopamine receptor family were isolated from Xenopus laevis. Based on the deduced amino acid sequence, two of the receptors (Xen D1A and Xen D1B) appear to be homologues of mammalian D1/D1A and D5/D1B receptors. The third receptor, termed Xen D1C, displays equal overall amino acid and nucleotide sequence identity (approximately 55%) with mammalian D1A and D1B/D5 receptors. In agreement with their structural similarities, Xen D1A and D1B receptors, when expressed in COS-7 cells, displayed pharmacological profiles that paralleled those of their mammalian counterparts, with dopamine and 2-amino-6,7-dihydroxytetralin exhibiting 10-fold higher affinity for D1B than for D1A. The Xen D1C receptor displayed an overall rank order of potency and pharmacological profile clearly indicative of a D1-like receptor, with individual affinities for most agonists higher than those for either Xen or mammalian D1/D1A and D5/D1B receptors, whereas antagonist Ki values were intermediate to those for the D1/D1A and D5/D1B receptors. All three receptors stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in response to dopamine or SKF-82526. Xen D1A, D1B, and D1C receptor mRNAs were differentially distributed, with all three receptors expressed in brain and only D1B and D1C receptors expressed in kidney. The existence of a receptor which lacks appreciable overall sequence similarity to, but displays pharmacological homology with, mammalian D1-like receptors lends strong support to the contention that additional mammalian D1-like receptor gene products may exist to allow for the expression of the full spectrum of D1-like dopamine receptor-mediated events.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen P. H., Gingrich J. A., Bates M. D., Dearry A., Falardeau P., Senogles S. E., Caron M. G. Dopamine receptor subtypes: beyond the D1/D2 classification. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jun;11(6):231–236. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90249-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnt J., Hyttel J., Sánchez C. Partial and full dopamine D1 receptor agonists in mice and rats: relation between behavioural effects and stimulation of adenylate cyclase activity in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar 24;213(2):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90690-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisbee C. A., Baker M. A., Wilson A. C., Haji-Azimi I., Fischberg M. Albumin phylogeny for clawed frogs (Xenopus). Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):785–787. doi: 10.1126/science.65013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitzer R. D., Omri G., De Vivo M., Carty D. J., Premont R. T., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Cotecchia S., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Coupling of the expressed alpha 1B-adrenergic receptor to the phospholipase C pathway in Xenopus oocytes. The role of Go. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):7532–7537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civelli O., Bunzow J. R., Grandy D. K. Molecular diversity of the dopamine receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1993;33:281–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.33.040193.001433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly S. A., Waddington J. L. Behavioural evidence for "D-1-like" dopamine receptor subtypes in rat brain using the new isochroman agonist A 68930 and isoquinoline antagonist BW 737C. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1993;113(1):45–50. doi: 10.1007/BF02244332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Sigal I. S., Candelore M. R., Register R. B., Scattergood W., Rands E., Strader C. D. Structural features required for ligand binding to the beta-adrenergic receptor. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3269–3275. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02645.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes R. P., Waddington J. L. Grooming and vacuous chewing induced by SK&F 83959, an agonist of dopamine 'D1-like' receptors that inhibits dopamine-sensitive adenylyl cyclase. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar 30;234(1):135–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90718-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder C. C., Albrecht F. E., Campbell T., Eisner G. M., Jose P. A. cAMP-independent, G protein-linked inhibition of Na+/H+ exchange in renal brush border by D1 dopamine agonists. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jun;264(6 Pt 2):F1032–F1037. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.6.F1032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder C. C., Blecher M., Jose P. A. Dopamine-1-mediated stimulation of phospholipase C activity in rat renal cortical membranes. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8739–8745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frail D. E., Manelli A. M., Witte D. G., Lin C. W., Steffey M. E., Mackenzie R. G. Cloning and characterization of a truncated dopamine D1 receptor from goldfish retina: stimulation of cyclic AMP production and calcium mobilization. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;44(6):1113–1118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingrich J. A., Caron M. G. Recent advances in the molecular biology of dopamine receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1993;16:299–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.16.030193.001503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandy D. K., Zhang Y. A., Bouvier C., Zhou Q. Y., Johnson R. A., Allen L., Buck K., Bunzow J. R., Salon J., Civelli O. Multiple human D5 dopamine receptor genes: a functional receptor and two pseudogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9175–9179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Calne D. B. Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):93–96. doi: 10.1038/277093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen J. T. Dopamine stimulates K+ efflux in the chick retina via D1 receptors independently of adenylyl cyclase activation. J Neurochem. 1993 Oct;61(4):1461–1469. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb13641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. F., Civelli O., Zhou Q. Y., Albert P. R. Cholera toxin-sensitive 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate and calcium signals of the human dopamine-D1 receptor: selective potentiation by protein kinase A. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Nov;6(11):1815–1824. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.11.1282671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahan L. C., Burch R. M., Monsma F. J., Jr, Sibley D. R. Expression of striatal D1 dopamine receptors coupled to inositol phosphate production and Ca2+ mobilization in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2196–2200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mailman R. B., Schulz D. W., Kilts C. D., Lewis M. H., Rollema H., Wyrick S. Multiple forms of the D1 dopamine receptor: its linkage to adenylate cyclase and psychopharmacological effects. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1986;22(3):593–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martens G. J. Expression of two proopiomelanocortin genes in the pituitary gland of Xenopus laevis: complete structures of the two preprohormones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3791–3798. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martens G. J., Groenen P. M., Gröneveld D., Van Riel M. C. Expression of the Xenopus D2 dopamine receptor. Tissue-specific regulation and two transcriptionally active genes but no evidence for alternative splicing. Eur J Biochem. 1993 May 1;213(3):1349–1354. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17887.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martens G. J., Herbert E. Polymorphism and absence of Leu-enkephalin sequences in proenkephalin genes in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):251–254. doi: 10.1038/310251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martens G. J., Molhuizen H. O., Gröneveld D., Roubos E. W. Cloning and sequence analysis of brain cDNA encoding a Xenopus D2 dopamine receptor. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):85–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80364-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillian M. K., He X. P., Hong J. S., Pennypacker K. R. Dopamine stimulates [3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate binding in cultured striatal cells. J Neurochem. 1992 Apr;58(4):1308–1312. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb11343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M. E., Shults J. M. Dopamine D1 receptor family agonists, SK&F38393, SK&F77434, and SK&F82958, differentially affect locomotor activities in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1993 Oct;46(2):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(93)90352-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash S. R., Godinot N., Caron M. G. Cloning and characterization of the opossum kidney cell D1 dopamine receptor: expression of identical D1A and D1B dopamine receptor mRNAs in opossum kidney and brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;44(5):918–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niznik H. B. Dopamine receptors: molecular structure and function. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Nov;54(1):1–22. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90134-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niznik H. B., Van Tol H. H. Dopamine receptor genes: new tools for molecular psychiatry. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 1992 Oct;17(4):158–180. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Hnatowich M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Bouvier M. Palmitoylation of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Mutation of Cys341 in the carboxyl tail leads to an uncoupled nonpalmitoylated form of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7564–7569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock N. J., Manelli A. M., Hutchins C. W., Steffey M. E., MacKenzie R. G., Frail D. E. Serine mutations in transmembrane V of the dopamine D1 receptor affect ligand interactions and receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17780–17786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pristupa Z. B., Wilson J. M., Hoffman B. J., Kish S. J., Niznik H. B. Pharmacological heterogeneity of the cloned and native human dopamine transporter: disassociation of [3H]WIN 35,428 and [3H]GBR 12,935 binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Jan;45(1):125–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues P. dos S., Dowling J. E. Dopamine induces neurite retraction in retinal horizontal cells via diacylglycerol and protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9693–9697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosengarten H., Schweitzer J. W., Friedhoff A. J. A subpopulation of dopamine D1 receptors mediate repetitive jaw movements in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1993 Aug;45(4):921–924. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(93)90140-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuldiner A. R., Phillips S., Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D., Roth J. Xenopus laevis contains two nonallelic preproinsulin genes. cDNA cloning and evolutionary perspective. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9428–9432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Monsma F. J., Jr Molecular biology of dopamine receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Feb;13(2):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunahara R. K., Guan H. C., O'Dowd B. F., Seeman P., Laurier L. G., Ng G., George S. R., Torchia J., Van Tol H. H., Niznik H. B. Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D5 receptor with higher affinity for dopamine than D1. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):614–619. doi: 10.1038/350614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunahara R. K., Niznik H. B., Weiner D. M., Stormann T. M., Brann M. R., Kennedy J. L., Gelernter J. E., Rozmahel R., Yang Y. L., Israel Y. Human dopamine D1 receptor encoded by an intronless gene on chromosome 5. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):80–83. doi: 10.1038/347080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiberi M., Jarvie K. R., Silvia C., Falardeau P., Gingrich J. A., Godinot N., Bertrand L., Yang-Feng T. L., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Caron M. G. Cloning, molecular characterization, and chromosomal assignment of a gene encoding a second D1 dopamine receptor subtype: differential expression pattern in rat brain compared with the D1A receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7491–7495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Undie A. S., Weinstock J., Sarau H. M., Friedman E. Evidence for a distinct D1-like dopamine receptor that couples to activation of phosphoinositide metabolism in brain. J Neurochem. 1994 May;62(5):2045–2048. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62052045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinshank R. L., Adham N., Macchi M., Olsen M. A., Branchek T. A., Hartig P. R. Molecular cloning and characterization of a high affinity dopamine receptor (D1 beta) and its pseudogene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22427–22435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D., LaRosa G. J., Simon M. I. G protein-coupled signal transduction pathways for interleukin-8. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):101–103. doi: 10.1126/science.8316840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi I., Jose P. A., Mouradian M. M., Canessa L. M., Monsma F. J., Jr, Sibley D. R., Takeyasu K., Felder R. A. Expression of dopamine D1A receptor gene in proximal tubule of rat kidneys. Am J Physiol. 1993 Feb;264(2 Pt 2):F280–F285. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.2.F280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q. Y., Grandy D. K., Thambi L., Kushner J. A., Van Tol H. H., Cone R., Pribnow D., Salon J., Bunzow J. R., Civelli O. Cloning and expression of human and rat D1 dopamine receptors. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):76–80. doi: 10.1038/347076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]