Abstract
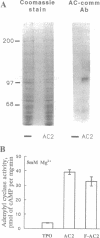
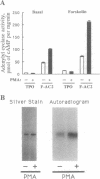
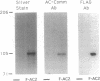
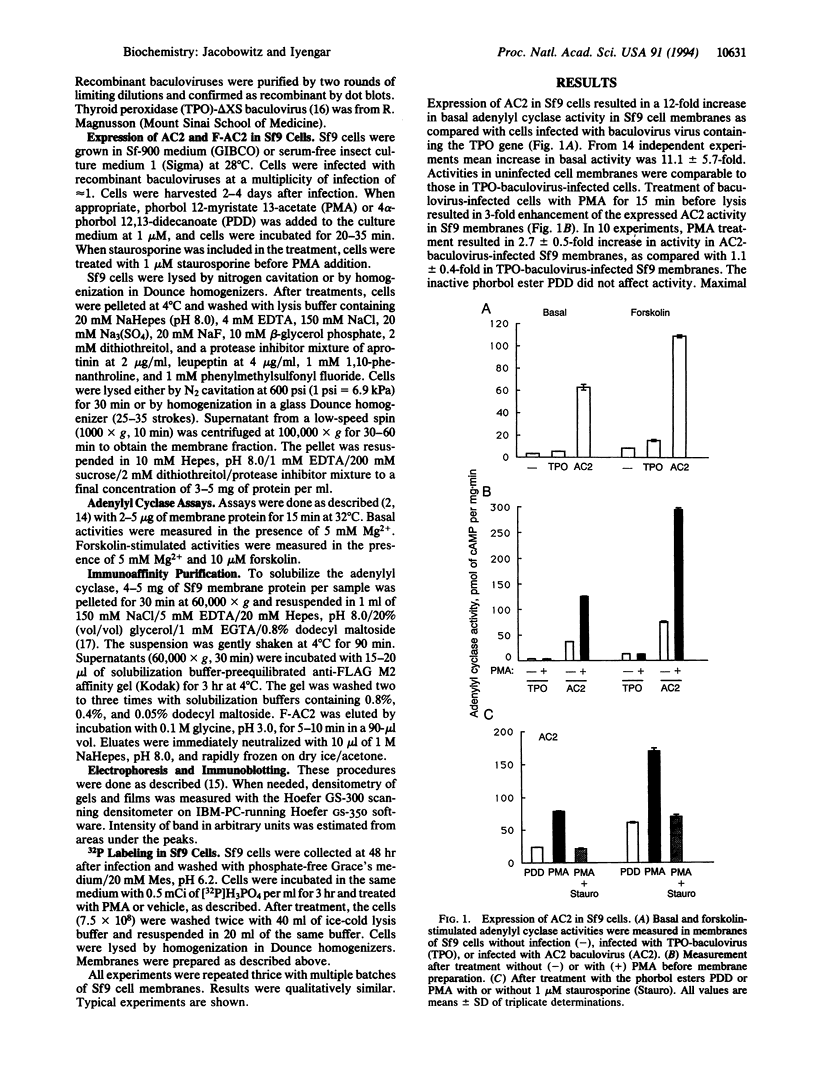
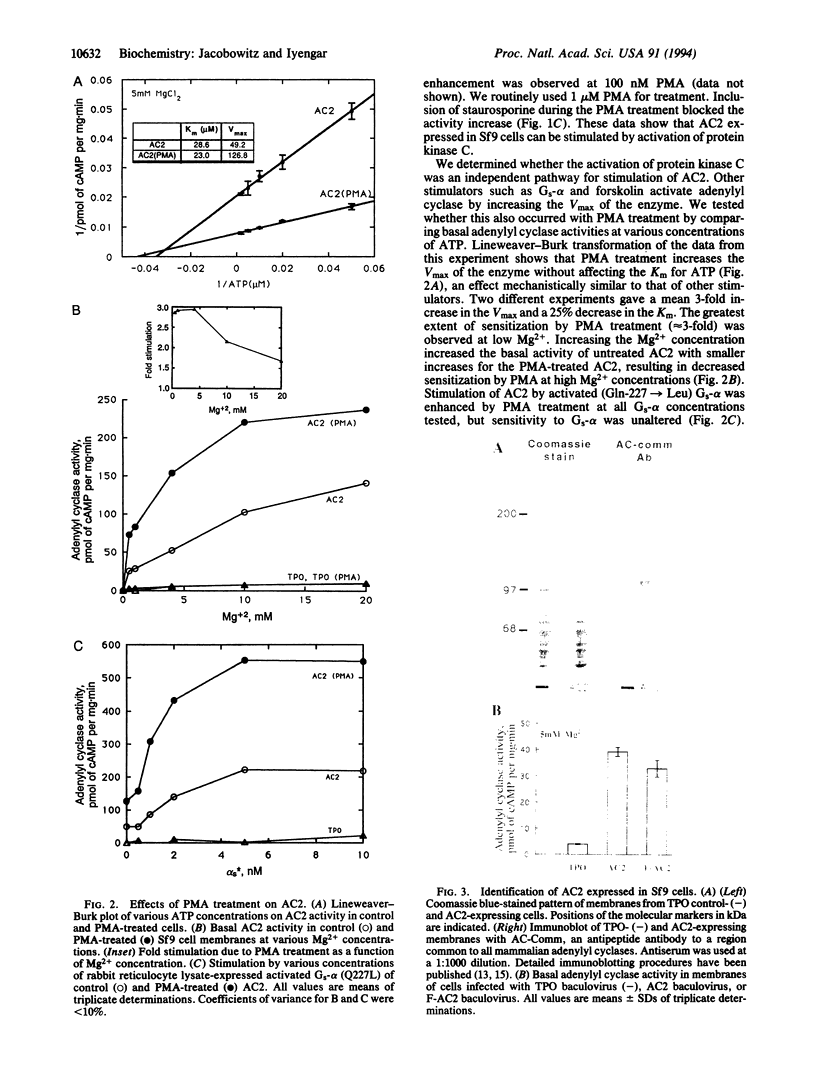
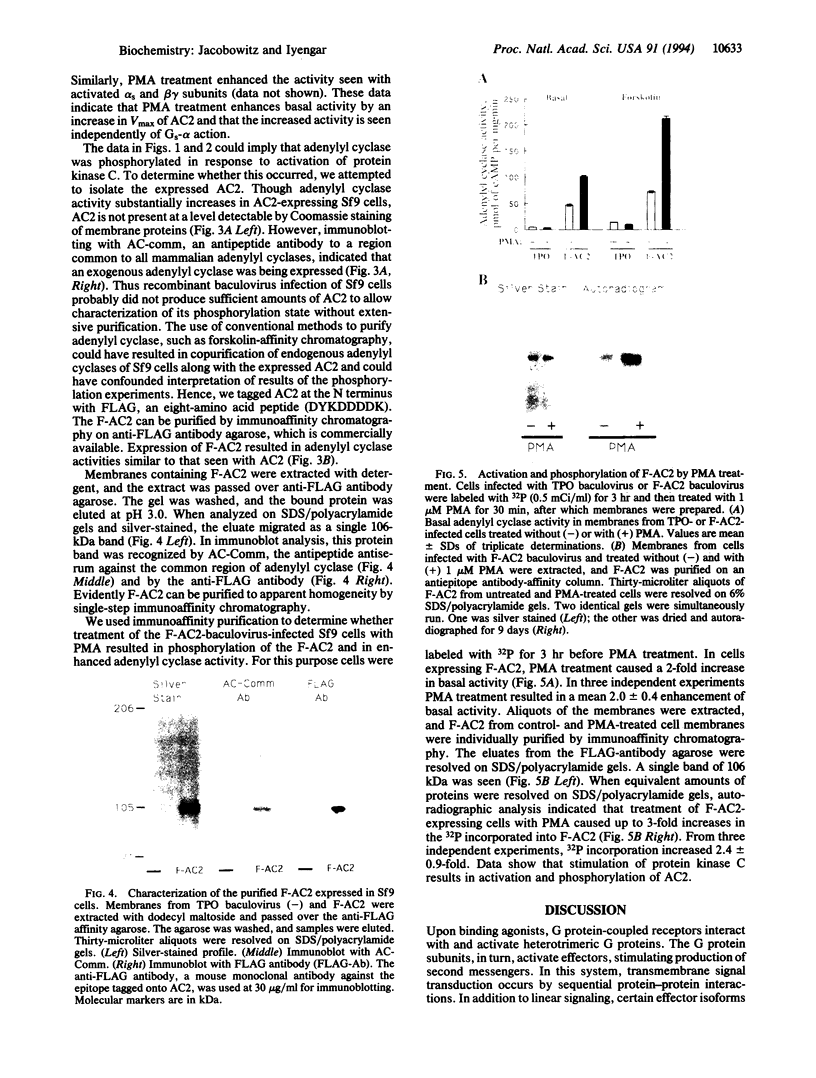
Adenylyl cyclase 2 was expressed in Sf9 cells by recombinant baculovirus infection. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) treatment of cells expressing adenylyl cyclase 2 (AC2) increased basal activity. This increase was blocked by staurosporine, a protein kinase C inhibitor. PMA treatment increased Vmax without affecting Km. Greatest increase in basal activity was seen at physiologically relevant Mg2+ concentrations. PMA treatment did not alter sensitivity to guanine nucleotide stimulatory factor (Gs) but enhanced stimulation at all concentrations of activated Gs alpha subunit tested. AC2 was tagged at the N terminus with an 8-amino acid epitope. Epitope-tagged AC2 was purified to apparent homogeneity in a single step by using an antiepitope antibody-affinity column. The eluate was resolved by SDS/PAGE. Silver staining of the gel showed a 106-kDa band. The purified protein was recognized by antipeptide antibody against a region common to all mammalian adenylyl cyclases. The epitope-tagged enzyme expressed in Sf9 cells was also stimulated by PMA. When cells were labeled with 32P and treated with PMA, a 3-fold increase in 32P incorporation of purified epitope-tagged AC2 was observed. We conclude that activation of protein kinase C results in phosphorylation and stimulation of AC2, a cell-surface G protein effector enzyme. Thus, covalent modification of cell-surface effectors may provide an independent mode for signal transmission through G protein pathways.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell J. D., Buxton I. L., Brunton L. L. Enhancement of adenylate cyclase activity in S49 lymphoma cells by phorbol esters. Putative effect of C kinase on alpha s-GTP-catalytic subunit interaction. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2625–2628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird I. M., Mason J. I., Oka K., Rainey W. E. Angiotensin-II stimulates an increase in cAMP and expression of 17 alpha-hydroxylase cytochrome P450 in fetal bovine adrenocortical cells. Endocrinology. 1993 Feb;132(2):932–934. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.2.8381079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushfield M., Murphy G. J., Lavan B. E., Parker P. J., Hruby V. J., Milligan G., Houslay M. D. Hormonal regulation of Gi2 alpha-subunit phosphorylation in intact hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 1;268(2):449–457. doi: 10.1042/bj2680449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camps M., Carozzi A., Schnabel P., Scheer A., Parker P. J., Gierschik P. Isozyme-selective stimulation of phospholipase C-beta 2 by G protein beta gamma-subunits. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):684–686. doi: 10.1038/360684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carty D. J., Padrell E., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Hildebrandt J. D., Iyengar R. Distinct guanine nucleotide binding and release properties of the three Gi proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6268–6273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vivo M., Chen J., Codina J., Iyengar R. Enhanced phospholipase C stimulation and transformation in NIH-3T3 cells expressing Q209LGq-alpha-subunits. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18263–18266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federman A. D., Conklin B. R., Schrader K. A., Reed R. R., Bourne H. R. Hormonal stimulation of adenylyl cyclase through Gi-protein beta gamma subunits. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):159–161. doi: 10.1038/356159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar R. Molecular and functional diversity of mammalian Gs-stimulated adenylyl cyclases. FASEB J. 1993 Jun;7(9):768–775. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.9.8330684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobowitz O., Chen J., Premont R. T., Iyengar R. Stimulation of specific types of Gs-stimulated adenylyl cyclases by phorbol ester treatment. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3829–3832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. A., Friedman J., Halligan R. D., Birnbaumer M., Clark R. B. Sensitization of adenylyl cyclase by P2 purinergic and M5 muscarinic receptor agonists in L cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;40(4):539–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Gilman A. G., Watanabe Y., Bauer S., Jakobs K. H. Protein kinase C phosphorylates the inhibitory guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory component and apparently suppresses its function in hormonal inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):431–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendler D. L., Brennan V., Davies T. F., Magnusson R. P. Expression of human thyroid peroxidase in insect cells using recombinant baculovirus. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1993 Jun;93(2):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(93)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig K. D., Conklin B. R., Herzmark P., Taussig R., Bourne H. R. Type II adenylylcyclase integrates coincident signals from Gs, Gi, and Gq. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):13900–13905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naghshineh S., Noguchi M., Huang K. P., Londos C. Activation of adipocyte adenylate cyclase by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14534–14538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peytremann A., Nicholson W. E., Brown R. D., Liddle G. W., Hardman J. G. Comparative effects of angiotensin and ACTH on cyclic AMP and steroidogenesis in isolated bovine adrenal cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Apr;52(4):835–842. doi: 10.1172/JCI107247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premont R. T., Iyengar R. Glucagon-induced desensitization of adenylyl cyclase in primary cultures of chick hepatocytes. Evidence for multiple pathways. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16087–16095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Murray M., Zachary I., Collins M. Protein kinase C activation enhances cAMP accumulation in Swiss 3T3 cells: inhibition by pertussis toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2282–2286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., LaCorbiere M., Whitlock C., Stallcup W. Alterations in the surface properties of cells responsive to nerve growth factor. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):718–723. doi: 10.1038/273718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Jeffs R. A., Daniel K., Nambi P., Lefkowitz R. J. Phorbol diester treatment promotes enhanced adenylate cyclase activity in frog erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Jan;244(1):373–381. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmoteit R., Schulzki H. D., Palm D., Mollner S., Pfeuffer T. Chemical and functional analysis of components of adenylyl cyclase from human platelets treated with phorbolesters. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 8;285(1):99–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80734-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden D., Vanecek J., Klein D. C., Thomas T. P., Anderson W. B. Activation of protein kinase C potentiates isoprenaline-induced cyclic AMP accumulation in rat pinealocytes. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):359–361. doi: 10.1038/314359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi J. S. Gene regulation. Circadian clocks à la CREM. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):299–300. doi: 10.1038/365299a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang W. J., Gilman A. G. Type-specific regulation of adenylyl cyclase by G protein beta gamma subunits. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1500–1503. doi: 10.1126/science.1962211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig R., Quarmby L. M., Gilman A. G. Regulation of purified type I and type II adenylylcyclases by G protein beta gamma subunits. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):9–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener E., Scarpa A. Activation of protein kinase C modulates the adenylate cyclase effector system of B-lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4324–4328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D., LaRosa G. J., Simon M. I. G protein-coupled signal transduction pathways for interleukin-8. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):101–103. doi: 10.1126/science.8316840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimasa T., Sibley D. R., Bouvier M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Cross-talk between cellular signalling pathways suggested by phorbol-ester-induced adenylate cyclase phosphorylation. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):67–70. doi: 10.1038/327067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M., Cooper D. M. Type-specific stimulation of adenylylcyclase by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):4604–4607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]