Abstract
Taxol, originally extracted from the bark of the western yew, Taxus brevifolia, is reportedly the first of a new class of anti-cancer agents. It acts by promoting and irreversibly stabilizing microtubule assembly, thus interfering with the dynamic processes required for cell viability and multiplication. With the aim of using immunological techniques to study the mechanism of action of taxol, a monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibody that mimics taxol was prepared, using an auto-anti-idiotypic strategy. It and its Fab fragment inhibited the binding of [3H]taxol to microtubules. Moreover, like taxol, both promoted the assembly of tubulin into microtubules. These findings provide an example of an anti-idiotypic antibody capable of assembling an organized supramolecular structure from soluble cellular components. In addition, it further establishes the ability of anti-idiotypic antibodies to be functional mimics of ligand molecules bearing no structural similarity to immunoglobulins. The variable regions of the antibody have been sequenced. With the exception of the complementarity-determining region 3, the sequence of the heavy chain variable region is strikingly similar to that of an anti-idiotypic antibody raised to anti-insulin. The finding that a polypeptide can mimic taxol raises the possibility that taxol acts as a peptidomimetic compound that interferes with the function of an endogenous polypeptide.
Full text
PDF

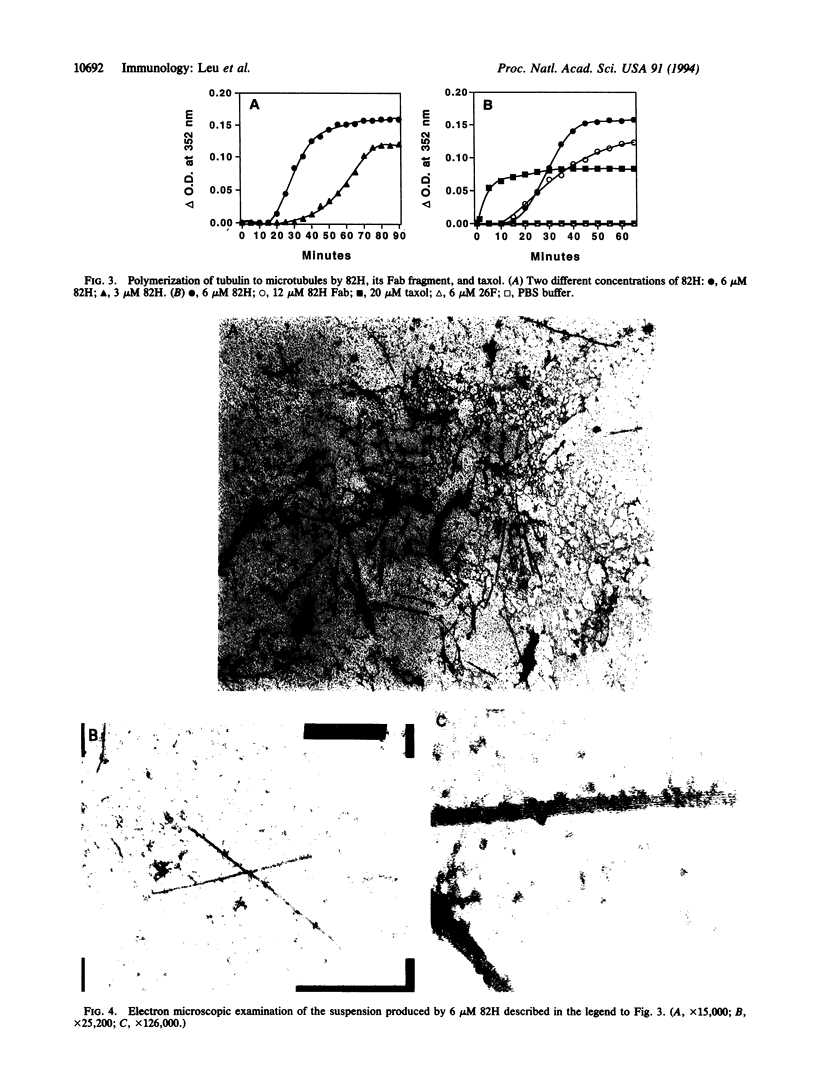


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berghammer H., Auer B. "Easypreps": fast and easy plasmid minipreparation for analysis of recombinant clones in E. coli. Biotechniques. 1993 Apr;14(4):524–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen B. X., Hubbard K., Ide H., Wallace S. S., Erlanger B. F. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody to thymidine glycol monophosphate. Radiat Res. 1990 Nov;124(2):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland W. L., Wassermann N. H., Sarangarajan R., Penn A. S., Erlanger B. F. Monoclonal antibodies to the acetylcholine receptor by a normally functioning auto-anti-idiotypic mechanism. Nature. 1983 Sep 1;305(5929):56–57. doi: 10.1038/305056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coloma M. J., Hastings A., Wims L. A., Morrison S. L. Novel vectors for the expression of antibody molecules using variable regions generated by polymerase chain reaction. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Jul 31;152(1):89–104. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coloma M. J., Larrick J. W., Ayala M., Gavilondo-Cowley J. V. Primer design for the cloning of immunoglobulin heavy-chain leader-variable regions from mouse hybridoma cells using the PCR. Biotechniques. 1991 Aug;11(2):152-4, 156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S. J., Schockmel G. A., Somoza C., Buck D. W., Healey D. G., Rieber E. P., Reiter C., Williams A. F. Antibody and HIV-1 gp120 recognition of CD4 undermines the concept of mimicry between antibodies and receptors. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):76–79. doi: 10.1038/358076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlanger B. F. Antibodies to receptors by an auto-anti-idiotypic strategy. Biochem Soc Trans. 1991 Feb;19(1):138–143. doi: 10.1042/bst0190138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlanger B. F. Auto-anti-idiotypy, autoimmunity and some thoughts on the structure of internal images. Int Rev Immunol. 1989;5(2):131–137. doi: 10.3109/08830188909061979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaulton G. N., Greene M. I. Idiotypic mimicry of biological receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:253–280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guéritte-Voegelein F., Guénard D., Lavelle F., Le Goff M. T., Mangatal L., Potier P. Relationships between the structure of taxol analogues and their antimitotic activity. J Med Chem. 1991 Mar;34(3):992–998. doi: 10.1021/jm00107a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K. Idiotypic networks and other preconceived ideas. Immunol Rev. 1984 Jun;79:5–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb00484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K. Towards a network theory of the immune system. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1974 Jan;125C(1-2):373–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leu J. G., Chen B. X., Schiff P. B., Erlanger B. F. Characterization of polyclonal and monoclonal anti-taxol antibodies and measurement of taxol in serum. Cancer Res. 1993 Mar 15;53(6):1388–1391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung S. O., Dion A. S., Pellegrini M. C., Goldenberg D. M., Hansen H. J. An extended primer set for PCR amplification of murine kappa variable regions. Biotechniques. 1993 Aug;15(2):286–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombes M., Desfosses B., Cittanova N., Erlanger B. F. A syngeneic monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibody with internal image properties restricted to a single aldosterone-binding system. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):4078–4083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombes M., Edelman I. S., Erlanger B. F. Internal image properties of a monoclonal auto-anti-idiotypic antibody and its binding to aldosterone receptors. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2528–2536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisonoff A., Lamoyi E. Implications of the presence of an internal image of the antigen in anti-idiotypic antibodies: possible application to vaccine production. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Dec;21(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parness J., Horwitz S. B. Taxol binds to polymerized tubulin in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):479–487. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parness J., Kingston D. G., Powell R. G., Harracksingh C., Horwitz S. B. Structure-activity study of cytotoxicity and microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol and related taxanes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Apr 14;105(3):1082–1089. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91080-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao S., Horwitz S. B., Ringel I. Direct photoaffinity labeling of tubulin with taxol. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 May 20;84(10):785–788. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.10.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao S., Krauss N. E., Heerding J. M., Swindell C. S., Ringel I., Orr G. A., Horwitz S. B. 3'-(p-azidobenzamido)taxol photolabels the N-terminal 31 amino acids of beta-tubulin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3132–3134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff P. B., Fant J., Horwitz S. B. Promotion of microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):665–667. doi: 10.1038/277665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff P. B., Horwitz S. B. Taxol assembles tubulin in the absence of exogenous guanosine 5'-triphosphate or microtubule-associated proteins. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3247–3252. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Gaskin F., Cantor C. R. Microtubule assembly in the absence of added nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):765–768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. W. Anti-insulin and regulatory anti-idiotypic antibodies use the same germ-line VHIX gene. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Sep;22(9):2445–2448. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine R. C., Green N. M. Electron microscopy of an antibody-hapten complex. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 14;27(3):615–617. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wani M. C., Taylor H. L., Wall M. E., Coggon P., McPhail A. T. Plant antitumor agents. VI. The isolation and structure of taxol, a novel antileukemic and antitumor agent from Taxus brevifolia. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 May 5;93(9):2325–2327. doi: 10.1021/ja00738a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zovich D. C., Orologa A., Okuno M., Kong L. W., Talmage D. A., Piantedosi R., Goodman D. S., Blaner W. S. Differentiation-dependent expression of retinoid-binding proteins in BFC-1 beta adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):13884–13889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



