Abstract
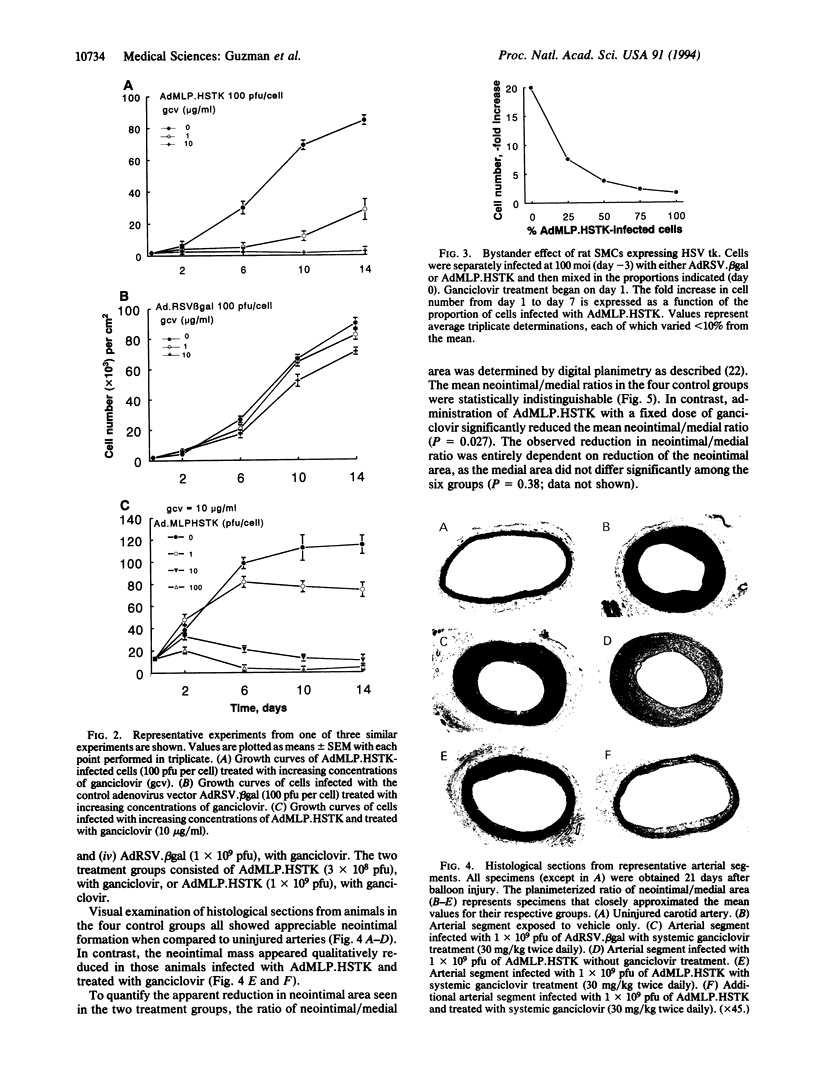
Restenosis, a process characterized in part by excessive smooth muscle cell (SMC) proliferation in areas of vascular injury, occurs in up to 50% of patients undergoing balloon angioplasty. In an effort to develop a treatment strategy for restenosis, we constructed a replication-deficient recombinant adenovirus (AdMLP.HSTK) containing the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene (HSV tk). This viral gene product phosphorylates the prodrug ganciclovir to form a nucleoside analog that inhibits DNA synthesis. Cultured primary rat SMCs infected with AdMLP.HSTK were completely growth-inhibited by incubation in ganciclovir-containing medium. In addition, when only a portion of the SMC population received the HSV tk transgene, an inhibitory effect on neighboring SMCs was evident. Evaluation of this strategy in vivo using a rat carotid balloon injury model demonstrated that local infection of injured arteries with AdMLP.-HSTK followed by 2 weeks of systemic ganciclovir treatment significantly (P < 0.01) reduced injury-induced SMC accumulation. In contrast, there was no suppression of injury-induced SMC accumulation in animals infected with AdMLP.HSTK but not receiving ganciclovir or in those animals infected with a control adenovirus and either treated or not treated with ganciclovir. These results demonstrate the potential utility of adenovirus-mediated gene transfer for treatment of restenosis after balloon injury.
Full text
PDF



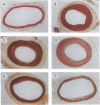
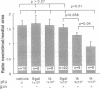
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. F. Human gene therapy. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):808–813. doi: 10.1126/science.1589762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banai S., Shou M., Correa R., Jaklitsch M. T., Douek P. C., Bonner R. F., Epstein S. E., Unger E. F. Rabbit ear model of injury-induced arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation. Kinetics, reproducibility, and implications. Circ Res. 1991 Sep;69(3):748–756. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.3.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr E., Carroll J., Kalynych A. M., Tripathy S. K., Kozarsky K., Wilson J. M., Leiden J. M. Efficient catheter-mediated gene transfer into the heart using replication-defective adenovirus. Gene Ther. 1994 Jan;1(1):51–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkner K. L. Expression of heterologous sequences in adenoviral vectors. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;158:39–66. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75608-5_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bi W. L., Parysek L. M., Warnick R., Stambrook P. J. In vitro evidence that metabolic cooperation is responsible for the bystander effect observed with HSV tk retroviral gene therapy. Hum Gene Ther. 1993 Dec;4(6):725–731. doi: 10.1089/hum.1993.4.6-725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Heyman R., Hsi M., Evans R. M. Targeting of an inducible toxic phenotype in animal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7572–7576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes A. W., Reidy M. A., Clowes M. M. Kinetics of cellular proliferation after arterial injury. I. Smooth muscle growth in the absence of endothelium. Lab Invest. 1983 Sep;49(3):327–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culver K. W., Ram Z., Wallbridge S., Ishii H., Oldfield E. H., Blaese R. M. In vivo gene transfer with retroviral vector-producer cells for treatment of experimental brain tumors. Science. 1992 Jun 12;256(5063):1550–1552. doi: 10.1126/science.1317968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferns G. A., Raines E. W., Sprugel K. H., Motani A. S., Reidy M. A., Ross R. Inhibition of neointimal smooth muscle accumulation after angioplasty by an antibody to PDGF. Science. 1991 Sep 6;253(5024):1129–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.1653454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flugelman M. Y., Jaklitsch M. T., Newman K. D., Casscells W., Bratthauer G. L., Dichek D. A. Low level in vivo gene transfer into the arterial wall through a perforated balloon catheter. Circulation. 1992 Mar;85(3):1110–1117. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.3.1110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruentzig A. R., King S. B., 3rd, Schlumpf M., Siegenthaler W. Long-term follow-up after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. The early Zurich experience. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 30;316(18):1127–1132. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704303161805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzman R. J., Lemarchand P., Crystal R. G., Epstein S. E., Finkel T. Efficient and selective adenovirus-mediated gene transfer into vascular neointima. Circulation. 1993 Dec;88(6):2838–2848. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.88.6.2838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzman R. J., Lemarchand P., Crystal R. G., Epstein S. E., Finkel T. Efficient gene transfer into myocardium by direct injection of adenovirus vectors. Circ Res. 1993 Dec;73(6):1202–1207. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.6.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass-Eisler A., Falck-Pedersen E., Alvira M., Rivera J., Buttrick P. M., Wittenberg B. A., Cipriani L., Leinwand L. A. Quantitative determination of adenovirus-mediated gene delivery to rat cardiac myocytes in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11498–11502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc G., Gal D., Takeshita S., Nikol S., Weir L., Isner J. M. Percutaneous arterial gene transfer in a rabbit model. Efficiency in normal and balloon-dilated atherosclerotic arteries. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):936–944. doi: 10.1172/JCI115970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. W., Trapnell B. C., Rade J. J., Virmani R., Dichek D. A. In vivo adenoviral vector-mediated gene transfer into balloon-injured rat carotid arteries. Circ Res. 1993 Nov;73(5):797–807. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.5.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimgruber P. P., Roubin G. S., Hollman J., Cotsonis G. A., Meier B., Douglas J. S., King S. B., Jr, Gruentzig A. R. Restenosis after successful coronary angioplasty in patients with single-vessel disease. Circulation. 1986 Apr;73(4):710–717. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.73.4.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemarchand P., Jones M., Yamada I., Crystal R. G. In vivo gene transfer and expression in normal uninjured blood vessels using replication-deficient recombinant adenovirus vectors. Circ Res. 1993 May;72(5):1132–1138. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.5.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner V., Reidy M. A. Proliferation of smooth muscle cells after vascular injury is inhibited by an antibody against basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3739–3743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastrangeli A., Danel C., Rosenfeld M. A., Stratford-Perricaudet L., Perricaudet M., Pavirani A., Lecocq J. P., Crystal R. G. Diversity of airway epithelial cell targets for in vivo recombinant adenovirus-mediated gene transfer. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):225–234. doi: 10.1172/JCI116175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolten F. L. Tumor chemosensitivity conferred by inserted herpes thymidine kinase genes: paradigm for a prospective cancer control strategy. Cancer Res. 1986 Oct;46(10):5276–5281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolten F. L., Wells J. M. Curability of tumors bearing herpes thymidine kinase genes transferred by retroviral vectors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Feb 21;82(4):297–300. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.4.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita R., Gibbons G. H., Ellison K. E., Nakajima M., Zhang L., Kaneda Y., Ogihara T., Dzau V. J. Single intraluminal delivery of antisense cdc2 kinase and proliferating-cell nuclear antigen oligonucleotides results in chronic inhibition of neointimal hyperplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8474–8478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse G. D., Shelton M. J., O'Donnell A. M. Comparative pharmacokinetics of antiviral nucleoside analogues. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1993 Feb;24(2):101–123. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199324020-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield E. H., Ram Z., Culver K. W., Blaese R. M., DeVroom H. L., Anderson W. F. Gene therapy for the treatment of brain tumors using intra-tumoral transduction with the thymidine kinase gene and intravenous ganciclovir. Hum Gene Ther. 1993 Feb;4(1):39–69. doi: 10.1089/hum.1993.4.1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plautz G., Nabel E. G., Nabel G. J. Selective elimination of recombinant genes in vivo with a suicide retroviral vector. New Biol. 1991 Jul;3(7):709–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragot T., Vincent N., Chafey P., Vigne E., Gilgenkrantz H., Couton D., Cartaud J., Briand P., Kaplan J. C., Perricaudet M. Efficient adenovirus-mediated transfer of a human minidystrophin gene to skeletal muscle of mdx mice. Nature. 1993 Feb 18;361(6413):647–650. doi: 10.1038/361647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidy M. A., Clowes A. W., Schwartz S. M. Endothelial regeneration. V. Inhibition of endothelial regrowth in arteries of rat and rabbit. Lab Invest. 1983 Nov;49(5):569–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. A., Siegfried W., Yoshimura K., Yoneyama K., Fukayama M., Stier L. E., Päkkö P. K., Gilardi P., Stratford-Perricaudet L. D., Perricaudet M. Adenovirus-mediated transfer of a recombinant alpha 1-antitrypsin gene to the lung epithelium in vivo. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):431–434. doi: 10.1126/science.2017680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. A., Yoshimura K., Trapnell B. C., Yoneyama K., Rosenthal E. R., Dalemans W., Fukayama M., Bargon J., Stier L. E., Stratford-Perricaudet L. In vivo transfer of the human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene to the airway epithelium. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):143–155. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90213-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G., Hambrecht R., Schlierf G., Niebauer J., Hauer K., Neumann J., Hoberg E., Drinkmann A., Bacher F., Grunze M. Regular physical exercise and low-fat diet. Effects on progression of coronary artery disease. Circulation. 1992 Jul;86(1):1–11. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.86.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. S., Holmes D. R., Jr, Topol E. J. The restenosis paradigm revisited: an alternative proposal for cellular mechanisms. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992 Nov 1;20(5):1284–1293. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(92)90389-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons M., Edelman E. R., DeKeyser J. L., Langer R., Rosenberg R. D. Antisense c-myb oligonucleotides inhibit intimal arterial smooth muscle cell accumulation in vivo. Nature. 1992 Sep 3;359(6390):67–70. doi: 10.1038/359067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. A., Mehaffey M. G., Kayda D. B., Saunders J. M., Yei S., Trapnell B. C., McClelland A., Kaleko M. Adenovirus mediated expression of therapeutic plasma levels of human factor IX in mice. Nat Genet. 1993 Dec;5(4):397–402. doi: 10.1038/ng1293-397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratford-Perricaudet L. D., Levrero M., Chasse J. F., Perricaudet M., Briand P. Evaluation of the transfer and expression in mice of an enzyme-encoding gene using a human adenovirus vector. Hum Gene Ther. 1990 Fall;1(3):241–256. doi: 10.1089/hum.1990.1.3-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabner J., Couture L. A., Gregory R. J., Graham S. M., Smith A. E., Welsh M. J. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer transiently corrects the chloride transport defect in nasal epithelia of patients with cystic fibrosis. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80063-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]