Abstract
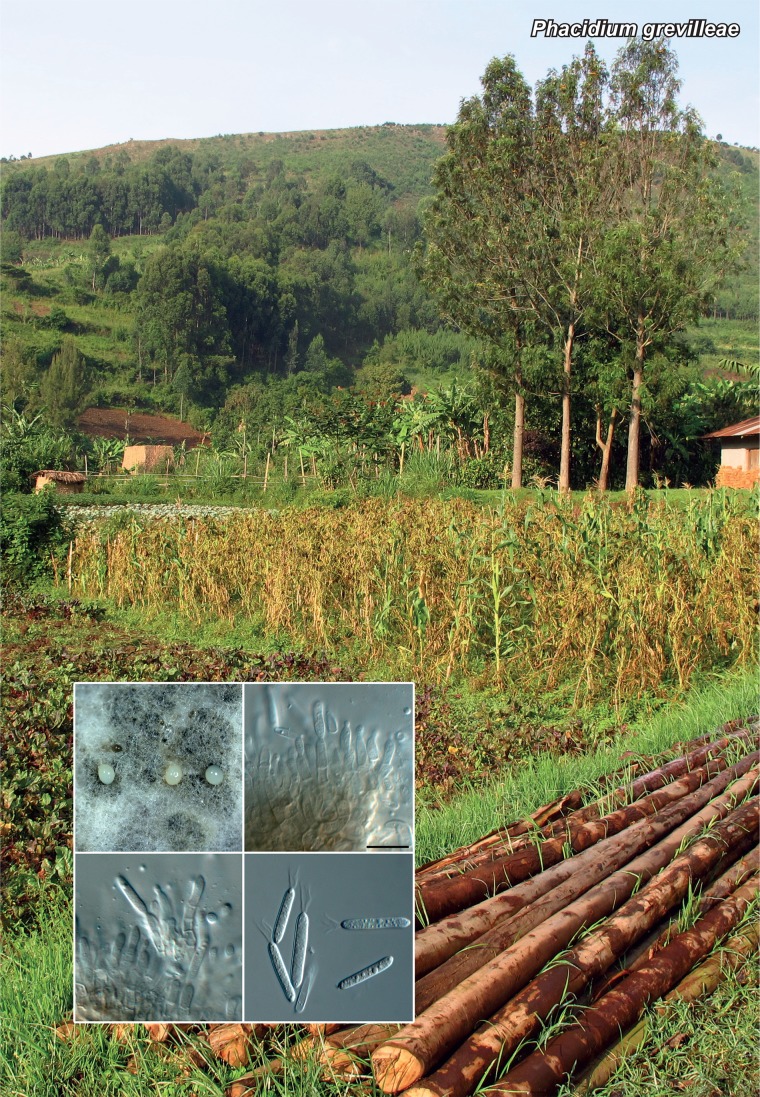
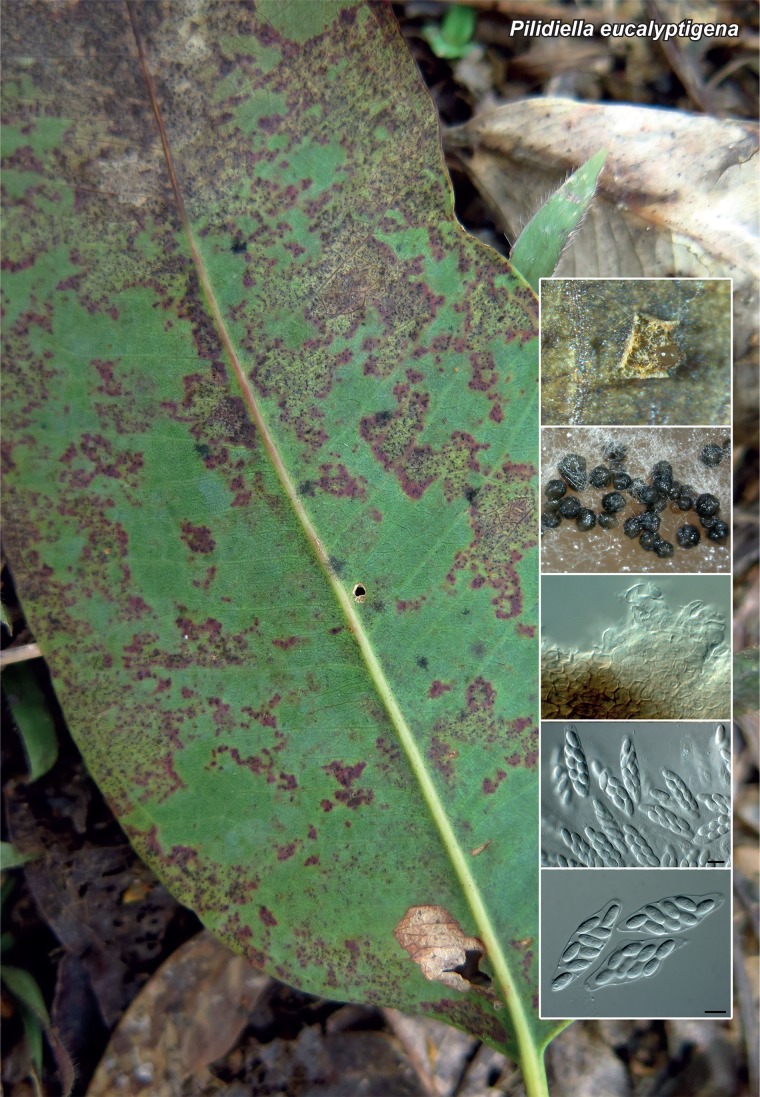
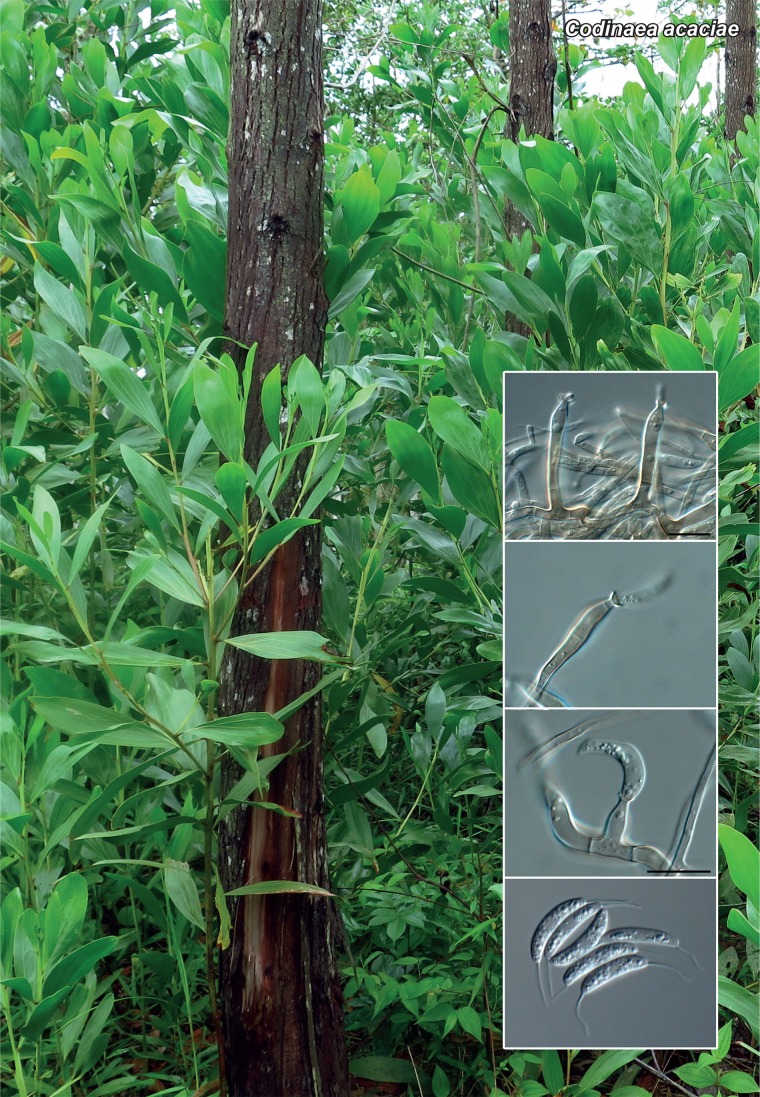
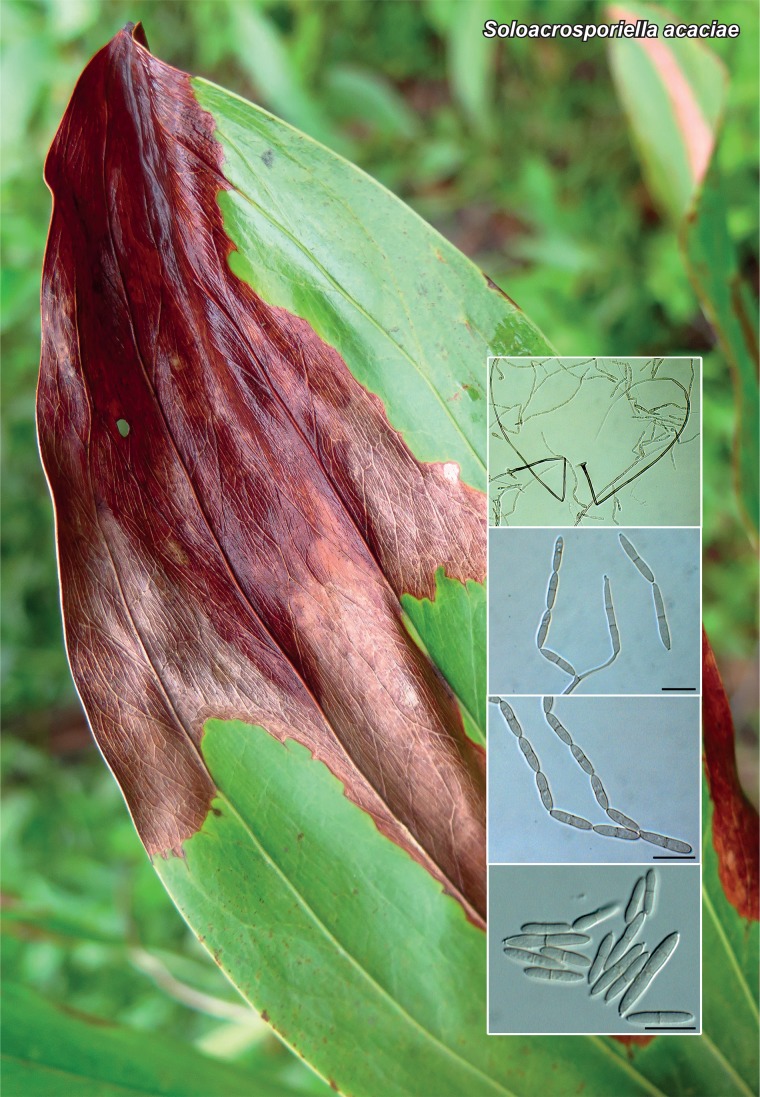
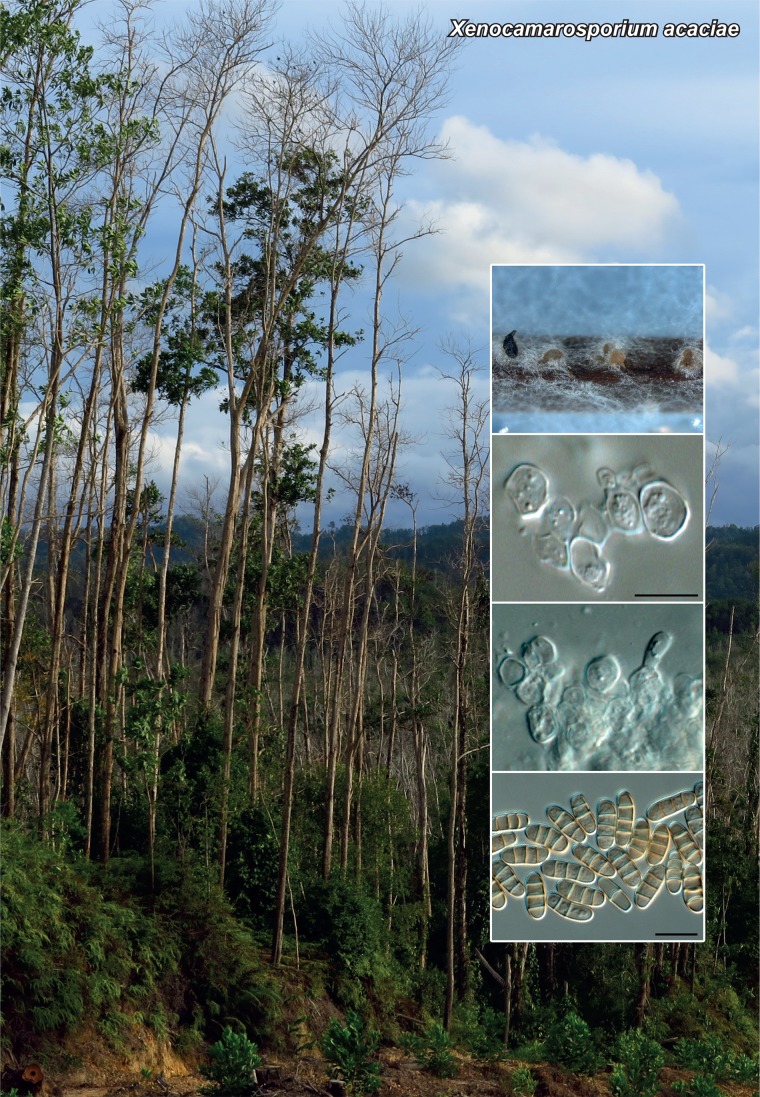
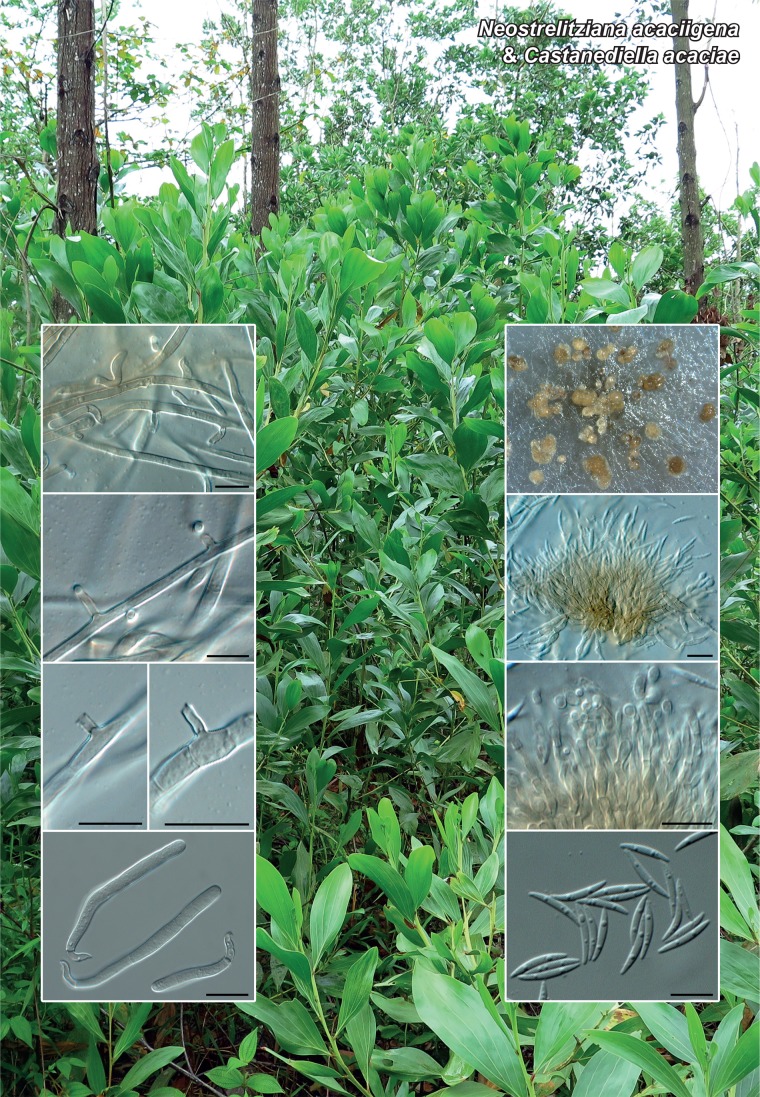
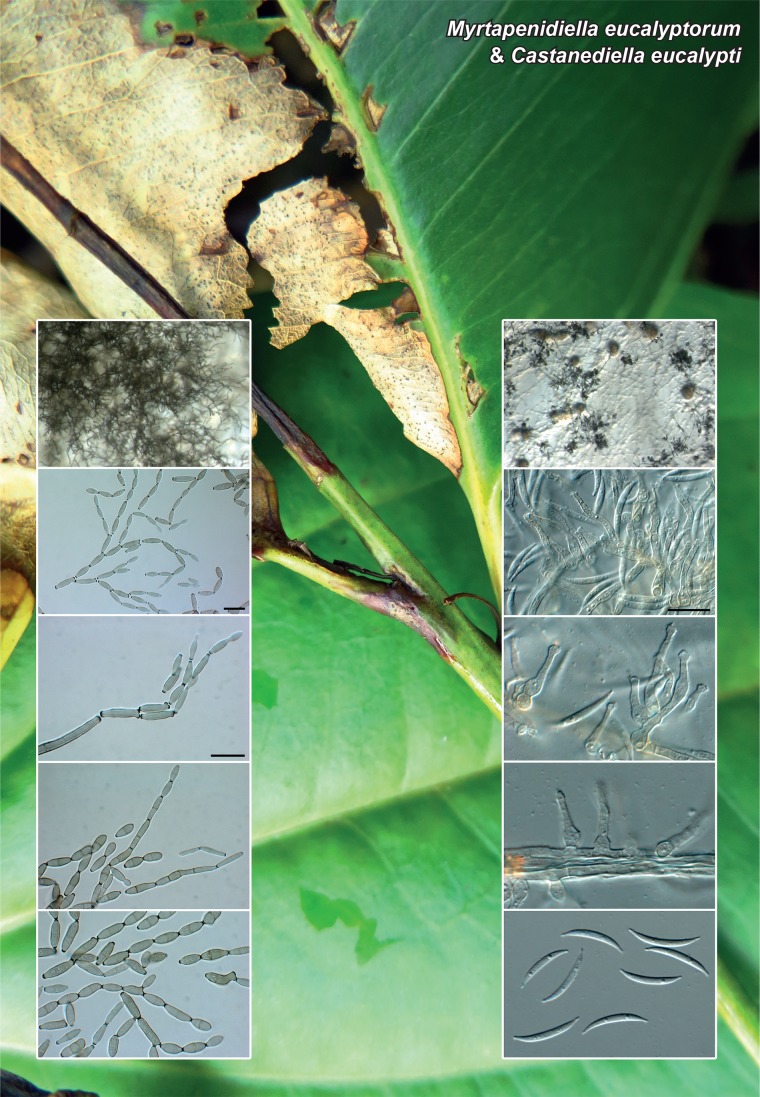
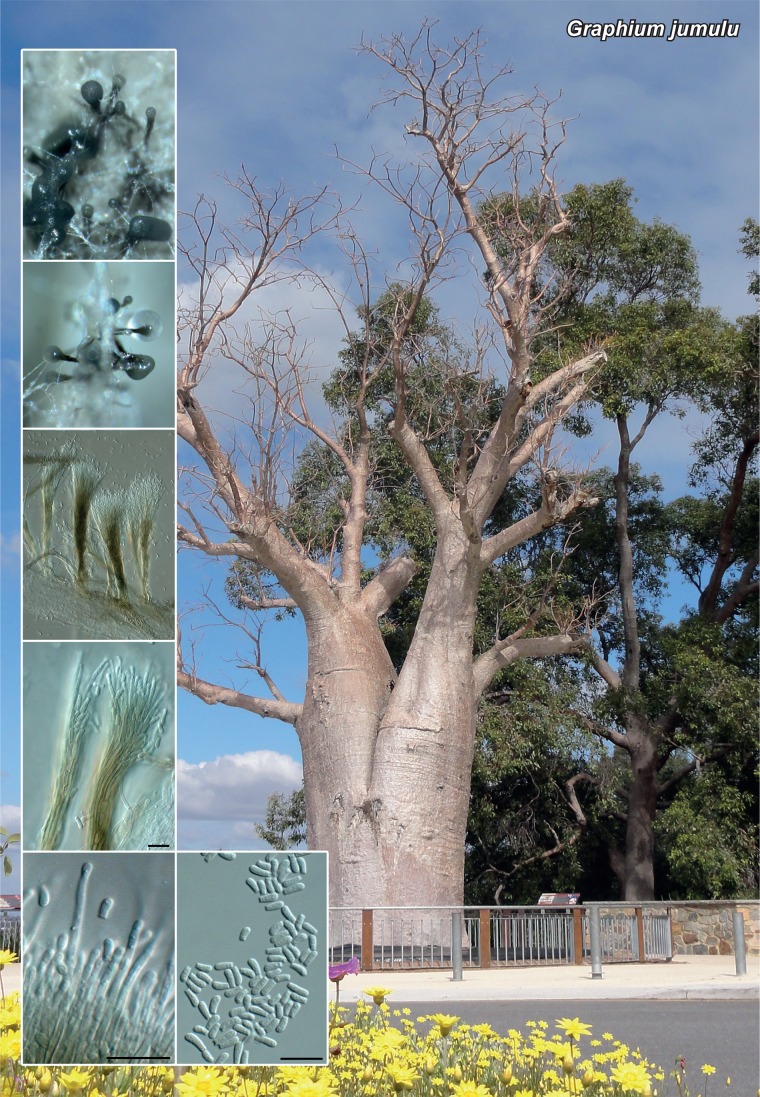
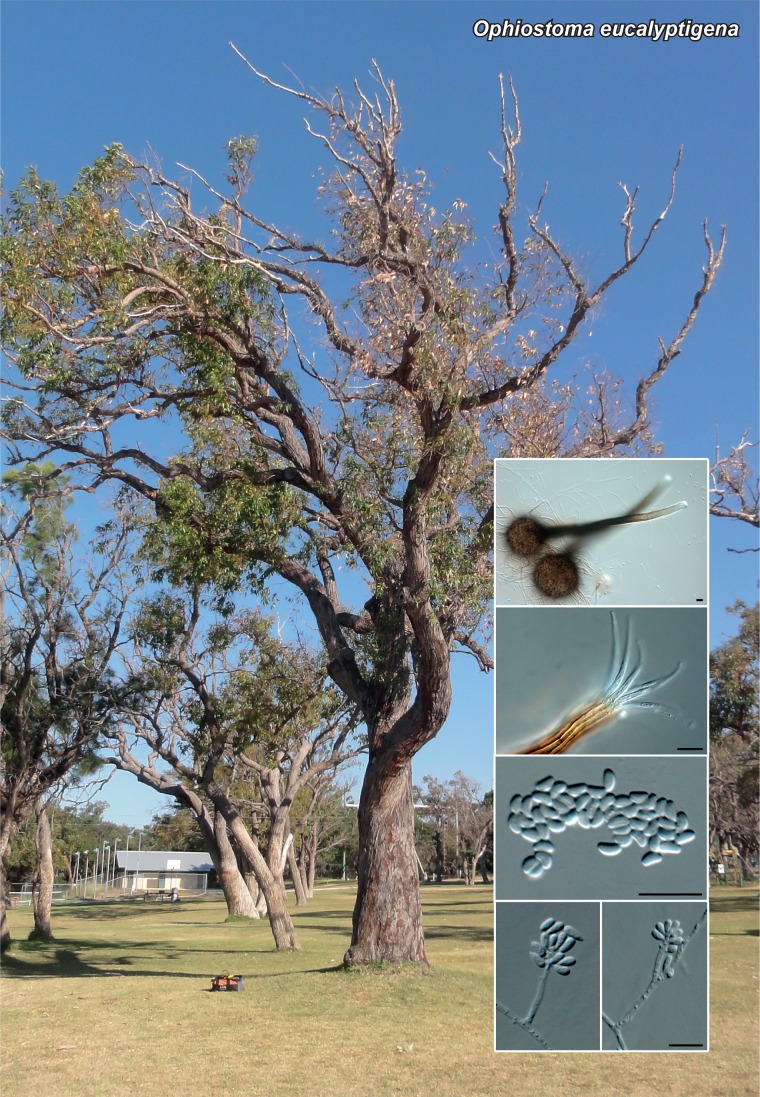
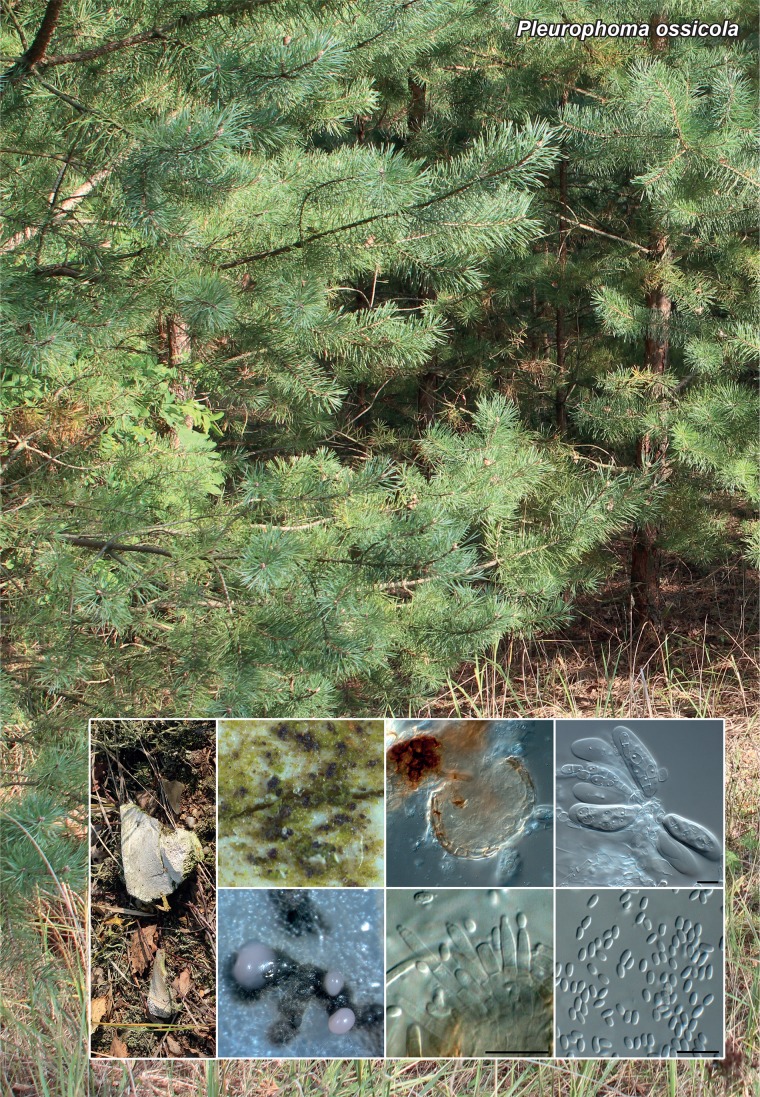
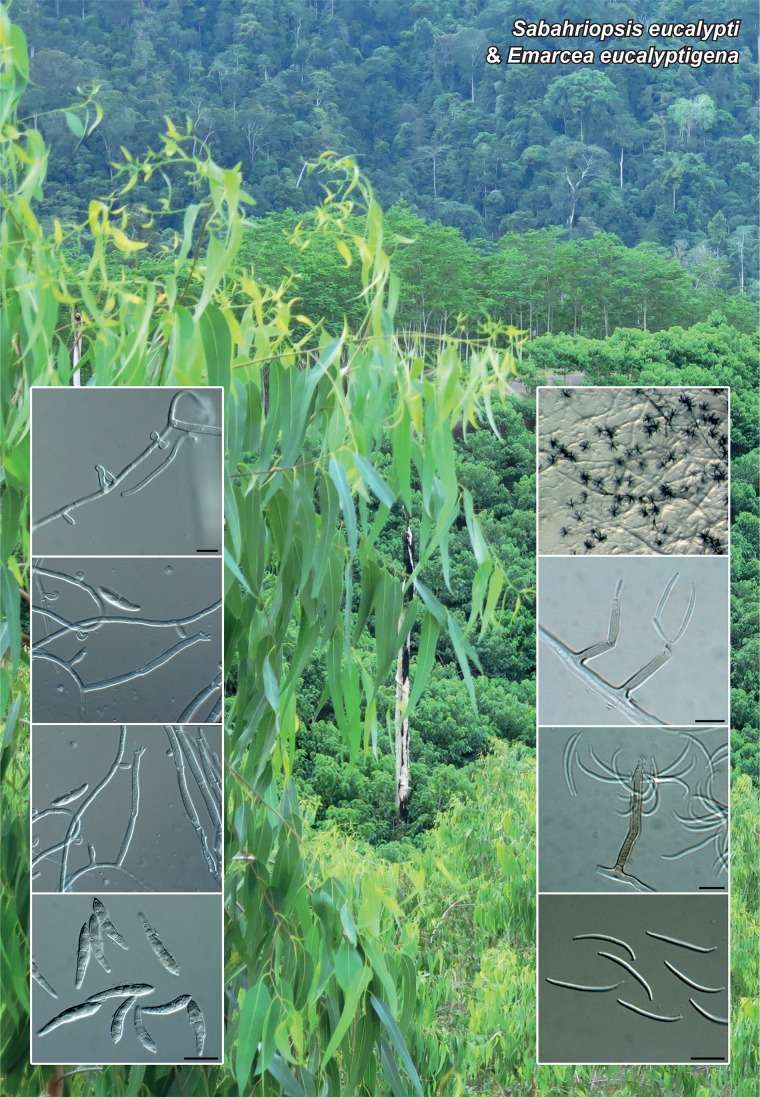
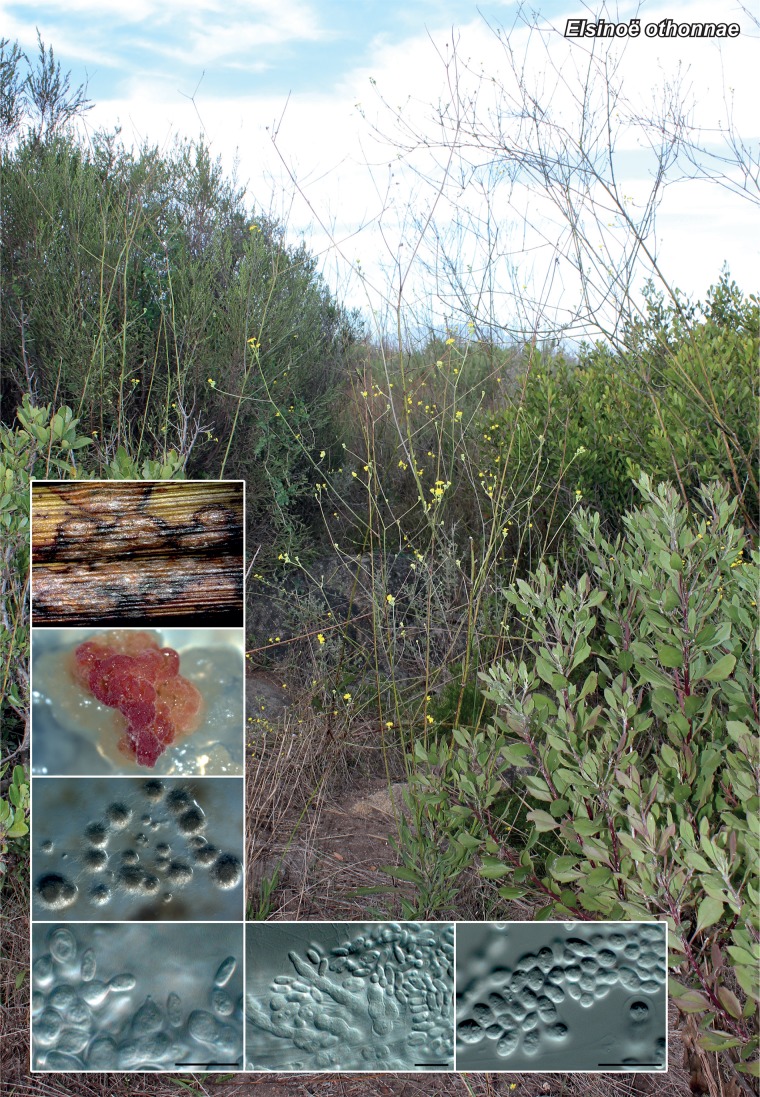
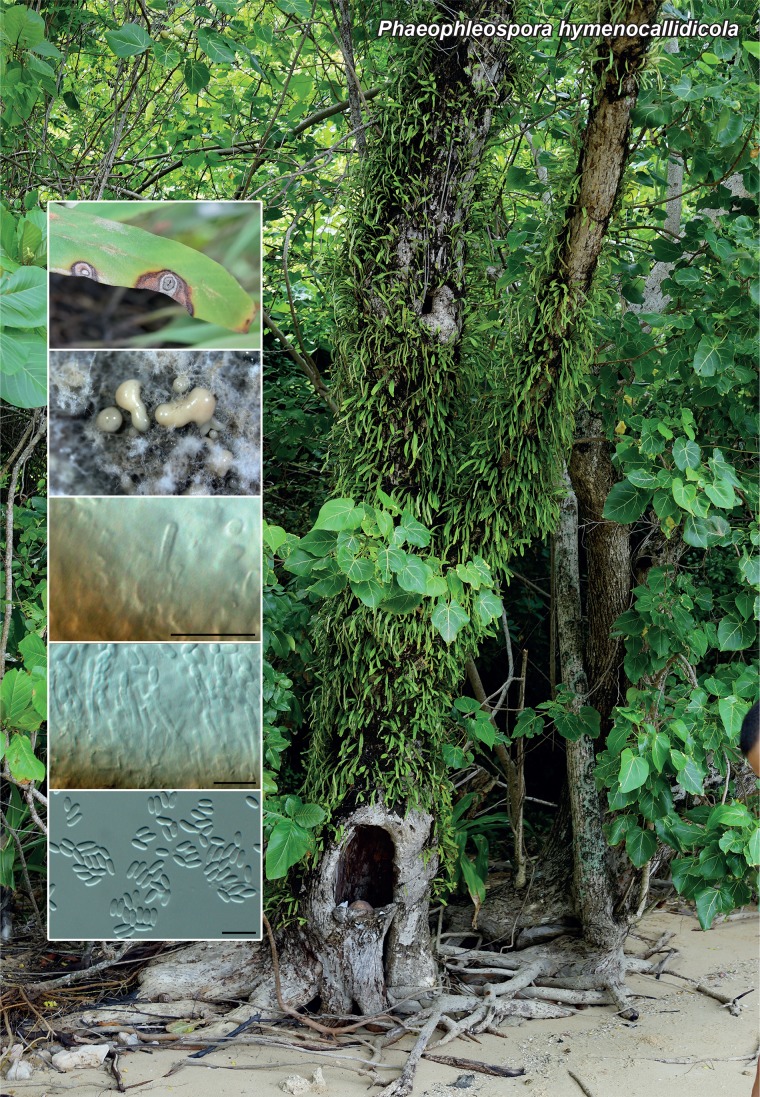
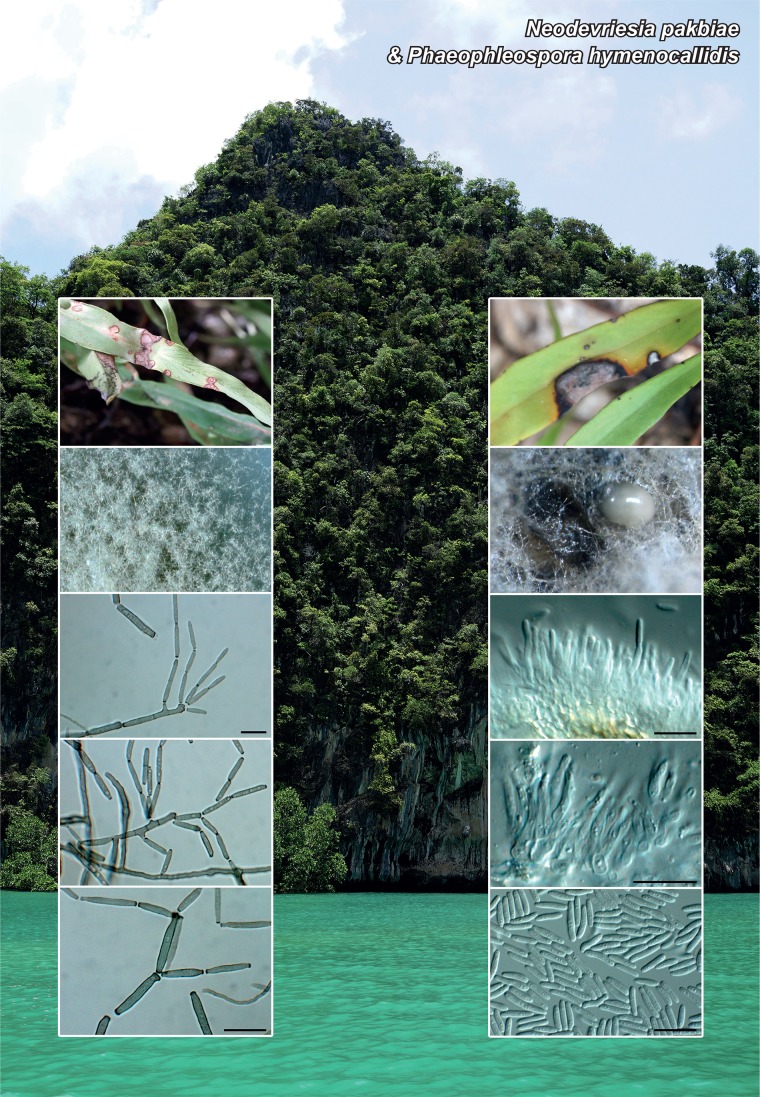
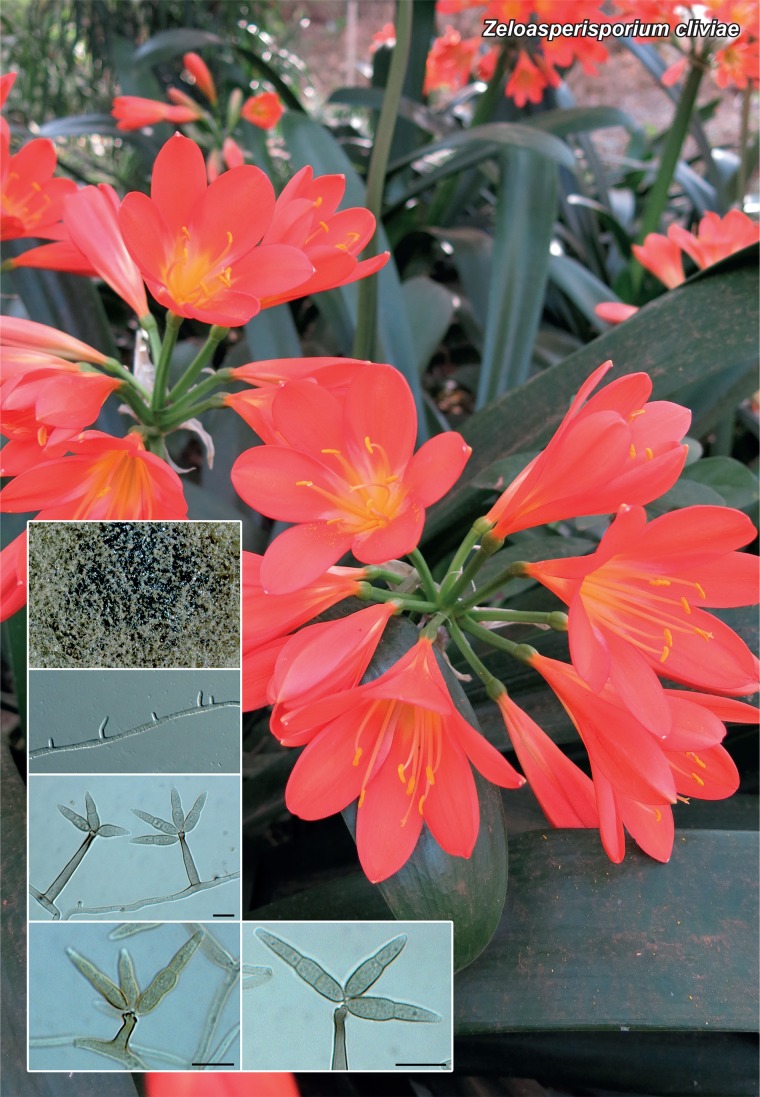
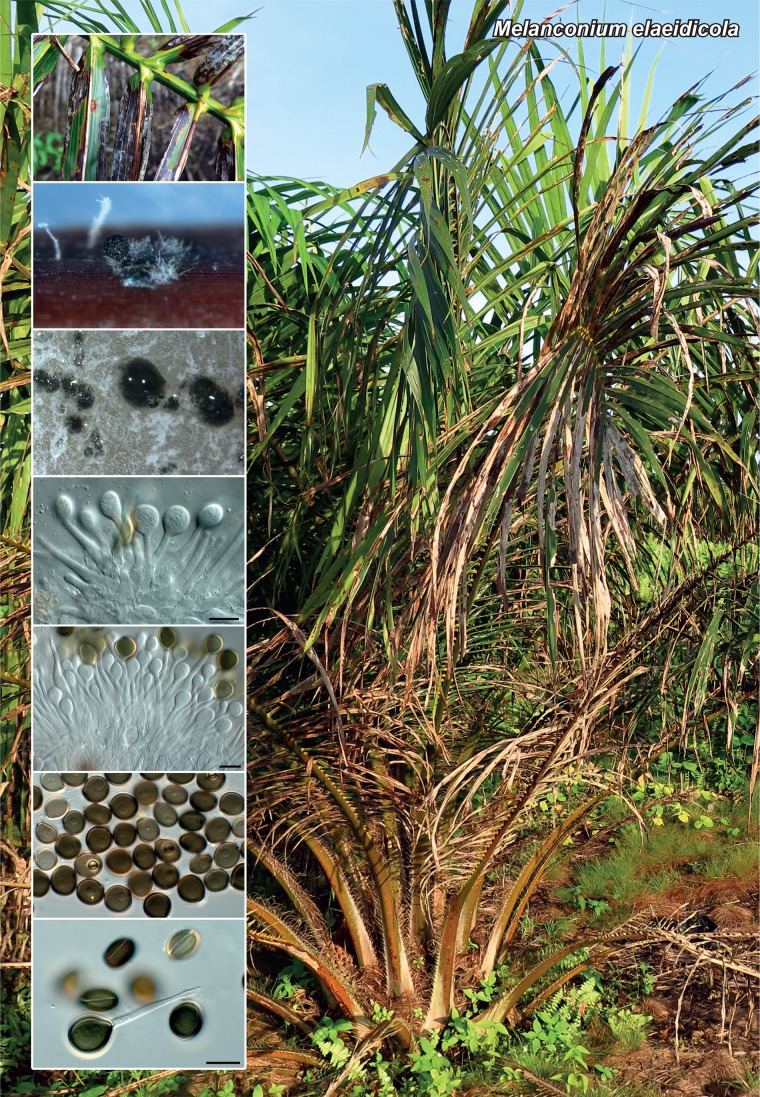
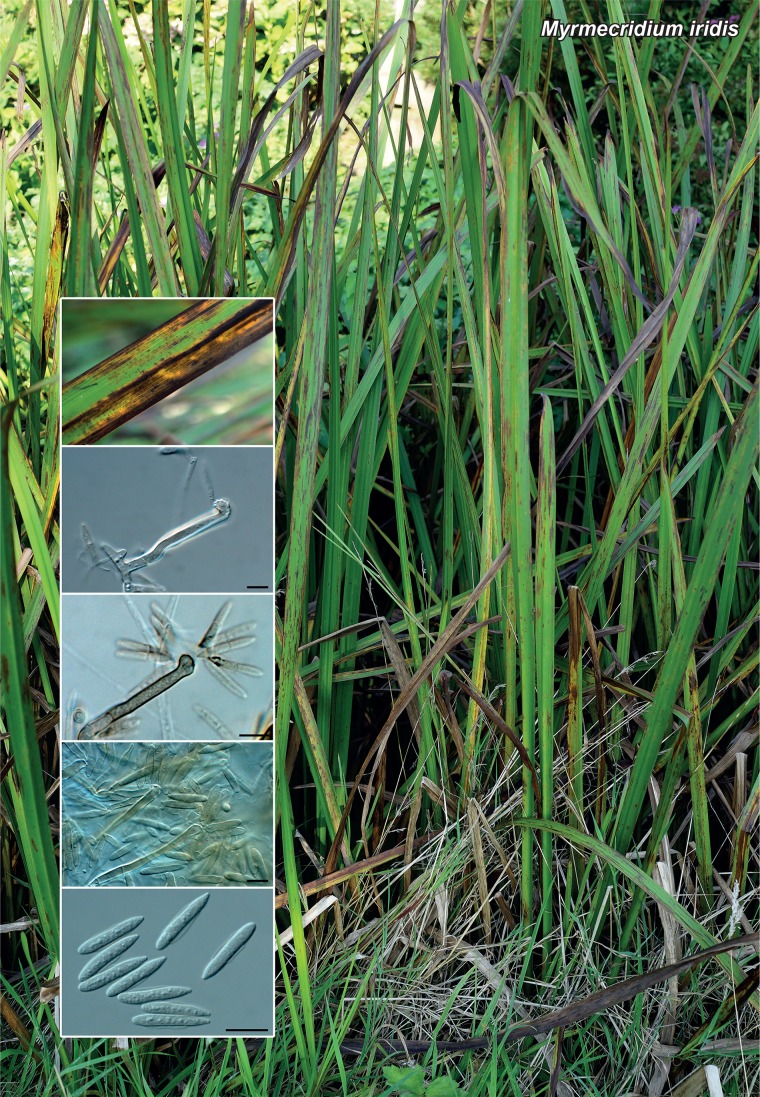
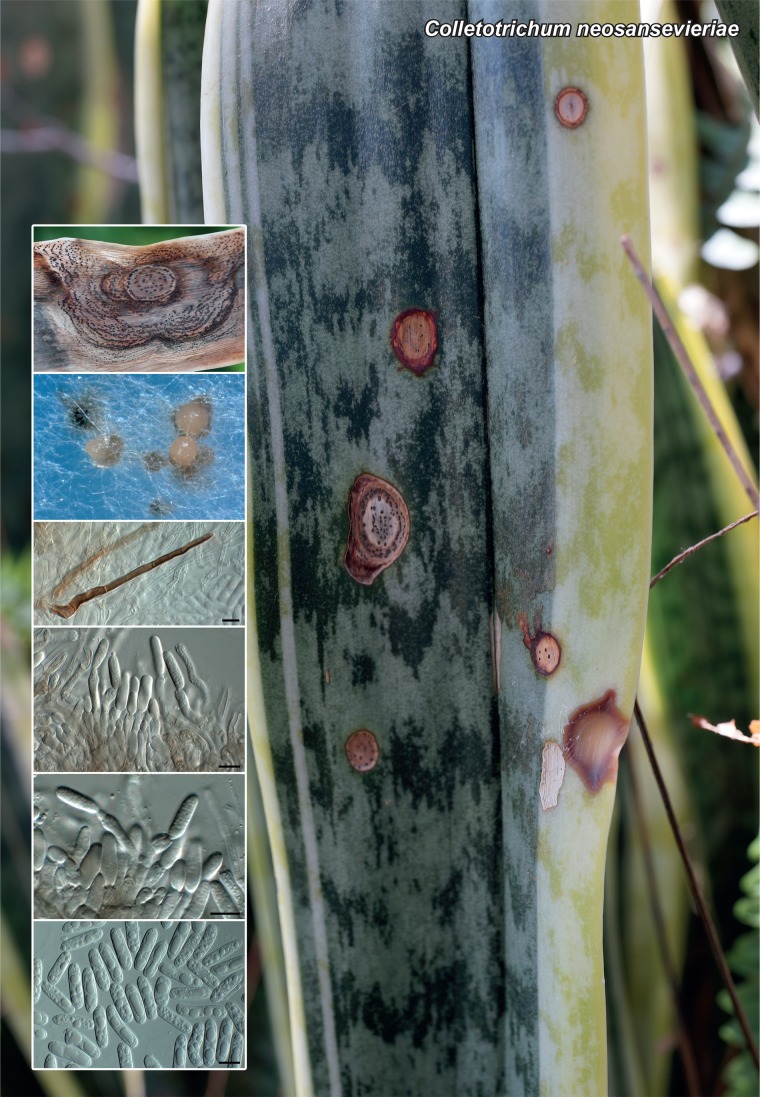
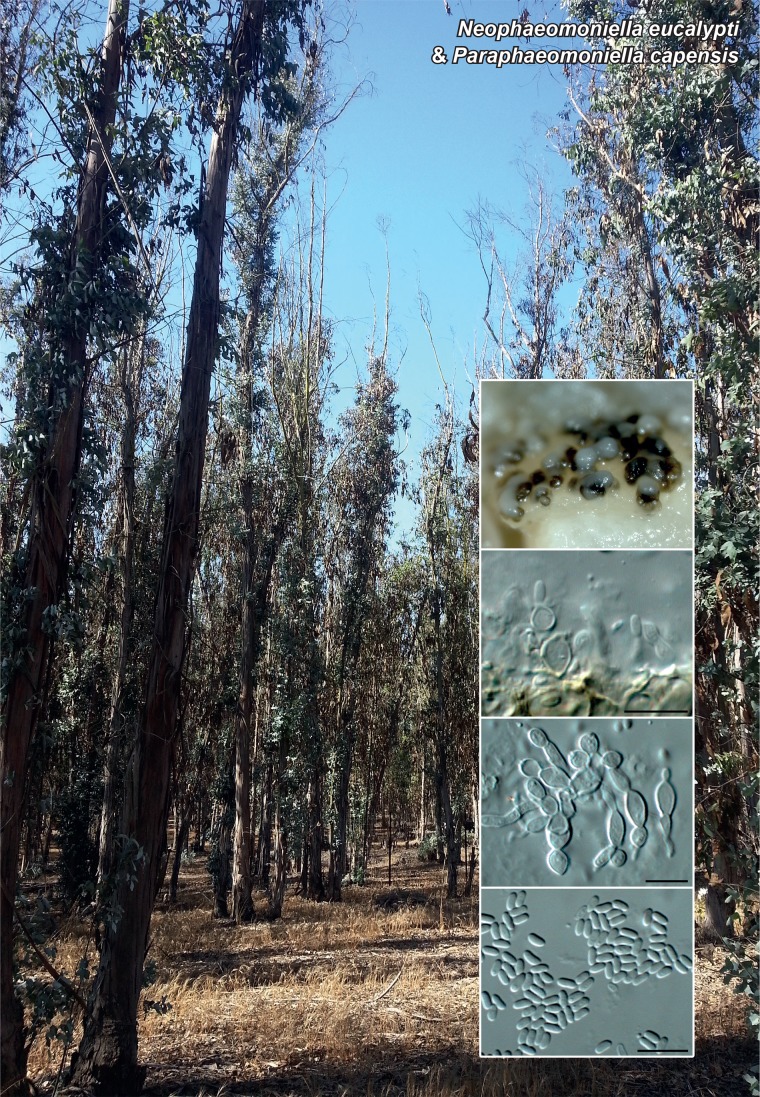
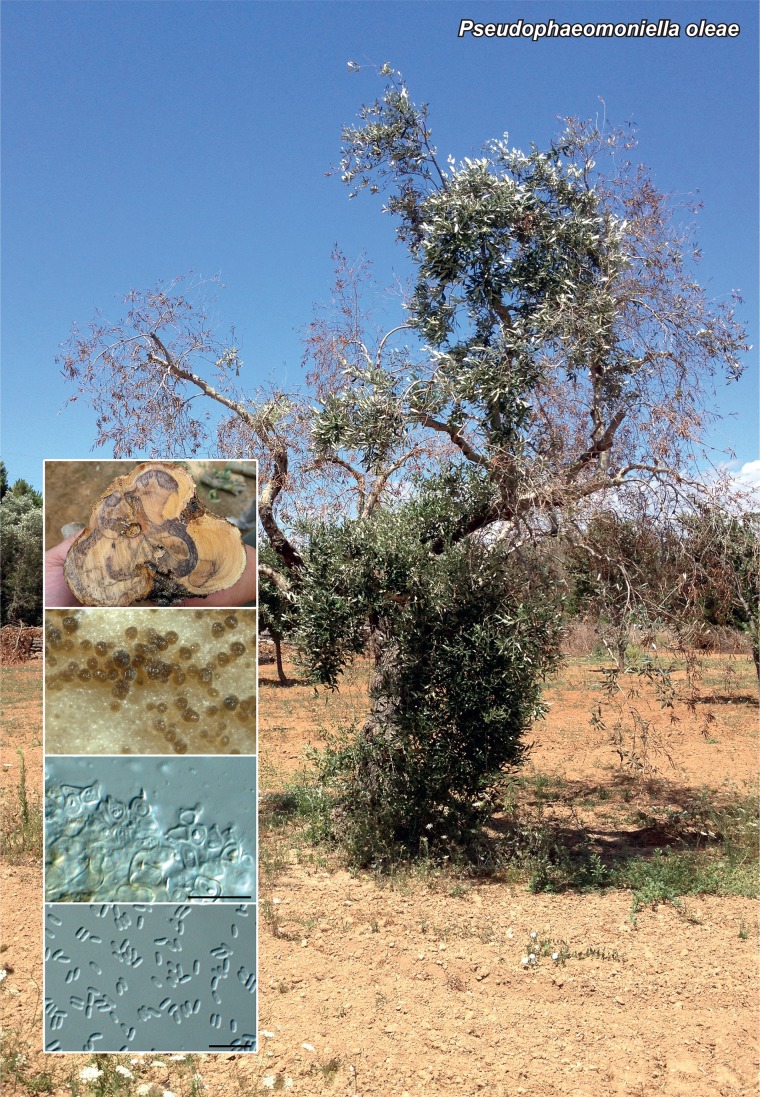
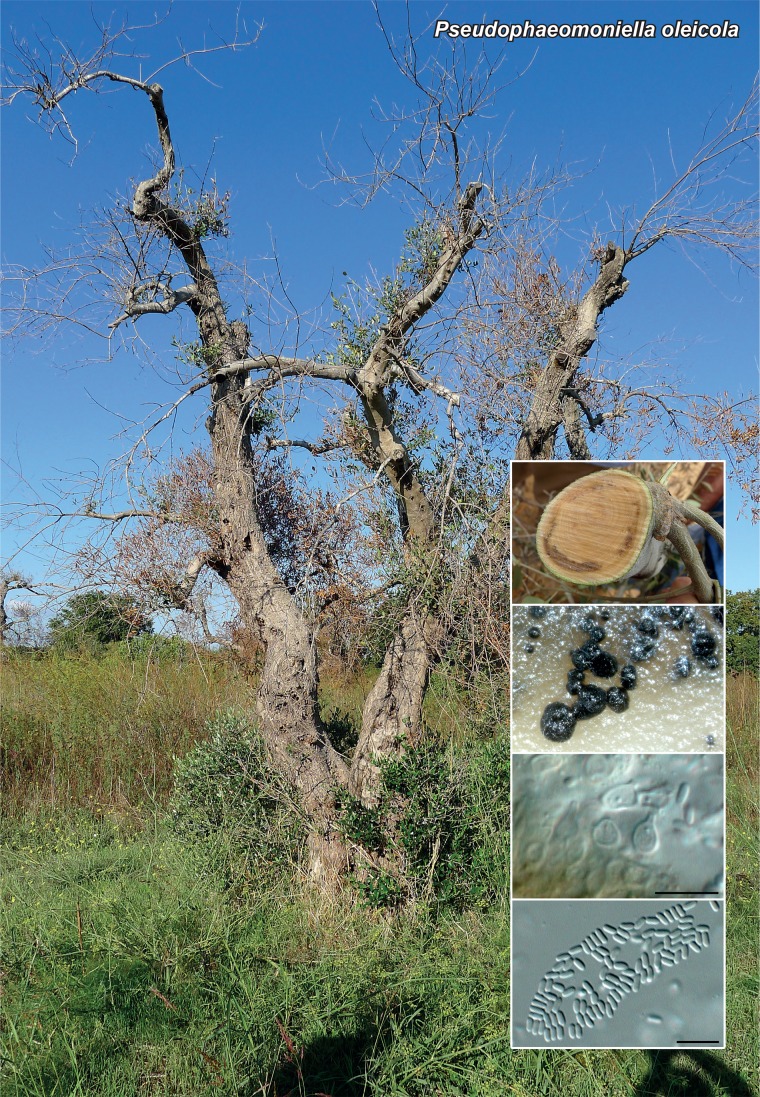
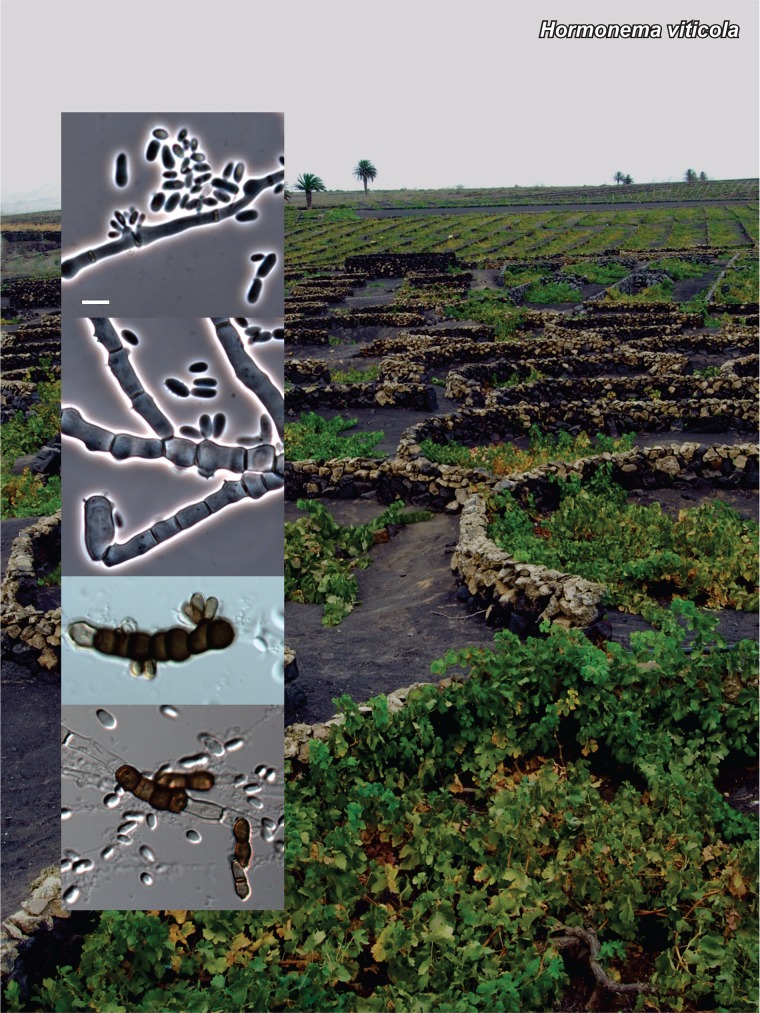
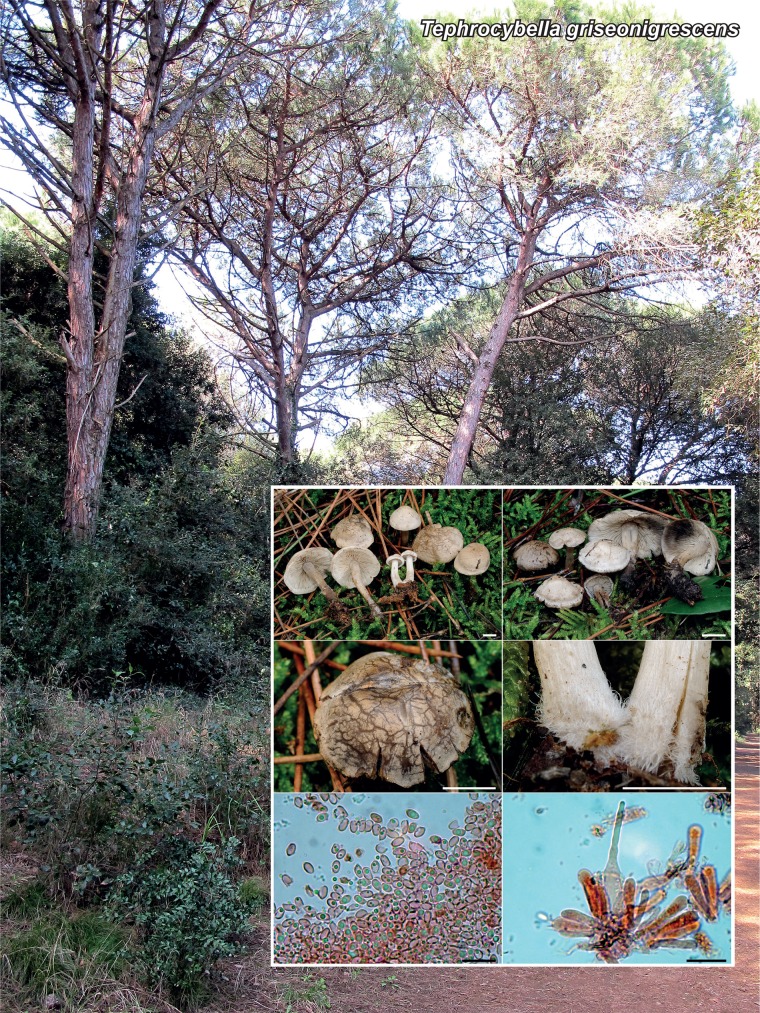
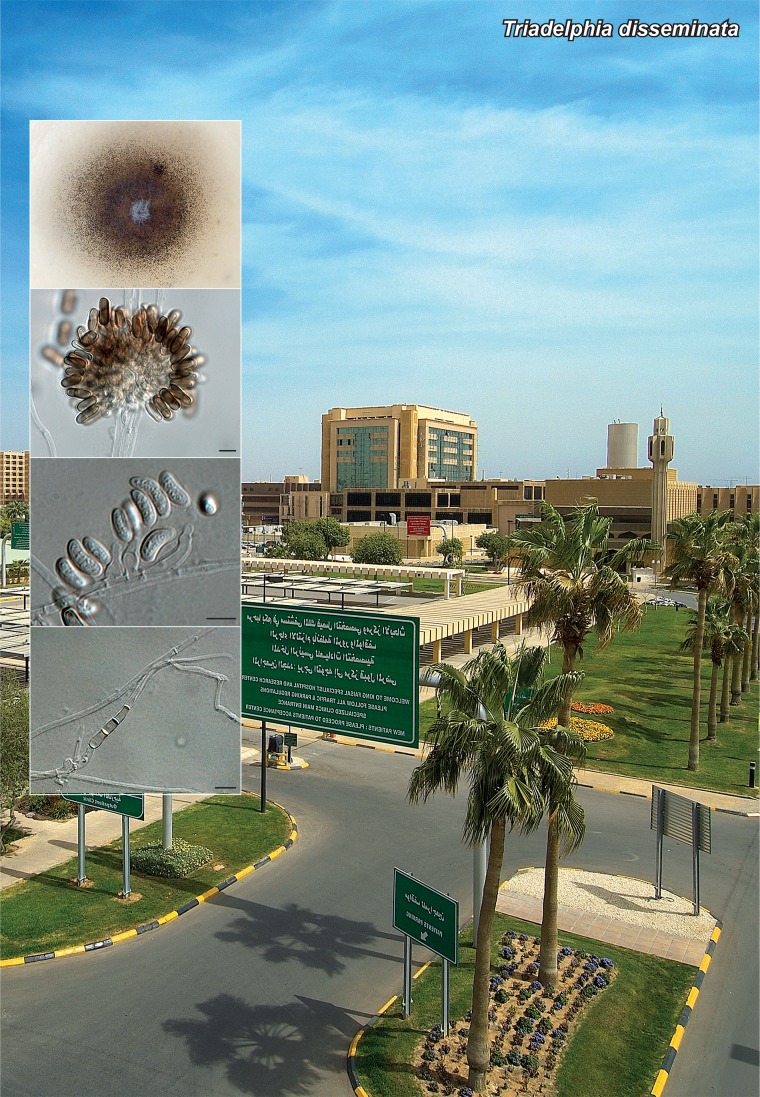
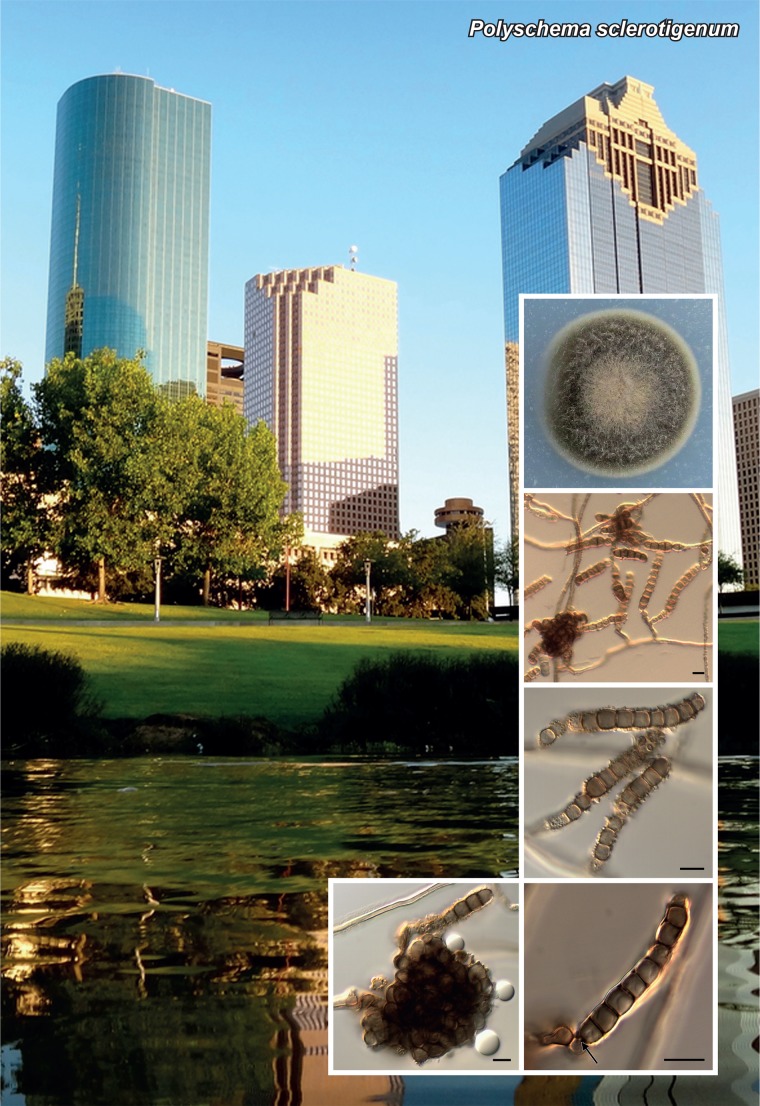
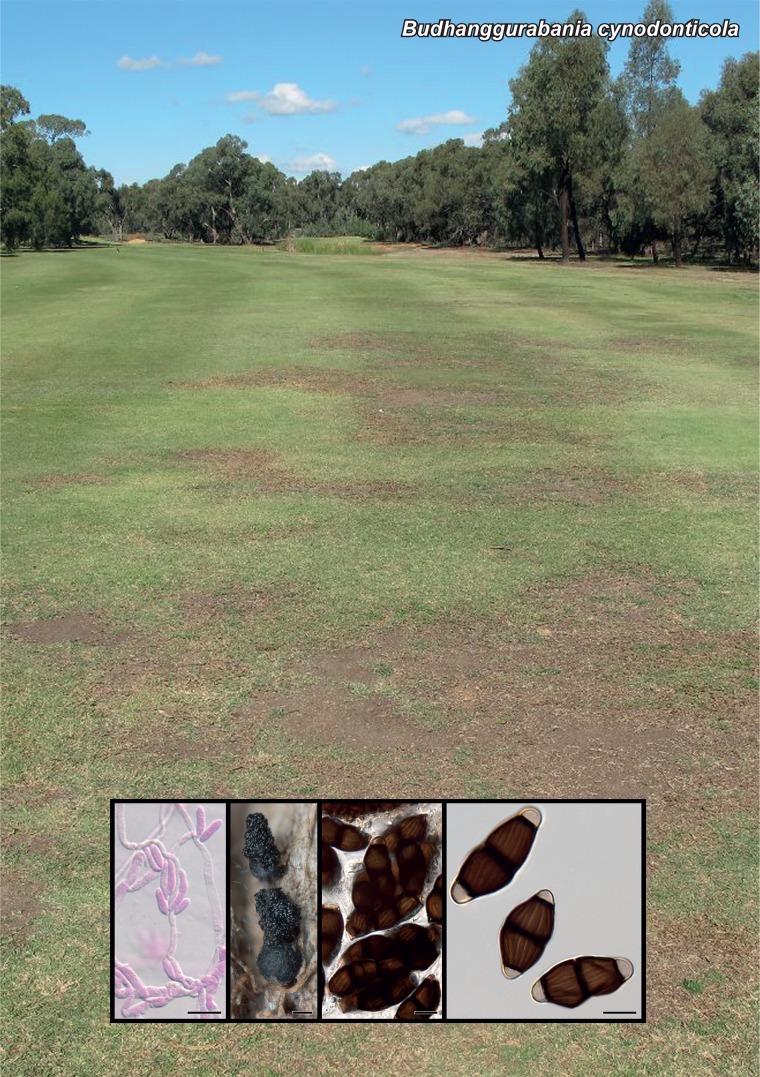
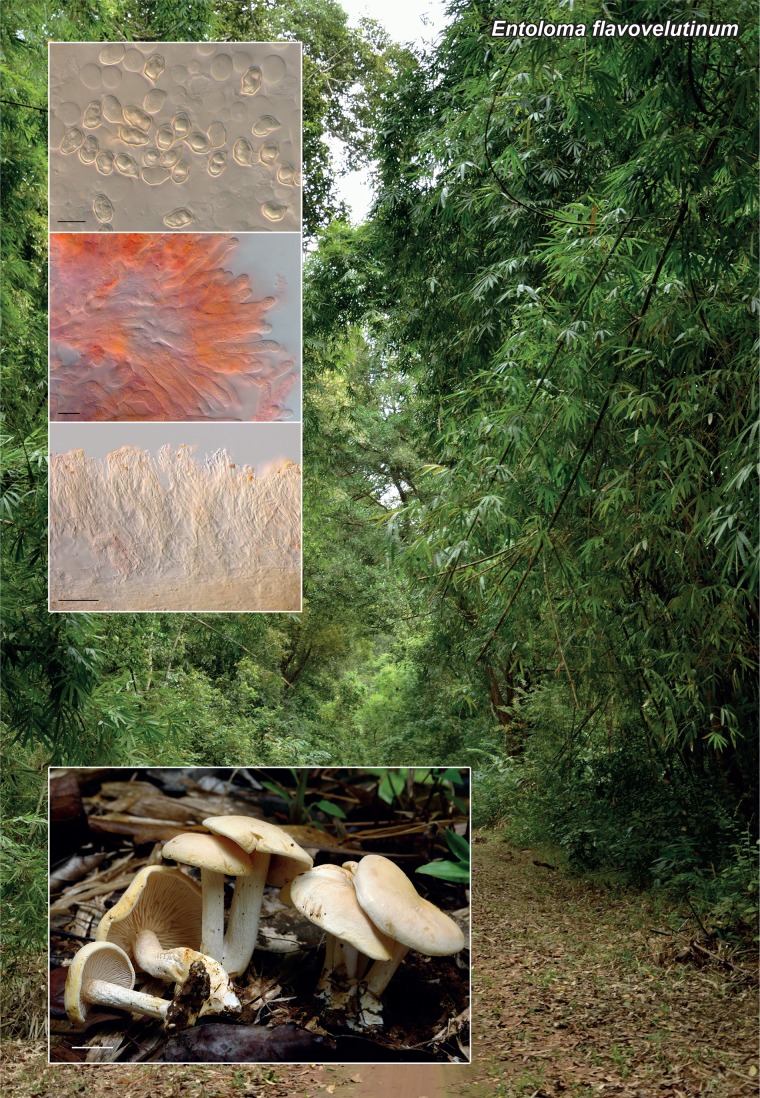
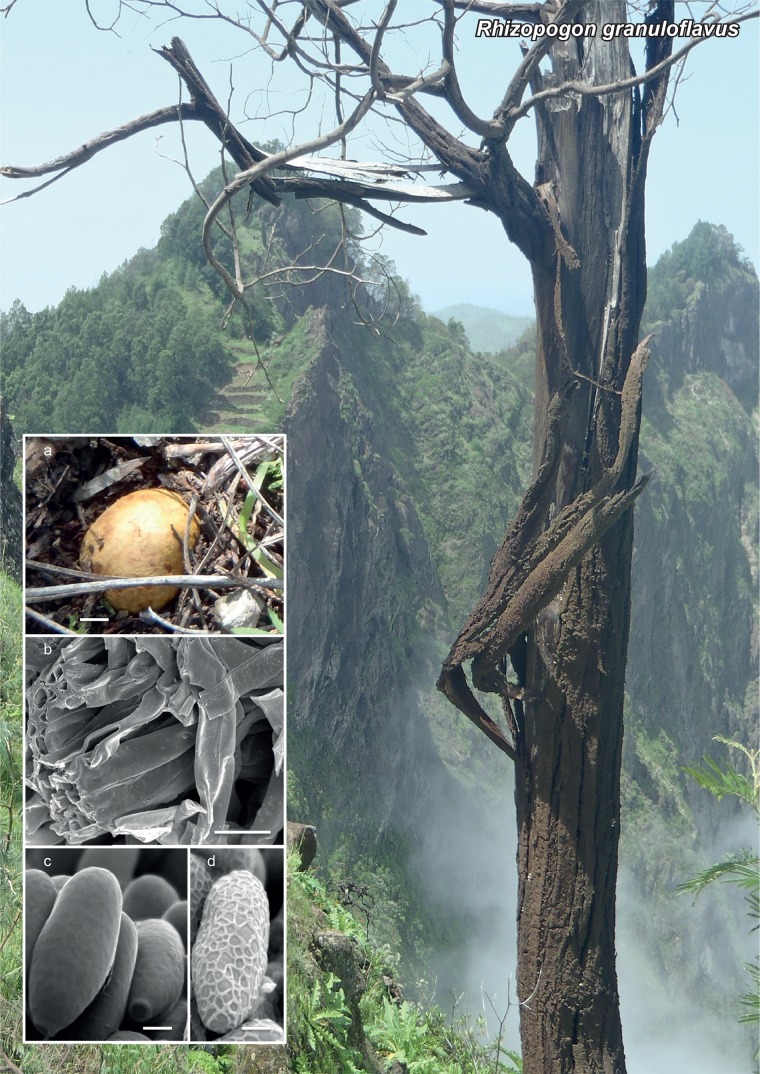
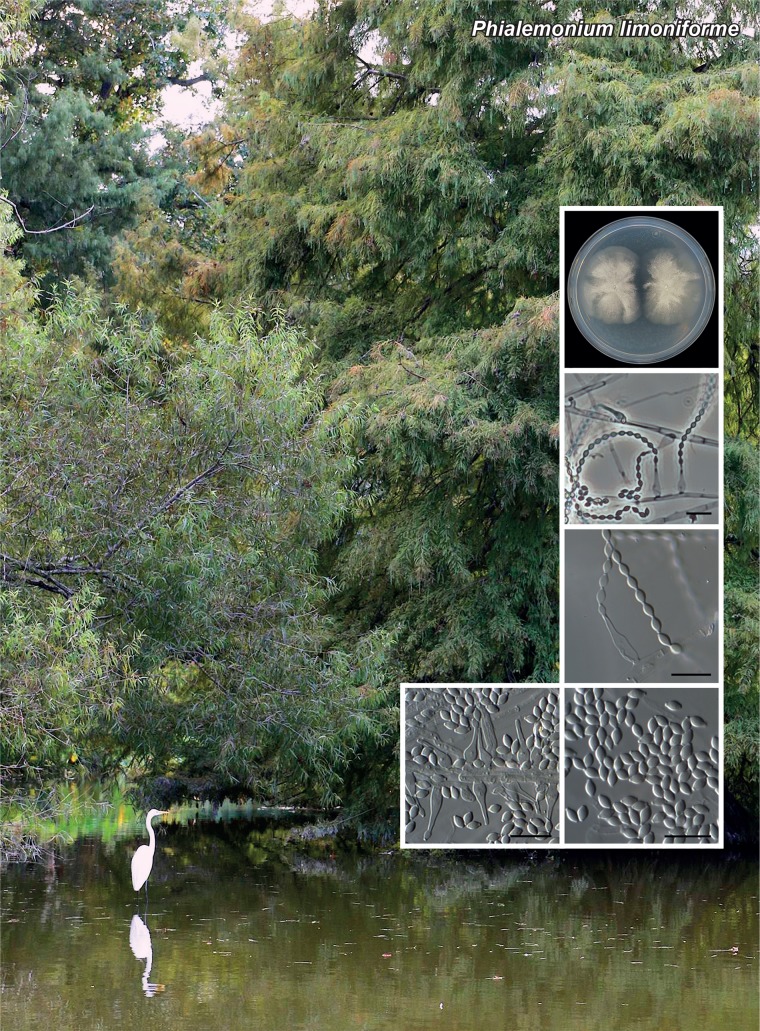
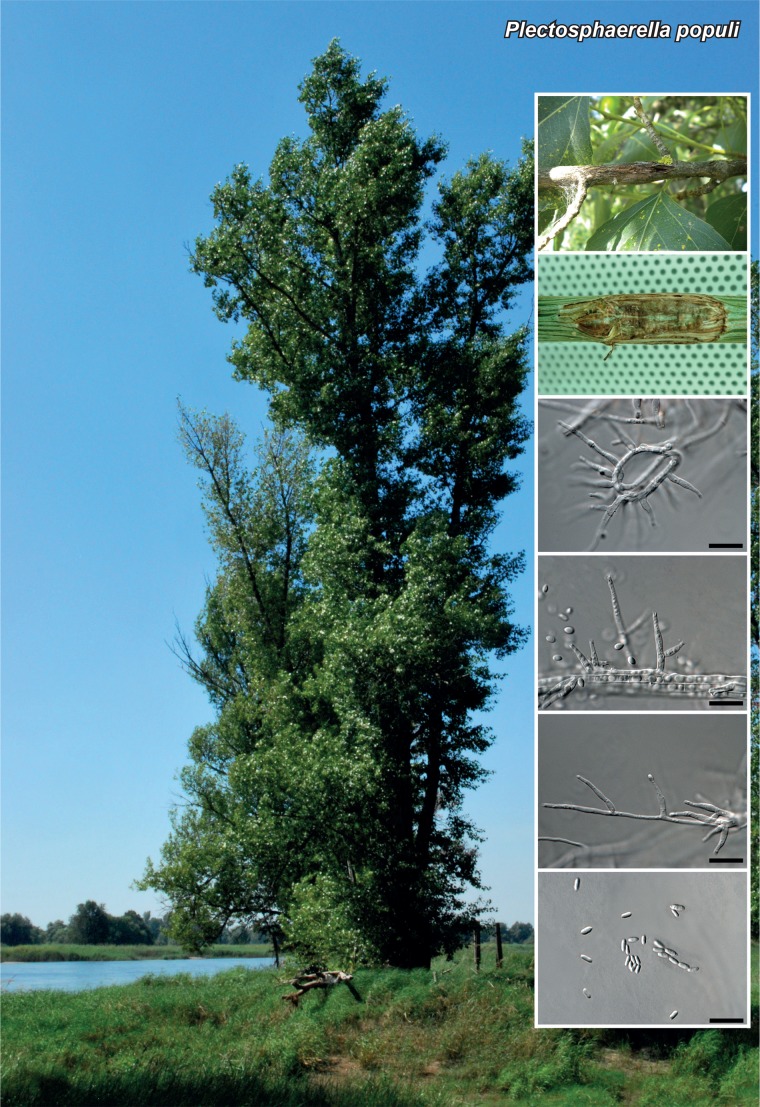
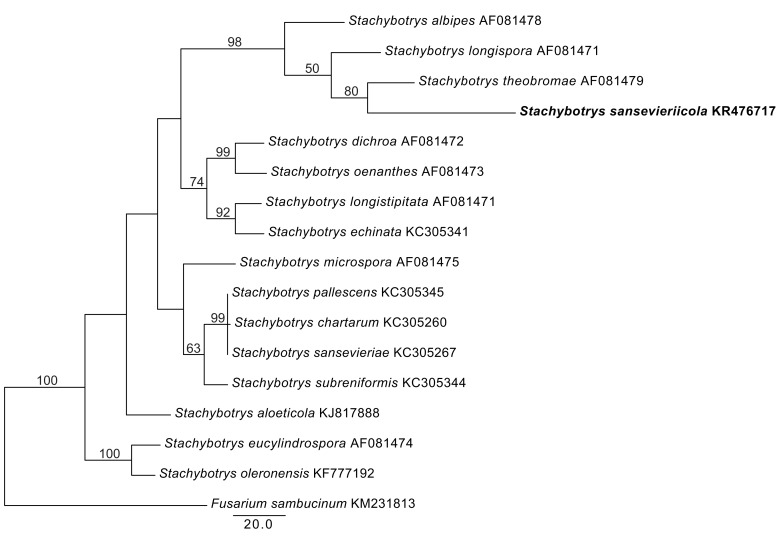
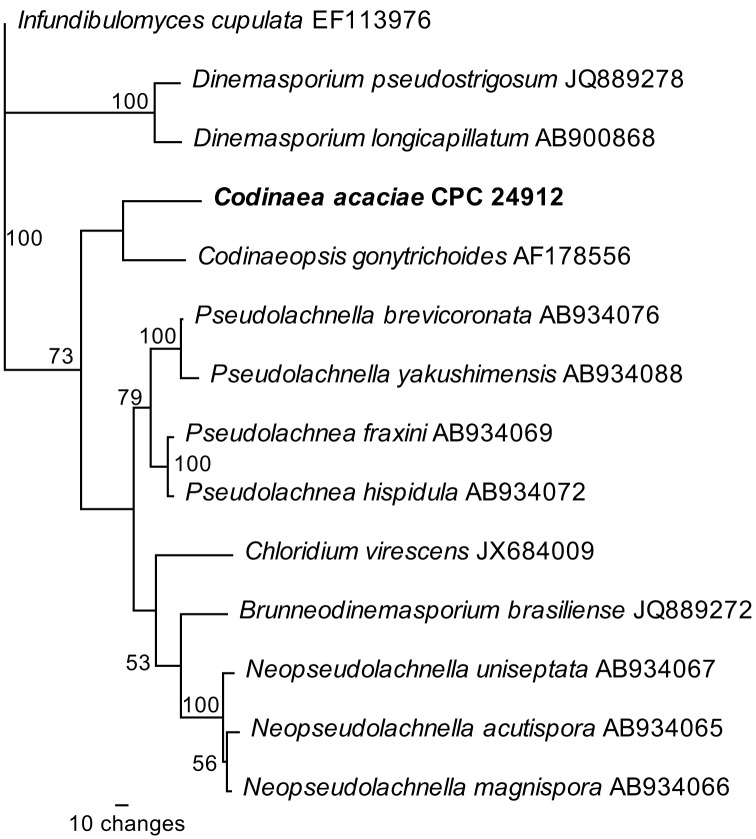
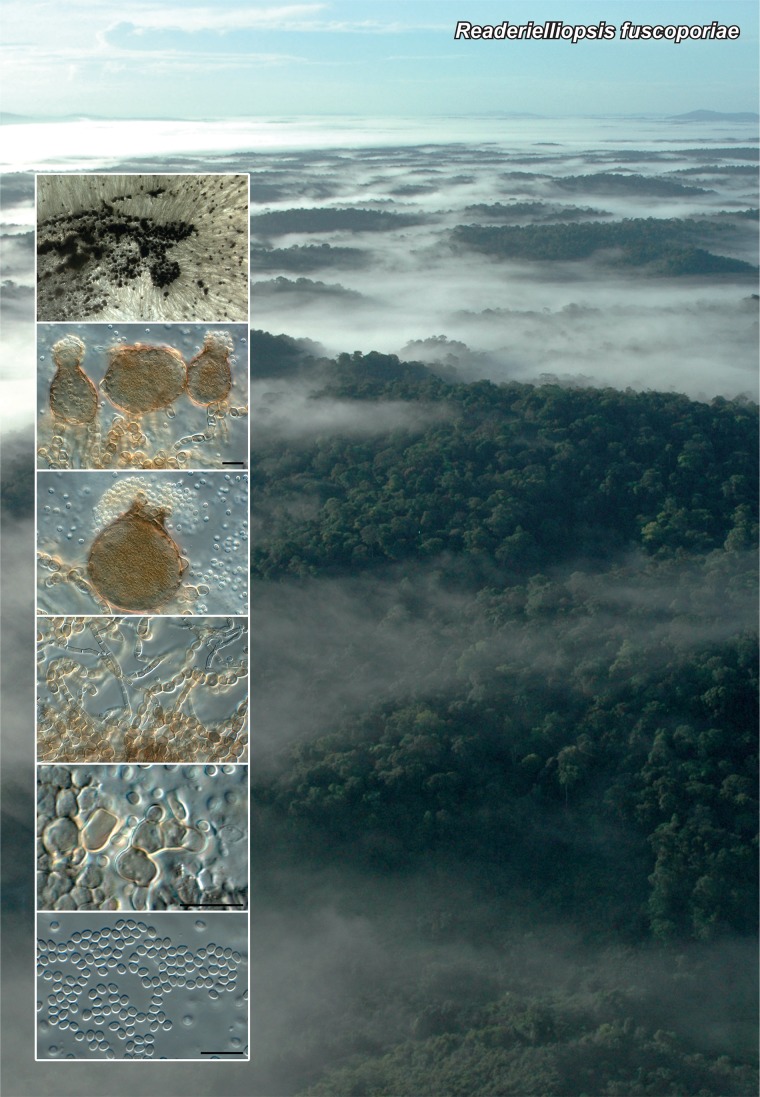
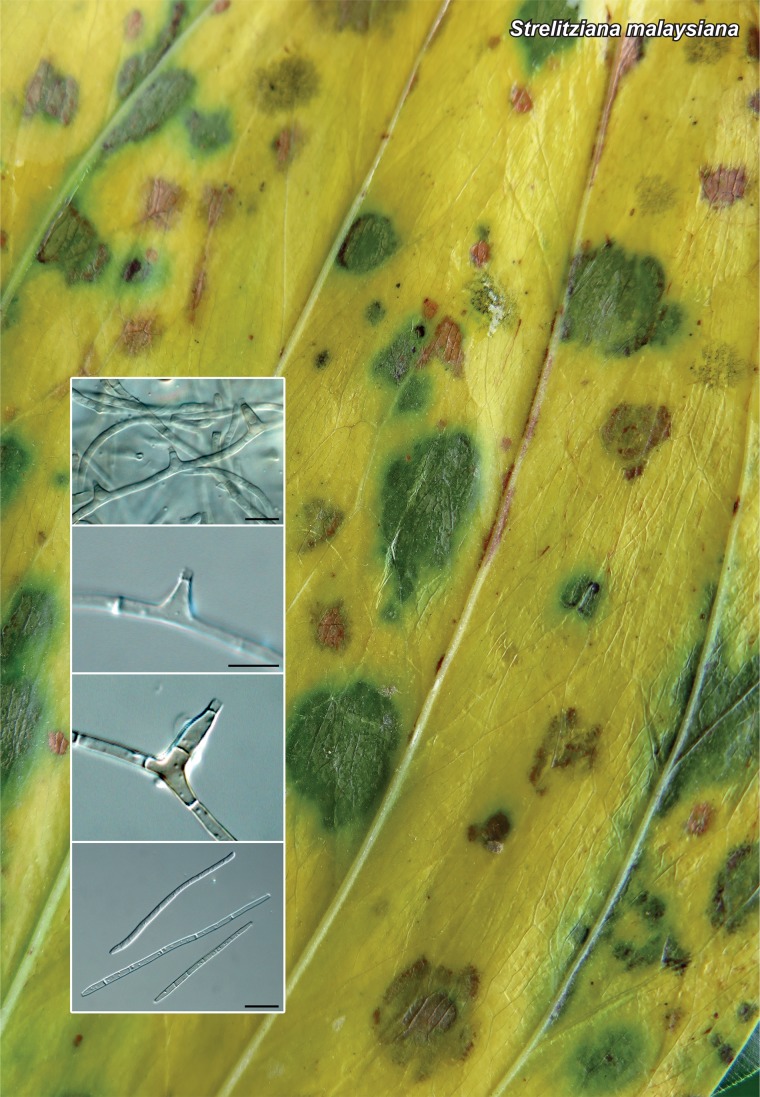
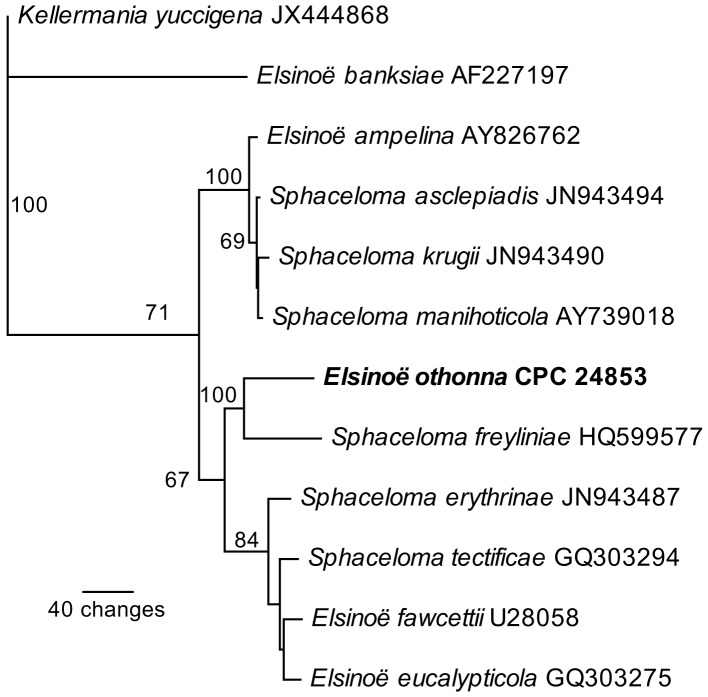
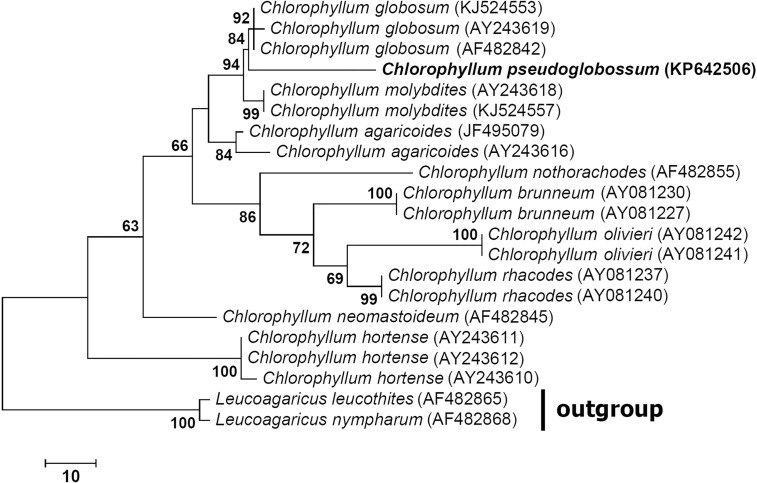
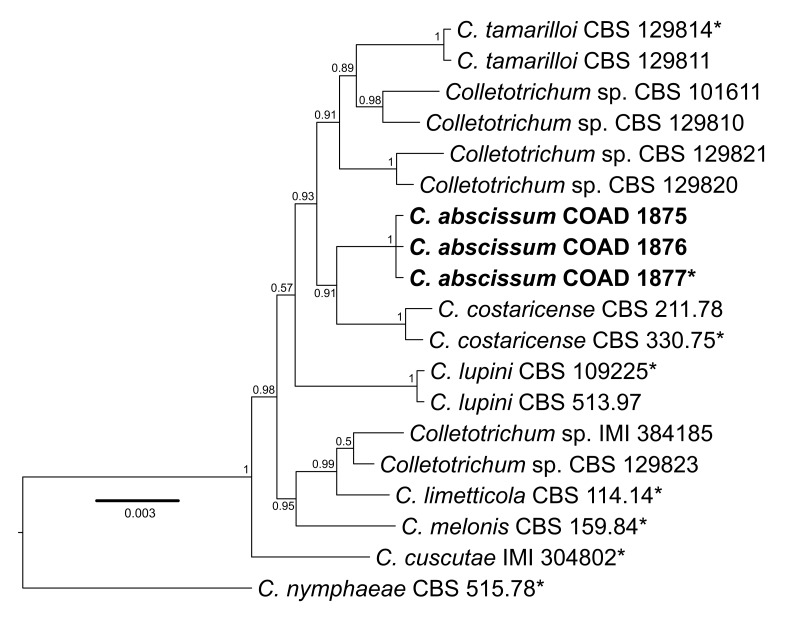
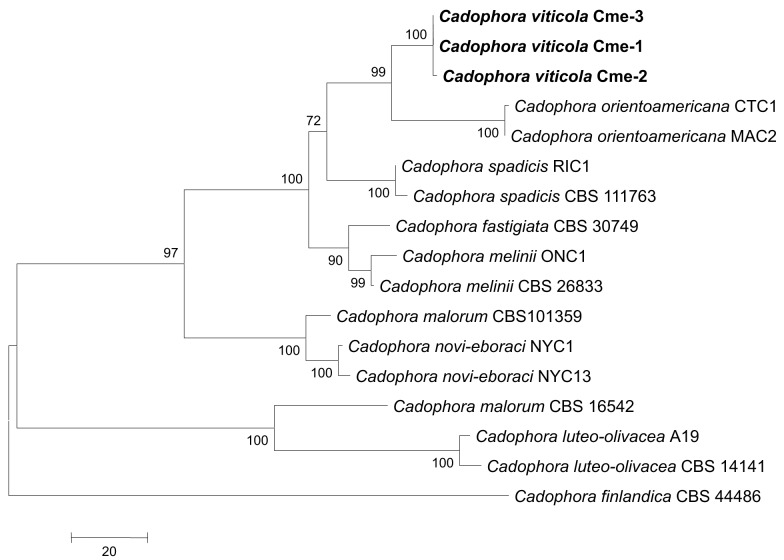
Novel species of fungi described in the present study include the following from Malaysia: Castanediella eucalypti from Eucalyptus pellita, Codinaea acacia from Acacia mangium, Emarcea eucalyptigena from Eucalyptus brassiana, Myrtapenidiella eucalyptorum from Eucalyptus pellita, Pilidiella eucalyptigena from Eucalyptus brassiana and Strelitziana malaysiana from Acacia mangium. Furthermore, Stachybotrys sansevieriicola is described from Sansevieria ehrenbergii (Tanzania), Phacidium grevilleae from Grevillea robusta (Uganda), Graphium jumulu from Adansonia gregorii and Ophiostoma eucalyptigena from Eucalyptus marginata (Australia), Pleurophoma ossicola from bone and Plectosphaerella populi from Populus nigra (Germany), Colletotrichum neosansevieriae from Sansevieria trifasciata, Elsinoë othonnae from Othonna quinquedentata and Zeloasperisporium cliviae (Zeloasperisporiaceae fam. nov.) from Clivia sp. (South Africa), Neodevriesia pakbiae, Phaeophleospora hymenocallidis and Phaeophleospora hymenocallidicola on leaves of a fern (Thailand), Melanconium elaeidicola from Elaeis guineensis (Indonesia), Hormonema viticola from Vitis vinifera (Canary Islands), Chlorophyllum pseudoglobossum from a grassland (India), Triadelphia disseminata from an immunocompromised patient (Saudi Arabia), Colletotrichum abscissum from Citrus (Brazil), Polyschema sclerotigenum and Phialemonium limoniforme from human patients (USA), Cadophora vitícola from Vitis vinifera (Spain), Entoloma flavovelutinum and Bolbitius aurantiorugosus from soil (Vietnam), Rhizopogon granuloflavus from soil (Cape Verde Islands), Tulasnella eremophila from Euphorbia officinarum subsp. echinus (Morocco), Verrucostoma martinicensis from Danaea elliptica (French West Indies), Metschnikowia colchici from Colchicum autumnale (Bulgaria), Thelebolus microcarpus from soil (Argentina) and Ceratocystis adelpha from Theobroma cacao (Ecuador). Myrmecridium iridis (Myrmecridiales ord. nov., Myrmecridiaceae fam. nov.) is also described from Iris sp. (The Netherlands). Novel genera include (Ascomycetes): Budhanggurabania from Cynodon dactylon (Australia), Soloacrosporiella, Xenocamarosporium, Neostrelitziana and Castanediella from Acacia mangium and Sabahriopsis from Eucalyptus brassiana (Malaysia), Readerielliopsis from basidiomata of Fuscoporia wahlbergii (French Guyana), Neoplatysporoides from Aloe ferox (Tanzania), Wojnowiciella, Chrysofolia and Neoeriomycopsis from Eucalyptus (Colombia), Neophaeomoniella from Eucalyptus globulus (USA), Pseudophaeomoniella from Olea europaea (Italy), Paraphaeomoniella from Encephalartos altensteinii, Aequabiliella, Celerioriella and Minutiella from Prunus (South Africa). Tephrocybella (Basidiomycetes) represents a novel genus from wood (Italy). Morphological and culture characteristics along with ITS DNA barcodes are provided for all taxa.
Keywords: ITS DNA barcodes, LSU, novel fungal species, systematics
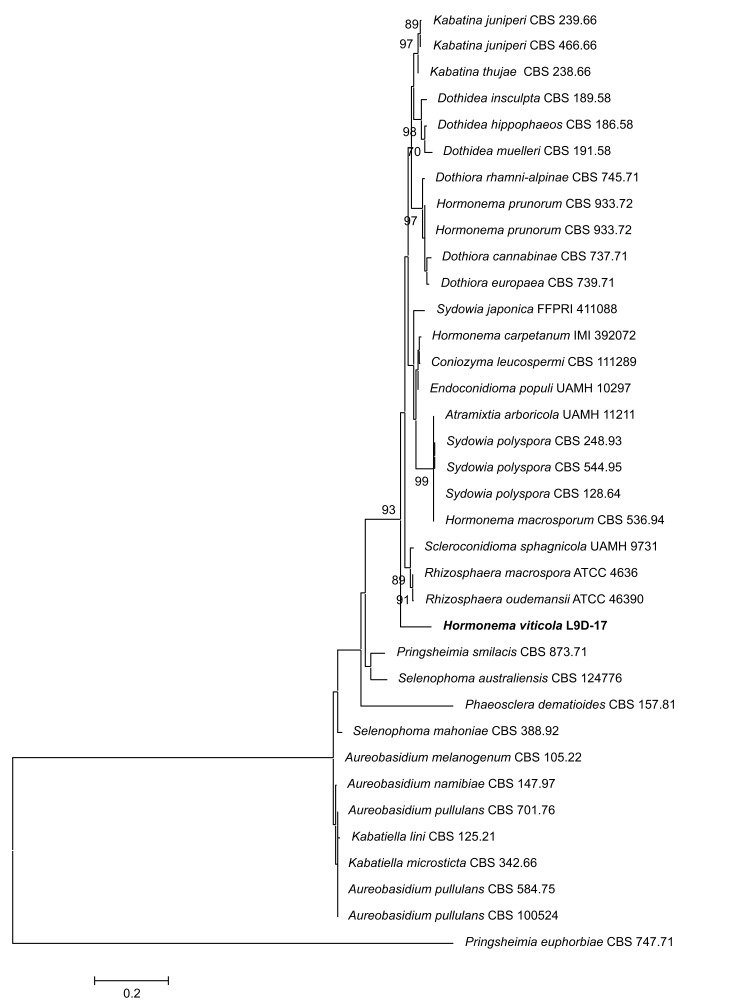
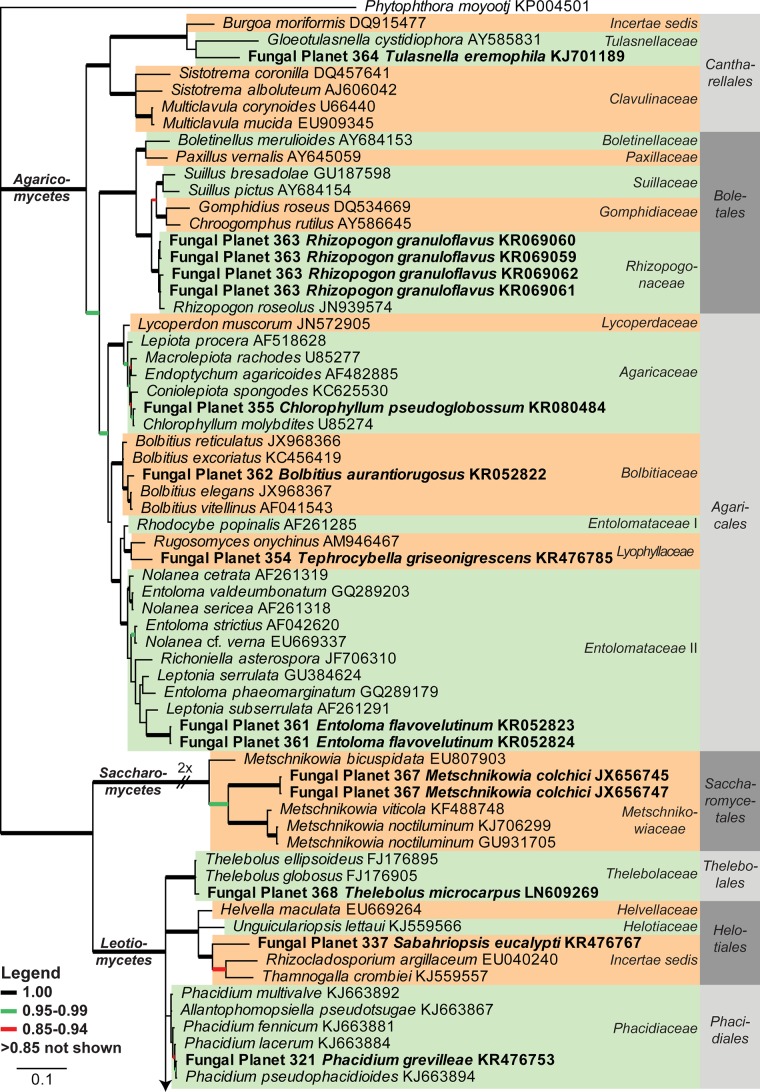
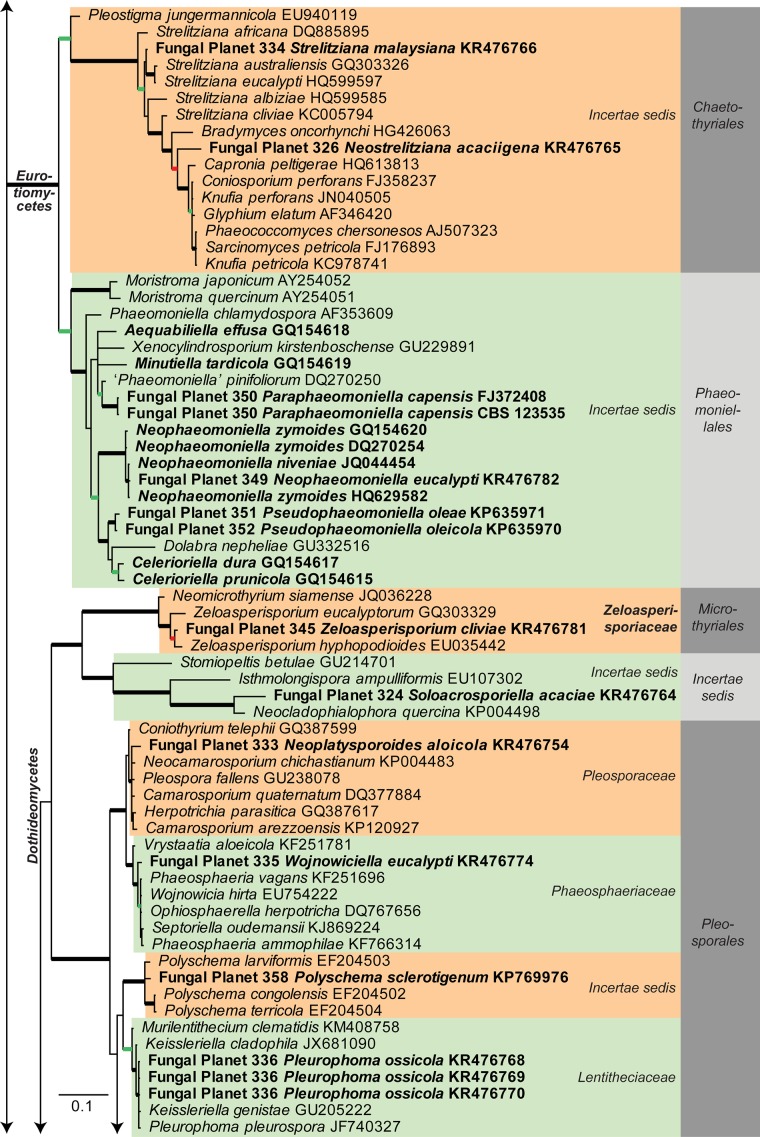
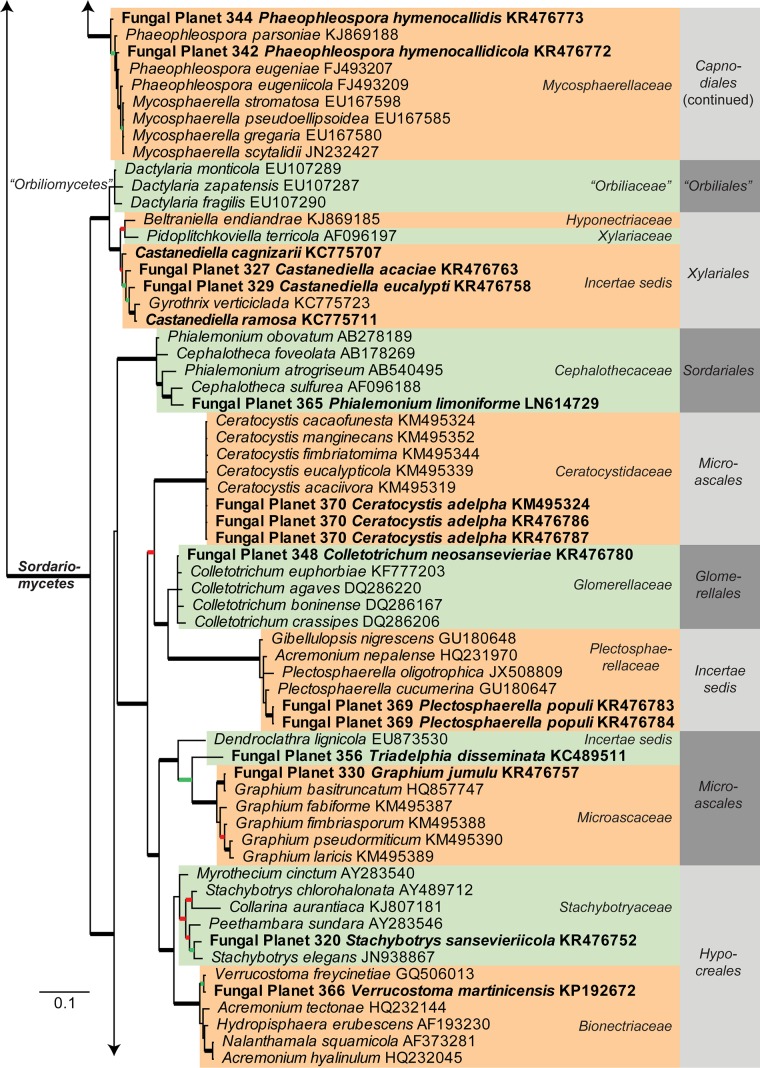
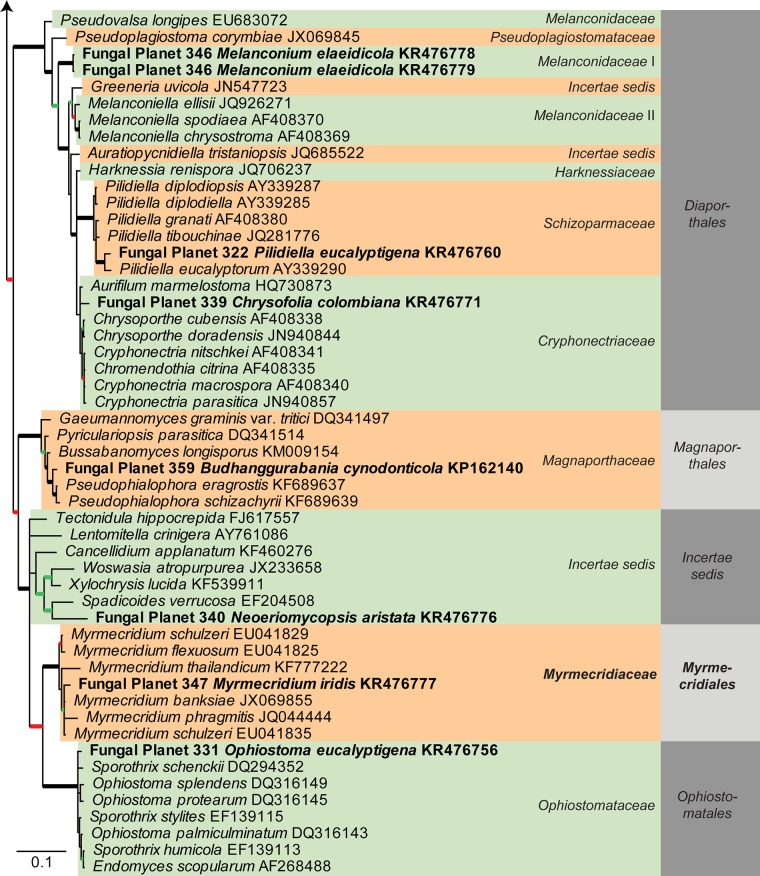
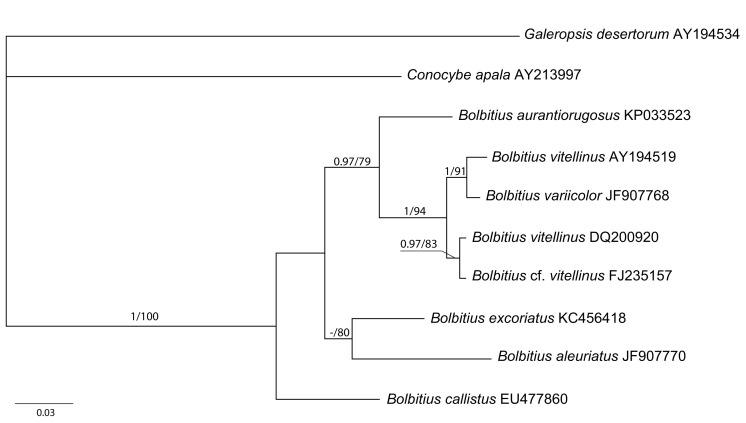
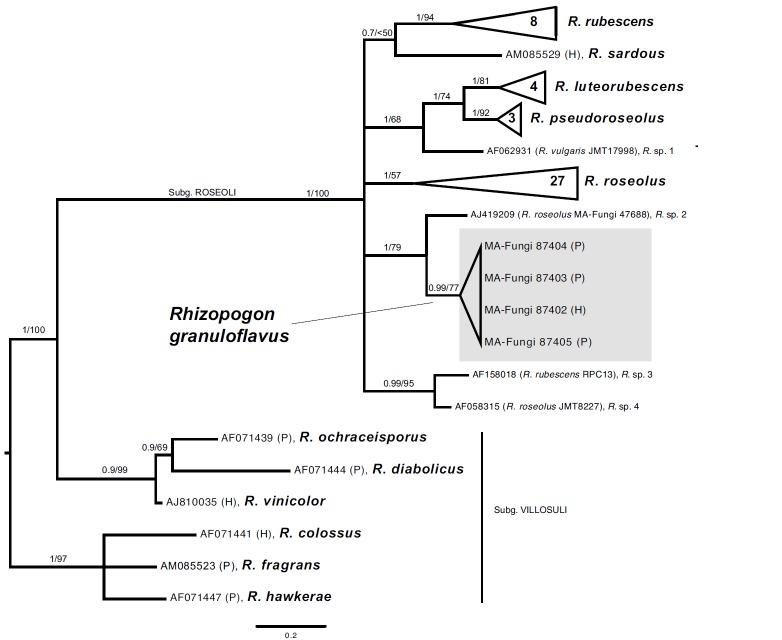
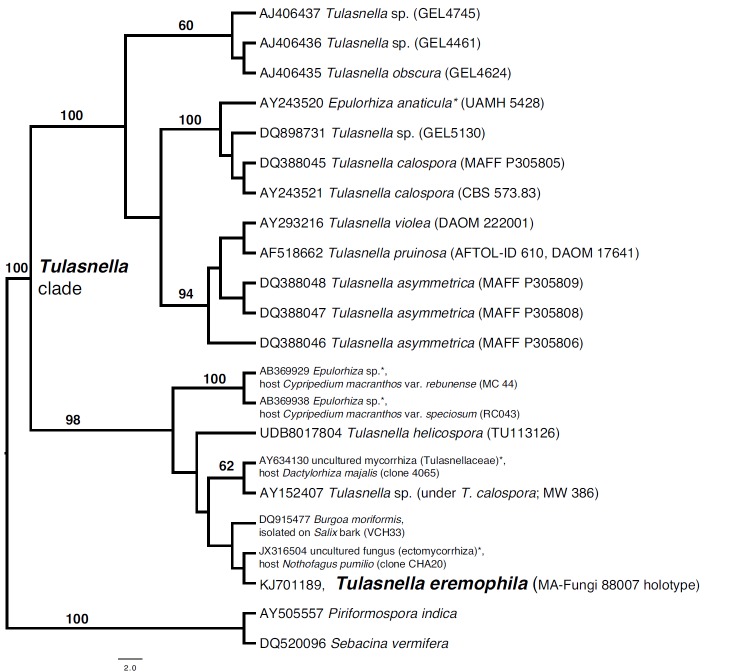
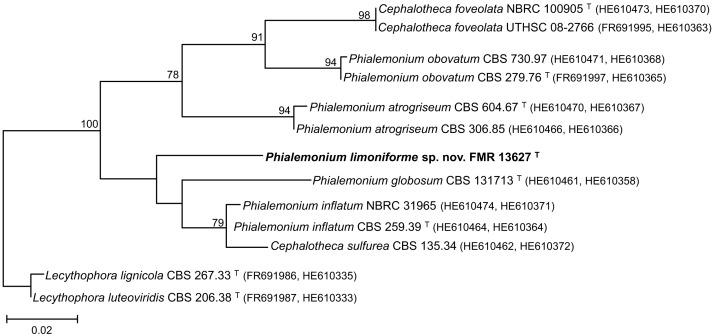
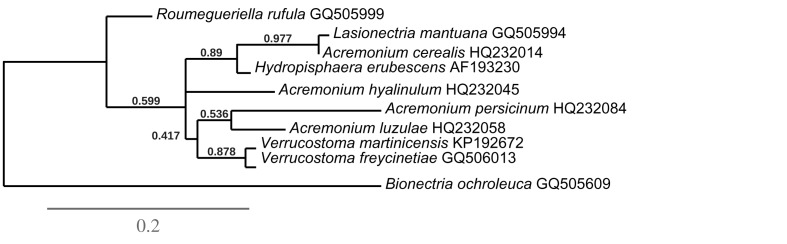
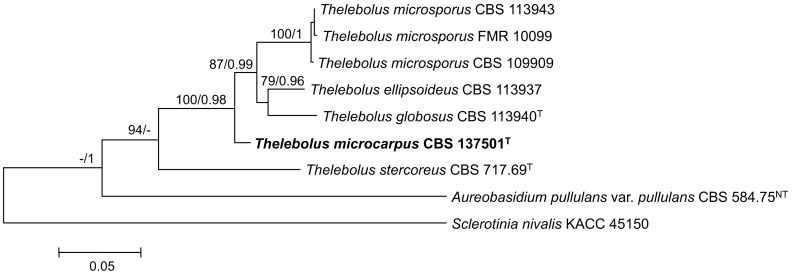
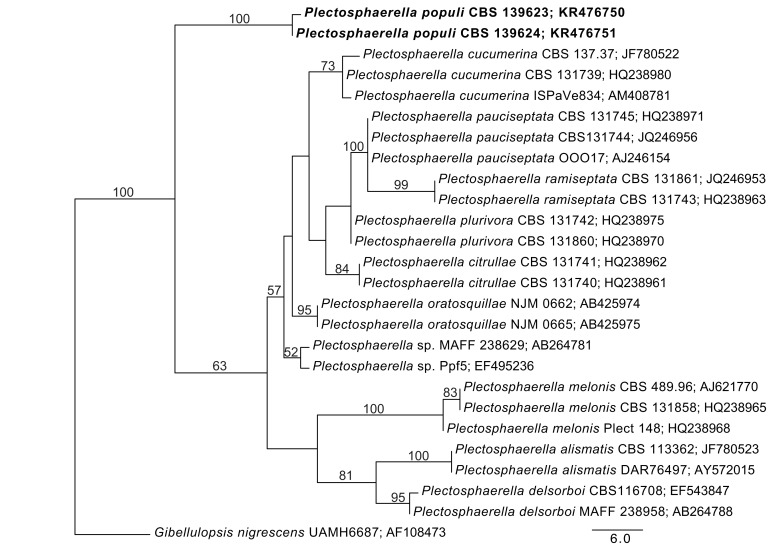
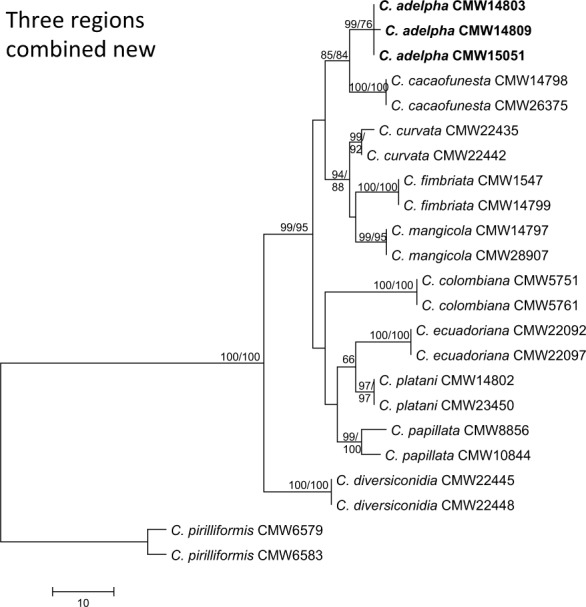
Consensus phylogram [part 1] (50 % majority rule) of 11 020 trees resulting from a Bayesian analysis of the LSU sequence alignment using MrBayes v. 3.2.1 (Ronquist et al. 2012). Bayesian posterior probabilities (PP) > 0.84 are indicated as colour-coded thickened lines and the scale bar represents the expected changes per site. Families and orders are indicated to the right of the tree and classes at the nodes to the left of the tree. Taxonomic novelties for which LSU sequences were available are shown in bold face. The alignment and tree were deposited in TreeBASE (Submission ID 17580). The tree was rooted to Phytophthora moyootj (GenBank KP004501).
Acknowledgments
Christian Lechat gratefully acknowledges Cesar Delnatte (DEAL, Martinique) fro the identification of the horst of Verrucostoma martinicensis. Alfredo Vizzini thanks Edmondo Grilli (Pescara, Italy), for comments on the text of Tephrocybella griseonigrescens. Dilnora Gouliamova was supported by a grant (D002-TK-176) from the Bulgarian Science Fund, EU F6 Synthesis program. She is grateful to K. Metodiev for permission to use the picture of Colchicum autumnale (http://www.bgflora.net/). Olga V. Morozova, Eugene S. Popov and Xiao-Lan He are grateful to V. Trunov, T.H. Li, C.Y. Deng, H. Huang and Y.W. Xia for valuable Entoloma collections. Alina V. Alexandrova was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project N 14-50-00029). Ekaterina F. Malysheva, Olga V. Morozova, Alexander E. Kovalenko and Eugene S. Popov acknowledge financial support from the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project 13-04-00838a and 15-04-04645a). Margarita Dueñas, María P. Martín and M. Teresa Telleria acknowledge financial support from the Plan Nacional I+D+I projects No. CGL2009-07231 and CGL2012-3559. They are also thankful to Marian Gleen (Seton Hall University, USA) for commenting on the text. Cony Decock gratefully acknowledges the financial support received from the FNRS / FRFC (convention FRFC 2.4544.10), the CNRS-French Guiana and the Nouragues staff, which enabled fieldwork in French Guiana, and the Belgian State – Belgian Federal Science Policy through the BCCM™ research programme. We also thank the CBS technical staff, A. van Iperen (cultures), M. Vermaas (photographic plates) and M. Starink-Willemse (DNA isolation, amplification and sequencing) for their invaluable assistance.
References
- Agustí-Brisach C, Gramaje D, García-Jiménez J, et al. 2013. Detection of black-foot and Petri disease pathogens in natural soils of grapevine nurseries and vineyards using bait plants. Plant and Soil 364: 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hedaithy SSA. 2001. First report of human infection due to the fungus Triadelphia pulvinata. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 39: 3386–3389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hedaithy SSA, Leathers CR. 1987. Country-wide search in Saudi Arabia for the etiologic agent of histoplasmosis. Proceedings of the Saudi Biological Society 10: 197–207. [Google Scholar]
- Arzanlou M, Crous PW. 2006. Strelitziana africana. Fungal Planet No. 8. CBS-KNAW Fungal Biodiversity Centre, Utrecht, The Netherlands. [Google Scholar]
- Arzanlou M, Groenewald JZ, Gams W, et al. 2007. Phylogenetic and morphotaxonomic revision of Ramichloridium and allied genera. Studies in Mycology 58: 57–93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assyov B, Petrova A, Dimitrov D, et al. (eds). 2006. Conspectus of the Bulgarian vascular flora, 3 ed Bulgarian Biodiversity Fund, Sofia. [Google Scholar]
- Beeli M. 1923. Champignons récoltés par le lt. Ghesquière dans le Bas-Congo et le Kasai. Revue Zoologique Africaine 12: B10–B17. [Google Scholar]
- Bellanger J-M, Moreau P-A, Corriol G, et al. 2015. Plunging hands into the mushroom jar: a phylogenetic framework for Lyophyllaceae (Agaricales, Basidiomycota). Genetica 143: 169–194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidartondo MI, Bruns TD, Weiss M, et al. 2003. Specialized cheating of the ectomycorrhizal symbiosis by an epiparasitic liverwort. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences 270: 835–842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bills GF, Collado J, Ruibal C, et al. 2004. Hormonema carpetanum sp. nov., a new lineage of dothideaceous black yeasts from Spain. Studies in Mycology 50: 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- Binder M, Hibbet DS, Larsson KH, et al. 2005. The phylogenetic distribution of resupinate forms across the major clades of mushrooms-forming fungi (Homobasidiomycetes). Systematics and Biodiversity 3: 113–157. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette RA, Held WB, Jurgens JA, et al. 2004. Wood-destroying soft rot fungi in the historic expedition huts of Antarctica. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 70: 1328–1335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boari A de Jesus. 2008. Estudos realizados sobre o amarelecimento fatal do dendezeiro (Elais Guineensis Jacq) no Brasil. Documentos 348, Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento Belém, PA, Embrapa Amazônia. [Google Scholar]
- Cannon PF, Damm U, Johnston PR, et al. 2012. Colletotrichum – current status and future directions. Studies in Mycology 73: 181–213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlucci A, Raimondo ML, Santos J, et al. 2012. Plectosphaerella species associated with root and collar rots of horticultural crops in southern Italy. Persoonia 28: 34–48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castañeda Ruiz RF, Decock C, Saikawa M, et al. 2000. Polyschema obclaviformis sp. nov., and some new records of hyphomycetes from Cuba. Cryptogamie Mycologia 21: 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Castañeda Ruiz RF, Fabré DE, Parra MP, et al. 1996. Some airborne conidial fungi from Cuba. Mycotaxon 60: 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Castañeda Ruiz RF, Gams W, Saikawa M. 1997. Three new conidial fungi (hyphomycetes) from Cuba. Nova Hedwigia 64: 473–483. [Google Scholar]
- Cejp K, Deighton FC. 1969. New genera and species and redispositions of some hyphomycetes, mainly African. Mycological Papers 117: 8–31. [Google Scholar]
- Cheewangkoon R, Crous PW, Hyde KD, et al. 2008. Species of Mycosphaerella and related anamorphs on Eucalyptus leaves from Thailand. Persoonia 21: 77–91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheewangkoon R, Groenewald JZ, Summerell BA, et al. 2009. Myrtaceae, a cache of fungal biodiversity. Persoonia 23: 55–85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen KH, Miadlikowska J, Molnár K, et al. 2015. Phylogenetic analyses of eurotiomycetous endophytes reveal their close affinities to Chaetothyriales, Eurotiales, and a new order – Phaeomoniellales. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 85: 117–130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen SF, Wingfield MJ, Roets F, et al. 2013. A serious canker disease caused by Immersiporthe knoxdaviesiana gen. et sp. nov. (Cryphonectriaceae) on native Rapanea melanophloeos in South Africa. Plant Pathology 62: 667–678. [Google Scholar]
- Clémençon H, Winteroff W. 1992. Lyophyllum maas-geesterani, eine neuer schwärzende Rasling. Persoonia 14: 533–536. [Google Scholar]
- Consiglio G, Contu M. 2002. Il genere Lyophyllum P. Karst. emend. Kühner, in Italia. Rivista di Micologia 45: 99–181. [Google Scholar]
- Constantinescu O, Samson RA. 1982. Triadelphia, a pleomorphic genus of hyphomycetes. Mycotaxon 15: 472–486. [Google Scholar]
- Crane C, Burgess TI. 2013. Luteocirrhus shearii gen. sp. nov. (Diaporthales, Cryphonectriaceae) pathogenic to Proteaceae in the South Western Australian Floristic Region. IMA Fungus 4: 111–122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch JA. 2014. Colletotrichum caudatum s.l. is a species complex. IMA Fungus 5: 17–30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Braun U, Groenewald JZ. 2007a. Mycosphaerella is polyphyletic. Studies in Mycology 58: 1–32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Braun U, Hunter GC, et al. 2013. a. Phylogenetic lineages in Pseudocercospora. Studies in Mycology 75: 37–114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Ferreira FA, Sutton BC. 1997. A comparison of the fungal genera Phaeophleospora and Kirramyces (coelomycetes). South African Journal of Botany: 63: 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Gams W. 2000. Phaeomoniella chlamydospora gen. et comb. nov., a causal organism of Petri grapevine decline and esca. Phytopathologia Mediterranea 39: 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Groenewald JZ. 2011. Why everlastings don’t last. Persoonia 26: 70–84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Shin HD. 2010. a. Strelitziana albiziae. Fungal Planet No. 56. CBS-KNAW Fungal Biodiversity Centre, Utrecht, The Netherlands. [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Shivas RG. 2010b. Strelitziana eucalypti. Fungal Planet No. 62. CBS-KNAW Fungal Biodiversity Centre, Utrecht, The Netherlands. [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Wingfield MJ. 2006. Anthostomella eucalyptorum. Fungal Planet No. 1. CBS-KNAW Fungal Biodiversity Centre, Utrecht, The Netherlands. [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Phillips AJL, Baxter AP. 2000. Phytopathogenic fungi from South Africa. University of Stellenbosch Printers, Department of Plant Pathology Press, South Africa. [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Quaedvlieg W, Hansen K, et al. 2014a. Phacidium and Ceuthospora (Phacidiaceae) are congeneric: taxonomic and nomenclatural implications. IMA Fungus 5: 173–193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Schoch CL, Hyde KD, et al. 2009a. Phylogenetic lineages in the Capnodiales. Studies in Mycology 64: 17–47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Schubert K, Braun U, et al. 2007b. Opportunistic, human-pathogenic species in the Herpotrichiellaceae are phenotypically similar to saprobic or phytopathogenic species in the Venturiaceae. Studies in Mycology 55: 214–216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Shivas RG, Quaedvlieg W, et al. 2014b. Fungal Planet description sheets: 214–280. Persoonia 32: 184–306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Shivas RG, Wingfield MJ, et al. 2012a. Fungal Planet description sheets: 128–153. Persoonia 29: 146–201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Summerell BA, Alfenas AC, et al. 2012b. Genera of diaporthalean coelomycetes associated with leaf spots of tree hosts. Persoonia 28: 66–75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Summerell BA, Carnegie AJ, et al. 2009b. Unravelling Mycosphaerella: do you believe in genera? Persoonia 23: 99–118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Summerell BA, Shivas RG, et al. 2011. Fungal Planet description sheets: 92–106. Persoonia 27: 130–162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Summerell BA, Shivas RG, et al. 2012c. Fungal Planet description sheets: 107–127. Persoonia 28: 138–182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Wingfield MJ. 1996. Species of Mycosphaerella and their anamorphs associated with leaf blotch disease of Eucalyptus in South Africa. Mycologia 88: 441–458. [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Wingfield MJ, Guarro J, et al. 2013b. Fungal Planet description sheets: 154–213. Persoonia 31: 188–296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Wingfield MJ, Schumacher RK, et al. 2014c. Fungal Planet description sheets: 281–319. Persoonia 33: 212–289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Wood AR, Okada G, et al. 2008. Foliicolous microfungi occurring on Encephalartos. Persoonia 21: 135–146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruywagen EM, Beer ZW De, Roux J, et al. 2010. Three new Graphium species from baobab trees in South Africa and Madagascar. Persoonia 25: 61–71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm U, Cannon PF, Woudenberg JHC, et al. 2012a. The Colletotrichum acutatum species complex. Studies in Mycology 73: 37–113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm U, Cannon PF, Woudenberg JHC, et al. 2012b. The Colletotrichum boninense species complex. Studies in Mycology 73: 1–36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm U, Fourie PH, Crous PW. 2010. Coniochaeta (Lecythophora), Collophora gen. nov. and Phaeomoniella species associated with wood necroses of Prunus trees. Persoonia 24: 60–80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm U, O’Connell RJ, Groenewald JZ, et al. 2014. The Colletotrichum destructivum species complex – hemibiotrophic pathogens of forage and field crops. Studies in Mycology 79: 49–84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beer ZW De, Duong TA, Barnes I, et al. 2014. Redefining Ceratocystis and allied genera. Studies in Mycology 79: 187–219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beer ZW De, Wingfield MJ. 2013. Emerging lineages in the Ophiostomatales. In: The Ophiostomatoid fungi: expanding frontiers. CBS Biodiversity Series 12. CBS-KNAW Fungal Biodiversity Centre, Utrecht, The Netherlands. [Google Scholar]
- Gruyter J De, Aveskamp MM, Woudenberg JHC, et al. 2009. Molecular phylogeny of Phoma and allied anamorph genera: Towards a reclassification of the Phoma complex. Mycological Research 113: 508–519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruyter J De, Woudenberg JHC, Aveskamp MM, et al. 2010. Systematic reappraisal of species in Phoma section Paraphoma, Pyrenochaeta and Pleurophoma. Mycologia 102: 1066–1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruyter J De, Woudenberg JHC, Aveskamp MM, et al. 2013. Redisposition of Phoma-like anamorphs in Pleosporales. Studies in Mycology 75: 1–36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoog GS De, Göttlich E, Platas G, et al. 2005. Evolution, taxonomy and ecology of the genus Thelebolus in Antarctica. Studies in Mycology 51: 33–76. [Google Scholar]
- Hoog GS De, Hermanides-Nijhof EJ. 1977. Aureobasidium and allied genera. Studies in Mycology 15: 166–173. [Google Scholar]
- Hoog GS De, Zalar P, Urzi C, et al. 1999. Relationships of dothideaceous black yeasts and meristematic fungi based on 5.8S and ITS2 rDNA sequence comparison. Studies in Mycology 43: 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Decock C. 2005. Anamorphic fungi from French Guyana species. Readeriella guyanensis sp. nov., a new coelomycetous species. Cryptogamie Mycologie 26: 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Deighton FC, Pirozynski KA. 1972. Microfungi. V. More hyperparasitic hyphomycetes. Mycological Papers 128: 1–110. [Google Scholar]
- Di Marco S, Calzarano F, Osti F, et al. 2004. Pathogenicity of fungi associated with a decay of kiwifruit. Australasian Plant Pathology 33: 337–342. [Google Scholar]
- Duong LM, Lumyong S, Hyde KD, et al. 2004. Emarcea castanopsidicola gen. et sp. nov. from Thailand, a new xylariaceous taxon based on morphology and DNA sequences. Studies in Mycology 50: 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Edathodu J, Al-Abdely HM, AlThawadi S, et al. 2013. Invasive fungal infection due to Triadelphia pulvinata in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 51: 3426–3429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis MB. 1976. More dematiaceous hyphomycetes. CABI Publishing, Kew, Surrey. [Google Scholar]
- Engelbrecht CJB, Harrington TC. 2005. Intersterility, morphology and taxonomy of Ceratocystis fimbriata on sweet potato, cacao and sycamore. Mycologia 97: 57–69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelbrecht CJB, Harrington TC, Alfenas AC, et al. 2007. Genetic variation in populations of the cacao wilt pathogen, Ceratocystis cacaofunesta. Plant Patholology 56: 923–933. [Google Scholar]
- Fourie A, Wingfield BD, Wingfield MJ, et al. 2014. Molecular markers delimit cryptic species in the Ceratocystis fimbriata sensu lato complex. Mycological Progress 14: 1020. [Google Scholar]
- Gams W, McGinnis M. 1983. Phialemonium, a new anamorph genus intermediate between Phialophora and Acremonium. Mycologia 75: 977–987. [Google Scholar]
- Ge ZW, Yang ZL. 2006. The genus Chlorophyllum (Basidiomycetes) in China. Mycotaxon 96: 181–191. [Google Scholar]
- Gramaje D, Mostert L, Armengol J. 2011. Characterization of Cadophora luteo-olivacea and C. melinii isolates obtained from grapevines and environmental samples from grapevine nurseries in Spain. Phytopathologia Mediterranea 50: S112–S126. [Google Scholar]
- Guarro J. 2012. Taxonomía y biología de los hongos causantes de infección en humanos. Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología Clínica 30: 33–39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halleen F, Crous PW, Petrini O. 2003. Fungi associated with healthy grapevine cuttings in nurseries, with special reference to pathogens involved in the decline of young vines. Australasian Plant Pathology 32: 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Halleen F, Mostert L, Crous PW. 2007. Pathogenicity testing of lesser-known vascular fungi of grapevines. Australasian Plant Pathology 36: 277–285. [Google Scholar]
- Hambleton S, Tsuneda A, Currah RS. 2003. Comparative morphology and phylogenetic placement of two microsclerotial black fungi from Sphagnum. Mycologia 95: 959–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansford CG. 1943. Contributions towards the fungus flora of Uganda – V. Fungi Imperfecti. Proceedings of the Linnean Society of London 1: 34–67. [Google Scholar]
- He XL, Li TH, Jiang ZD, et al. 2012. Four new species of Entoloma s.l. (Agaricales) from southern China. Mycological Progress 11: 915–925. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera CM, Pozo MI. 2010. Nectar yeasts warm the flowers of a winter-blooming plant. Proceedings of the Royal Society 277: 1827–1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbet DS, Thorn RG. 2001. Basidiomycota: Homobasidiomycetes. In: McLaughlin DJ, McLaughlin EG, Lemke PA. (eds), The mycota. VIIB. Systematics and Evolution: 121–128. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. [Google Scholar]
- Hirooka Y, Rossman AY, Samuels GJ, et al. 2012. A monograph of Allantonectria, Nectria, and Pleonectria (Nectriaceae, Hypocreales, Ascomycota) and their pycnidial, sporodochial, and synnematous anamorphs. Studies in Mycology 71: 1–210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak E. 1980. Entoloma (Agaricales) in Indomalaya and Australasia. Beihefte Nova Hedwigia 65; Cramer, Germany. [Google Scholar]
- Huang F, Chen GQ, Hou X, et al. 2013. Colletotrichum species associated with cultivated citrus in China. Fungal Diversity 61: 61–74. [Google Scholar]
- Hui FL, Chen L, Li ZH, et al. 2013. Metschnikowia henanensis sp. nov., a new anamorphic yeast species isolated from rotten wood in China. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 103: 899–904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hujslová M, Kubátová A, Chudíčková M, et al. 2010. Diversity of fungal communities in saline and acidic soils in the Soos National Natural Reserve, Czech Republic. Mycological Progress 9: 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Jie C-Y, Zhou Q-X, Zhao W-S, et al. 2013. A new Myrmecridium species from Guizhou, China. Mycotaxon 124: 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kalamees K. 2004. Palearctic Lyophyllaceae (Tricholomataceae) in Northern and Eastern Europe and Asia. Scripta Mycologica 18: 3–134. [Google Scholar]
- Kerry E. 1990. Microorganisms colonizing plants and soil subjected to different degrees of human activity, including petroleum contamination, in the Vestfold Hills and MacRobertson Land, Antarctica. Polar Biology 10: 423–430. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk PM. 1982. New or interesting microfungi V. Microfungi colonizing Laurus nobilis leaf litter. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 78: 293–303. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk PM. 1983. New or interesting microfungi IX. Dematiaceous hyphomycetes from Esher Common. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 80: 449–467. [Google Scholar]
- Klaubauf S, Tharreau D, Fournier E, et al. 2014. Resolving the polyphyletic nature of Pyricularia (Pyriculariaceae). Studies in Mycology 79: 85–120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornerup A, Wanscher JH. 1978. Methuen handbook of colour, 3rd ed London, Eyre Methuen. [Google Scholar]
- Kottke I, Beiter A, Weiβ M, et al. 2003. Heterobasidiomycetes form symbiotic associations with hepatics: Jungermanniales have sebacinioid mycobionts while Aneura piguis (Metzgeriales) is associated with Tulasnella species. Mycological Research 107: 957–968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuthubutheen AJ, Nawawi A. 1991. A key to Dictyochaeta and Codinaea species. Mycological Research 95: 1224–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Lachance MA, Starmer WT, Rosa CA, et al. 2001. Biogeography of the yeasts of ephemeral flowers and their insects. FEMS Yeast Research 1: 1–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrey JD, Binder M, Diederich P, et al. 2007. Phylogenetic diversity of lichen-associated homobasidiomycetes. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 44: 778–789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee HB, Park JY, Jung HS, et al. 2006. Phaeomoniella zymoides and Phaeomoniella pinifoliorum spp. nov., new acid-tolerant epiphytic fungi isolated from pine needles in Korea. Mycologia 98: 598–611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lima WG, Sposito MB, Amorim L, et al. 2011. Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, a new causal agent of citrus post-bloom fruit drop. European Journal of Plant Pathology 131: 157–165. [Google Scholar]
- Liu F, Cai L, Crous PW, et al. 2014. The Colletotrichum gigasporum species complex. Persoonia 33: 83–97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo J, Walsh E, Zhang N. 2014. Four new species in Magnaporthaceae from grass roots in New Jersey pine barrens. Mycologia 106: 580–588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi O, Bartoli A, Rambelli A. 1978. Two new species of Triadelphia from rhizosphere of Loudetia simplex in the Ivory Coast. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 71: 148–154. [Google Scholar]
- Manimohan P, Noordeloos ME, Dhanya AM. 2006. Studies on the genus Entoloma (Basidiomycetes, Agaricales) in Kerala State, India. Persoonia 19: 45–93. [Google Scholar]
- Martín MP, García MA. 2009. How many species in the Rhizopogon roseolus group? Mycotaxon 109: 111–128. [Google Scholar]
- Massee GE. 1898. Fungi exotici, I. Bulletin of Miscellaneous Informations of the Royal Botanical Gardens Kew 1898: 113–136. [Google Scholar]
- Mchau GRA, Crous PW, Phillips AJL. 1998. Molecular characterisation of some Elsinoë isolates from leguminous hosts. Plant Pathology 47: 773–779. [Google Scholar]
- Middlehoven WJ, Hoog GS De. 1997. Hormonema schizolunatum, a new species of dothiaceous black yeasts from phyllosphere. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 71: 297–305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore RT. 1987. The genera of Rhizoctonia-like fungi: Ascorhizoctonia, Ceratorhiza gen. nov., Epulorhiza gen. nov., Moniliopsis, and Rhizoctonia. Mycotaxon 29: 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Morin L, Shivas RG, Piper MC, et al. 2010. Austropleospora osteospermi gen. et sp. nov. and its host specificity and distribution on Chrysanthemoides monilifera ssp. rotundata in Australia. Fungal Diversity 40: 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Mossebo DC, Akoa A, Atanga Étémé R. 2000. Macrolepiota globosa et Nothopanus nsimalenensis, duex nouvelles espèces fongiques du Cameroun. Mycotaxon 76: 267–278. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M, Ohzono M, Iwai H, et al. 2006. Anthracnose of Sansevieria trifasciata caused by Colletotrichum sansevieriae sp. nov. Journal of General Plant Pathology 72: 253–256. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T. 1973. Studies on degradation and cellulolytic activity of microfungi. Studia Forestalia Suecica 104; Stockholm, Sweden. [Google Scholar]
- Perdomo H, García D, Gené J, et al. 2013. Phialemoniopsis, a new genus of Sordariomycetes, and new species of Phialemonium and Lecythophora. Mycologia 105: 398–421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdomo H, Sutton DA, García D, et al. 2011. Molecular and phenotypic characterization of Phialemonium and Lecythophora isolates from clinical samples. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 48: 1209–1216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peres NA, MacKenzie SJ, Peever TL, et al. 2008. Postbloom fruit drop of citrus and Key lime anthracnose are caused by distinct phylogenetic lineages of Colletotrichum acutatum. Phytopathology 98: 345–352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfenning L, Oberwinkler F. 1993. Ophiostoma bragantinum n. sp., a possible teleomorph of Sporothrix inflata, found in Brazil. Mycotaxon 46: 381–385. [Google Scholar]
- Pradeep CK, Vrinda KB, Varghese Shibu P, et al. 2012. New species of Entoloma (Basidiomycetes, Agaricales) from Kerala State, India. Mycotaxon 120: 331–342. [Google Scholar]
- Quaedvlieg W, Binder M, Groenewald JZ, et al. 2014. Introducing the Consolidated Species Concept to resolve species in the Teratosphaeriaceae. Persoonia 33: 1–40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranghoo VM, Hyde KD. 1998. Ascolacicola aquatica gen. et sp. nov. and a new species of Ascotaiwania from wood submerged in a reservoir in Hong Kong. Mycologia 90: 1055–1062. [Google Scholar]
- Ranghoo VM, Hyde KD, Liew ECY, et al. 1999. Family placement of Ascotaiwania and Ascolacicola based on DNA sequences from the large subunit rRNA gene. Fungal Diversity 2: 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Rayner RW. 1970. A mycological colour chart. Commonwealth Mycological Institute and British Mycological Society, Kew. [Google Scholar]
- Réblová M, Winka K. 2000. Phylogeny of Chaetosphaeria and its anamorphs based on morphological and molecular data. Mycologia 92: 939–954. [Google Scholar]
- Révay Á. 1992. A new species of Triadelphia from Hungary. Studia Botanica Hungarica 23: 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Rivero M, Hidalgo A, Alastruey-Izquierdo A, et al. 2009. Infections due to Phialemonium species: case report and review. Medical Mycology 47: 766–774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts P. 2004. Tulasnella echinospora: an unusual new species from Great Britain and Sweden. Cryptogamie Mycologique 25: 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ronquist F, Teslenko M, Van der Mark P, et al. 2012. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology 61: 539–542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossman AY, Farr DF, Castlebury LA. 2007. A review of the phylogeny and biology of the Diaporthales. Mycoscience 48: 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Ruibal C, Gueidan C, Selbmann L, et al. 2009. Phylogeny of rock-inhabiting fungi related to Dothideomycetes. Studies in Mycology 64: 123–133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saccardo PA. 1892. Supplementum Universale, Pars II. Discomyceteae-Hyphomyceteae. Sylloge Fungorum 10: 1–964. [Google Scholar]
- Samuels GJ, Barr ME, Lowen R. 1993. Revision of Schizoparme (Diaporthales, Melanconidaceae). Mycotaxon 46: 459–483. [Google Scholar]
- Séguy E. 1936. XXX Code Universel des couleurs. Edt. P. Lechevalier, 51 pl; Paris. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert K, Morgan-Jones G, Gams W, et al. 2011. The genera of Hyphomycetes. CBS Biodiversity Series no. 9: 1–997. CBS-KNAW Fungal Biodiversity Centre, Utrecht, The Netherlands. [Google Scholar]
- Shearer CA, Crane JL. 1971. Fungi of the Chesapeake Bay and its tributaries. I. Patuxent River. Mycologia 63: 237–260. [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker RA, Babcock CE. 1992. Applanodictyosporous Pleosporales: Clathrospora, Comoclathris, Graphyllium, Macrospora, and Platysporoides. Canadian Journal of Botany 70: 1617–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J. 2008. A rapid bootstrap algorithm for RAxML web-servers. Systematic Biology 75: 758–771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton BC. 1980. The Coelomycetes: fungi imperfecti with pycnidia, acervuli, and stromata. Kew, Commonwealth Mycological Institute. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton BC, Hodges CS., Jr 1978. Eucalyptus microfungi: Chaetendophragmiopsis gen. nov. and other hyphomycetes. Nova Hedwigia 29: 593–607. [Google Scholar]
- Swart L, Crous PW, Kang J-C, et al. 2001. Differentiation of species of Elsinoë associated with scab disease of Proteaceae based on morphology, symptomatology, and ITS sequence phylogeny. Mycologia 93: 365–379. [Google Scholar]
- Swofford DL. 2003. PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and other methods). Version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Massachusetts. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, et al. 2011. MEGA 5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis using Maximum Likelihood, evolutionary distance, and Maximum Parsimony methods. Molecular Biology and Evolution 28: 2731–2739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, et al. 2013. MEGA 6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution 30: 2725–2729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travadon R, Lawrence PD, Rooney-Latham S, et al. 2015. Cadophora species associated with wood-decay of grapevine in North America. Fungal Biology 119: 53–66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trichies G. 2006. Hétérobasidiomycètes inusuels ou nouveaux découverts en France. Bulletin de la Société Mycologique France 122: 29–60. [Google Scholar]
- Tzean SS, Chen JL. 1989. A new species of Triadelphia from Taiwan. Mycologia 81: 626–631. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay HP. 1966. Soil fungi from North-East Brazil. Mycopathologia et Mycologia applicata 30: 276–286. [Google Scholar]
- Van Niekerk JM, Groenewald JZ, Verkley GJM, et al. 2004. Systematic reappraisal of Coniella and Pilidiella, with specific reference to species occurring on Eucalyptus and Vitis in South Africa. Mycological Research 108: 283–303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vellinga EC. 2002. New combinations in Chlorophyllum. Mycotaxon 83: 415–417. [Google Scholar]
- Vellinga EC. 2003. Chlorophyllum and Macrolepiota (Agaricaceae) in Australia. Australian Systematic Botany 16: 361–370. [Google Scholar]
- Venkateshwarlu N, Reddy SM, Reddy SR. 1996. Hyphomycetes from Warangal-III. Indian Phytopathology 49: 339–341. [Google Scholar]
- Verkley GJM, Dukik K, Renfurm R, et al. 2014. Novel genera and species of coniothyrium-like fungi in the Montagnulaceae (Ascomycota). Persoonia 32: 25–51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen M, Gryzenhout M, Wingfield MJ, et al. 2011. New records of the Cryphonectriaceae from southern Africa including Latruncellus aurorae gen. sp. nov. Mycologia 103: 554–569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voglmayr H, Rossman AY, Castlebury LA, et al. 2012. Multigene phylogeny and taxonomy of the genus Melanconiella (Diaporthales). Fungal Diversity 57: 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Voronin LV. 1986. De Hormonemate macrosporo Voronin sp. nov., clavi specierum generis Hormonema Lagerb. et Melin adjecta notula. Novosti Sistematiki Nizshikh Rastenii 23: 118–120. [Google Scholar]
- Watling R. 1987. Observations on the Bolbitiaceae – 30. Agaricus callistus Peck. Mycologia 79: 310–313. [Google Scholar]
- Watling R. 1994. Observations on Malaysian Bolbitiaceae with records from Solomon Islands. Garden’s Bulletin Singapore 45: 359–381. [Google Scholar]
- Weir BS, Johnston PR, Damm U. 2012. The Colletotrichum gloeosporioides species complex. Studies in Mycology 73: 115–180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiβ M, Bauer R, Begerow D. 2004. Spotlights on heterobasidiomycetes. In: Agerer R, Piepenbring M, Blanz P. (eds), Frontiers in basidiomycete mycology: 7–48. IHW-Verlag, Eching. [Google Scholar]
- Whitton SR, McKenzie EHC, Hyde KD. 2000. Dictyochaeta and Dictyochaetopsis species from the Pandanaceae. Fungal Diversity 4: 133–158. [Google Scholar]
- Wijayawardene NN, Hyde KD, Bhat DJ, et al. 2014. Camarosporium-like species are polyphyletic in Pleosporales; introducing Paraconiothyrium and Pseudoconiothyrium gen. nov. in Montagnulaceae. Cryptogamie, Mycologie 35: 177–198. [Google Scholar]
- Wijayawardene NN, Song Y, Bhat DJ, et al. 2013. Wojnowicia viburni sp. nov. from China and its phylogenetic placement. Sydowia 65: 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Wilken MP, Steenkamp ET, Wingfield MJ, et al. 2014. DNA loss at the Ceratocystis fimbriata mating locus results in self-sterility. PLoS ONE 9:e92180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingfield MJ. 1985. Reclassification of Verticicladiella based on conidial development. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 85: 81–93. [Google Scholar]
- Yurlova NA, Hoog GS De, Gerrits van der Ende AHG. 1999. Taxonomy of Aureobasidium and allied genera. Studies in Mycology 43: 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zalar P, Gostinčar C, Hoog GS De, et al. 2008. Redefinition of Aureobasidium pullulans and its varieties. Studies in Mycology 61: 21–38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang R, Yang HL, Sun GY, et al. 2009. Strelitziana mali, a new species causing sooty blotch on apple fruit. Mycotaxon 110: 477–485. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y, Hagen F, Stielow B, et al. 2015. Phylogeography and evolutionary patterns in Sporothrix spanning more than 14 000 human and animal case reports. Persoonia 35: 1–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]