Abstract
HgsDb, a database is developed to organize the data under a single platform to facilitate easy access for researcher to get information on migration and molecular risk assessment. In past, human beings migrate from one place to other over the globe in search of food and better habitat, where they got adapted. These adaptations are visible in the form of change in color, facial pattern, average height, eye shape, hair texture, etc. This leads to origin of different race of human being. The adaptations are remarkable when move from equator to either poles. There are hundreds of different haplogroups reported on both maternal and paternal sites. This database provides overview of seventy-six major Haplogroup of mt-DNA and Y-DNA with their sub classes supplemented with structural information of individual Haplogroup responsible for various factor such molecular risk assessment, migration and origin. They help genealogist to gain deep insight information about their maternal and paternal patterns. , we had collected data from open source such as National Center for Biotechnology (NCBI), to develop this database for providing information, which Will helps the medical biology, molecular biology, genealogy and for designing personalized medicine.
Availability
Keywords: Haplogroup, HgsDb, Molecular risk assessment, mt-DNA, Y-DNA
Background
Haplogroup is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a SNP mutation [1]. Y-Chromosomal DNA (Y-DNA) and Mitochondrial DNA (mt-DNA) haplogroups are most studied in human genetics; their exchange of genetic information is independent to each other. Y-DNA passes along patrilineal lineages and mt-DNA passes along matrilineal lineage both pertain to deep ancestral origins dating back to thousands of years. Figure 1 showing the overview to the database. Large numbers of haplogroups have been reported till date, we have reported 42 main branch of mt- DNA and 34 Y-DNA every Haplogroup represents a major role in the phylogenetic tree of mankind.
Figure 1.
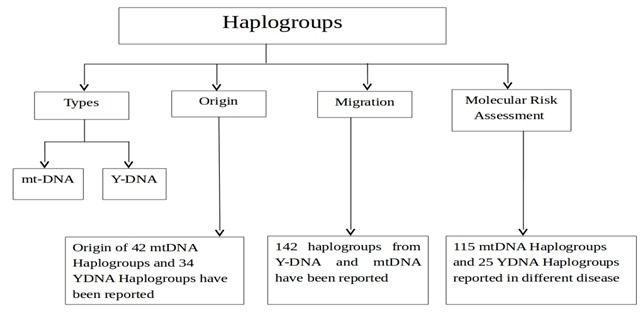
Flow Chart of HgsDb
Y-DNA and mt-DNA have emerged as a marker of choice to study the genetic history of human populations [2]. We had collected data from NCBI reporting Origin of haplogroups i.e., seventy-Six reported main branch Figure 2A and responsible Haplogroup of various disease as Molecular risk assessment (MRA) constitute 140 haplogroups involved in risk factors as in Figure 2B. Studies on various complex conditions such as ischemic cardiovascular, cancer, metabolic, male infertility, mortality, and longevity, and infectious diseases, etc. are associated with hgs have been reported to be associated with Y-DNA and mt-DNA hgs [3–4]. In this section, we had developed a unique database that possesses information of both mt-DNA and Y-DNA haplogroups. Diversity of both haplogroups in modern populations has been used to retrace important past human migration constituting one forty two haplogroups as in Figure 3. Comparison of the Y-DNA and mt- DNA along with human history has suggested different migration patterns of males and females.
Figure 2.
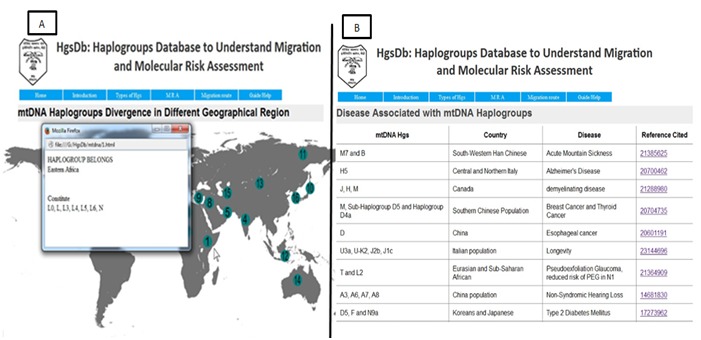
A is showing origin of different haplogroups at different place and B is showing the risk assessment of various haplogroups.
Figure 3.
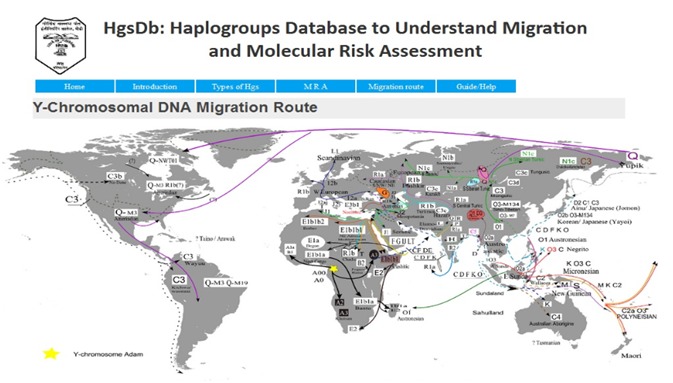
Migration route showing different haplogroups subtypes migrating at different geographical place.
Methodology
Data information about the migration and molecular risk assessment was collected through literature survey through PubMed [5].
Origin, evolution, molecular risk assessment and migration route of mt-DNA and Y-DNA hgs types has been studied over different period of time throughout the world. The relation between haplogroups with various human disorders has been already reported [6]. We had collected data about all those haplogroups and diseases. Web pages are designed as front tier for showing data from databases and entering data that has to be stored in databases. We followed HTML approach for the creation of the database. The front end of the database was designed with Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML) for creating web pages and Cascading Style Sheets (CSS), a style sheet language, for enriching the look and format of the web pages. An open source JavaScript library was used to generate visual effects on the web pages that display search results.
Database access:
The list of Haplogroups from different continents has been organized here. The database is easy to access and retrieve information of both mt-DNA and Y-DNA. Information possesses geographical distribution of different haplogroups and the risk they have been carried at the molecular level. (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
Screenshot from the web interface of HgsDb showing overview to different geographical conditions.
Conclusion
HgsDb 1.0 is a database that will enable effortless pursuit of relevant knowledge on Haplogroups. HgsDb 1.0 will help in Molecular Risk Assessment, personalized drug designing, prebirth cure by disease diagnosis, to determine genetic variation related to disease/environmental effects, knowledge of deep ancestry or traces of the human origin, to know about evolutionary history, genetic relation with other populations, and description of specific population at molecular level in the world.
Personalized medicines enable to respond against different pathogen and chemicals by understanding the variations in human DNA sequences and how these changes are responsible for development of any disease [7].
These markers are not only helpful in tracking human genealogy but also in tracing diseases among different populations based on their migration and corresponding adaptations, if any, in the form of mutation. So, they are helpful in tracking time period of evolution of different populations, mutations as well as many diseases. Molecular risk assessment of each haplogroups in HgsDb is linked with PubMed for validation and authentication of data retrieved. We are continuously putting our efforts to update the data possessing information regarding the information of different haplogroups. Additional search and retrieval features will also be added to enhance the usability of the web interface in future.
Significance of this work
Access to this database will allow understanding the molecular risk assessment associated with each group which led to help in development of personalized drug to particular disease, study genetic variations, deep ancestral knowledge to trace human origin, and genetic relation to migrated populations.
Acknowledgments
This study was conducted in the Department of Biotechnology, G.B. Pant Engineering College (GBPEC), Pauri Garhwal (Uttarakhand). Authors gratefully acknowledge the necessary computational facilities and constant supervision provided by the Department of Biotechnology, GBPEC. DA and VS are thankful to TEQIP-II (Technical Education Quality Improvement Program) for fellowship.
Footnotes
Citation:Arora et al, Bioinformation 11(6): 272-275 (2015)
References
- 1. http://www.isogg.org/course/glossary.htm.
- 2.Wan QH, et al. Electrophoresis. 2004;25:2165. doi: 10.1002/elps.200305922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Benn M, et al. Circulation. 2008;17:2492. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.756809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fang H, et al. BMC Cancer. 2010;12:421. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed.
- 6.Hofmann S, et al. Hum mol Genet. 1997;6:1835. doi: 10.1093/hmg/6.11.1835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chan IS, Ginsburg GS. Ann Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2011;12:217. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-082410-101446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


